Schiff-Sherrington Syndrome
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Etiology
Severe injury between T3/L3
#1 cause
Fractures
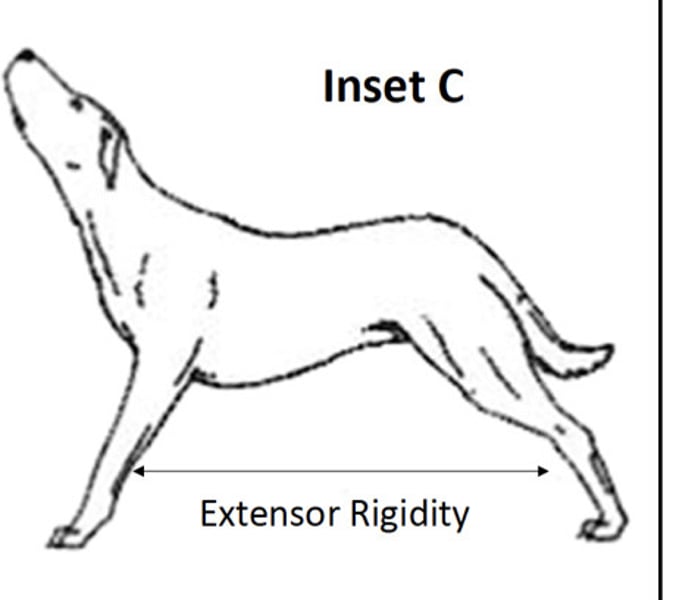
Signs
-increased extensor tone of forelimbs
-paralysis of hindlimbs
-anesthesia caudal to lesion
Confusing LMN signs first few hours
-result from spinal shock
-decreased reflexes
-decreased tone
-looks like LMN injury BUT IT IS NOT!!!
Recovery from spinal shock = return of reflexes
-myotactic first
-withdrawls next
-hypotonia (10-14 days)
Recovery over several weeks
-signs become consistent with UMN injury
-hypertonia/hyperreflexia
-guarded prognosis
Border neurons
Neurons in L1-L5 spinal cord segments that coordinate fore- and hindlimb activity
Normal effect of border neurons
Predominately inhibitory
Explain the role of border neurons in schiff-sherrington
IDK?????
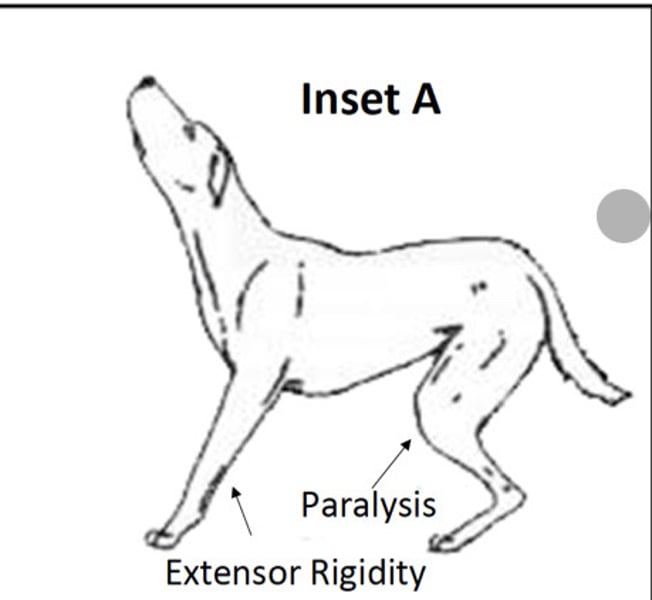
Decerebellate rigidity
-lesions rostral to cerebellum
-loss of cerebellar inhibition of tone in forelimbs
-increased externsor tone in forelimbs
-opisthotonus
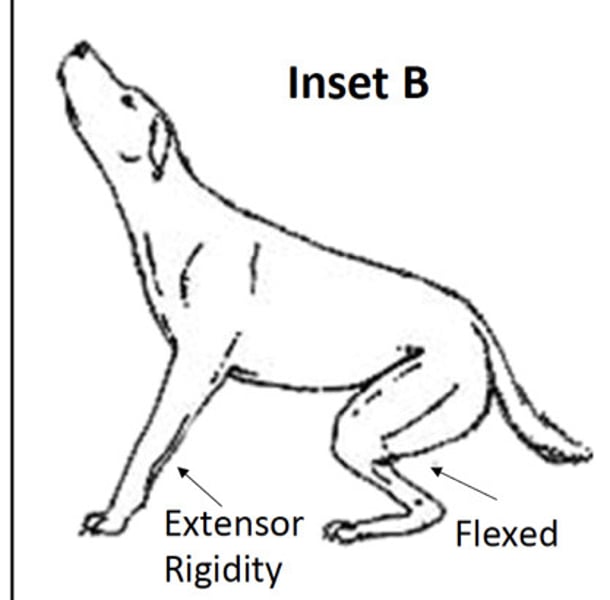
Decrebrate rigidity
-transection of midbrain
-loss of descending inhibition
-increased extensor tone throughout body
-opisthotonus