11.4 Growth Unemployment and Inflation in the AD AS Model and Exploring Keynes Law and Say s Law in the AD AS model
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
True or false?
In the AD/AS framework, when short-run macroeconomic equilibrium GDP is significantly below potential GDP, there is cyclical unemployment but it is very low.
False
The AD/AS diagram shows cyclical unemployment by how close the economy is to the potential or full GDP employment level. Relatively low cyclical unemployment for an economy occurs when the level of output is close to potential GDP. Conversely, high cyclical unemployment arises when the output is substantially to the left of potential GDP on the AD/AS diagram.
If rising input prices affect many or most firms across the economy, then the aggregate supply curve will shift, causing __________.
Select the correct answer below:
inflationary pressure
potential output to increase
a leftward movement along the aggregate curve.
a rightward movement along the aggregate demand curve.
inflationary pressure
One source of inflationary pressures can occur due to a rise in input prices that affects many or most firms across the economy—perhaps an important input to production like oil or labor—and causes the aggregate supply curve to shift back to the left.
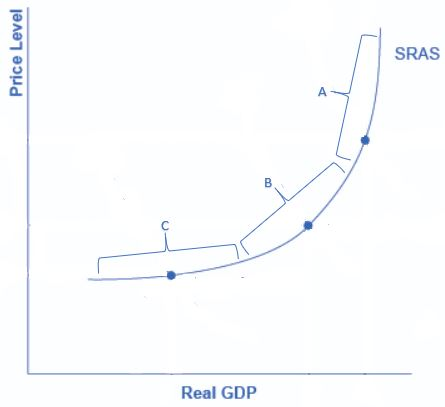
Along which segment of the short-run aggregate supply curve does an economy obtain its full employment level of output?
A
On the neoclassical zone of the SRAS curve, the SRAS is near-vertical portion and is located on the right-hand side. If the AD curve crosses this portion of the SRAS curve then the output is at or near potential GDP, and the size of potential GDP pretty much determines the level of output in the economy. Since the equilibrium is near potential GDP, cyclical unemployment is low in this economy, which means the economy is approaching its natural rate of unemployment, or its full employment level of output.
c if Along the Keynesian zone of an aggregate supply curve, it is near-horizontal. In the Keynesian zone, the equilibrium level of real GDP is far below potential GDP, the economy is in recession, and cyclical unemployment is high. If aggregate demand shifted to the right or left in the Keynesian zone, it will determine the resulting level of output (and thus unemployment). However, inflationary price pressure is not much of a worry in the Keynesian zone, since the price level does not vary much in this zone.
Which of the following is the best definition of cyclical unemployment?
Select the correct answer below:
unemployment in excess of the natural rate of unemployment
the percentage of the working age population in an economy who are looking for a job
the percentage of the working age population who are in the labor force but who do not have jobs but are currently looking
the unemployment rate that would exist in a healthy economy from the combination of economic and social factors
unemployment in excess of the natural rate of unemployment
Cyclical unemployment is defined as the unemployment in excess of the unemployment that exists at the natural level of employment. Low cyclical unemployment for an economy occurs when the level of output is close to potential GDP and high cyclical unemployment arises when the output is substantially to the left of potential GDP on the AD/AS diagram
Inflationary pressures happen when __________.
Select the two correct answers below.
Select all that apply:
aggregate demand is close to full employment and shifts even closer to full employment
potential output shifts to the right
aggregate supply decreases as a result of increases in input prices which are widely used throughout the economy
there is a leftward movement along the aggregate demand curve.
aggregate demand is close to full employment and shifts even closer to full employment
aggregate supply decreases as a result of increases in input prices which are widely used throughout the economy
The AD/AS framework implies two ways that inflationary pressures may arise. One possible trigger is if aggregate demand continues to shift to the right when the economy is already at or near potential GDP and full employment, thus pushing the macroeconomic equilibrium into the AS curve's steep portion. An alternative source of inflationary pressures can occur due to a rise in input prices that affects many or most firms across the economy—perhaps an important input to production like oil or labor—and causes the aggregate supply curve to shift back to the left.
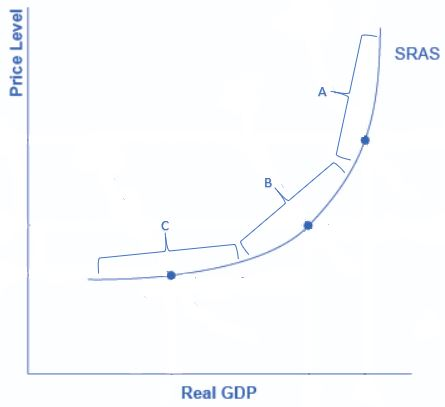
Which of the following segments represents the intermediate range of the aggregate supply curve?
B
In the intermediate zone, aggregate supply is neither near-vertical nor near-horizontal. Instead, it is upward sloping. In this range, we might expect unemployment and inflation to move in opposing directions. For instance, a shift of AD to the right will move output closer to potential GDP and thus reduce unemployment, but will also lead to a higher price level and upward pressure on inflation. Conversely, a shift of AD to the left will move output further from potential GDP and raise unemployment, but will also lead to a lower price level and downward pressure on inflation.
Inflationary pressure can occur if _________.
(Select all the apply. Hint: There are 2 correct answers.)
Select all that apply:
input prices that affect many or most firms across the economy increase
aggregate demand continues to shift to the right when the economy is already at or near potential GDP and full employment
aggregate demand continues to shift to the left when the economy is already at or near potential GDP and full employment
input prices that affects many or most firms across the economy decrease
input prices that affect many or most firms across the economy increase
aggregate demand continues to shift to the right when the economy is already at or near potential GDP and full employment
The AD/AS framework implies two ways that inflationary pressures may arise. One possible trigger is if aggregate demand continues to shift to the right when the economy is already at or near potential GDP and full employment, thus pushing the macroeconomic equilibrium into the AS curve's steep portion.An alternative source of inflationary pressures can occur due to a rise in input prices that affects many or most firms across the economy—perhaps an important input to production like oil or labor—and causes the aggregate supply curve to shift back to the left.
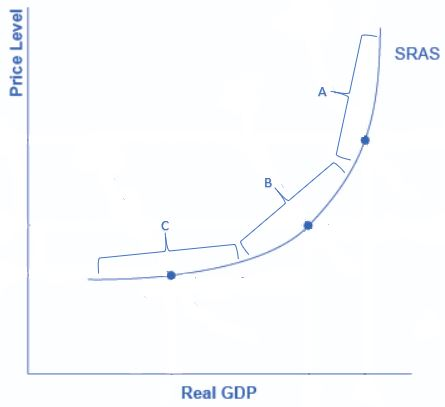
On the aggregate supply curve below:
Which segment represents output levels for which there is a clear negative relationship between unemployment and inflation?
B
In the intermediate zone, aggregate supply is neither near-vertical nor near-horizontal. Instead, it is upward sloping. In this range, we might expect unemployment and inflation to move in opposing directions. For instance, a shift of AD to the right will increase real GDP and thus reduce unemployment, but will also lead to a higher price level or inflation. Conversely, a shift of AD to the left will reduce real GDP and raise unemployment, but will also lead to a lower price level and downward pressure on inflation.
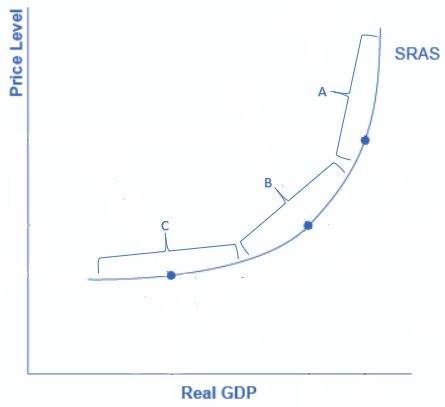
Within which of the following segments of the aggregate supply curve is the economy furthest away from its full employment level of output?
C
Along the Keynesian zone of an aggregate supply curve, it is near-horizontal. In the Keynesian zone, the equilibrium level of real GDP is far below potential GDP, the economy is in recession, and cyclical unemployment is high. If aggregate demand shifted to the right or left in the Keynesian zone, it will determine the resulting level of output (and thus unemployment). However, inflationary price pressure is not much of a worry in the Keynesian zone, since the price level does not vary much in this zone.
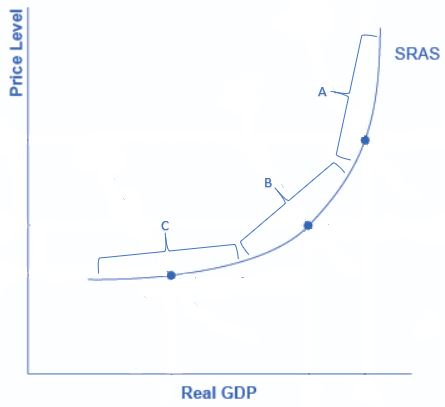
On the short-run aggregate supply curve below, in which section is unemployment at or near the natural rate of unemployment?
A
On the neoclassical zone of the SRAS curve, the SRAS is near-vertical. If the AD curve crosses this portion of the SRAS curve then the output is at or near potential GDP. Since the equilibrium is near potential GDP, cyclical unemployment is low in this economy, which means the economy is approaching its natural rate of unemployment, or its full employment level of output.