Rnr Deserts
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
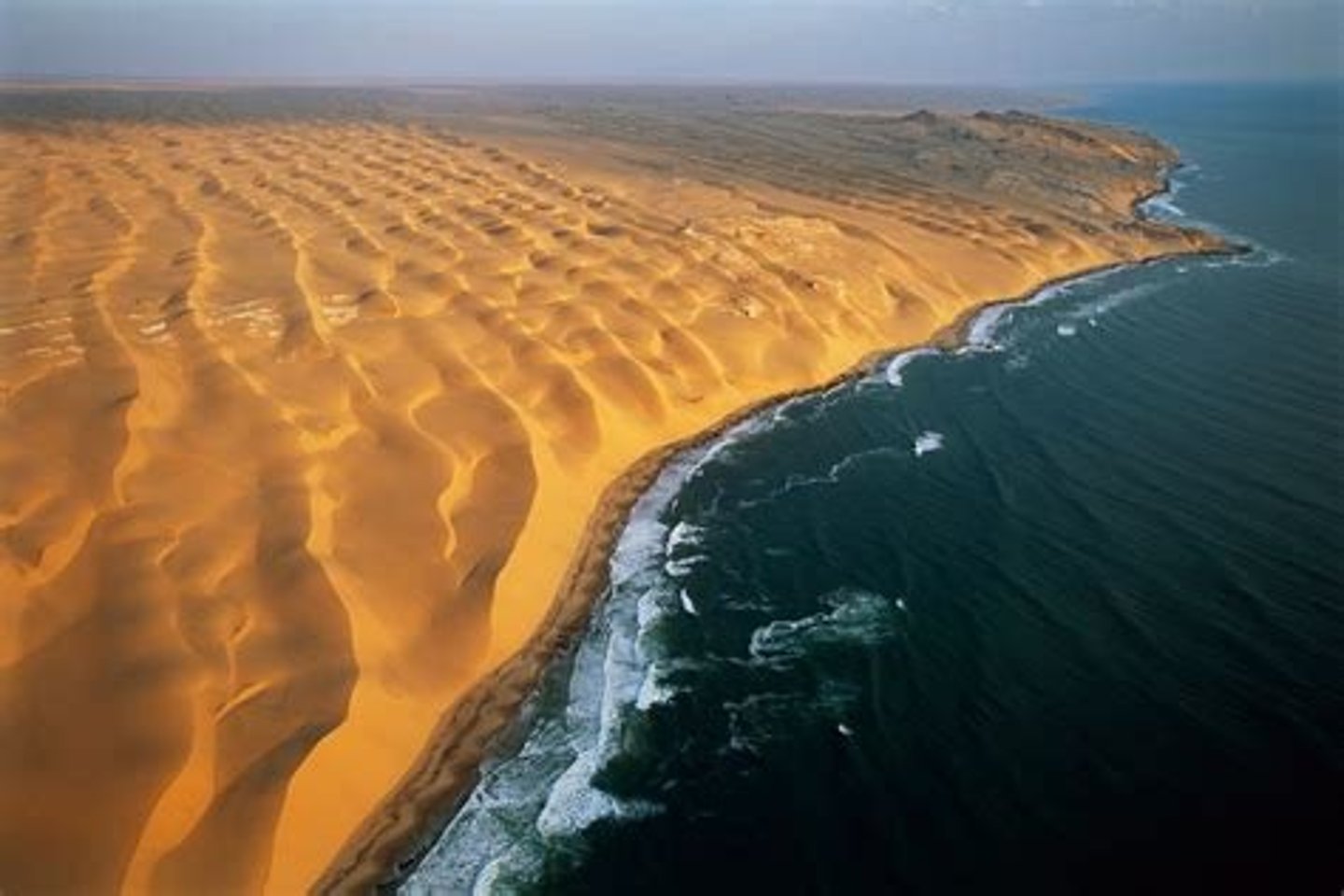
Coastal Deserts
usually occur on western continental edges and are affected by cold coastal currents that inhibit rainfall to adjacent land masses, although morning fogs provide water to a relatively high diversity of plants and invertebrates

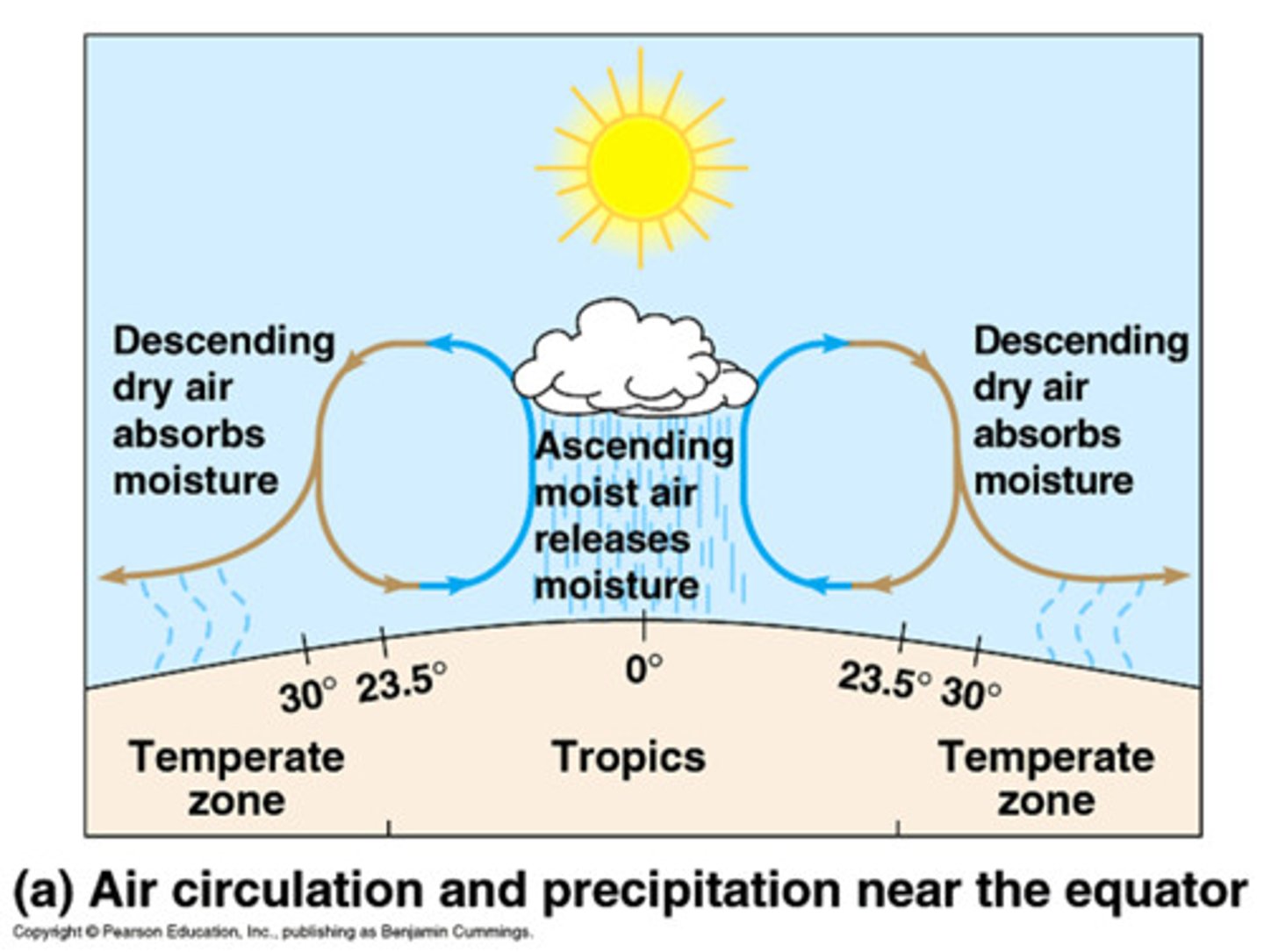
Hadley Cell Circulation
The model that explains global air circulation and precipitation patterns according to latitudinal differences.
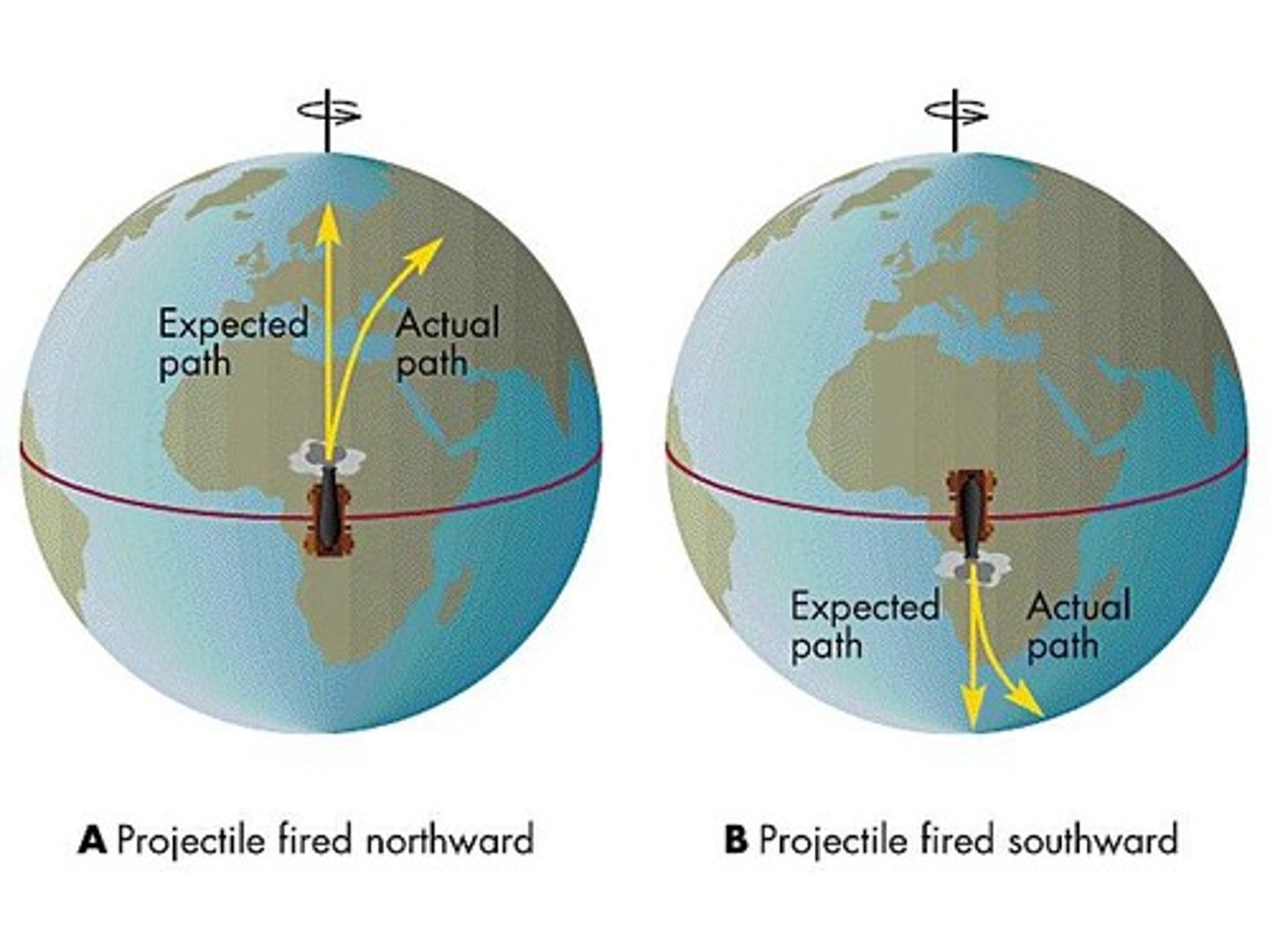
Coreolis effect
The effect of Earth's rotation on the direction of winds and currents.
Mid-latitude deserts
are poleward of the Trade Wind Deserts, and are impacted by dry Westerly air currents moving towards the Polar Cell. Are classified as "cold" deserts, with winter. temperatures often below 10 C
. Taklamakan Desert in southcentral China
. Great Basin in the western U.S.
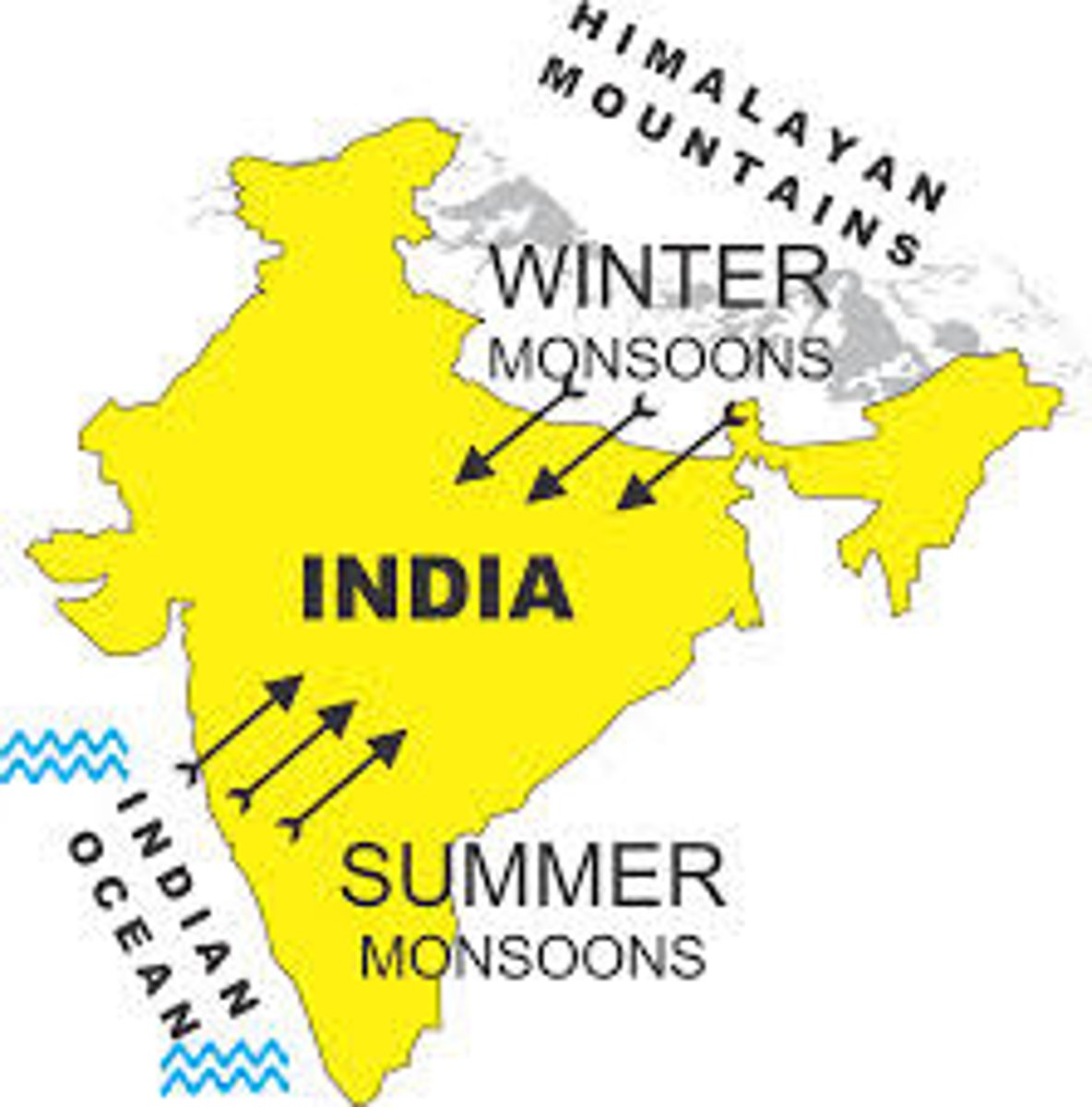
Monsoon Deserts
are caused by seasonal wind shifts, e.g., the Rajasthan Desert in western India, which receives dry air from the Himalayas and Siberia during the winter, but moist air from the ocean during summer heating (rising air)
Examples of morphological and physiological adaptations that plants have created in order to live in the desert
. smaller leaves
. sunken stomata that only opens at night to reduce water loss
. spines are to help protect itself from harm, but ALSO to provide shade for plants
. rolled leaves trap moist air above
. hair on lower leaf to trap moisture
. dormancy leaf incision
. desiccation-resistant seeds in deserts
. extensive shallow root systems for rapid water uptake after rainfall (cactus), or deep roots (phreatophytes) to access deeper water sources (60 m in mesquite trees)
. They have large diameter xylem for transferring large amounts of water from the ground to the canopy, and often lose considerable water to transpiration
Examples of Behavioral and Physiological adaptations that animals have created in order to live in the desert
. Dew collection on scales
. Big radiative ears to help them cool down
. Fat/water storage
. Uric acid secretion
. Salt excretion
. Burrowing
. Crepuscular/nocturnal activity periods
- Thorny Devil
- Namib desert beetle
Dew collection on scales: animal example
- Jackrabbit
- Fennec Fox
Radiative ears: animal example
- Gila Monster
- Camel
Fat/water storage: animal example
Dorcas Gazelle
Uric acid secretion: animal example
Roadrunner
Salt excretion: animal example
- desert skinks
- Desert Toad
- Desert Tortoise (escape heat)
- Horned Lizard (access heat at night)
Burrowing: animal example
-Kangaroo Rat
-Rattlesnake
-scorpions
- geckos
- owls
Crepuscular/nocturnal activity periods: animal example
closable nostrils, ear hairs, eyelashes, and nictitating membrane to protect their eyes from sand
What do camels have that helped them adapt to their environment?
Phreatophytes
are plants that have become adapted to arid and semi-arid ecosystems by developing extensive root systems that extend to the water table
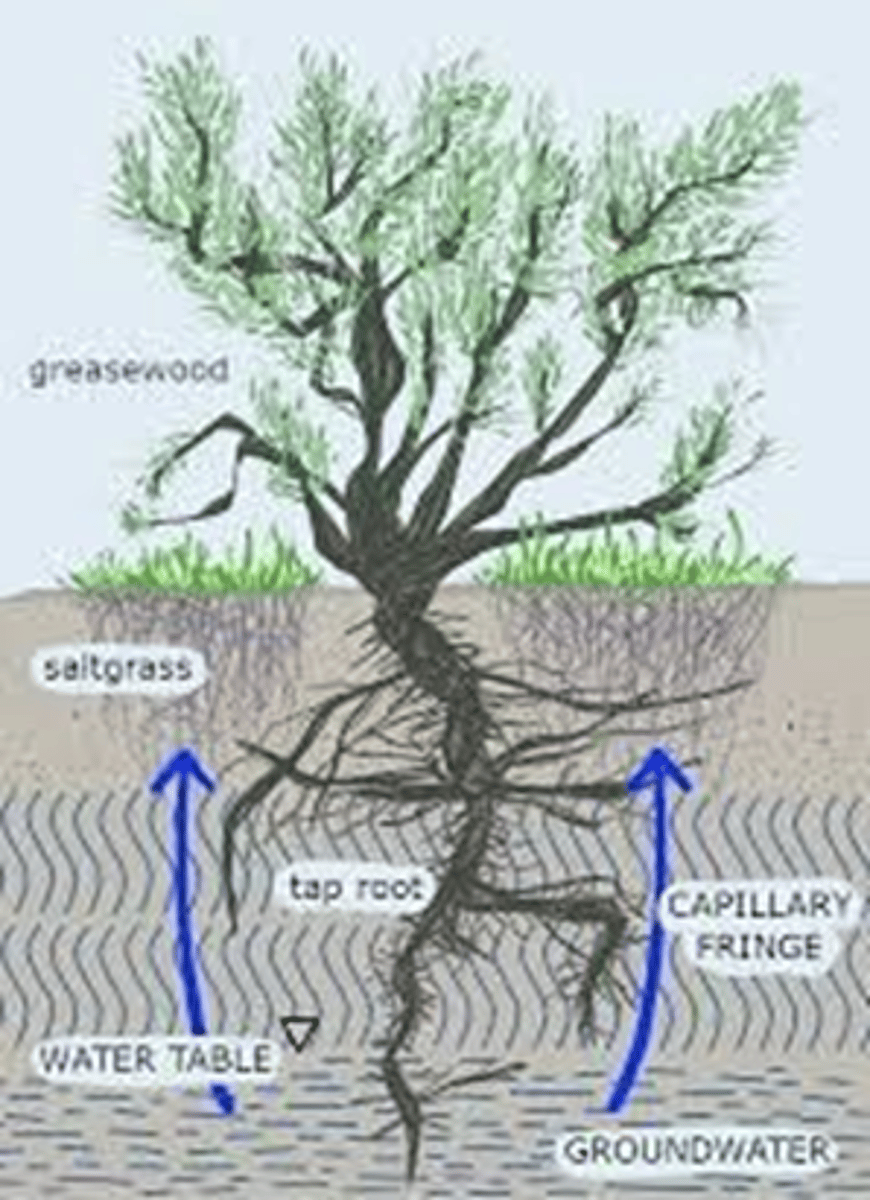
Phreatic zone
saturated zone below the water table
Polar Deserts
Cold, dry areas of high pressure at the poles. Occur in areas where precipitation averages <25 cm and mean temperatures during the warmest month is <10 C. Antarctica's Dry Valley has been ice-free for thousands of years.
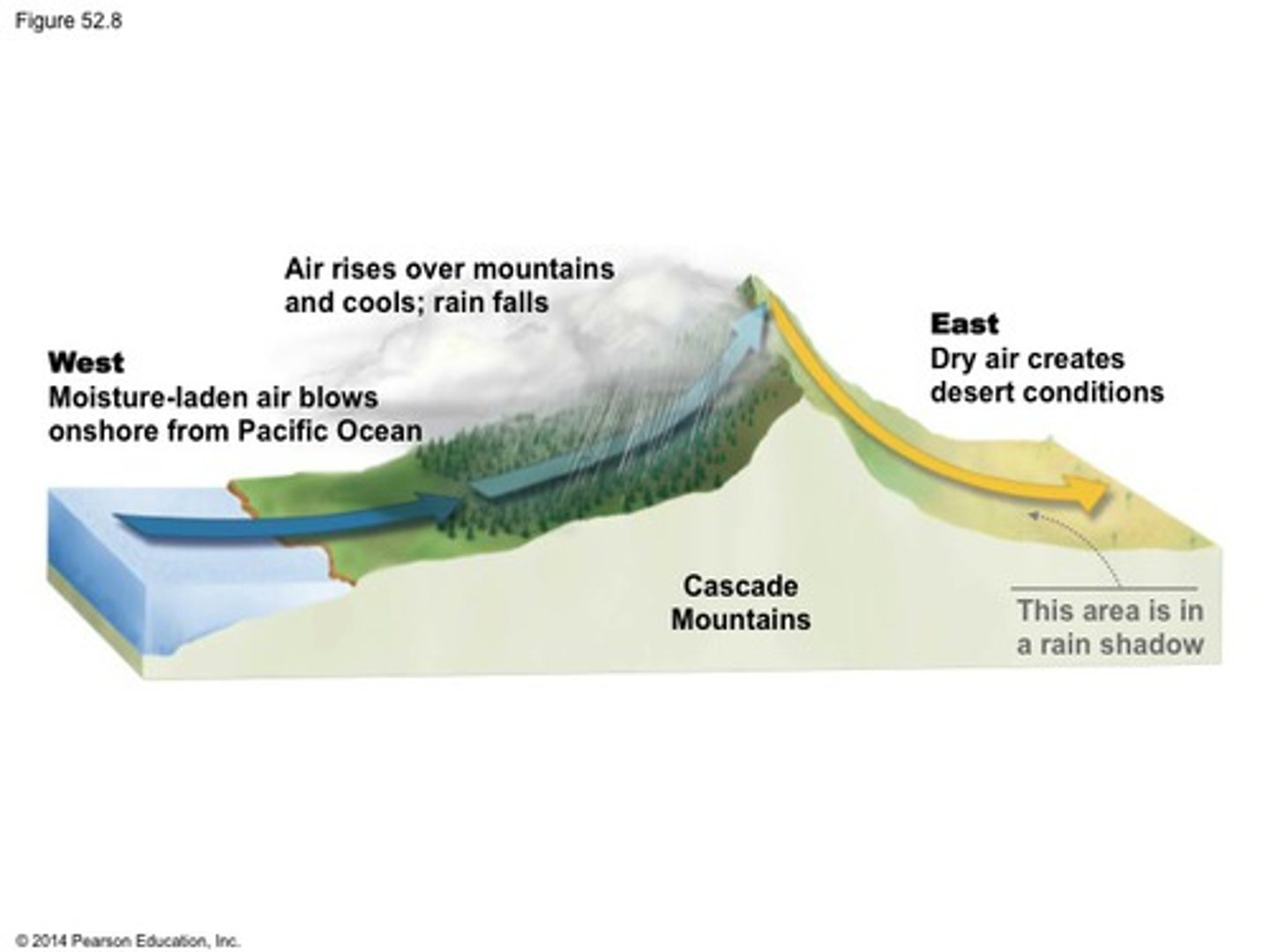
Rain shadow deserts
Desert formed on the leeward side of a mountain range because the height of the mountain prevents most moisture from crossing over it
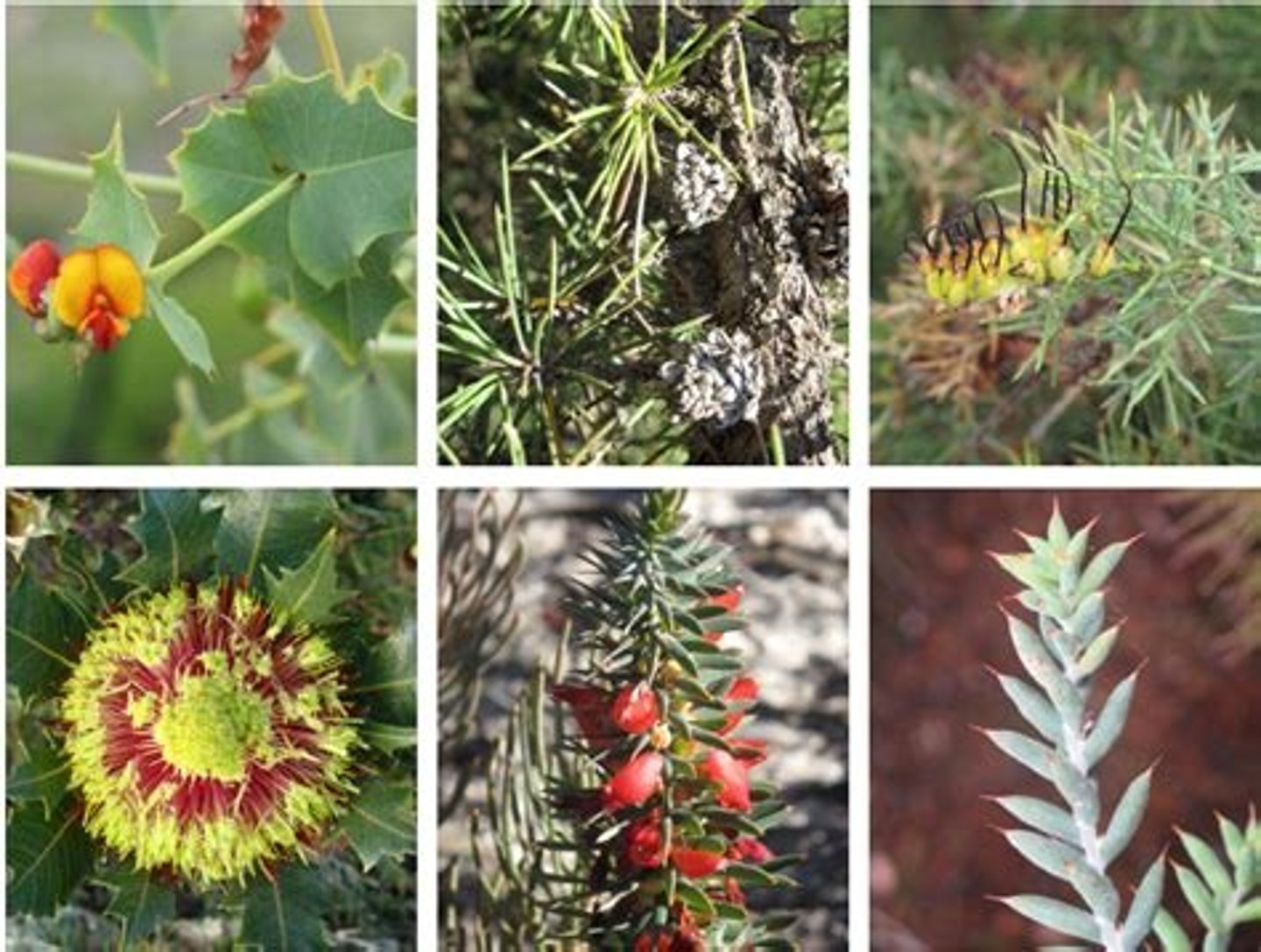
Sclerophyllous plants
a type of vegetation that has hard leaves, short internodes and leaf orientation parallel or oblique to direct sunlight.

Trade Winds deserts
are impacted by dry air currents (descending Hadley Cell circulation) moving towards the equator, which dissipate clouds (absorb water) and maximize incoming solar radiation. Temperatures in the Sahara have been recorded at 57 C (135 F)

Xerophytes
plants with adaptations that enable them to survive in dry habitats or habitats where water is in short supply in the environment.
- Cacti
- Prickly pear
- Bromeliads
Soil salinitization
occurs when water soluble salts, such as NaSO4, CaSO4, or MgSO4, accumulate in the soil. Water seeping from the soil evaporates, leaving the salts behind. Making it harder for plants to absorb water in salty soil
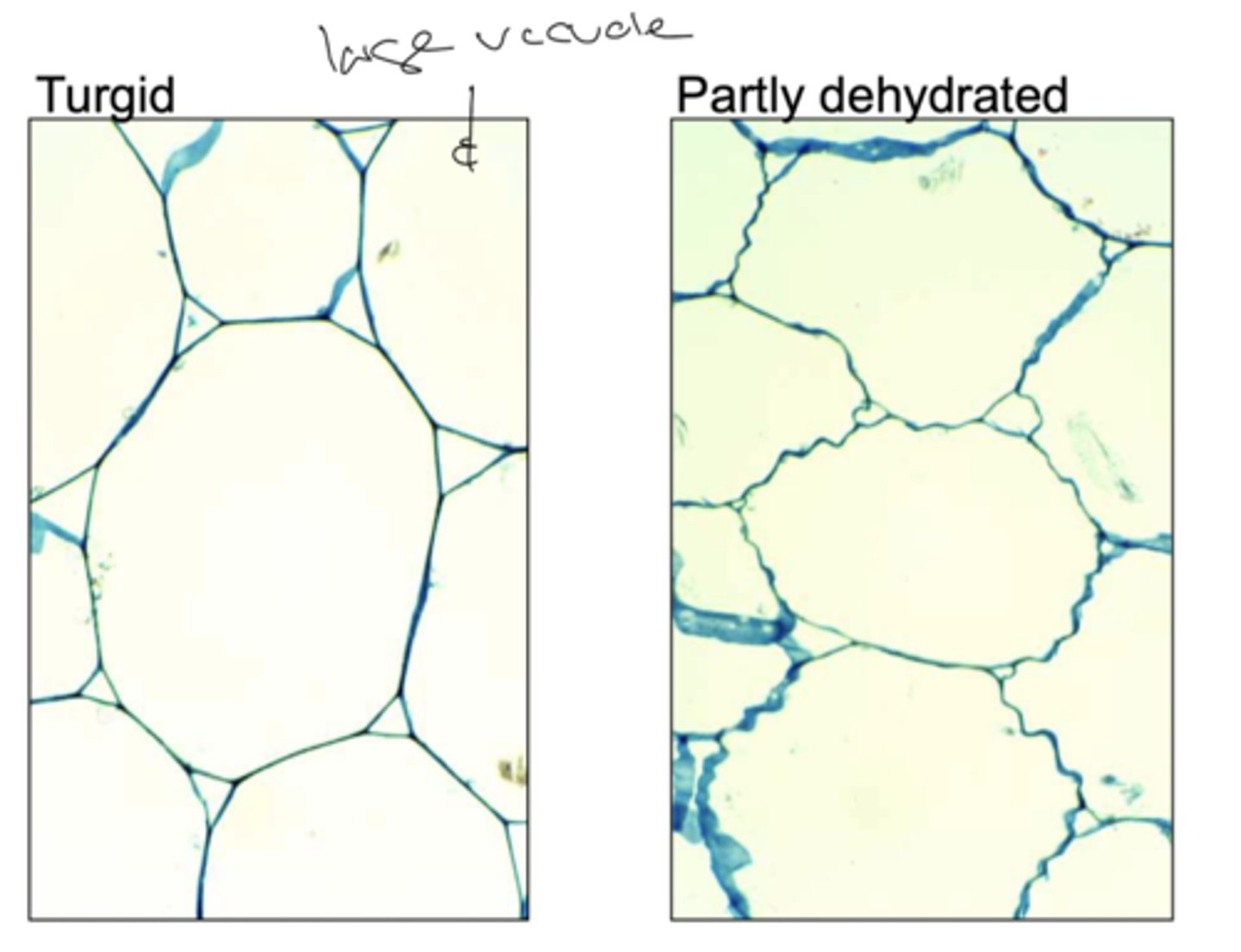
Hydrenchyma
special water storage tissue with elastic cell walls that can swell when water is abundant, and collapse during dry periods as the plant uses the stored water.
Transpirational loss
Water loss through evaporation from plant surfaces.