254: Unit 4 Fluoro / QC
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
fluoroscopy primary function
provides real-time dynamic viewing of anatomic structures
motion of circulation
motion of internal structures
conventional fluoro
less than 5 mA
high patient dose
long exposure time
continuous exposure
ABC
automatic brightness control
other names for ABC
ADC
ABS
AERC
ADC
automatic dose control
ABS
automatic brightness stablization
image intensifier purpose
reduce patient dose by decreasing the amount of x ray photons needed for imaging purposes
image intensifier
intercept the X-ray photons and convert them into visible light
amplify or intensify this light signal
reduce patient dose by decreasing x ray photons needed
contains cathode & anode
output phosphor
a fluorescent screen
receives the electrons from the photocathode
absorbs electrons and emits light photons
made a thin layer of silver activated zinc cadmium sulfate phosphor
anode
positively charged end
serves to attract the electrons emitted from the photocathode
in front of the output phosphor
a hole in the center allows electrons to pass and interact with the output phosphor
how do the electrons pass through to interact with the output phosophor?
a hole in the center of the anode
electrostatic lenses
a series of negatively charged electrodes
focuses and accelerates the electrons emitted from the photocathode toward the anode
uses electrostatic repulsion
pushes the electron stream toward the middle
input phosphor
first element of the image intensifier
scintillator screen
absorbs X-ray photons and emits light
constructed of cesium iodide crystals
flux gain
energy gained during acceleration from the photocathode to the output phosphor
light photons / x ray photons
flux gain equation
number of output light photons / number of input x ray photons
minifcation gain
the concentration of photoelectrons from the input phosphor to the output phosphor
(input screen)2 / (output screen)2
brightness gain
the product of the flux gain and the minifcation gain
product of X-ray photons coming in to how many light photons come out
brightness gain equation
minification gain (flux gain)
multi-field image intensification purpose
magnify the image
multi-field image intensification
increasing the voltage of the electrostatic lenses & uses a smaller input phosphor
brings focal spot closer to input phosphor and away from output phosphor
magnifies the image sent to the output phosphor
magnification factor
ratio of diameters available to diameters used
patient dose ____ when using magnification factor
increases
why does patient dose increase when using magnification factor?
An image intensifier uses a smaller section of the input screen & systems ABC will increase the exposure to increase the exposure to keep the image bright
advantages of magnification factor
better spatial resolution
better contrast resolution
disadvantage of magnification factor
higher patient dose
CCD advantages
high spatial resolution
high SNR
high DQE
no warm-up required
no lag or blooming
no spatial distortion
no maintenance
unlimited life
unaffected by magnetic fields
linear response
lower patient radiation dose
FPIR
flat panel image receptor
Flat panel image receptor takes the place of
the image intensifier
Flat panel image receptor is made of
cesium iodide (scintillator)
amorphous silicon (photodetector)
Flat panel image receptor magnification
done electronically
No increase in patient dose
Flat panel image receptor advantages
distortion-free images
constant image quality over the entire image
improved contrast resolution over the entire image
high DQE at all radiation dose levels
rectangular image area coupled to a similar image monitor
multiple detector system
uses 3 TFT detectors
detectors switch between static and dynamic imaging
The tube is below the patient
AERC
automatic exposure rate control
automatic brightness control
automatically adjust the kvp and mAs based on patient attenuation to maintain consistent brightness of contrast of the image
single detector system
single TFT detector used for static and dynamic imaging
X-ray tube above the patient
allows for longer SIDs for a greater variety of exams
cost-effective
can be used remotely by a radiologist
digital fluoroscopy
higher mA
lower patient dose
shorter exposure time
pulsed exposure
intensification process
x rays → light → photon electrons → light
pulse progressive fluoroscopy
uses a high-power generator
Pulses the x ray production from the fluoro x ray tube synchonrously with the detector signal
interrogation time
time required for the generator to come on a produce the necessary kVp and mAse
extinction time
time required to shut the generator down in preperation for the next pulse
duty cycle
the fraction of time the x ray tube is energized
LIH
last image hold
DSA
digital subtraction angiography
post processing
window/level
invert
filtering edge enhancement
mobile fluoro (CR) minimum source to skin distance
12” (30 cm)
stationary fluoro minimum source to skin distance
15” (38 cm)
audible timer
5 mins
primary source of exposure for tech/ rad
the patient
lead apron & gloves
0.5 Pb/eq
bucky slot cover / protective curtain
0.25 mm / Pb eq
general purpose table top expsosure should not exceed
100 mGya/min
high level (IR) tabletop exposure should not exceed
200 mGya/min
Quality Assurance
deals with people
radiology reports
repeat rates
image QA
quality control
deals with instrumentation & equipments
equipments performance evaluations
QC step 1
acceptance testing
QC step 2
periodic monitoring
QC step 3
maintenance and repair
acceptance testing
testing the new equipment once you receive it
not done by the people who created the equipment
done by a medical physicist
periodic monitoring
routine evaluation of the x ray producing or image processing equipment
maintenance and repair
a dedicated analysis of each image to identify deficiencies and artifacts
filtration
tested annually
greater than or equal to 2.5 mm Al
collimation
semiannually
plus / minus 2% SID
Focal spot size
annually
plus / minus 50%
Calibration of kVp
annually
plus/minus 10%
exposure timer accuracy
annually
plus/minus 5% with exposures greater than 10 ms
exposure linearity
annually
plus/ minus 10% less than or equal to 10 ms
exposure reproducibility
annually
plus / minus 5%
primary test for effective FSS
slit camera
Multiple Detectors in Room
fluoroscopic
upright imaging
recumbent imaging
viewing systems
LCD monitors (used more)
Plasma monitors
AEC testing
test the exposure readout using varying thicknesses of material (Al)
no matter the thickness the receptor readout should be the same N
,
SMPTE pattern
used for observing gross deviations in luminance
determines spatial resolution & contrast resolution
DICOM
digital imaging and communication
GSDF
gray scale display function
allows medical images to be transferred at a DICOM standard to be displayed on any DICOM device with a consistent grayscale
ensures images are displayed the same way on different monitors
TG18
used to check for contrast and spatial resolution display quality on the radiologist's monitor
evaluates for
geometric distortion
reflection
luminance
display resolution
display noise
ACR
recommends that all digital display devices utilize TG 18 patterns in formats that can be displayed on the digital monitor for evaluation purpose
medical physicist
test as appropriate
annually
post repair
acceptnace testing
periodic review of the facility QC program
QC technologist
routinely,l as established by the department QC program
ability to acquire the TG 18 QC test pattern and use it on each digital display device regularly
staff technologist
daily
visually monitor workstations for indications of malfunction
geometric distortion
lines in pattern should appear straight
pincushion distortion
barrel like distortion
display noise
any high-frequency fluctuations or patterns that interfere with the detection of the true signal on
conventional
continuous exposure
Vidicon TV Camera Tube
low mA
higher patient dose
CCD took the place of _____
Vidicon TV Camera Tube
digital
post processing
ADC
FPIR
CCD
pulsed exposure
high mA
low patient dose
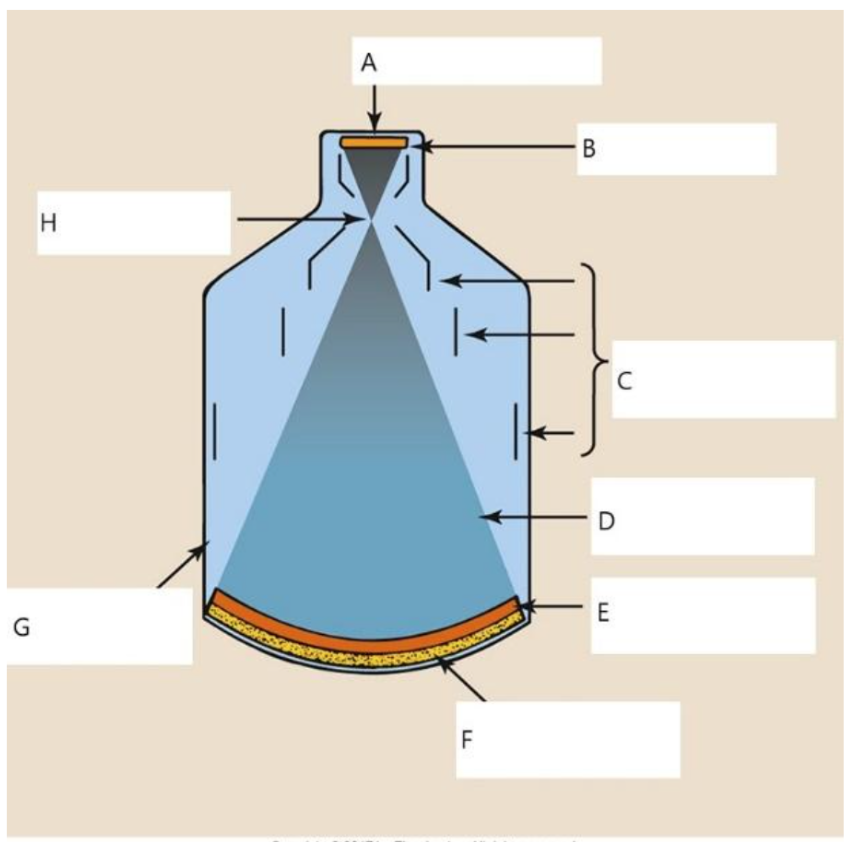
A
output phosphor
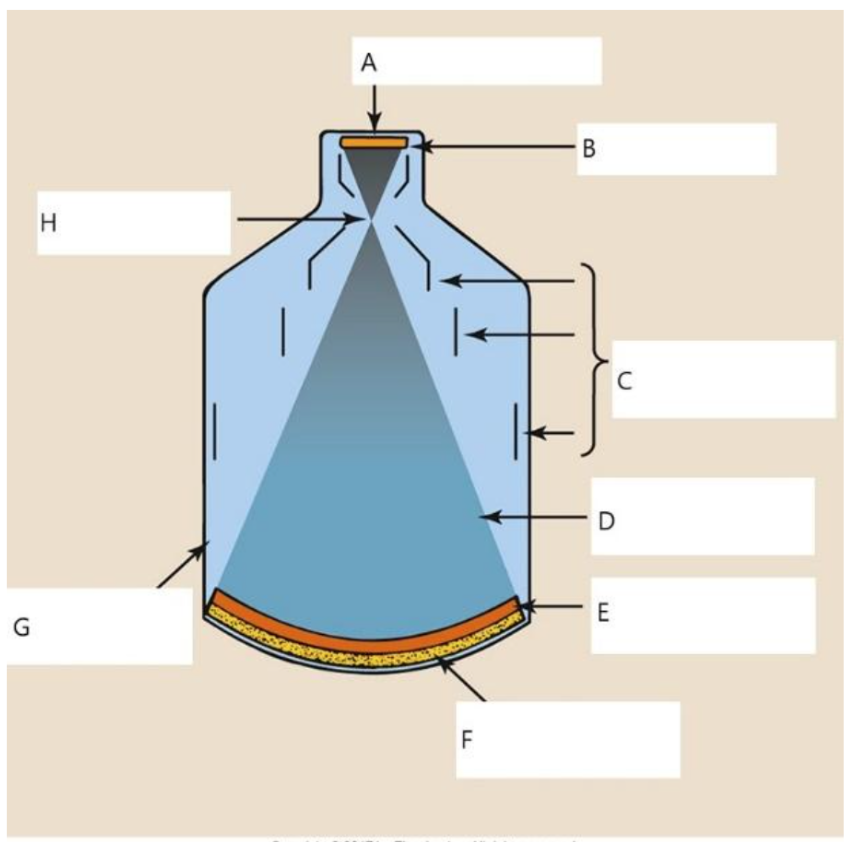
B
anode
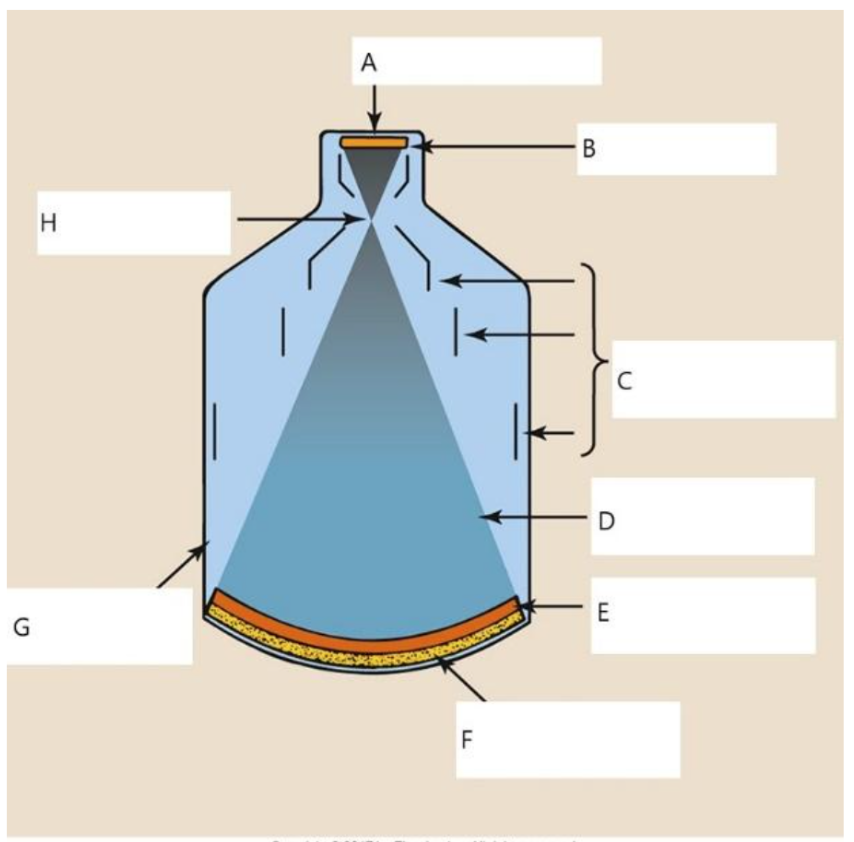
C
electrostatic lenses
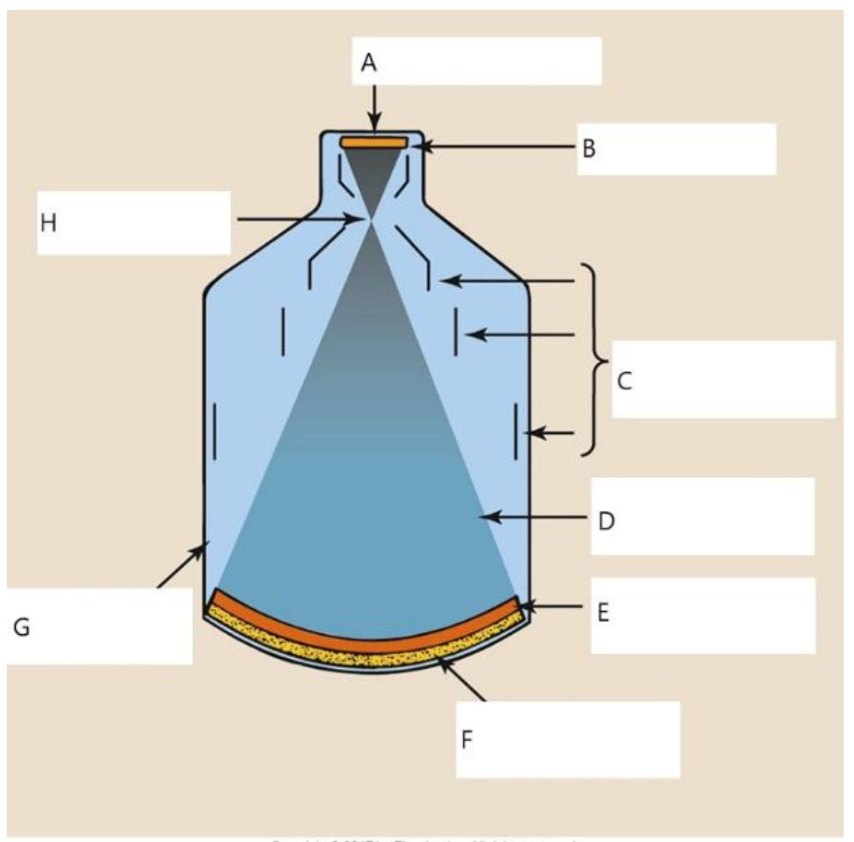
D
electrons
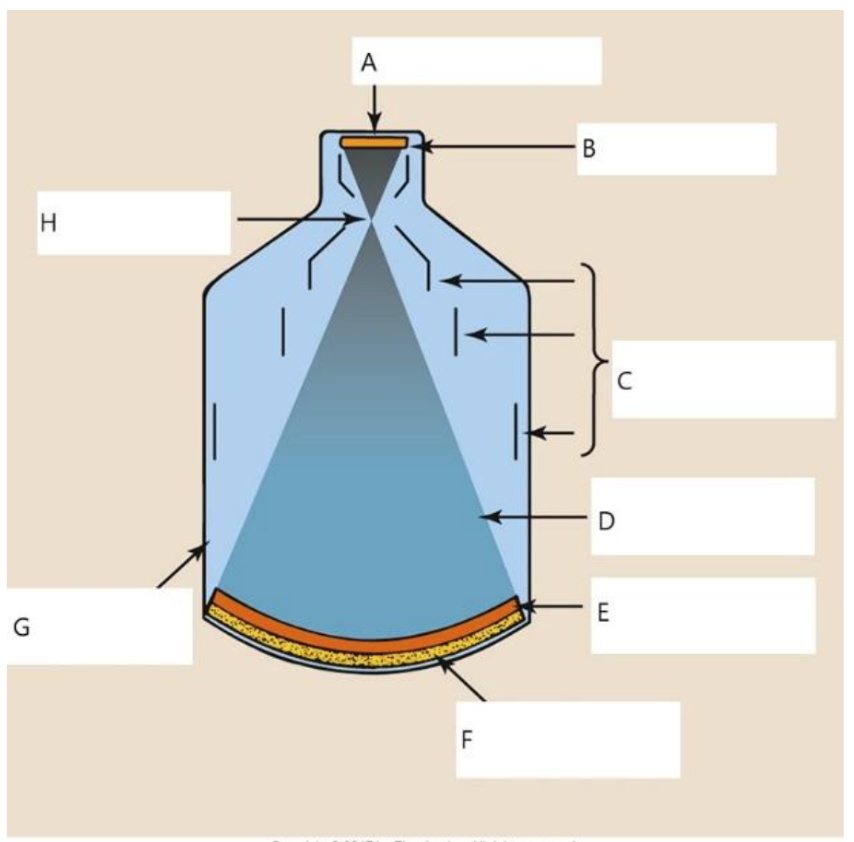
E
photocathode
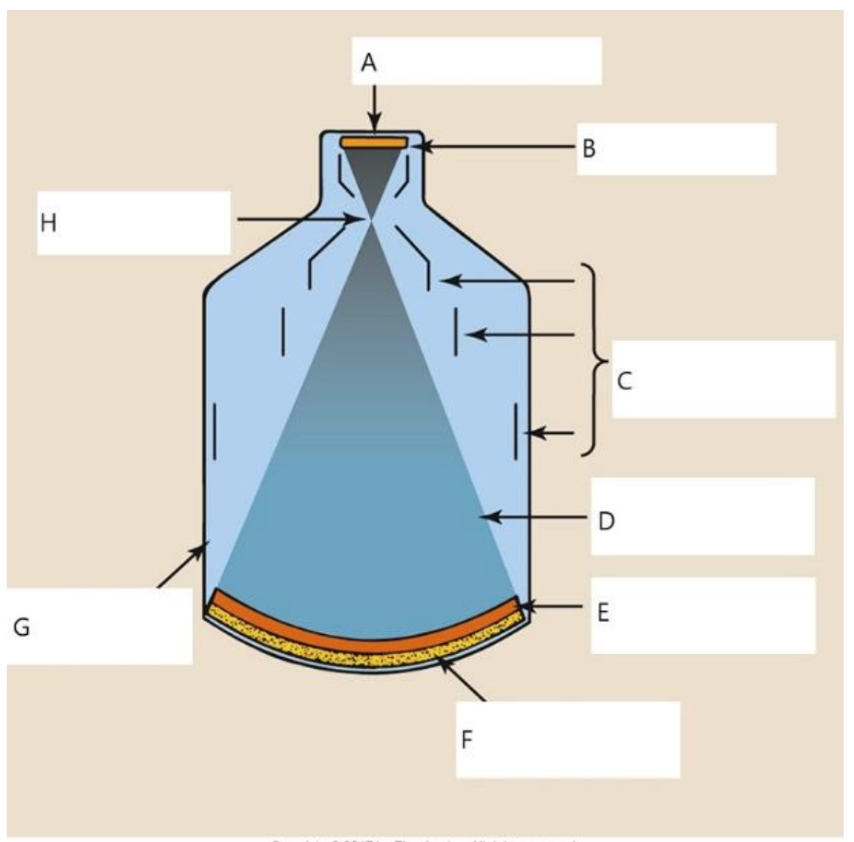
F
input phosphor
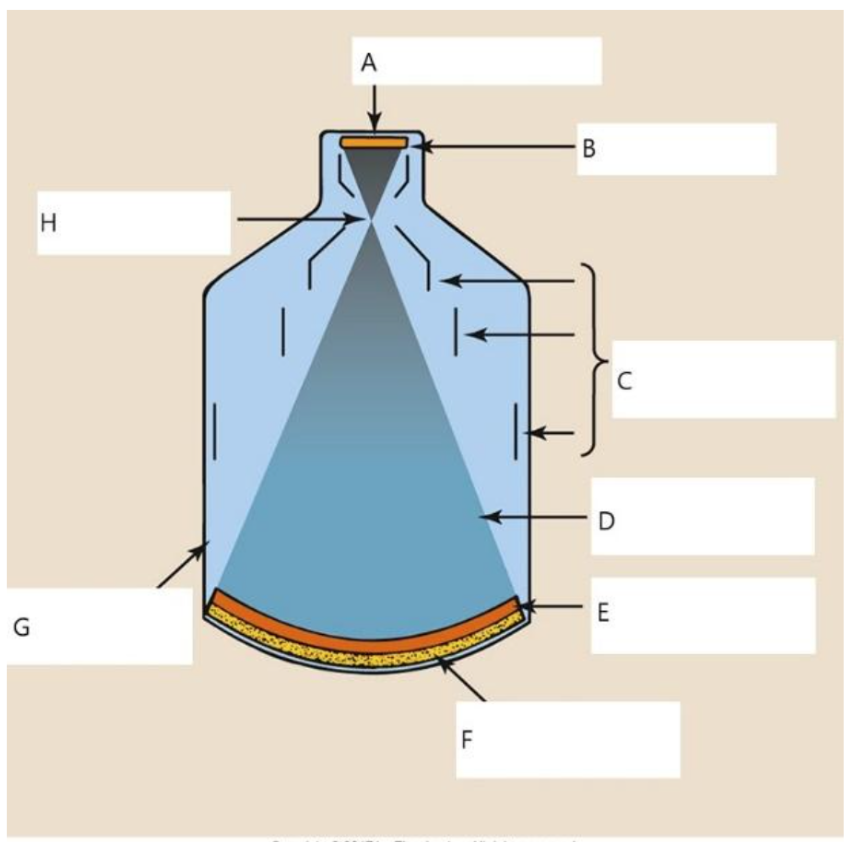
G
glass envelope

H
focal point
at what stage of image intensified fluoroscopy is the number of photons the lowest
when entering the input phosphor