Physical Assessment Quiz 4 Chapter 22,23,24 Professor Kramer Keiser University
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
187 Terms
Chapter 22
Abdomen Physical Assessment
*How do you perform an abdominal exam?*
Inspect, Auscultation, Percussion, Palpate
*What are the internal organs inside the abdominal cavity called?*
the viscera
*What lines the abdominal cavity and covers surface (visceral) of most organs?*
peritoneum
**Which viscera maintain characteristic shape?**
solid viscera
What is included in the solid viscera?
liver, pancreas, spleen, adrenal glands, kidneys, ovaries and uterus
**The shape of the hollow viscera depends on what?**
content
What is included in the hollow viscera?
Stomach, gallbladder, small intestine, colon, and bladder
**How many quadrants is the abdomen divided into?**
4 quadrants: RUQ, LUQ, RLQ, LLQ
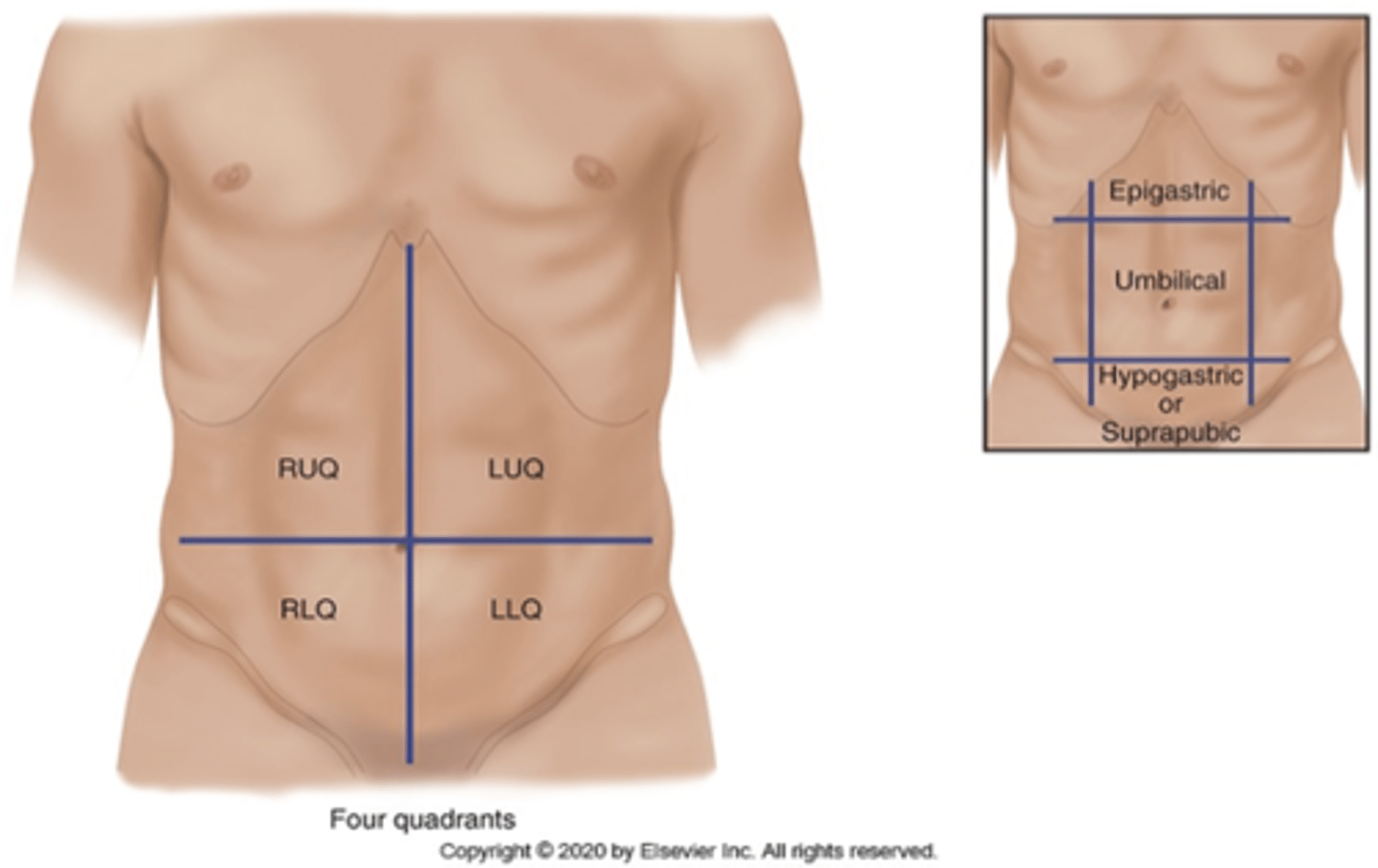
**What is the midline organs of the abdomen?**
Midline organs—aorta, uterus if enlarged and bladder if distended
**What is pyrosis?**
heartburn
A burning sensation in the upper abdomen. ....upward into your throat, and you may have a sour taste in your mouth. Also known as indigestion.
**Until age 7 what do newborns and infants breathe more with?**
their abdomen
**In a abdominal wall of a aging adult the wall musculature ______________
relaxes
**What decreases in a aging adult?**
a. salivation decreases leading to dry mouth
b. decreased sense of taste
*What is delayed with the esophagus and GI in aging adults?*
Esophageal emptying and gastric acid secretion are delayed.
constipation is frequently reported
**In the gallbladder what increases with age?**
gallstones
**What is impaired within the liver as you age?**
though liver size decreases, most liver functions remain normal however drug metabolism is impaired
**What standardizes symptoms for constipation?**
ROME III standardizes symptoms criteria for functional constipation.
**What is the criteria for Rome III?**
for constipation, a patient must have experienced at least 2 of the following symptoms over the preceding 3 months: Fewer than 3 bowel movements per week. Straining. Lumpy or hard stools. Sensation of anorectal obstruction. Sensation of incomplete defecation. Manual maneuvering required to defecate.
Common causes of constipation in a older adult?
a. Decreased physical activity
b. Inadequate intake of water
c. Low-fiber diet
d. Side effects of medications
e. Irritable bowel syndrome
f. Bowel obstruction
g. Hypothyroidism
h. Inadequate toilet facilities, that is, difficulty ambulating to i.toilet may cause a person to deliberately retain stool until it becomes hard and difficult to pass
**What is lactase?**
digestive enzyme necessary for absorption of carbohydrate lactose (milk sugar).
**What are some lactose intolerance symptoms?**
have abdominal pain, bloating, and flatulence when milk products are consumed
**What ethnicity is 100% lactose intolerant?**
100% American Indians.
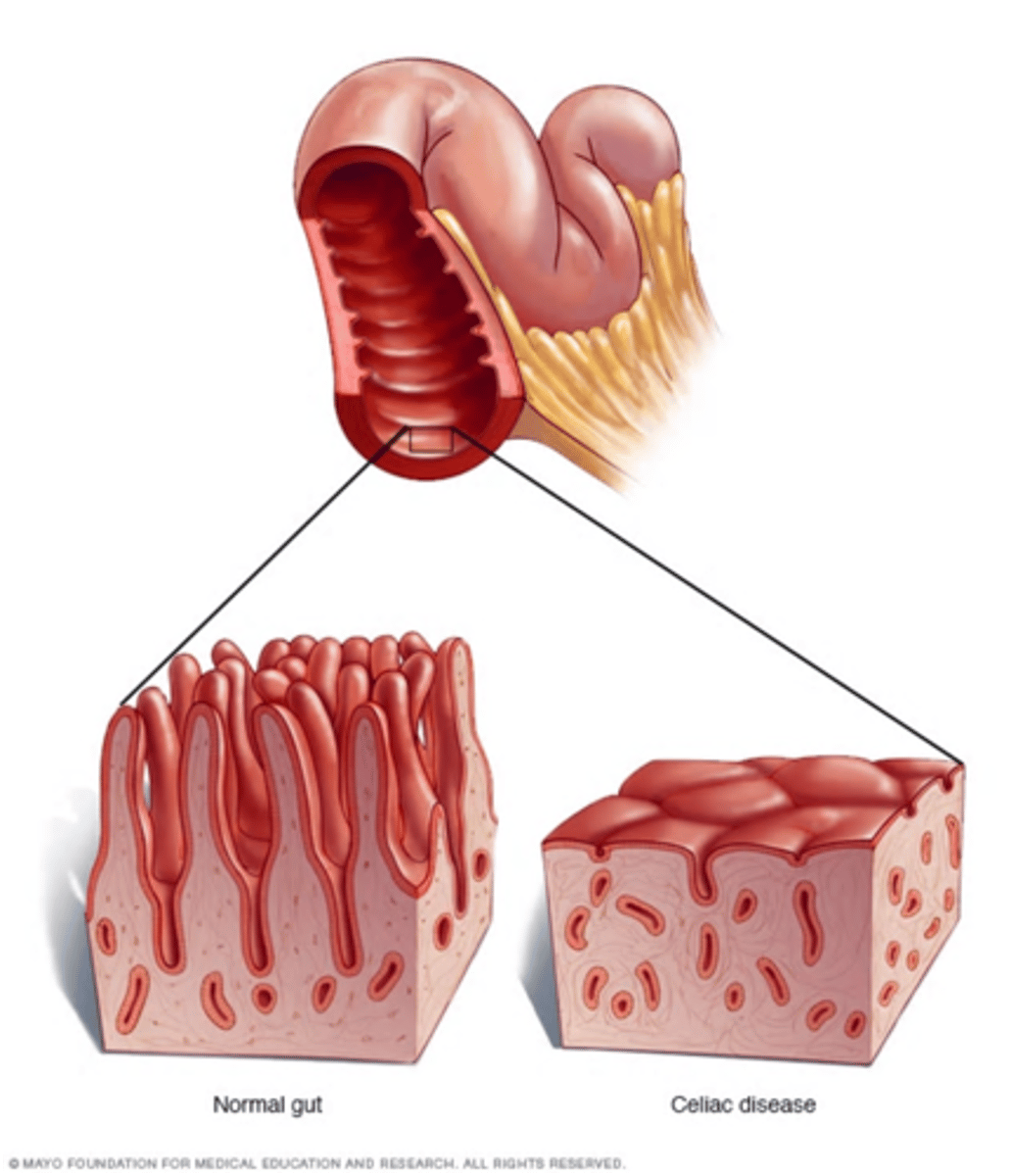
**Celiac disease is what?**
a. Autoimmune disorder
b. Intolerant of gluten
**With appetite, you should ask about?**
a. changes in appetite—time period and amount.
b. changes in weight—loss or gain (amount) and time period.
*With Dysphagia you should ask about?*
a. any difficulty in swallowing.
b. onset and associated symptoms.
With food intolerance you should ask about?
a. type of food reaction that occurs.
b. use of Rx or OTC medication—amount and frequency.
c. **Pyrosis: Burning sensation in upper abdomen** (Heartburn or indigestion)
With nausea and vomiting ask about?
a. onset, frequency, type and amount.
b. associated symptoms and/or triggers.
c. recent foods eaten and/or travel habits.
With bowel habits you should ask about?
a. frequency, color, consistency, diarrhea or constipation.
b. any recent changes.
c. laxative use—type, amount and frequency.
With past abdominal history ask about?
a. GI disease/pathology.
b. GI diagnostic procedures.
c. GI surgeries and clinical response
With medications ask about?
a. Rx and OTC.
b. alcohol—type, amount, and frequency.
c. smoking history.
With a nutritional assessment ask about?
dietary history.
*What is pyloric stenosis?*
Congenital narrowing of the pyloric sphincter. Narrowing of the sphincter or the opening from the stomach to the small intestine. Symptoms are projectile vomiting after feeding
**When assessing the abdomen you should do what prior to palpation and percussion?**
auscultate
When inspecting the abdomen you should look for?
contour
symmetry
umbilicus
skin: moles are common finding
pulsation or movement
hair distribution
demeanor
When looking at a abdominal mass you should note?
location
size
shape
and consistency (soft, hard , or firm)
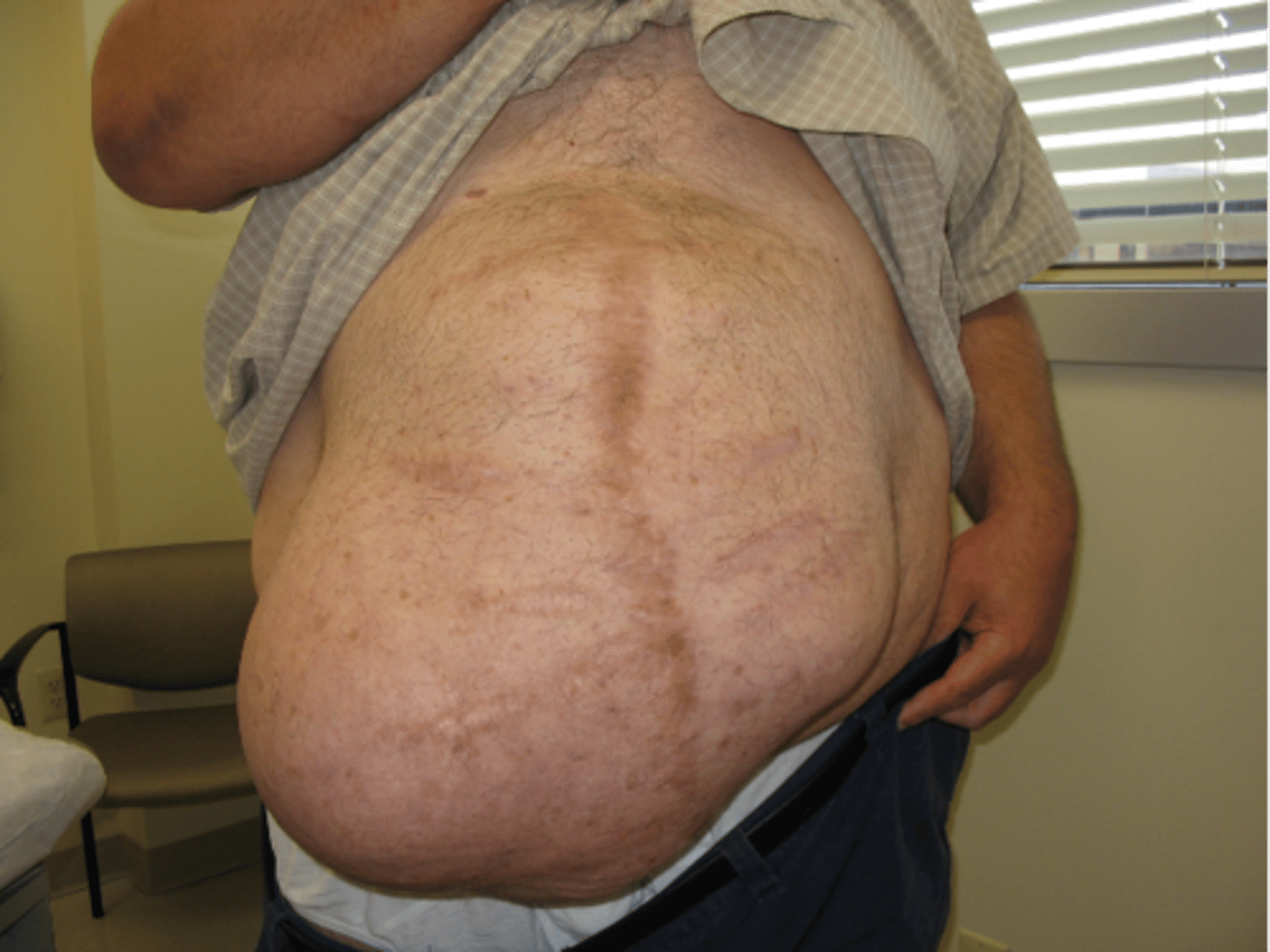
**What are ascites?**
Abnormal Accumulation of serous fluid built up in the abdomen due to Liver failure leading to decrease in protein (Albumin) that comes from the liver.
Why do we auscultate first?
percussion and palpation can increase peristalsis, which would give a false interpretation of bowel sounds. **Always start at the RLQ**
**How often should bowel sounds occur per minute? **
occurring irregularly anywhere from 5 to 30 times per minute
What are hypoactive bowel sounds?
decreased, can follow abdominal surgery or with inflammation
What are hyperactive bowel sounds?
loud, high-pitched signal increased motility
**What is borborygmus?**
sound of hyper peristalsis
*Perfectly "silent abdomen" is uncommon; therefore you must listen for?*
5 minutes by your watch before deciding bowel sounds are completely absent. If completely absent you would just notify the provider.
*Using firmer pressure when checking vascular sounds?*
Using firmer pressure, check over aorta, renal arteries, iliac, and femoral arteries, especially in people with hypertension.
A orta
R enal arteries
I lilac
F emoral arteries
**You should not auscultate for initial placement of what?**
a. NG tube
b. Evidence-based practice (EBP) confirming initial placement by imaging study and continued assessment by external tube length and pH of stomach aspirate
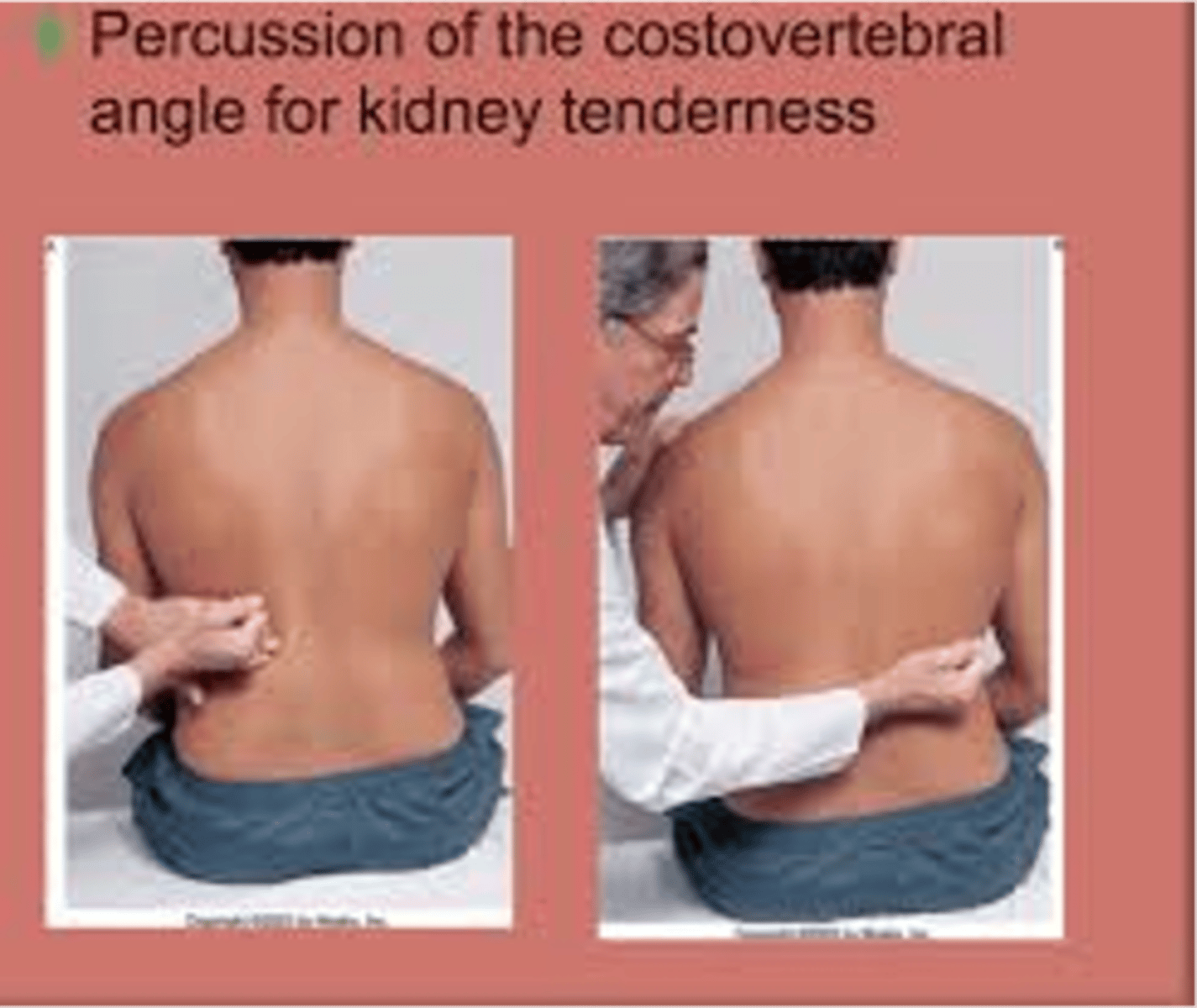
**CVA angle kidney tenderness**
Positive finding indicates inflammation of the kidney.
A person normally feels thud but no pain
**What is the Blumberg sign?**
also referred to as rebound tenderness is a clinical sign in which there is pain upon removal of pressure rather than application of pressure to the abdomen. It is indicative of peritonitis.
**What is McBurneys point?**
Right side of the abdomen
corresponds with the appendix
incision site during appendectomy
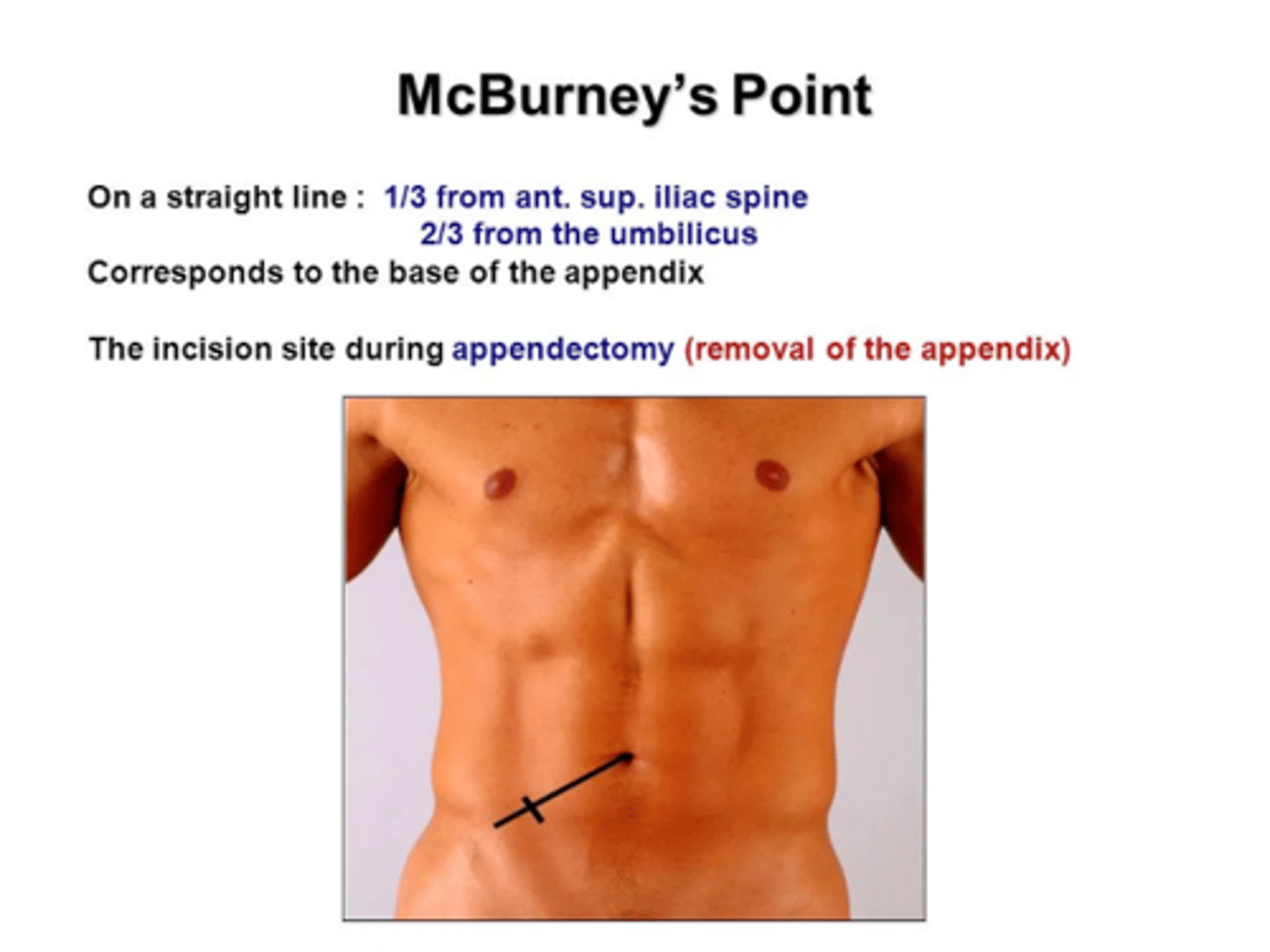
Iliopsoas Muscle Test
a. place your hand over the right thigh and push downward as the patient is trying to raise the leg flexing the hip
b. positive RLQ pain associated with a retrocecal or perforated appendicitis
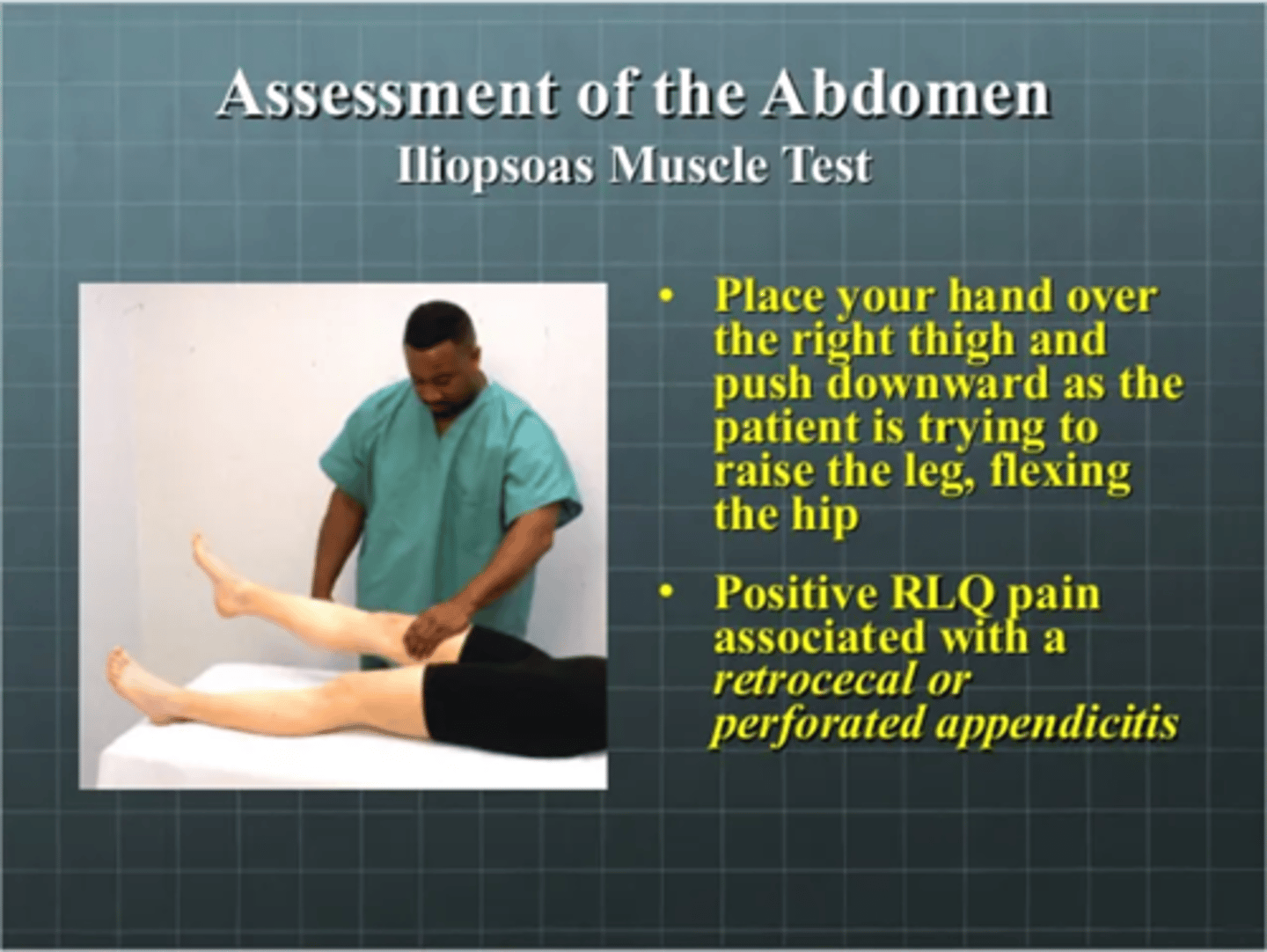
**Obturator Muscle Test**
flex the right leg at the hip and knee at a right angle then rotate the leg internally and externally
pain indicative of inflammatory process over obturator muscle
--ruptured appendix
--pelvic abscess
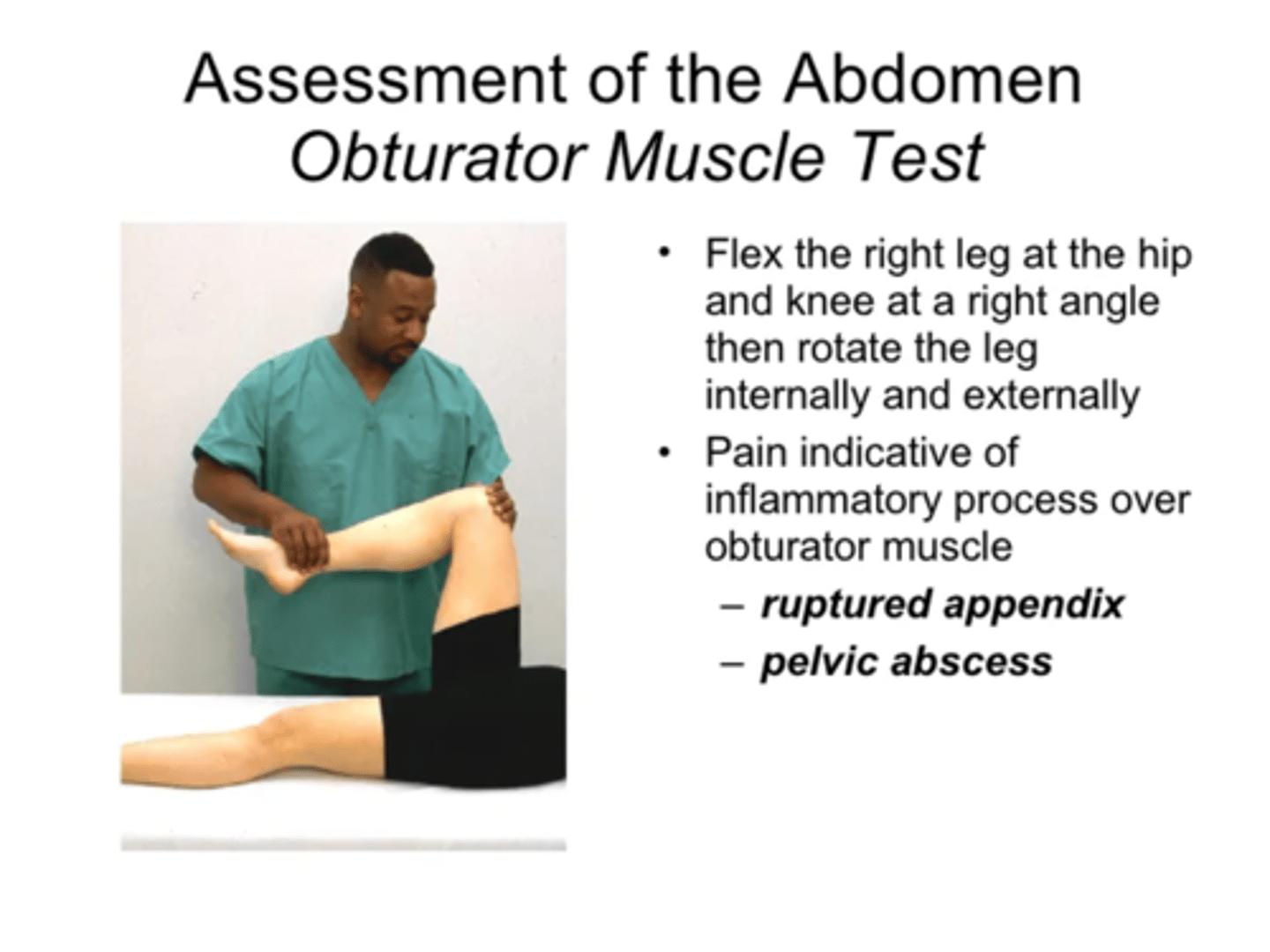
What is the Alvarado (MANTRELS) score?
a. This scoring system combines findings to assist evaluation in patients with RLQ pain.
b. 7 or more= acute appendicitis
**When palpating the abdomen, what do you begin with?**
Do a light palpation then proceed to deep palpation
Judge size, location, and consistency of certain organs and screen for an abnormal mass or tenderness.
**Light and deep palpation, with either technique you should note?**
note location
size
consistency
mobility of any palpable organs and presence of any abnormal enlargement, tenderness, or masses
**How should you figure out what you are palpating since most say it all "feels the same" **
Helps to memorize anatomy and visualize what is under each quadrant as you palpate
**When palpating the sigmoid colon what should you feel?**
Mild tenderness
If you identify a mass you should note the following?
Location
Size
Shape
Consistency: soft, firm, hard
Surface: smooth, nodular
Mobility, including movement with respirations
Pulsatility
Tenderness
What is the function of the spleen?
filter blood and help fight infections
**Are you able to palpate a spleen? **
Normally spleen is not palpable and must be enlarged three times its normal size to be felt.
*When palpating the kidneys, what will you feel with the right and left? *
Right kidney: Feel no change or feel smooth muscle mass, Either is normal
Left kidney: Feel no change with inhalation Not normally palpable, 1 cm higher than right kidney
**Left kidney will be higher than the right kidney**
**How wide should the aorta be when you palpate it? If it is widen what does that mean?**
a. Normally it is 2.5 to 4 cm wide in adult and pulsates in an anterior direction.
b. Widened in the presence of abdominal aortic aneurysm
What is Wharton's jelly?
soft substance that cushions the entire umbilical cord and prevents kinking or obstruction
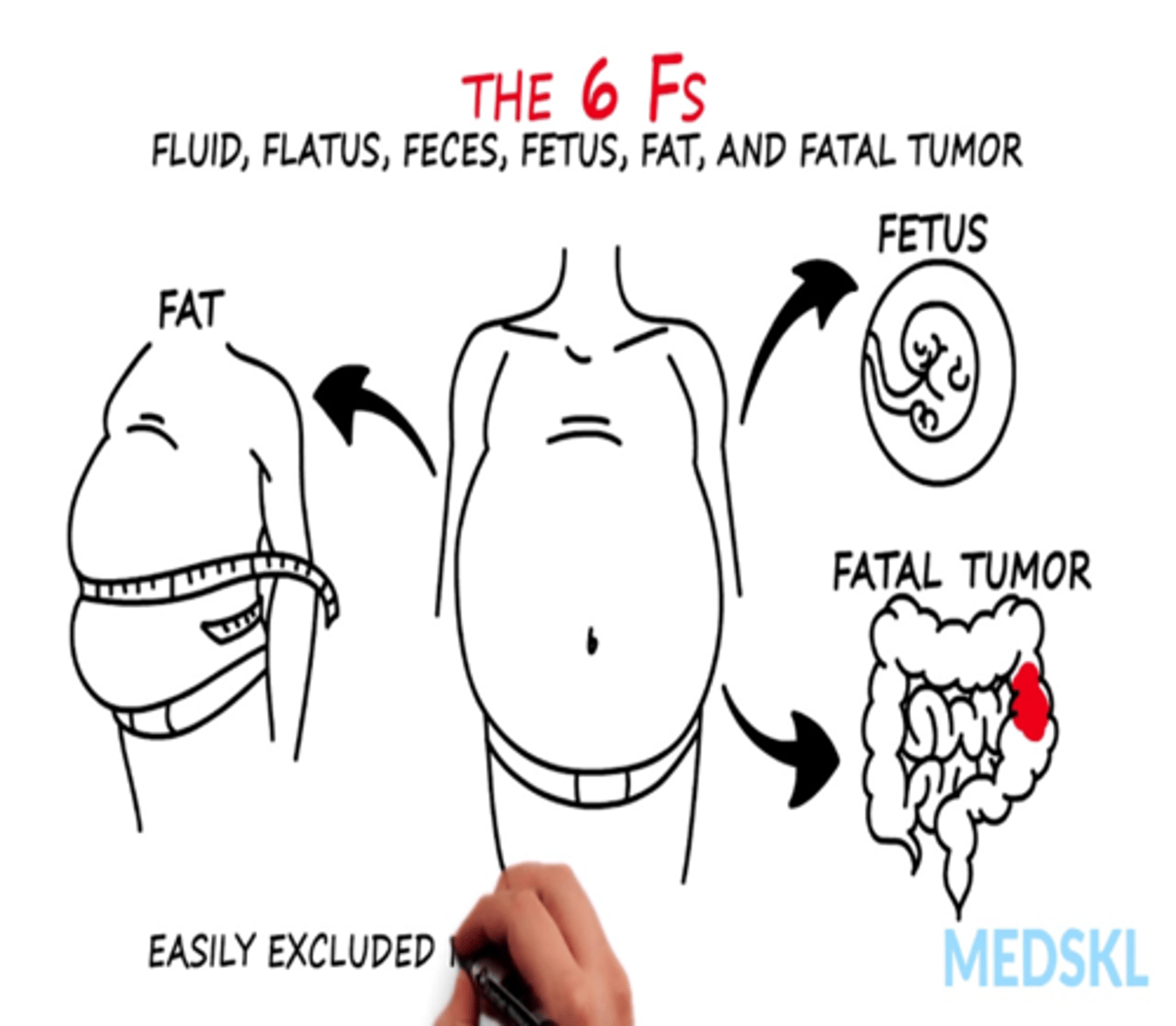
Abnormal findings you may see with abdominal distention?
(the 6 F's--Fluid, Flatus, Feces, Fetus, Fat, Fatal Tumor)
Obesity
Air or gas
Ascites
Ovarian cyst
Pregnancy
Feces
Tumor
What is a hernia from?
incompletely healed surgical wound
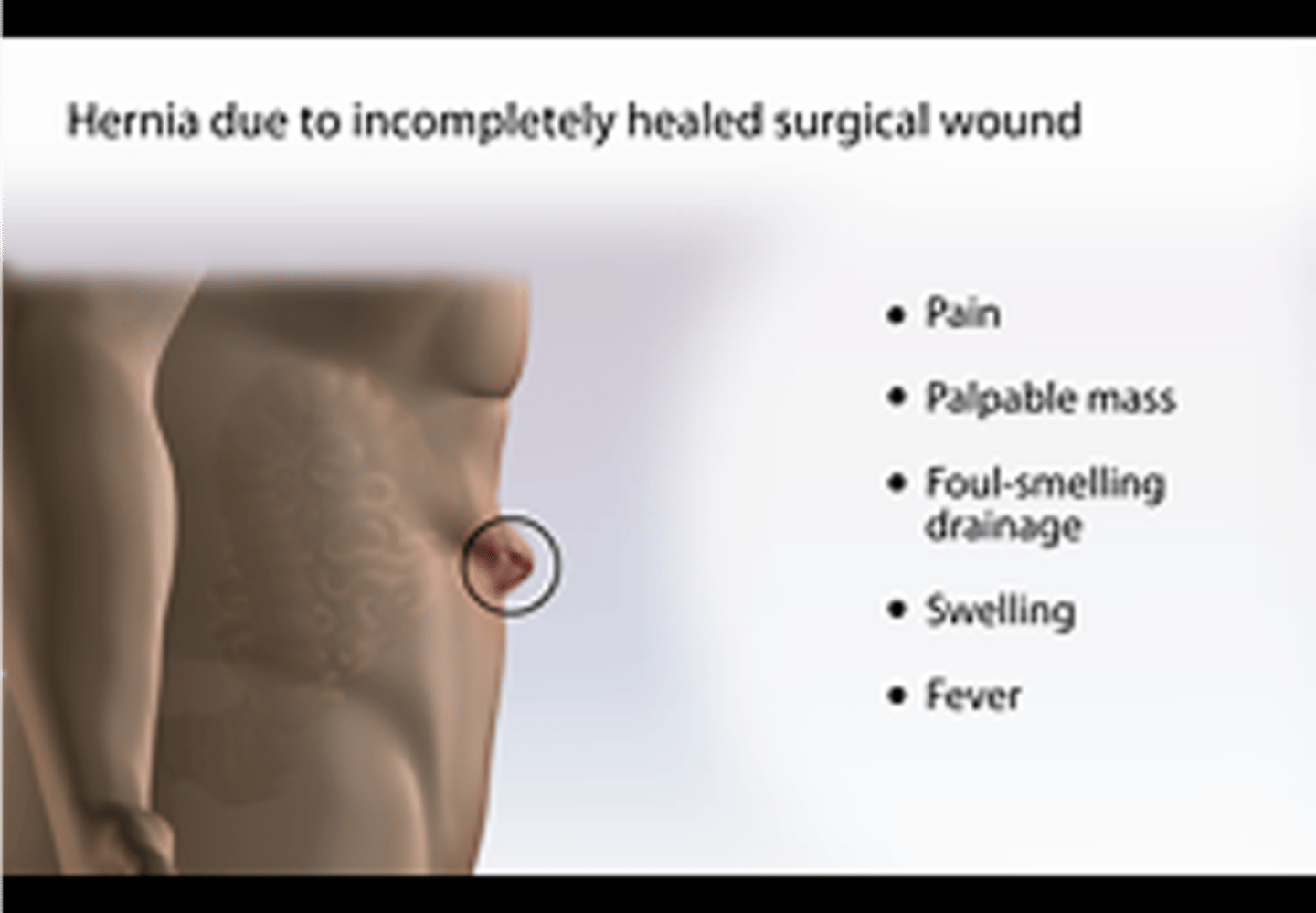
What may you see with a hernia?
pain
palpable mass
foul-smelling drainage
swelling
fever
Abnormal bowel sounds
Succussion splash
Marked peristalsis
Hypoactive bowel sounds
Hyperactive bowel sounds
**What is a succussion splash?**
gastric splash
sloshing sound heard through stethoscope
often reflect presence of gas and fluid in obstructed organ
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases include
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease
**With IBD you may see**
Increased bowel sounds/peristalsis
Hyperactive bowel sounds
Frequent, and often severe, watery stools (acute phase)
Changes in stool color
Abdominal pain; urgency (sudden painful need to defecate), cramping
Describing muscular rigidity includes
A. The patient complains of pain while pushing their palms together as part of the exam
B. A board like hardness of the muscles
C. Usually becomes more painful with increased intraabdominal pressure when the patient is going from a lying to sitting position
D. Is more evident to the examiner when the patient is standing while assessing for balance
B. A board like hardness of the muscles
Chapter 23
Musculoskeletal Sytsem
7 Functions of the skeleton
1. protection
2. movement
3. blood production
4. support (legs support the body)
5. support (vertebrae support the head)
6. Protection
7. Mineral Storage
What does the musculoskeletal system consist of
bones, joints, muscles
What are the musculoskeletal system functions?
Needed for support and to stand erect
Needed for movement
To encase and protect inner vital organs
To produce RBCs in the bone marrow
Serve as a reservoir for storage of essential minerals
**joints or articulations are**
places of union of two or more bones (functional unit of musculoskeletal system)
**What are ligaments?**
fibrous bands from one bone to another that strengthen the joint and prevent unwanted movements
** Think of like a rubber band**
**What is bursa?**
enclosed fluid filled sac that serves as a cushion; Function to synthesize synovial fluid to allow joints to move easily
**Muscle—skeletal, voluntary control connected by what?**
tendon to bone
**Fibrous, Cartilaginous and Synovial Joints are the**
functional units of the musculoskeletal system
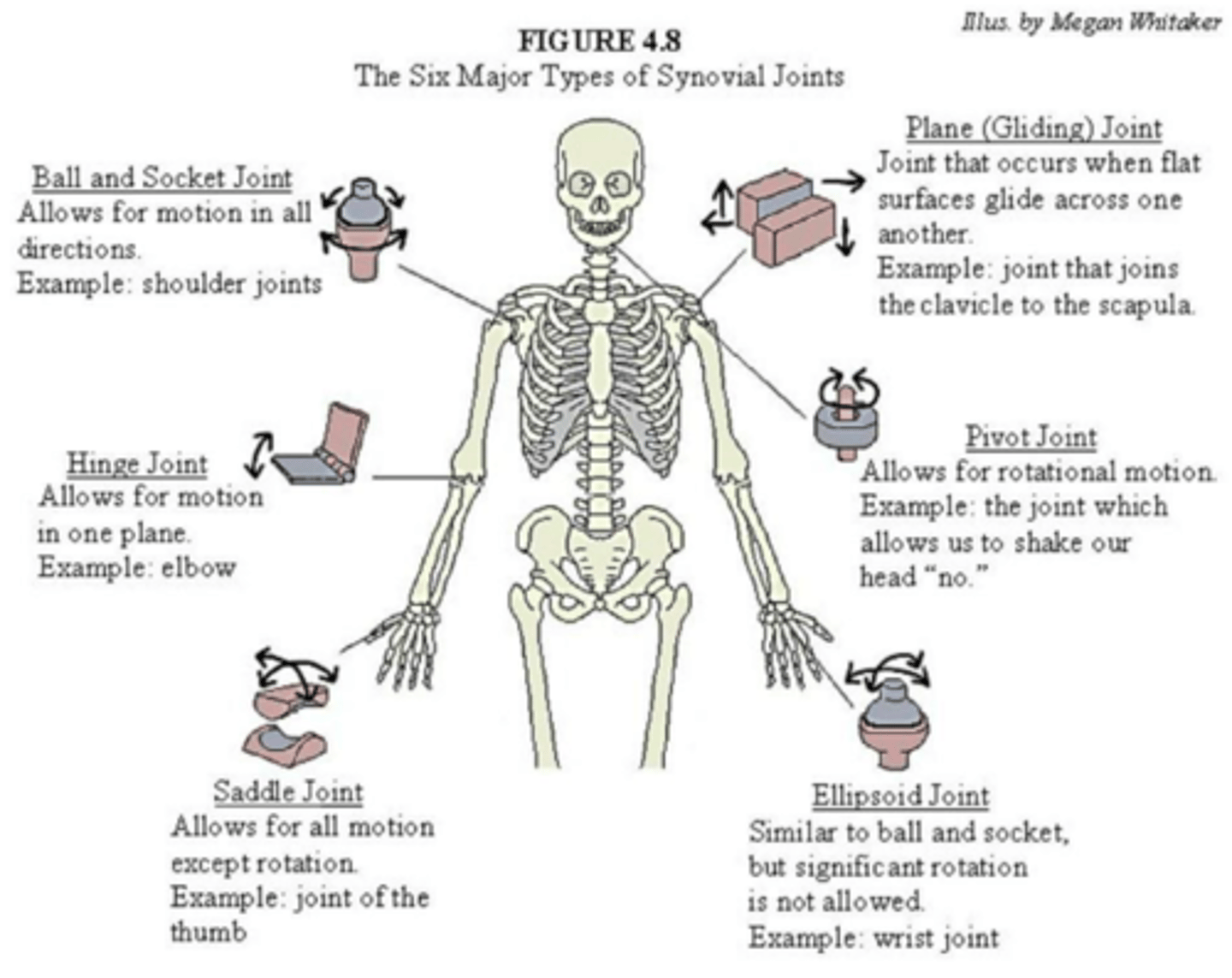
The six major types of synovial joints?
Skeletal Muscles produce what movements?
Flexion
Extension
Abduction
Adduction
Pronation
Supination
Circumduction
**Flexion**
bending limb at joint
**Extension**
straightening a limb at a joint
**Abduction**
Movement away from the midline of the body
**Adduction**
moving a limb toward the midline of the body
**Pronation**
turning the forearm so the palm is down
**Supination**
turning the forearm so that the palm is up
**Circumduction**
moving the arm in a circle around the shoulder
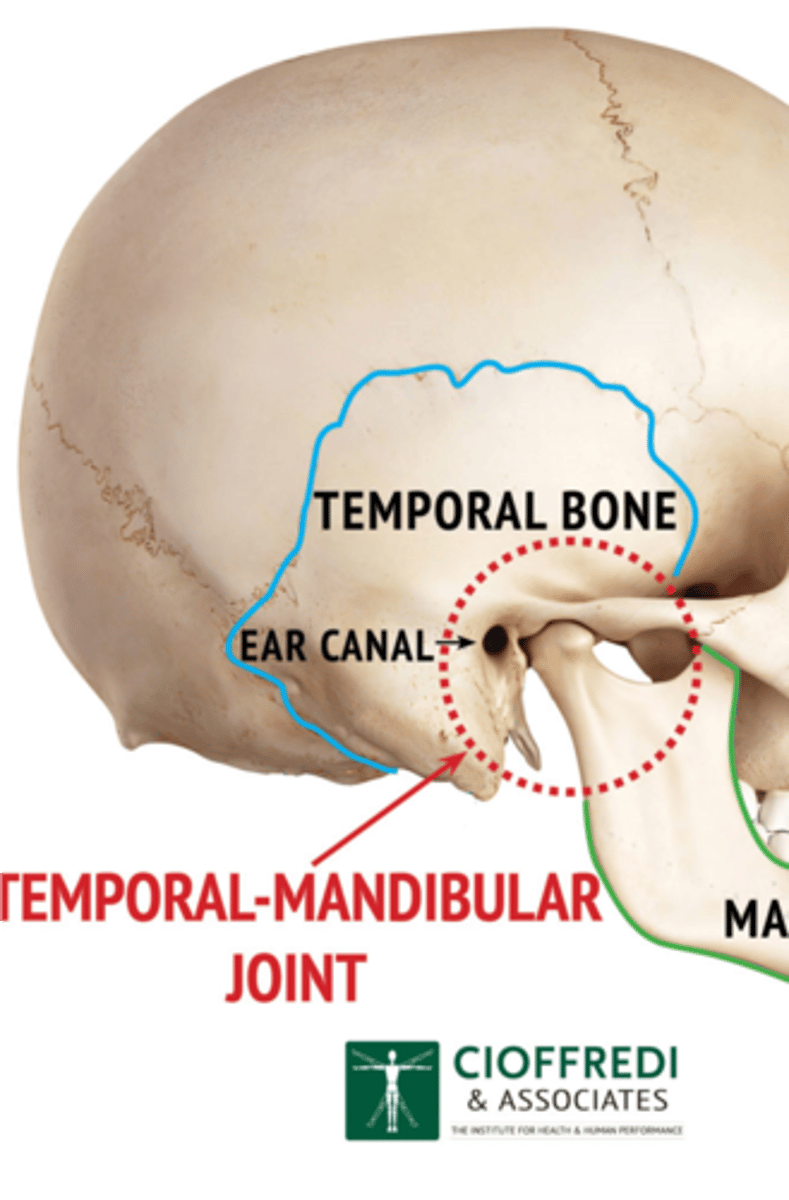
**Where can you feel the temporomandibular joint?**
Can feel it in depression anterior to tragus of ear
permits jaw function of speaking and chewing.
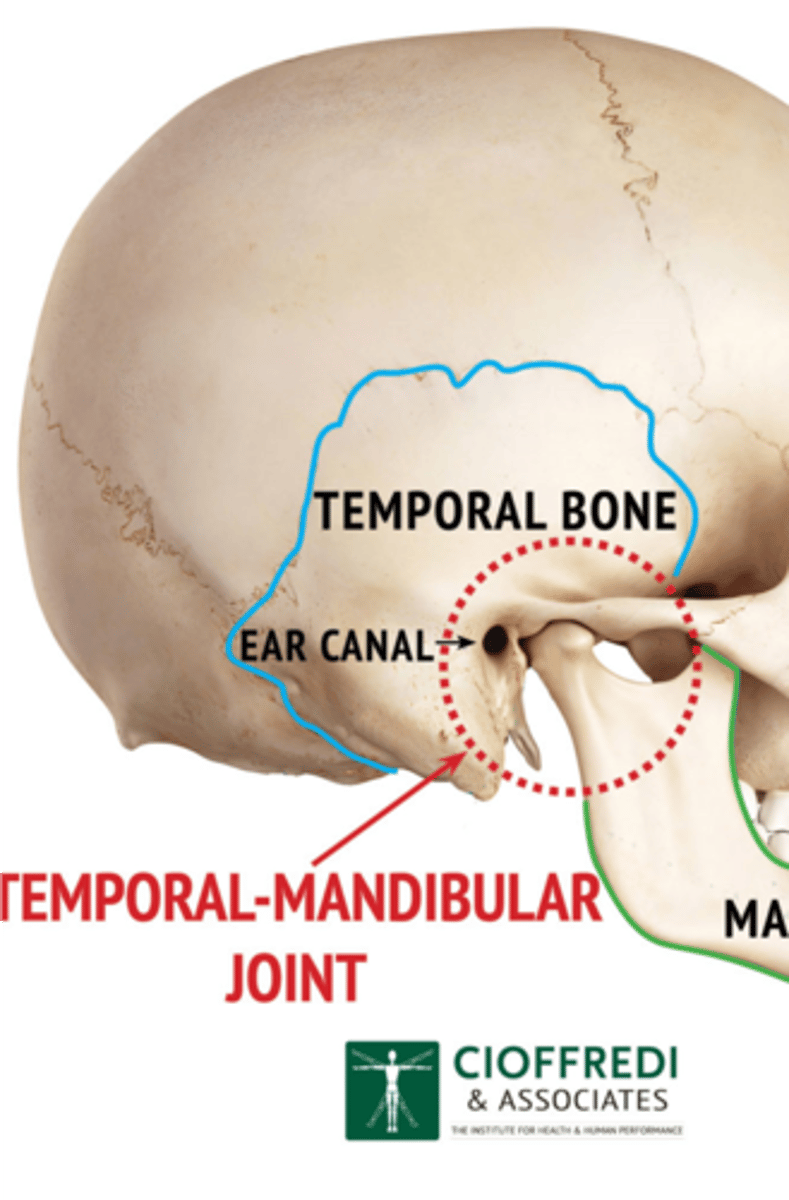
What does the TMJ motions allow?
Hinge action to open and close jaws
Gliding action for protrusion and retraction
Gliding for side-to-side movement of lower jaw
How many vertebrae make up the spine?
33
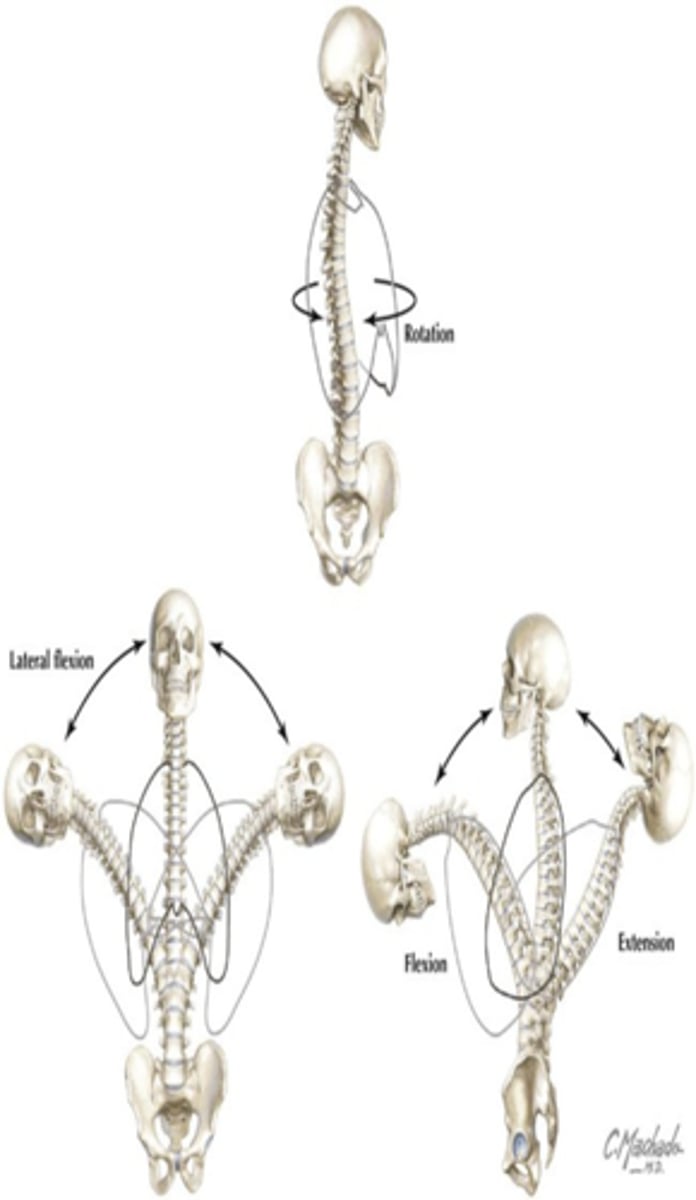
**Motions of the vertebral**
Flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation
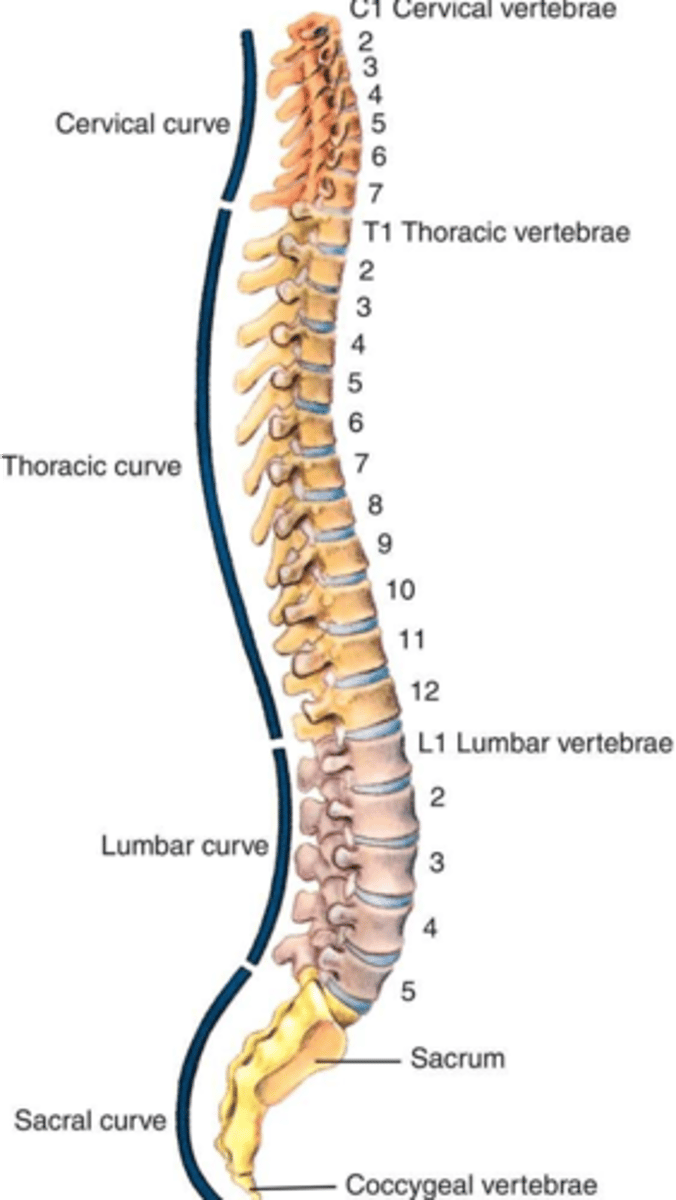
What makes up the vertebrae?
a. 7 cervical
b. 12 thoracic
c. 5 lumbar
d. 5 sacral
e. 3 to 4 coccygeal
**Ossification to true bones continues where?**
utero
**What are epiphyses?**
specialized growth plates at the end of long bones
**After age 40 resorption occurs more rapidly than deposition what does this put you at risk for?**
Osteoporosis
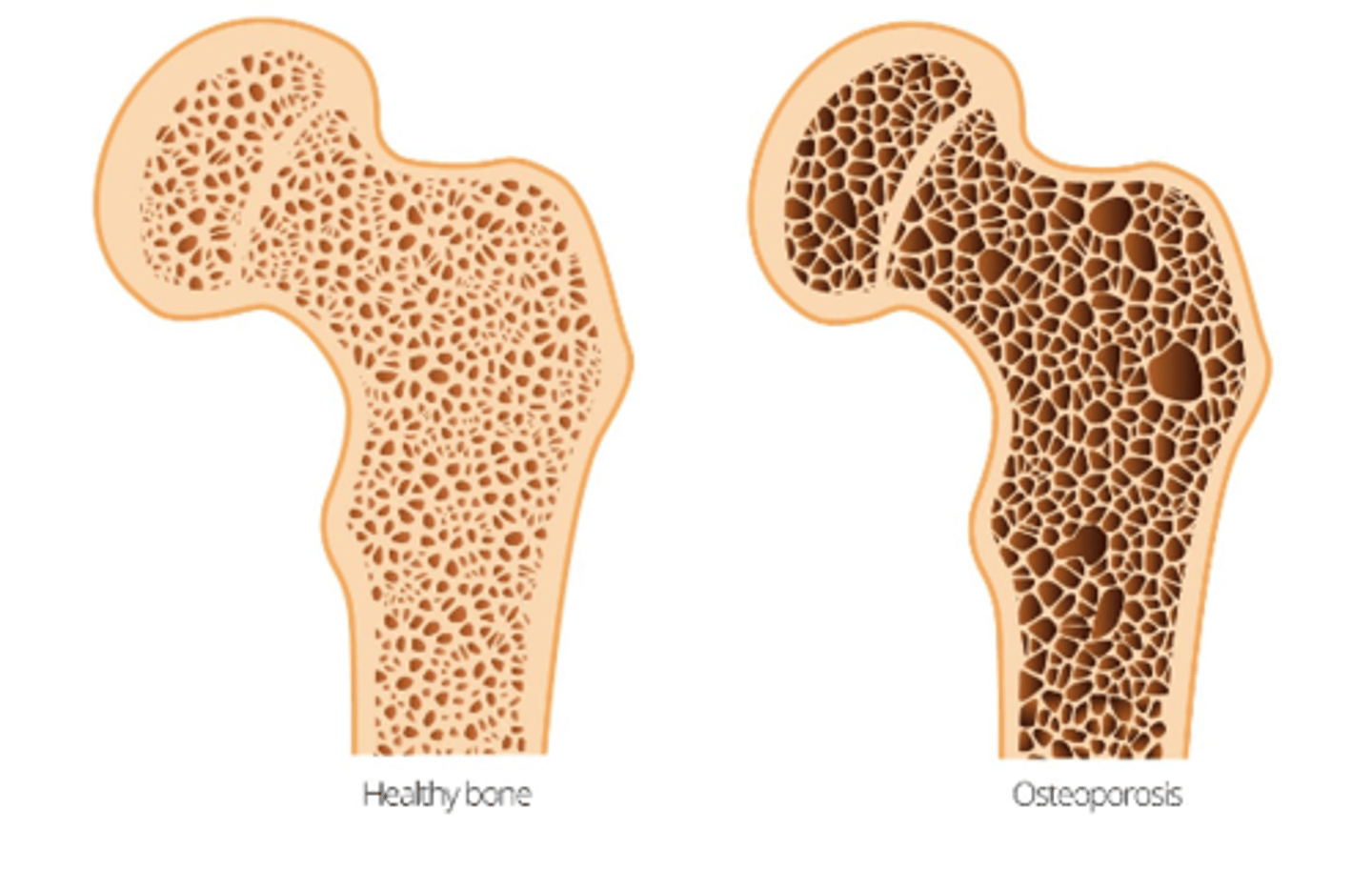
**What is Low BMD (bone mineral density) consistent predictor of?**
hip and vertebral fractures
**Think of being more at risk for osteoporosis**
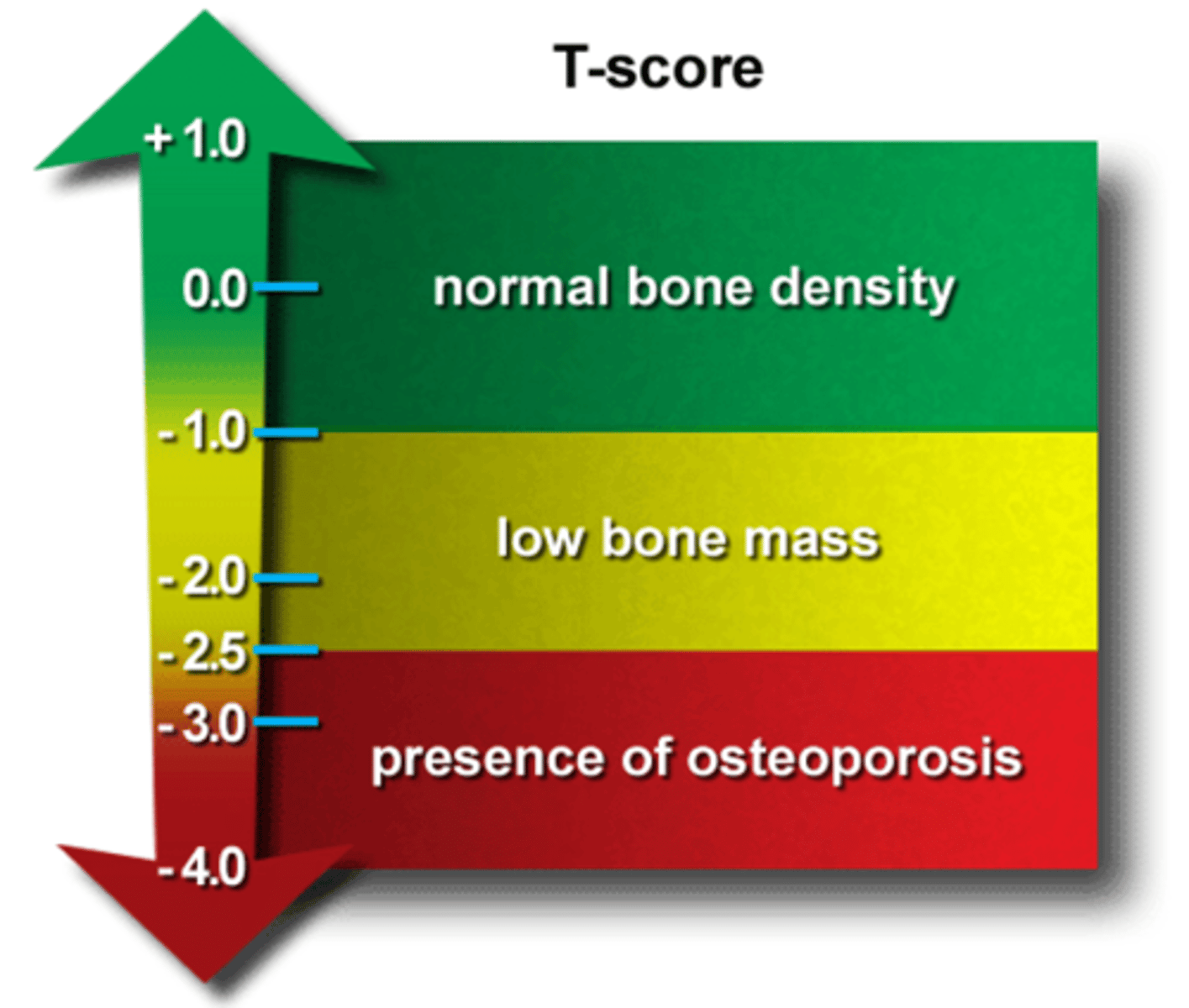
**Who has a increased risk of decline of BMD? **
Earlier peak and rapid decline of BMD associated with increased fracture risk in Caucasian women
**DEXA Scan**
bone density scan
**An X-ray that can check for any signs of osteopenia, osteoporosis, or other bone problems.
The order of Examination for the musculoskeletal system?
Inspection
Palpation
ROM (2 types: active and passive)
What are the 2 types of ROM?
active and passive