Zahin, Nailah- APWH Unit 7 Flashcards
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
1
New cards
Mexican Revolutions 7.1
The Mexican Revolution was a series of regional conflicts in Mexico that defined political and economic reform
1) Internal and external factors such as foreign influence on private investments led to to change in the state as Mexico adopted a constitution leading economical, educational, and political reform
1) Internal and external factors such as foreign influence on private investments led to to change in the state as Mexico adopted a constitution leading economical, educational, and political reform

2
New cards
Russian Revolution 7.1
The Russian Revolution occurred in the Soviet Union as an act of addressing the political issues in the state.
1) The internal factors of the government not supporting industrialization led to external factors as they had lost wars due to a lack of a strong military. This led to creation of a nation under communism and the state shifting to power under the Bolsheviks
1) The internal factors of the government not supporting industrialization led to external factors as they had lost wars due to a lack of a strong military. This led to creation of a nation under communism and the state shifting to power under the Bolsheviks

3
New cards
Causes of WWI 7.2
Causes of WWI include militarism, alliances, imperialism, nationalism, and the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
2) Causes of WWI include nationalism that promotes militarism, imperialism, induced weak alliances and the assassination of Austria-Hungary’s archduke. Consequences include political instability of weaker nations, the dismantlement of previous dominating nations, treaties, and economic drought.
2) Causes of WWI include nationalism that promotes militarism, imperialism, induced weak alliances and the assassination of Austria-Hungary’s archduke. Consequences include political instability of weaker nations, the dismantlement of previous dominating nations, treaties, and economic drought.

4
New cards
Total War 7.3
Total War is a term used to describe a type of warfare in which an entire nation and it’s population uses all its resources towards achieving victory in a war
3) Governments used methods of mobilizing all resources and turning industries to produce for the cause of the war to conduct war by inducing competition
3) Governments used methods of mobilizing all resources and turning industries to produce for the cause of the war to conduct war by inducing competition

5
New cards
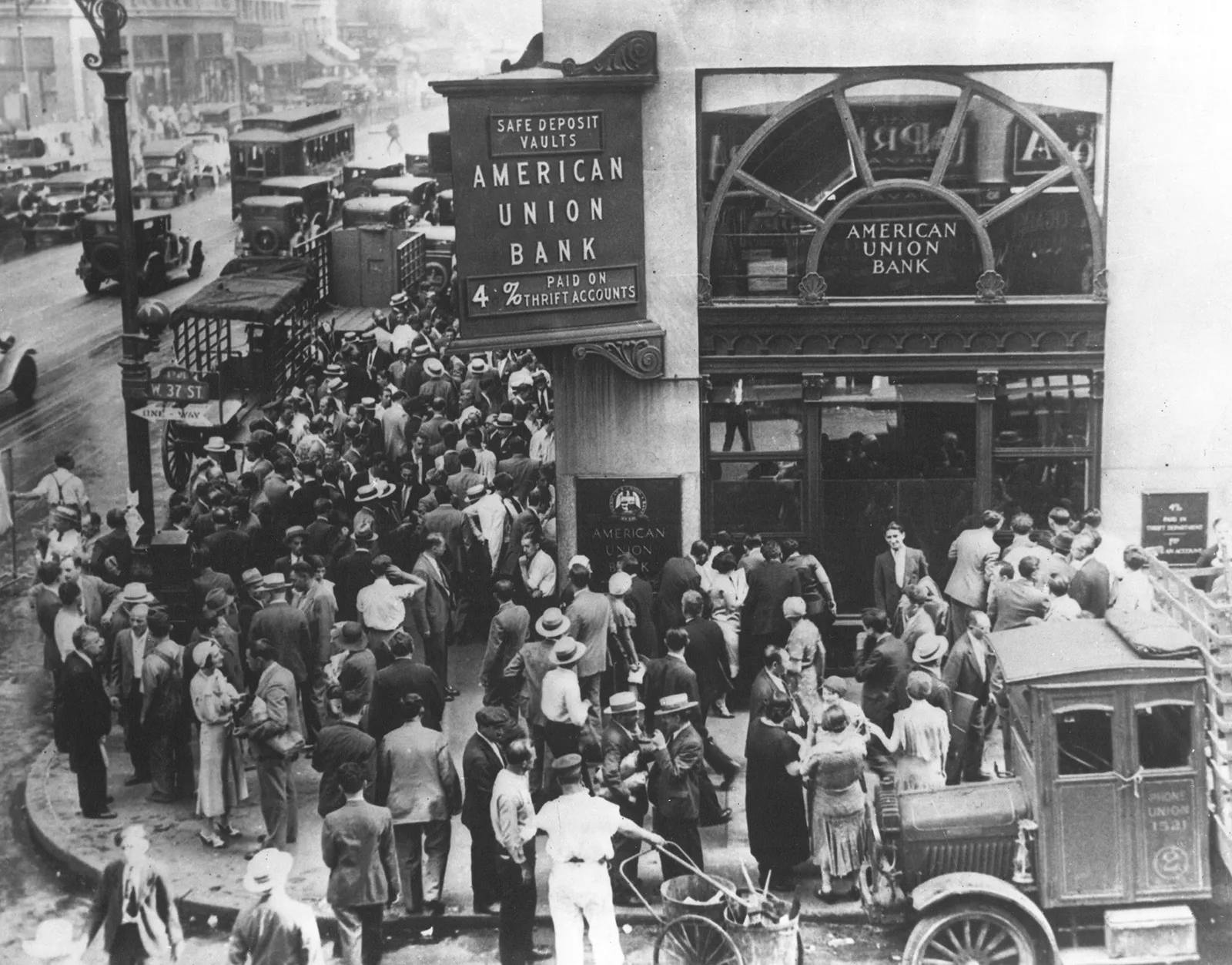
Great Depression 7.4
The Great Depression was a severe economic downfall and affected countries across the globe. It began with the stock market crash and resulted in inflation and poverty with many businesses failing, losing jobs, and life savings llost
4) Governments and large nations across the world created systems changing their methods of production and public spending to sustain the economical drought
4) Governments and large nations across the world created systems changing their methods of production and public spending to sustain the economical drought

6
New cards
New Deal 7.4
The New Deal was a set of policies and programs introduced
by FDR to promote recovery and reform to the economy.
4) The american government increased their involvement in the market economy to restore and stimulate economic growth and prosperity after the depression and WWI
by FDR to promote recovery and reform to the economy.
4) The american government increased their involvement in the market economy to restore and stimulate economic growth and prosperity after the depression and WWI

7
New cards
Five Year Plans (Soviet Union) 7.4
The Soviet Union started the Five-Year-Plan to induce a series of economic developments to rapidly industrialize, produce good efficiently, and collectivize agriculture
4) The Soviet Union established the five year plan in an attempt to modernize and repair the economy after the depression to become self sufficient and create a system to strengthen the nation’s security through communism
4) The Soviet Union established the five year plan in an attempt to modernize and repair the economy after the depression to become self sufficient and create a system to strengthen the nation’s security through communism

8
New cards
Fascist Corporatist Economy 7.4
Fascist Corporatist economies were started in Italy and adopted by Hitler in Nazi Germany controlling the economy and promoting nationalism by establishing an industry where all private investments go towards the state.
4) The creation of fascism was used to restore the economy after the Great Depression by uniting all industries to sustain efficient of the central economy.
4) The creation of fascism was used to restore the economy after the Great Depression by uniting all industries to sustain efficient of the central economy.

9
New cards
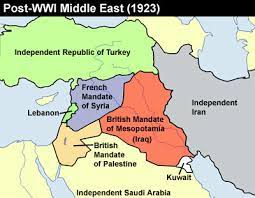
Mandates 7.5
The mandate system was a compromise between the Allies' wish to retain the former German and Turkish colonies and their pre-Armistice declaration that annexation of territory was not their aim in the war.
5) This shifted control of territories and created peaceful annexations of territory during war after dismantling an empire
5) This shifted control of territories and created peaceful annexations of territory during war after dismantling an empire
10
New cards
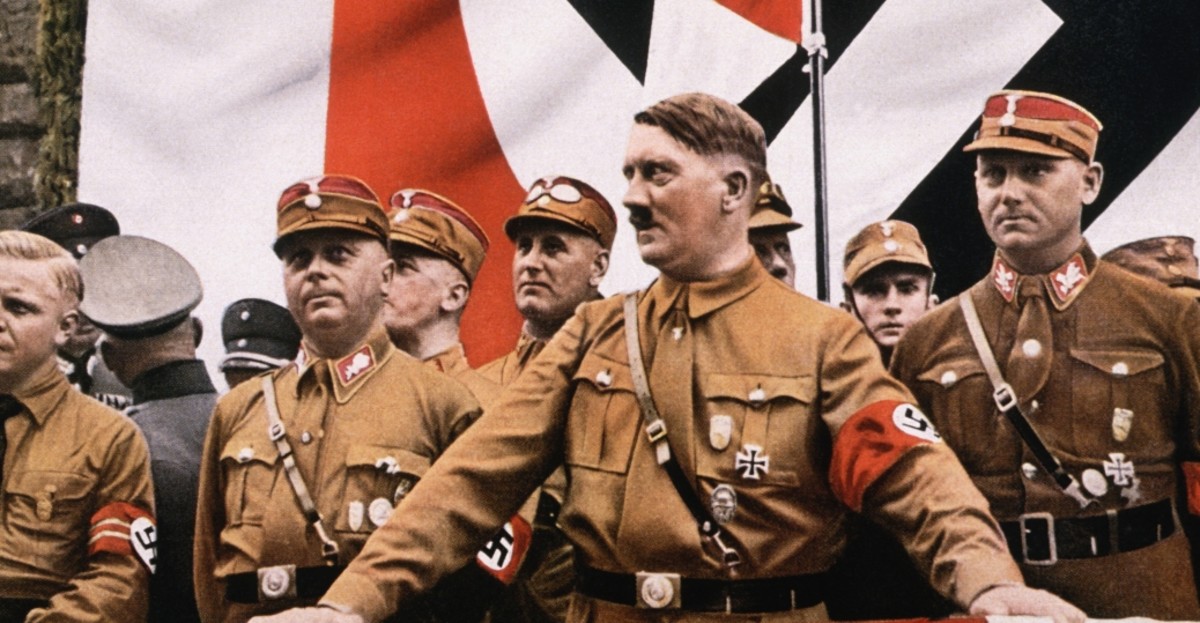
Causes of WWII 7.6
Causes of WWII include lasting political tension from WWI, economic instability, and failure of peace led by the League of Nations
6) Causes include social, political, and economic factors. Consequences of WWII include millions of deaths as a result of the total war, new national borders, and the emergence of new dominant political powers to promote peace.
6) Causes include social, political, and economic factors. Consequences of WWII include millions of deaths as a result of the total war, new national borders, and the emergence of new dominant political powers to promote peace.

11
New cards
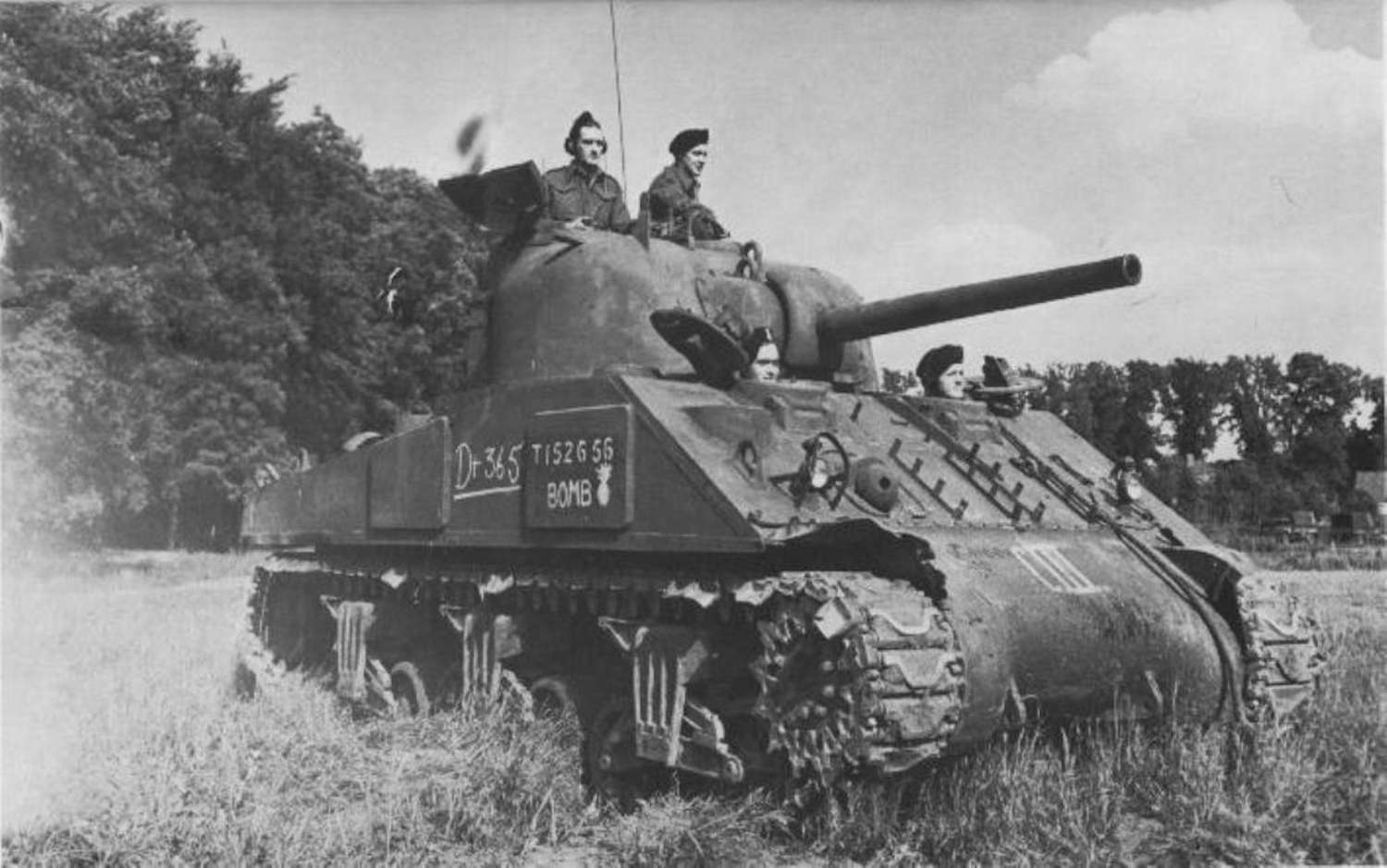
New Military Tech WWII 7.7
Military technology include radars, submarines, ships, new arms, atomic bombs, and barbed wire
7) Similarities include that states used advanced technology such as bombs and arms to conduct war. Differences include that US prioritized naval warfare while Germany and many European states stayed on land
7) Similarities include that states used advanced technology such as bombs and arms to conduct war. Differences include that US prioritized naval warfare while Germany and many European states stayed on land

12
New cards
Holocaust 7.8
The Holocaust was a genocide during WWII led by Hitler and the Nazi Party under an act of nationalism
8) Causes include scientific ideology “proving” the superiority of the aryan race and abolishment of anyone that does not fit the German standard, also rooted in anti-semitism that led to war. Consequences led to mass amounts of Jewish and German deaths and displacement and migration of Jewish seeking refuge in other countries
8) Causes include scientific ideology “proving” the superiority of the aryan race and abolishment of anyone that does not fit the German standard, also rooted in anti-semitism that led to war. Consequences led to mass amounts of Jewish and German deaths and displacement and migration of Jewish seeking refuge in other countries

13
New cards
Ukrainian Genocide 7.8
The Ukrainian Genocide was a man-made famine by the peasant class that occurred in Soviet Ukraine with between 3-7 million deaths
8) Causes include government policies and totalitarian rule of Stalin’s agriculture impositions. Consequences include mass deaths as a result of famine and government instability
8) Causes include government policies and totalitarian rule of Stalin’s agriculture impositions. Consequences include mass deaths as a result of famine and government instability
