A-Level Economics OCR (Chapter 1)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is scarcity? (also known as the “basic economic problem”)
Refers to the situation caused when people have unlimited wants when there are limited resources.
What are economic goods?
Refers to goods that are scarce, for example, gold
What are free goods?
Refers to goods that are normally not scarce, for example, gases in the Earth’s atmosphere
What is poverty?
Refers to the situation where individuals lack the basic necessities of life.
What is poverty? (2)
Refers to the situation where individuals have low incomes relative to their fellow citizens.
What is the difference between free and economic goods?
Economic goods are higher in demand then supply, whereas free goods are higher in supply than demand.
Why and how does scarcity impact choice?
The existence of scarcity forces people to make decisions on a local and national level because of the lack of resources;
- Locally, people must prioritise consumption of the products they have and would like to have.
- Nationally, governments and businesses must make choices between alternative sources of resources.
What are positive statements?
Refers to statements that are factual, for example, a report listing the economic effects of higher tobacco taxes.
What are normative statements?
Refers to statements that have a value judgement about what is supposed to be reality, for example, a report listing how higher tobacco taxes discriminates against smokers.
What is a value judgement?
Refers to a statement that is purely based on one’s opinion or beliefs, for example, a report listing why discrimination against smokers is good/bad.
What are economic agents?
Refers to individuals or groups that make economic decisions about how to allocate scarce resources, for example, water.
What are the 3 key economic agents?
1) Consumers (e.g, households)
2) Producers (e.g, firms)
3) Governments
What are the aims of a consumer and how do they act as an economic agent?
Aim => To purchase products that give them a sense of satisfaction.
Actions taken? => Demands products from producers, Makes choices about income and labour.
What are the aims of a producer and how do they act as an economic agent?
Aim => To generate profit from consumers (also consider non-profit objectives!)
Actions taken? => Produce goods and services through using production factors (land, labour, enterprise and capital)
What are the aims of a government and how do they act as an economic agent?
Aim => Have different objectives depending on socio-economic conditions. Some include; raising federal revenue, pursuing expenditure programs and providing economic stability.
Actions taken? => Taxation, legislation, Market regulation
Why might economic agents not act in a rational manner?
1) Consumers => May not maximise the utility of their purchased products/ May purchase products that serve no use.
2) Producers => May have non-financial objectives, for example, charity
3) Governments => May act on inaccurate and misrepresentative information.
What is opportunity cost?
Refers to the value of the next-best alternative in decision-making.
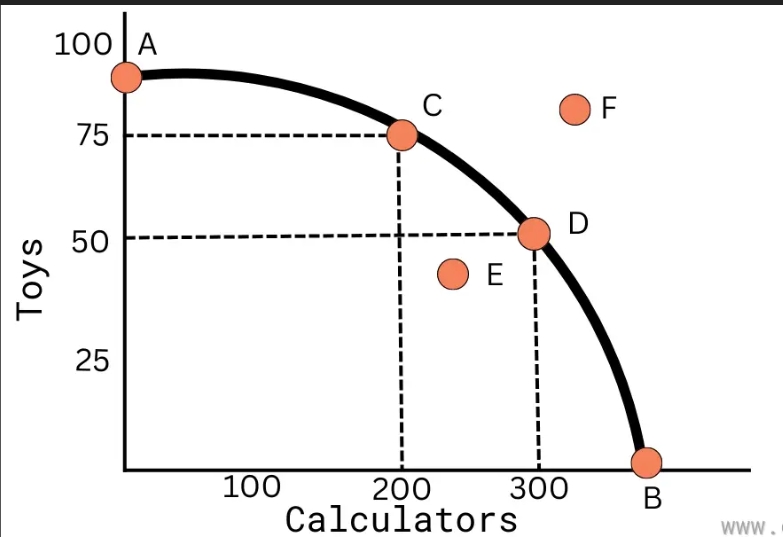
What is a PPC? (Probability Possibility Curve)
Refers to the curve/frontier that shows the maximum combinations of 2 products that can be produced in a set time and a given volume of available resources.
What are capital goods?
Refers to goods used as part of production processes as an investment into the economy, for example, trucks.
What are consumer goods?
Refers to goods used for present use by consumers for consumption, for example, TV’s.
What are some the factors that influence a PPC’s gradient?
Some of the factors include;
1) Productivity
2) Efficiency
3) “The Law of Increasing Opportunity Cost”
4) Resource availability (Input Availability)
What is long-run economic growth?
Refers to economic expansion in productive sectors of an economy over time.
What are the 4 factors of production?
Some of the factors include;
1) Land
2) Labour
3) Capital
4) Enterprise
(note = Producers must make decisions about the mix of inputs used to produce an output.)
What are factors of production?
Refers to the human and physical resources used in the production process.
How are the factors of production “rewarded”?
Some the ways include;
1) Land => Rent
2) Labour => Wages/Salaires
3) Capital => Interest
4) Enterprise => Profit