alkenes
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
what are the reagents and conditions for the addition of H2 to an alkene?
H2 and Pd catalyst
How does the catalyst assist the addition of H2 to an alkene?
The 2 H atoms bond to the Pd surface first
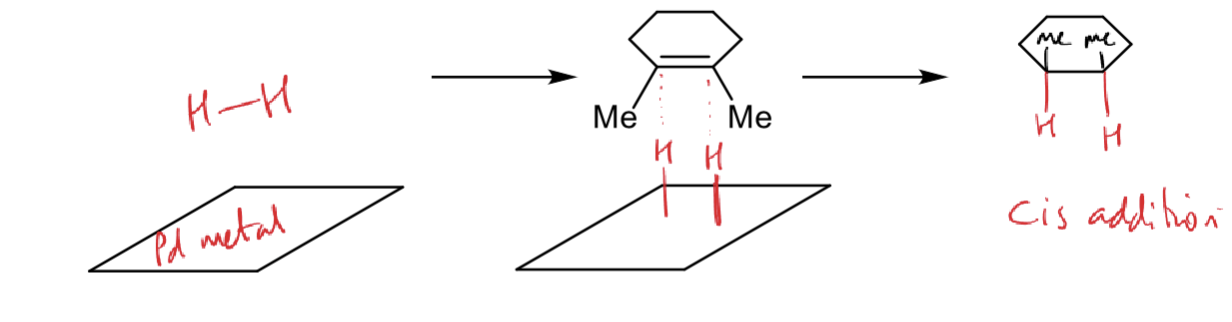
what is the outcome when an alkyne reacts with H2 and Lindlar’s catalyst?
what is Lindlar’s catalyst?
alkene and no further reaction
Pd on BaSO4/CaCO3
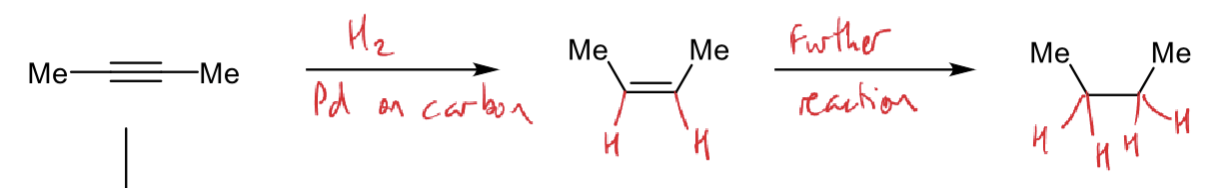
how to react an alkyne to an alkane (reagents and conditions)?
what are the steps?
H2 and Pd on carbon
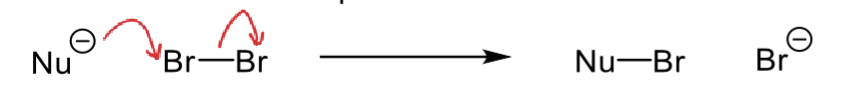
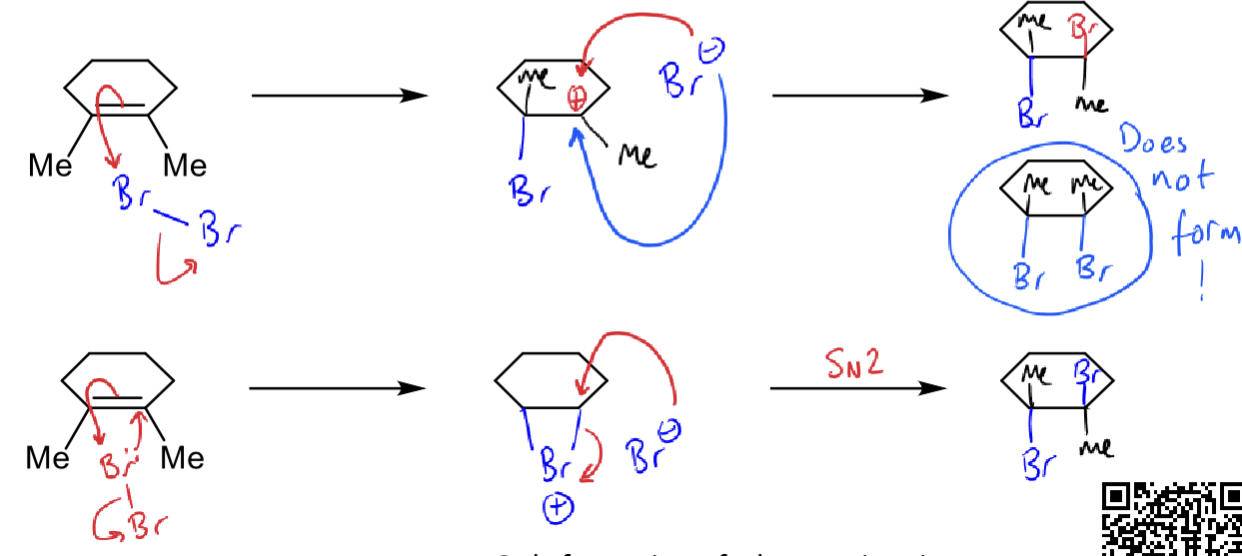
what are the two possible mechanisms with alkenes as nucleophiles?
example is Br2 as electrophile
why is only one possible?
SN2 (two bonds to one Br)
only the bottom mechanism is possible as only the trans alkene forms so top cannot be possible
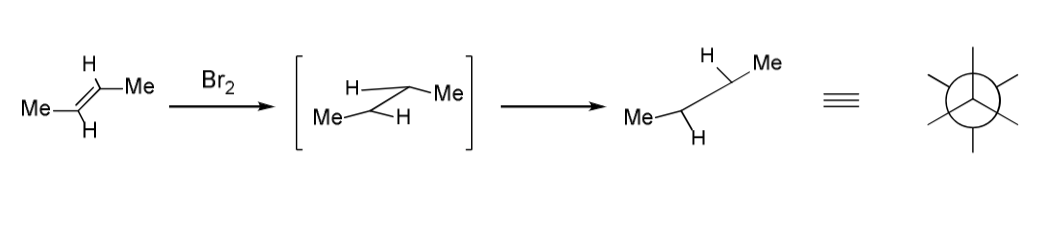
how does stereospecificity work for the addition of bromine to an alkene?
the product matches the stereoisomer of the starting material (ie if starts as trans alkene then will finish as trans)
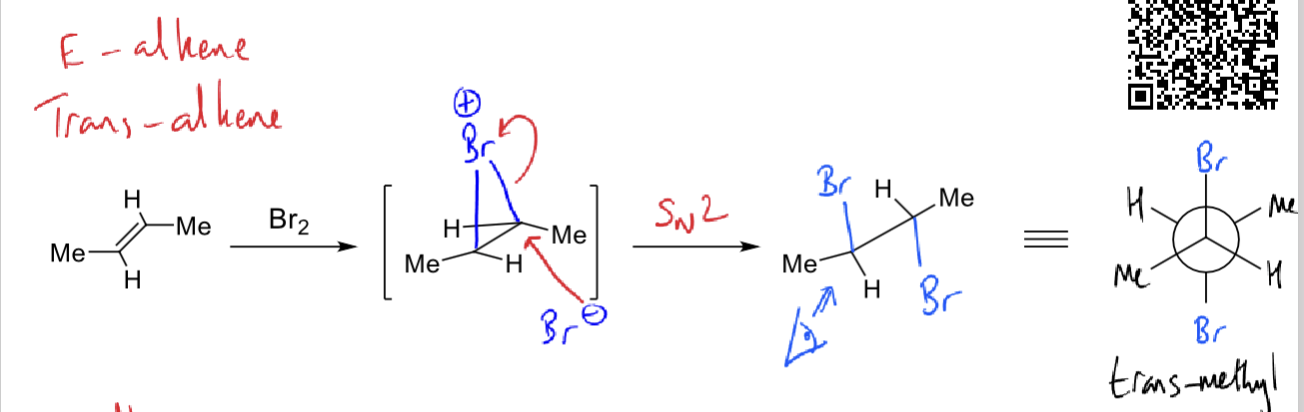
draw mechanism for addition of bromine
is it trans/cis?
trans methyl
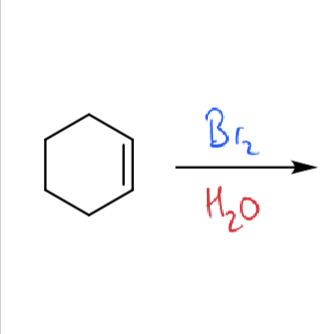
how do bromonium ions react with water?
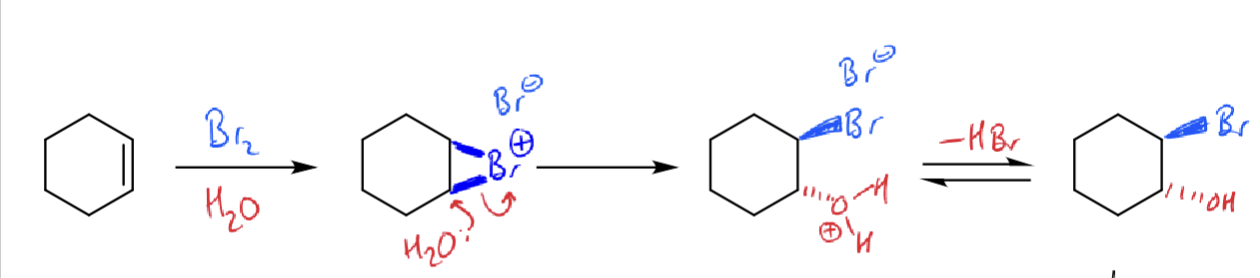
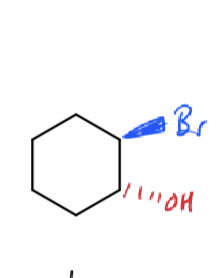
how to make epoxides from bromohydrins?
NaH
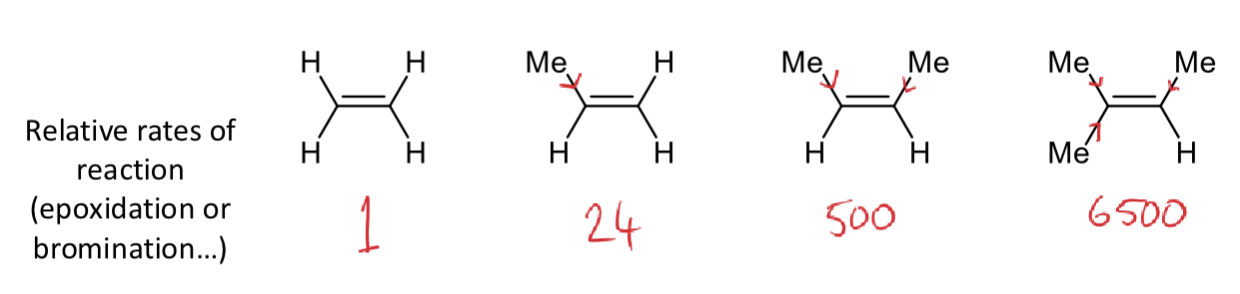
how does increasing the alkyl substitution on the alkene affect the rate?
why?
increases the rate
inductive effects
which product is given when H-X is added to an unsymmetrical alkene (Markovnikov’s rule)?
intermediate?
transition state?
the more highly substituted
the most stable cation intermediate gives the most substituted product
lowest energy transition state gives more substituted
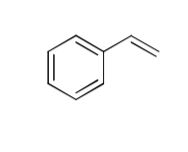
what are the two paths when H-Br is added to this molecule?
draw both energy diagrams for each carbocation
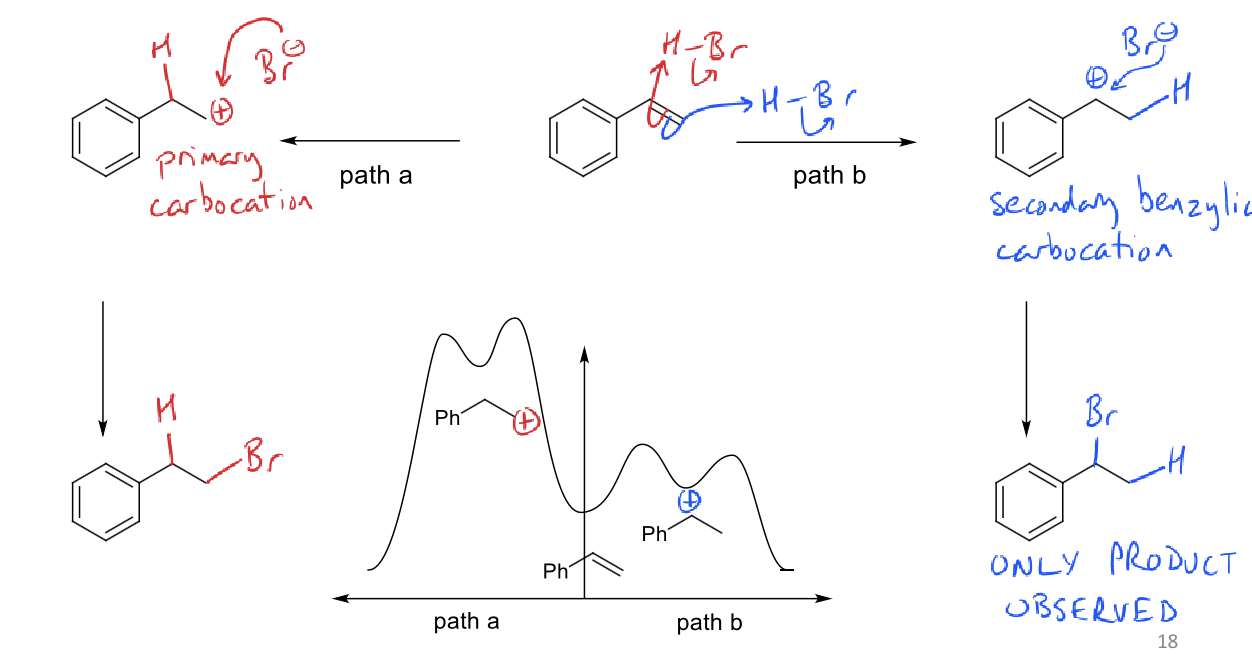
why does this reaction not obey Markovnikov’s rule?
there is no carbocation intermediate
in hydroboration, which end of the alkene does boron attach to?
the least hindered end
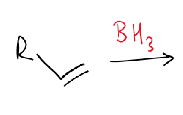
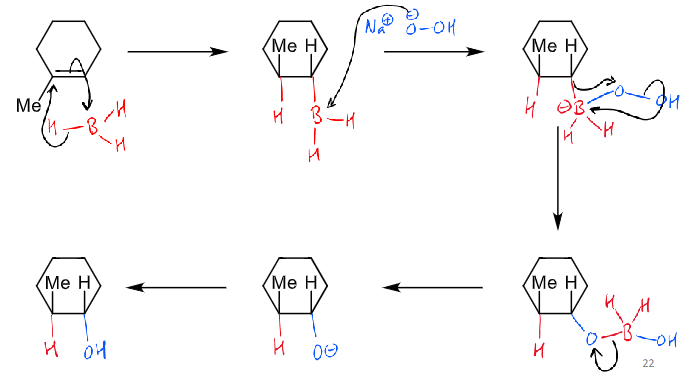
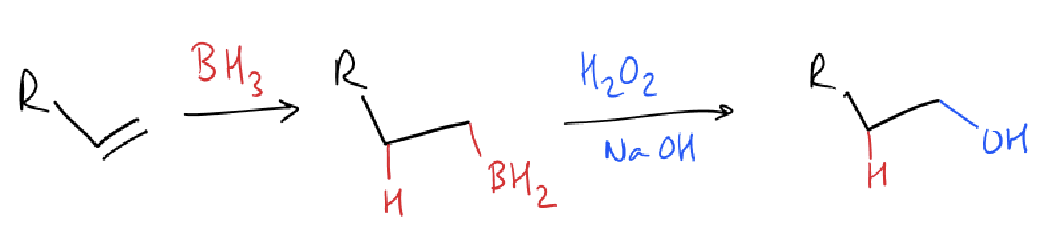
what is the hydroboration reaction?
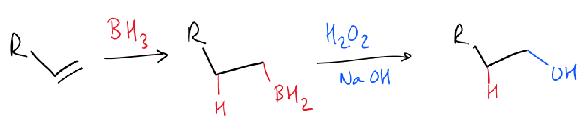
what is the hydroboration mechanism?
is addition cis/trans?
planes in terms of O?
alkyl migration is stereospecific - oxygen stays in same face as boron
cis addition of boron and hydrogen