MCHE 3920 Shape Casting of Metals Week 3
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
3200 BCE
Oldest shape castings date back to?
3 main benefits of shape casting
Provides complex shapes, wide range of materials, and economical for large parts and high volume production
Auto, aero, machinery, pipes, construction equipment
Where are shape castings normally found?
slowly, oxidation
When filling a mold for shape casting: it is best to fill it _____ to prevent splashing and thus _________, and helps prevent gas entrapment
higher, not cast, cast
castings normally have _______ alloy content: Steel w/ Fe<2% C is typically _______, while Fe 2-4% C is typically _______
Lower viscosity, lower melting temp
Reasons why castings have higher alloy content
eutectic composition
What do we want casting metals to be near?
mechanical properties, decrease
Higher alloy content comes at expense of _________; toughness, ductility and fatitgue strength all ________ by presence of alloy
mechanical performance
what is a trade off w/ castability
liminal
Filling speed: want slow speeds s.t. flow is ________
turbulence
laminar flow minimizes _________ and thus oxidation and loss of material props
lower productivity, chance of cold running (cold shut)
trade offs of low filling speeds:
gates, injection pressure
_____ increase fill speed, increasing _________
preheated molds, energy consumption, costs
___________ preven cold running- increases __________ and ______
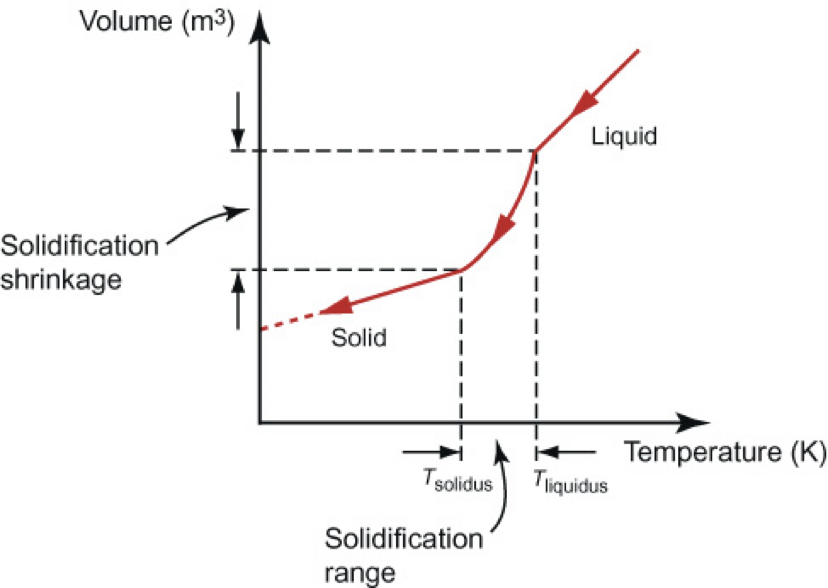
solidification range
rate of volume reduction is highest where?
Tpouring to Tsolidus- specific heat, liquid phase
Phase 1/3 of cooling:
Liquid to solid, latent heat of fusion
Phase 2/3 for cooling:
Tsolidus to RT, specific heat solid phase
Phase 3/3 of cooling:
add extra material during filling
What do we do about solidification shrinkage?
make mold bigger
what do we do about shrinkage after solidification?
how long is take for part to be cool and strong enough for handling (seconds)
Chorinov’s rule shows what?
large solid castings, underestimates
Chorinov’s rule works well for ______, but ________ time for hollow thin-walled parts
inner wall doesn’t absorb as much heat as outer walls
Why does Chorinov’s rule underestimate for hollow parts
solidification/cooling time, casting, insulator, V/A
For parts with walls <4mm, chorinov’s underestimates ________ becuase the mold expands while ________ contracts, creating an air gap that acts as an __________, a better model is proportional to _____
Porosity, internal stresses, distortion
3 main casting defects:
gas bubbles
second main cause for porosity: are released during solidification and trapped in the solid
shrinkage porosity
first main cause for porosity: not enough extra material in casting to account for solidification shrinkage
poorly designed, solidifies
shrinkage porosity occurs when a mold is ________, or a runner _______, blocking flow into thicker section
disperse gas into the solid so that only forms small bubbles
how to minimize gas bubbles effects
thinner
which cast sections cool quicker
temperature gradients
different sections w diff thicknesses cool at diff rates, leading to ____________ w/i the casting
eth=CLTE*deltaT
thermal strain equation
stresses exceed yield stress
when can permanent deformation occur in casting
computer simulation
bc of complex geometries, predicting internal stresses in casting requires ____________
casting metallurgy
choosing best alloy for the job
crystalline
metals have a what grain structure?
grain boundary
where grains grow w/i solid and along mold wall and impinge on each other
0.05,5
cast grans are typically ____ to_____ mm large
cooling rate, fast cooling, smaller grain, better properties
grain size dictated by _______, ______ leads to _________ leads to ________
improve processability, improve material properties, minimize impurities/improve microstructure
3 reasons alloying elements are used:
true
T/F: alloying elements can intro impurities that can be detrimental
segregation
non-unifrom distribution of dissolved elements during solidification
atomic soup
in liquid state, alloy elements dissolved in:
purer, enriched, impurities
during cooling, first solids formed are ______ than average, so remainder is relatively ________ which will lead to ___________
grain boundaries
last part to solidify in casting
inoculants
high melting point powders added before pouring
smaller, segregation
as liquid cools, solids form around the inoculant promoting ______ grains and less _________
small, tensile strength, poisoning
sometimes _____ additions of the right element can improve the _________ of a cast metal (this is known as _______)
silica sand a bonding agent
in sand casting, what forms the mold
wooden/plastic/metal patterns
in sand casting, what are used to form negative space in the mold
low, tolerances
patterns only support ___ filling speeds and pressures, and have poor ________
larger grains
in sand casting, long solidification times means

parting plane
in sand casting: plane where drag and cope meet

sprue
sand casting molds are filling through
feeder
in a sand casting mold, what shows when filling is complete
gravity die casting
casting method that uses reusable steel dies
finer microstructure
in gravity die casting, shorter cycle times lead to
smoother, tolerances, low, limited, aluminum, magnesium
gravity die casting: _____ products and good control over _______, filling speeds are _____, product size is more _______ than sand casting, ______ and _______ commonly cast using this method
low pressure die casting
casting method using reusable steel dies with pressures from 2 to 5 bar
aluminum and magenesium
elements commonly used in low pressure die casting
high pressure die casting
casting method w espensive steel dies up to 2000 bar
sand cores, sliding elements
high pressure die casting cannot use _______ but can use ________
fast throughput, lower quality, thinner products
with high injection speeds in high pressure die casting:
zinc, aluminum, magnesium
high pressure die casting is limited to these elements
investment casting
casting method using a wax-made pattern attached to the sprue (rare)
ceramic slurry, wax, mold, destroyed, complex geometries
investment casting: dipped into a _________ that cures while ____ melts away, hollow ceramic shell is then used as the ______, after casting the shell is ______. good for ________