Types of Muscle Fibers uni 6
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Sources of energy

Stored ATP
ATP present in muscle fibers
5-6 sec

Aerobic cellular respiration
Requires glucose and O2
Slow
But very efficient

Glycolysis

Doesn’t require oxygen
Aerobic cellular respiration

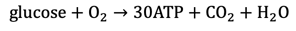

Types of contraction
Power, speed and duration
ATP source in muscle fibers
Red fibers and white fibers
red fibers?

White fibers in muscle fibers?

Types of muscle fibers
Slow oxidative fibers (SO)

Fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers (FOG)

Fast glycolytic fibers (FG)
Fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers (FOG)?

Fast glycolytic fibers (FG)?

Slow oxidative fibers (SO)?

Muscle tissue
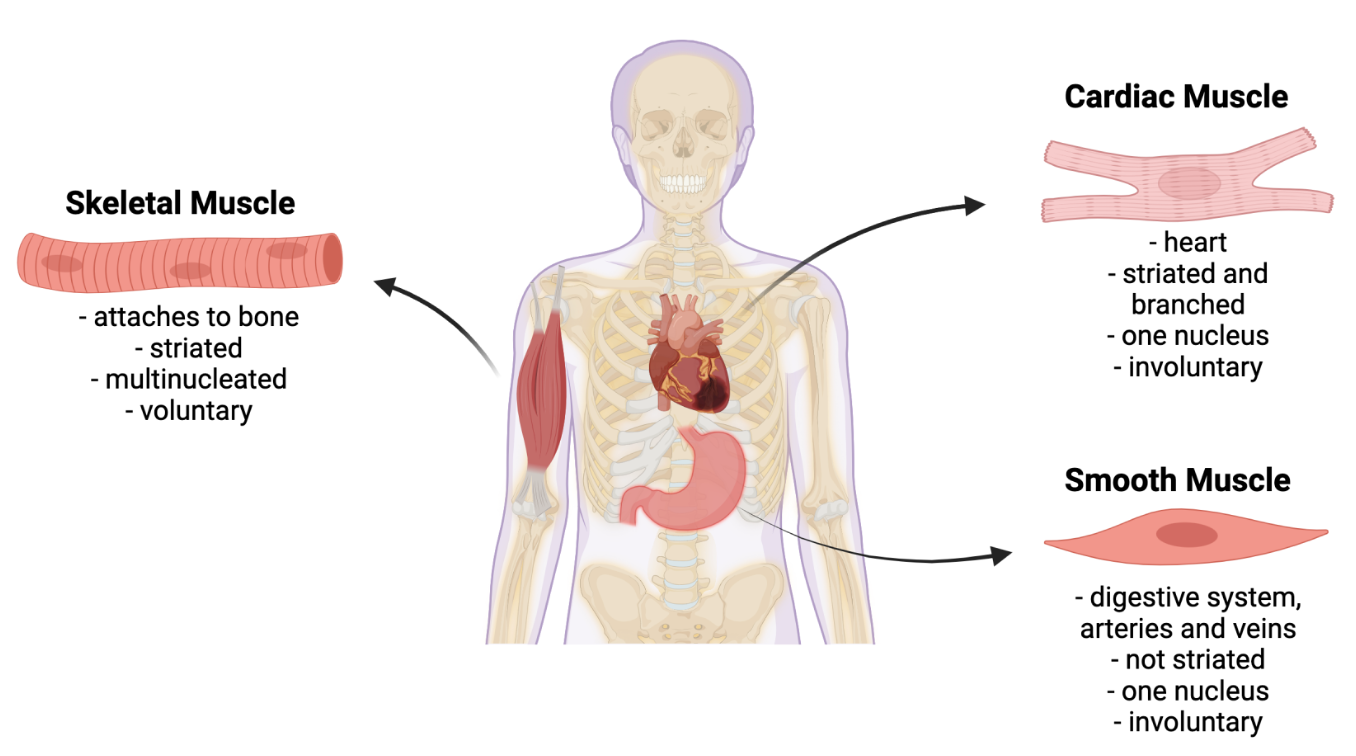
Cardiac muscle
Functions to pump blood continuously
Contracts 10-15X longer than skeletal muscle to a single action potential
Stimulated by autorhythmic muscle fibers
Self-excitable
Not neurogenic
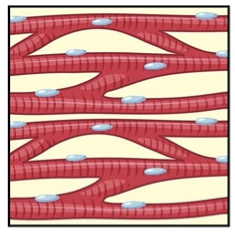
Smooth muscle

Motor unit in muscle tissue
Composed of a motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it innervates
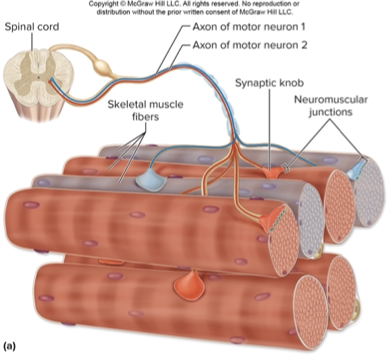
2 types of motor unit

Exercise-induced muscle damage

Aging
In part due to decreased levels of physical activity there is a slow, progressive loss of skeletal muscle mass
Replaced by fibrous connective tissue and adipose tissue
Can be avoided or slowed with weight bearing exercises
Continues to make proteins and maintains muscle