Building bodies 1: Cells to tissues
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
next: - complete the slides which i left incomplete - add on whats in the end of the pdf to this
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
What are cells arranged into?
tissues
What is a tissue
a collection of similar cells ± support cells
Where do tissues come from
the 3 embryonic primary germ layers
What are the 3 primary germ layers
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
What are the 4 basic tissue types?
epithelium
connective tissue
muscle
nerve
What is epithelia?
covering and lining of membranes of the body, so have a free surface
many types of epithelium, e.g., in lungs, tongue
separated from the surrounding tissue by the basement membrane
are specialised according to function (e.g., surface specialisations/cell junctions)
protect underlying tissue from outside world
protects/separates areas within the body
helps hold tissues together
thermoregulation
hormone release
absorption
Where do we find epithelia?
epithelia on surface
endothelium (sub) - lining blood vessels
mesothelium (sub) - lining body cavities
Only bottom layer of epithelia attached to the basement membrane
.
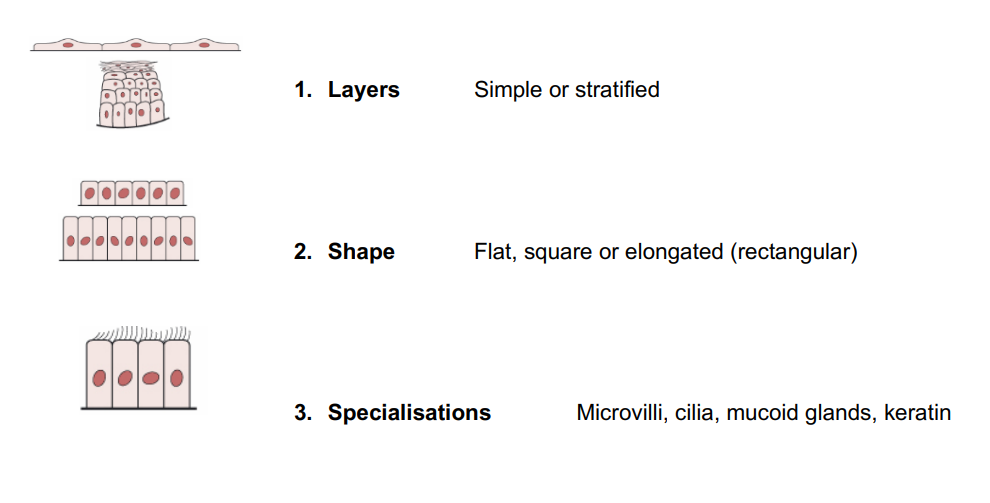
Classification of epithelial cell layers
Simple squamous
Simple cuboidal
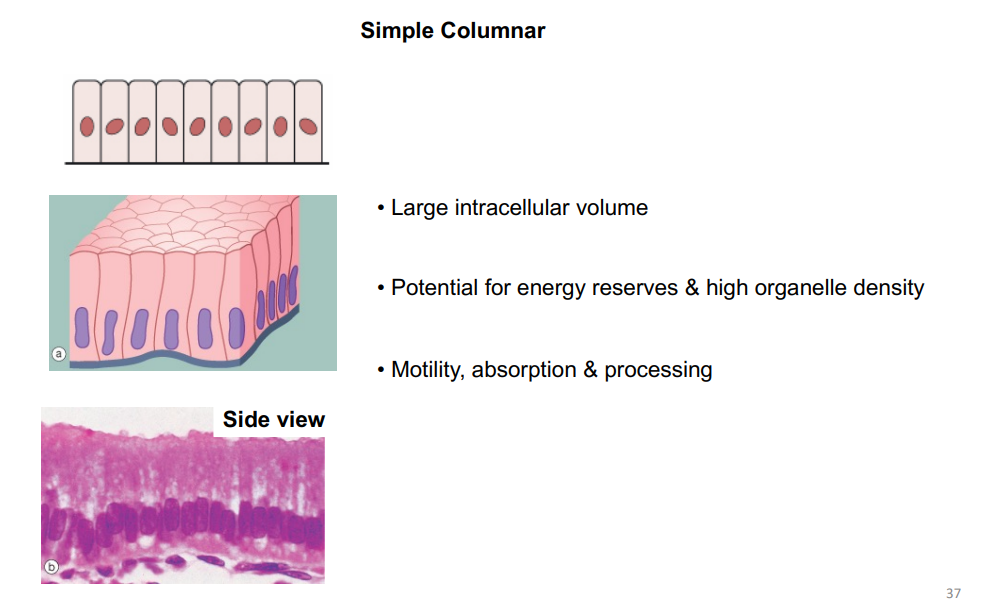
Simple columnar
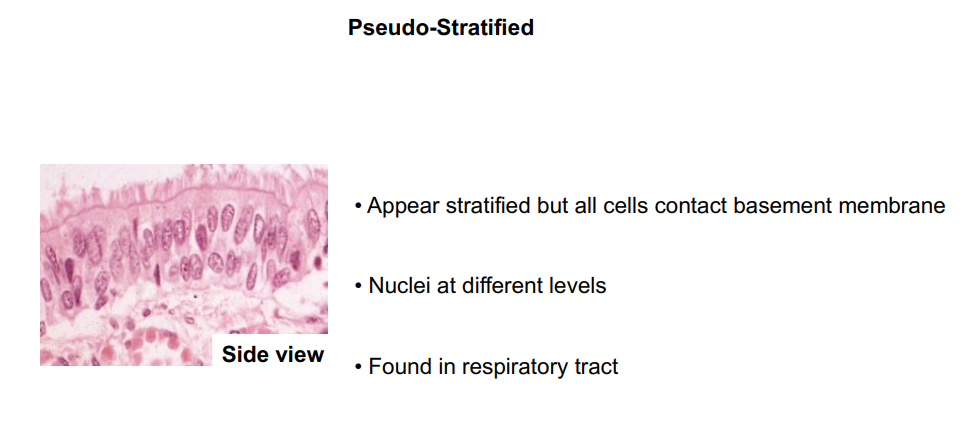
Pseudo-stratified
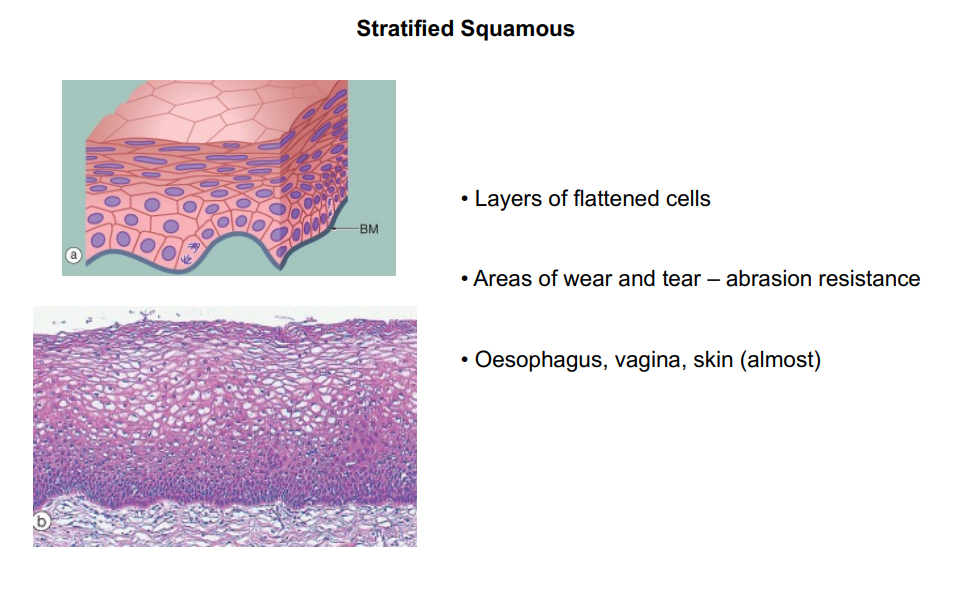
Stratified squamous
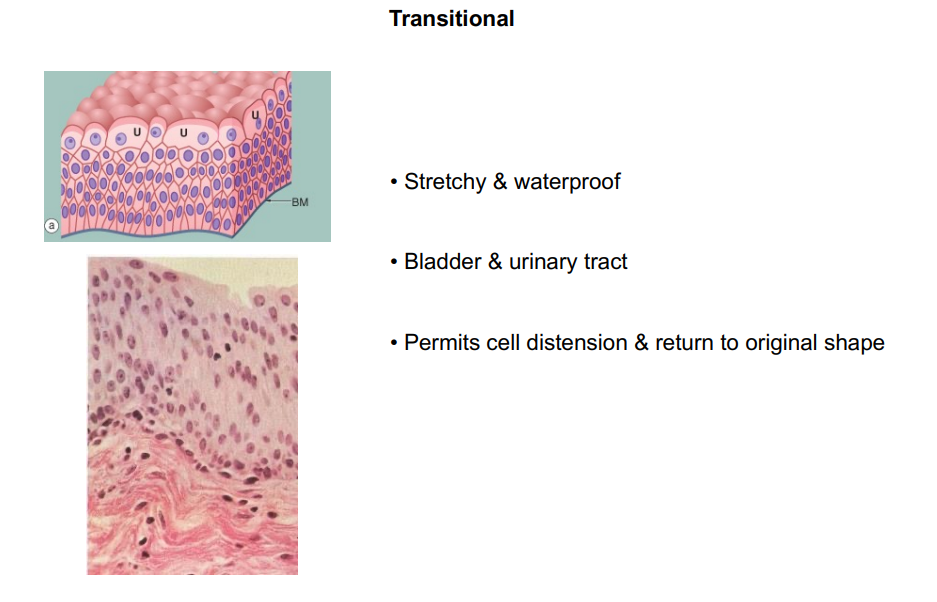
Transitional
simple
1 layer
(in gut and gall bladder)
stratified
many layers
squamous
flat
columnar
taller than wide
in 3 dimension
cuboidal
square shaped
good for blood flow
in 3 dimension
low
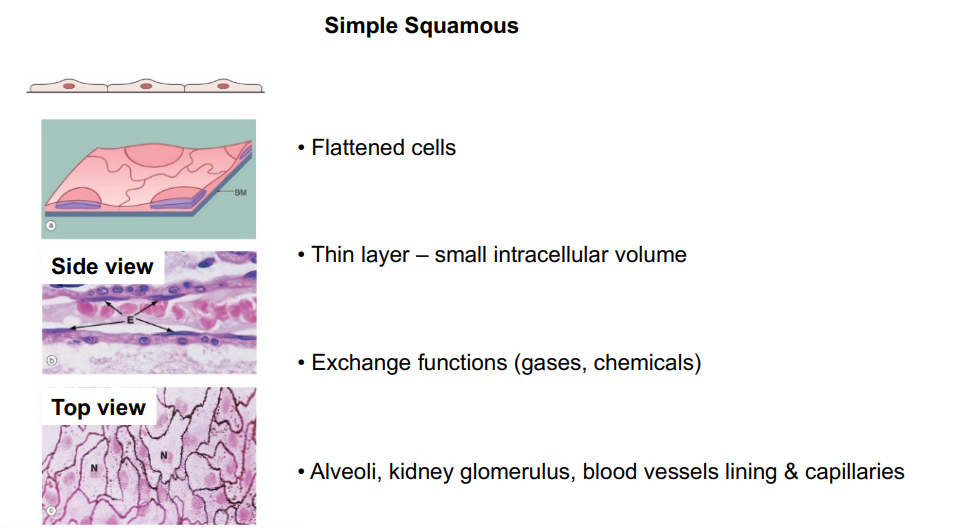
What does simple squamous epithelium look like?
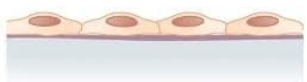
Where is simple squamous epithelium located?
Airsacs of lungs
lining of the heart
blood vessels
lymphatic vessels
What is the function of the simple squamous epithelium?
Allows materials to pass through by diffusion and filtration
Secretes lubricating substances
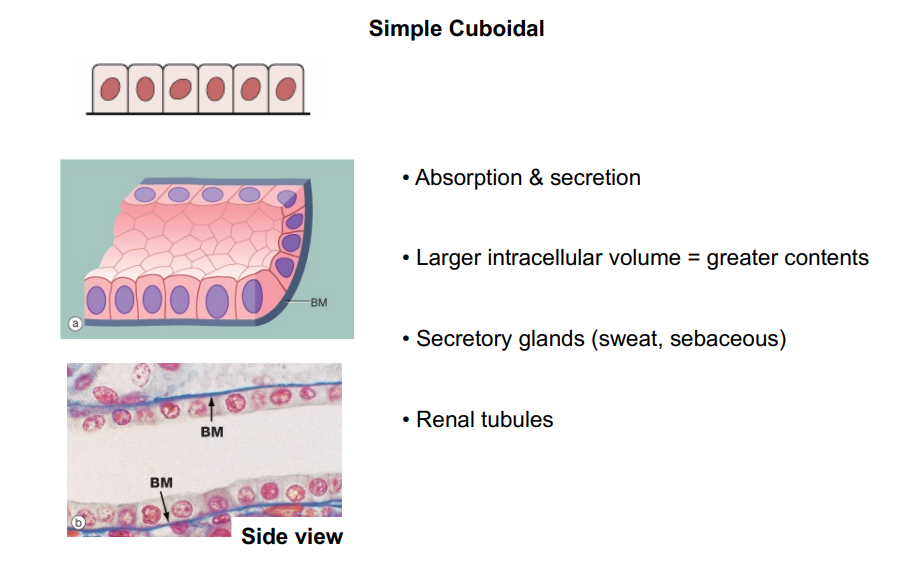
What does the structure of simple cuboidal epithelium look like?

Where is simple cuboidal epithelium located?
In ducts and secretory portions of small glands and in kidney tubules
What is the function of simple cuboidal epithelium?
Secretes and absorbs
What does simple columnar epithelium look like?
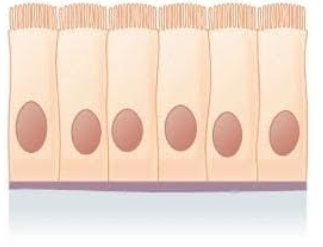
Where is the simple columnar epithelium located?
Ciliated tissues in:
larger bronchioles
uterine tubes
uterus
Smooth (non-ciliated tissues) in:
digestive tract
bladder
What is the function of simple columnar epithelium?
Absorbs
secretes mucus and enzymes
What does pseudostratified columnar epithelium look like?
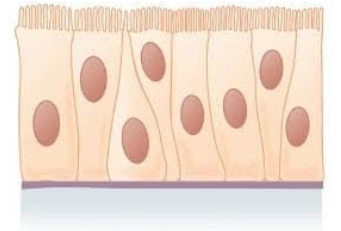
Where is pseudostratified epithelium located?
Ciliated tissue lines the bronchi, trachea, and much of the upper respiratory tract
What is the function of pseudostratified epithelium?
Secretes mucus; ciliated tissue moves mucus
What does the stratified squamous epithelium look like?
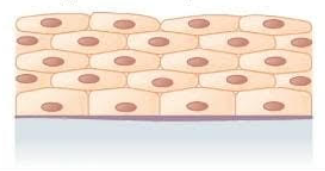
What is the location of stratified squamous epithelium?
Lining of:
esophagus
mouth
vagina
What is the function of stratified squamous epithelium?
Protects against abrasion
What does stratified cuboidal epithelium look like?
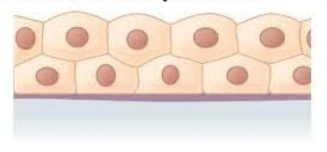
What is the location of stratified cuboidal epithelium?
sweat glands
salivary glands
mammary glands
What is the function of stratified cuboidal epithelium?
Protective tissue
What does the stratified columnar epithelium look like?
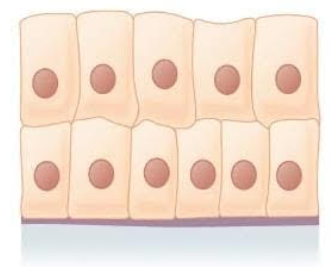
Where is the stratified columnar epithelium located?
male and female urethrae
ducts of some glands
What is the function of stratified column epithelium?
secretes
protects
What does transitional epithelium look like?
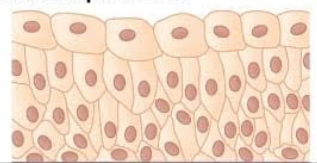
Where is transitional epithelium located?
Lining of:
bladder
urethra
ureters
What is the function of transitional epithelium?
Allows the urinary organs to expand and stretch
Cilia that waft mucus, have gaps with goblets tails at the bottom, linked to gas exchange
.
e.g., urothelium/transitional epithelium characteristics
protective
stretches a lot
secretory/absorptive
facilitate diffusion
stratified squamous
mouth
simple squamous
alveolar
simple squamous
endothelium layers
What is a basement membrane
sheets of matric at the interface of function tissue (epithelium) and support tissue (connective tissue)
composed mainly of:
type IV collagen
glycoproteins (laminin secreted by epithelial cells)
Fibronectin from fibroblasts and glycosaminoglycans
What is basement membrane mainly composed of?
type IV collagen
glycoproteins (laminin secreted by epithelial cells)
Fibronectin from fibroblasts and glycosaminoglycans
Functions of basement membrane
adhesion
barrier (permeability)
organisation of cells (controlling growth and differentiation)
Pathology of the basement membrane (BM)
Disorders:
renal disease
cancer
genetic disease
Skin pathology:
epidermolysis bullosa - separation of epidermis and dermis
blistering
If you want more secretion then? Or when you need to protect it?
Fold the epithelium
Make glands
(sweat glands have ducts)
Generally, secretory portion are
columnar
Generally ducts are
cuboidal epithelium
Shapes of gland
tubular, acinar or mixed
in its simplest form it is a single cell e.g., Goblet cell in the GI tract
simple or compound (branched)
A great majority of cancers are derived from epithelial cells. What are these called?
Carcinomas
Cancer in glands is called adenocarcinoma
what can glands produce
hormones
sweat
saliva
mucus
acids
What are the 2 types of glands?
Exocrine and endocrine
What do exocrine glands do?
secrete their products onto the epithelial surface directly or via a duct for local action e.g., sweat glands, liver
What do endocrine glands do?
release their secretions directly into the blood to act on different tissues e.g., pituitary and thyroid glands
Collagen is a connective tissue
made of 3 separate collagen molecules wrapped together in an alpha helix
support tissue of body
Where does (collagen) originate from
embryonic mesoderm
What are connective tissues made of?
cells, fibres and matrix
What are connective tissues characterised by
by the abundance of the matrix with few cells
What is connective tissue made up of?
cells (5%)
extracellular matrix (ECM) (95%)
What is ECM composed of?
fibres (collagen and elastin)
ground substance (glycoproteins and glycosaminoglycans)
What secretes ECM for most tissues?
the fibroblast
What is collagen
a structural protein
provides tensile strength and structural strength and structural support
there are at least 16 different types but mainly types I,II, III (reticulin) and IV
What does elastin provide
Elasticity
Collagen synthesis, how many steps would i like to memorise this in haha
4
Step 1 of collagen synthesis
Procollagen polypeptide chains are synthesized on the ribosomes of the rough endoplasmic reticulum and secreted into the lumen,
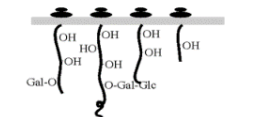
Step 2 of collagen synthesis
where they are modified by hydroxylation of certain proline and lysine residues and glycosylation before chain association and triple helix formation
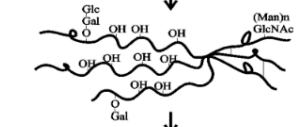
Step 3 of collagen synthesis
The procollagen molecules are secreted into the extracellular space where the N and C propeptides are cleaved by specific proteases.
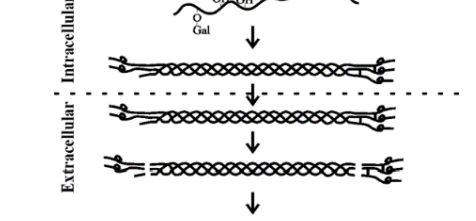
Step 4 of collagen synthesis
The collagen molecules then assemble into fibrils, which are stabilized by the formation of covalent crosslinks
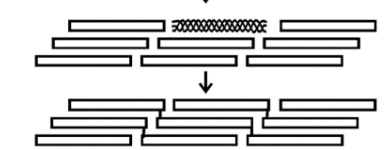
Collagen structure in detail
provide tensile strength
reduced tensile strength from collagen disorders causes tissue laxity, joint hypermobility and susceptibility to injury e.g., Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (type 1 collagen disorder)
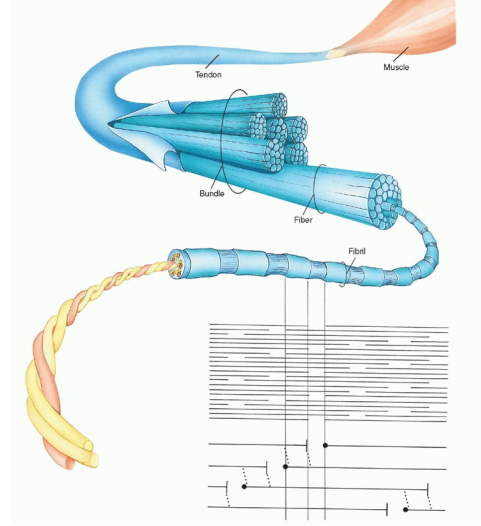
pic of collagen fibres
fibroblasts with fibrocytes
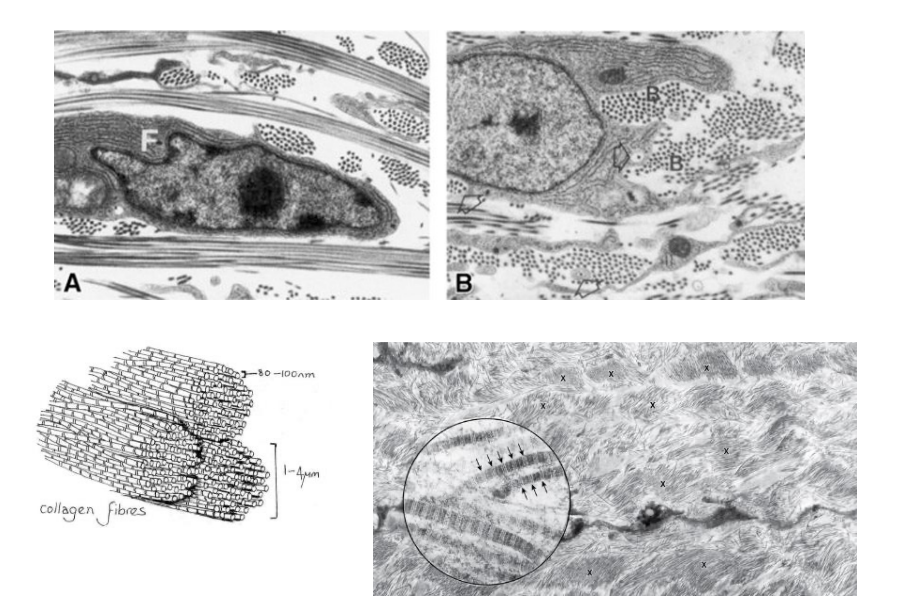
Reticulum
Type III collagen - branched

Elastin fibres do what
stretching and elastic recoil
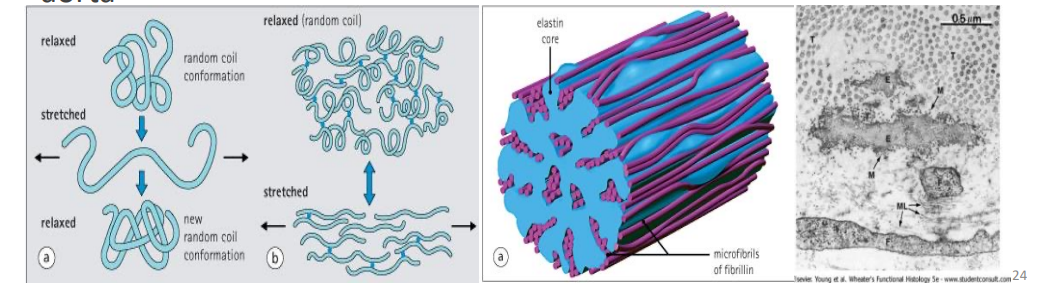
What polymerises to elastin?
tropoelastin
What do elastin fibred require for assembly?
fibrillin
Marfans syndrome
genes coding for fibrillin defective - rupture of strucaorta
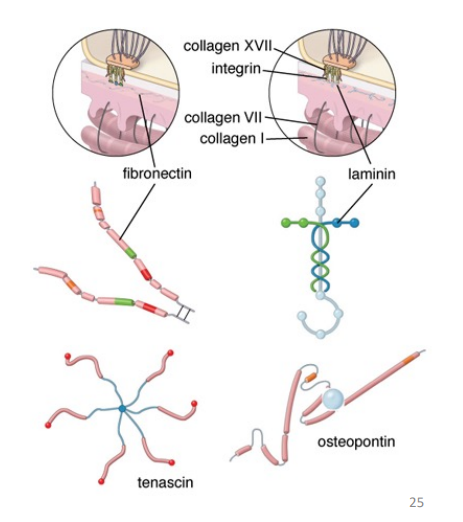
structural glycoprotein examples
• Fibrillin - microfibrils 8-12nm - links to elastin
• Fibronectin - deposition and orientation of collagen and its links to cells via integrin
• Laminin - major component of Basement Membrane
What is Glycosaminoglycan (GAG)
polysaccharide chains that attract water
What are the 4 groups of GAGs
Chondroitin sulfate
Heparan sulfate
Hyaluronan
Keratan sulfate
GAGs form the centre of the intervertebral disc, forming what?
a compression resistant core
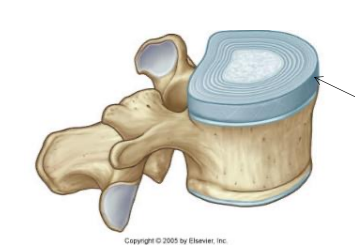
What about this pic of GAG?
GAGs form the centre of the intervertebral disc forming a compression resistant core
Why is histology the connective tissue looks pale pink with few cells (because epithelium is purple)
The properties of connective tissue are varied and result from the characteristics of what?
the extracellular matrix
What provides multiple tissue types?
Variation in the type, composition and arrangement of the macromolecules
What does connective tissue form
the structural framework of many body tissues
What are the 4 structural frameworks of connective tissue and give examples of each
Loose: packing material
Dense: tough physical support - dermis, organ capsule, ligaments, tendons
Areolar: fatty
Specialised support: cartilage and bone
Organisation and function of connective tissue: metabolic?
adipose tissue
Organisation and function of connective tissue: immune?
contains immune cells
(mast cells, tissue macrophages, WBCs, plasma cells) and effect repair
Organisation and function of connective tissue: mechanical and structural role?
carry blood and lymph vessels
Organisation and function of connective tissue: exchanges?
Mediate exchanges of nutrients, metabolites, and waste products from blood and tissues
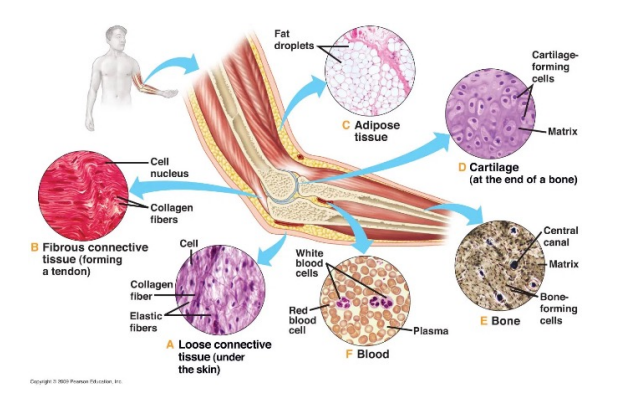
Give examples of the range of connective tissue types
fibrous connective tissue (forming a tendon)
cartilage (at the end of a bone)
adipose tissue
bone
blood (because it has a matrix - plasma)
loose connective tissue (under the skin)