Density Dependent Population Growth
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Why is density important?
Exponential growth until limited by resources
How is exponential growth modelled?
B0, D0=Density independent per-capita birth and death rates
b, d=Density dependent per-capita birth and death rates
Basic structure of population growth model: Discrete Time models (Exponential growth)
Nt+1=NtR
Basic structure of population growth model: Discrete Time models (Generic Growth Function)
Nt+1=Ntf(Nt)
Basic structure of population growth model: Discrete Time models (Per-capita growth term)
f(Nt)=R
Basic structure of population growth model: Discrete Time models (Negative density dependence)
f(Nt)=er(1-Nt/K)
Basic structure of population growth model: Continuous Time models (Exponential growth)
dN/dt=Nr
Basic structure of population growth model: Continuous Time models (Generic growth function)
dN/dt=Nf(N)
Basic structure of population growth model: Continuous Time models (Per-capita growth term)
f(N)=r
Basic structure of population growth model: Continuous Time models (Negative density dependence)
f(N)=r(1-N/K)
What is the term for feedback density dependence in negative density dependence equation?
1-Nt/K
Role of state variable?
Express and record the “thing” that is modelled
What does the mean filed model state?
One number
What are parameters?
Biological elements we think affect the state variables of interest
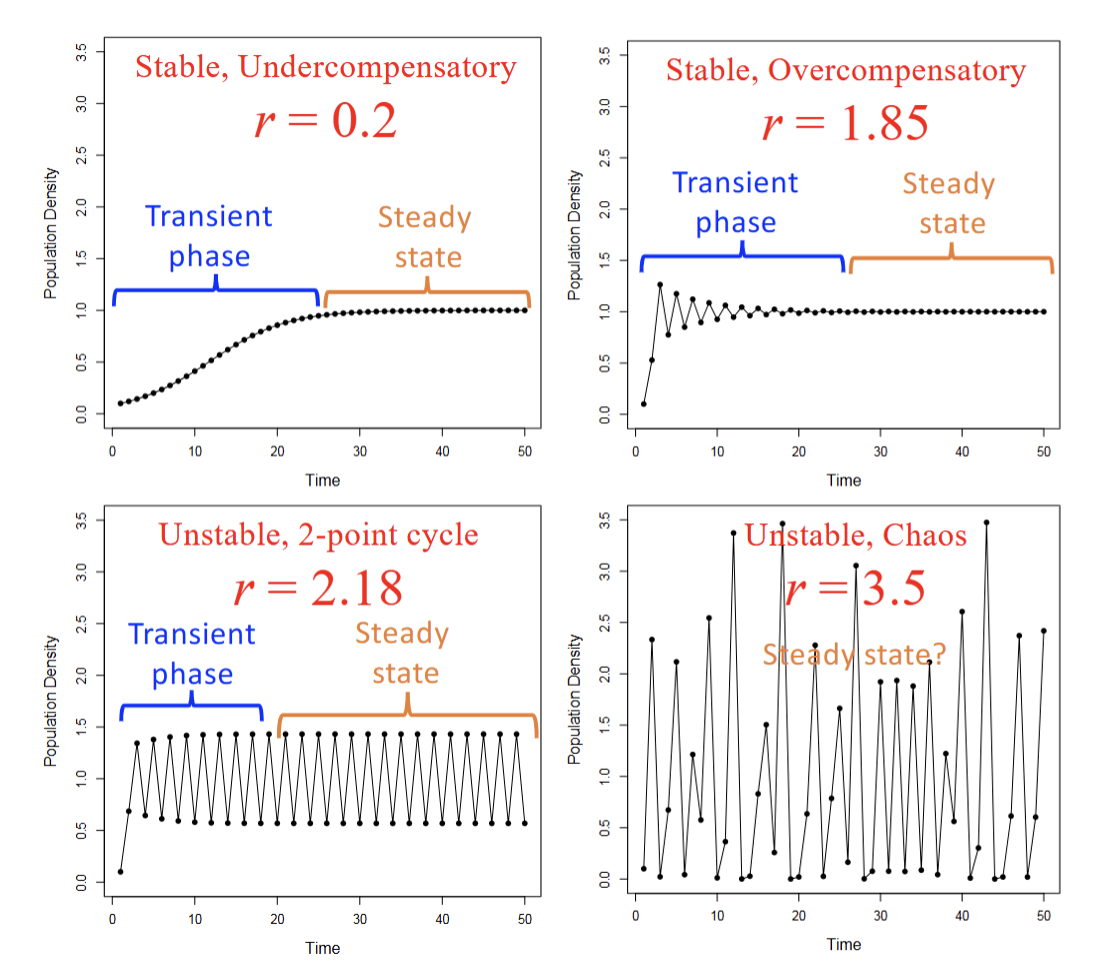
What is stability?
Population returning to a certain point after disturbance
What is instability?
Cycles/Chaos
How does discrete time dynamics get affected when there is a varying K?
Increases transient phase
-If K gets bigger=bigger transient phase
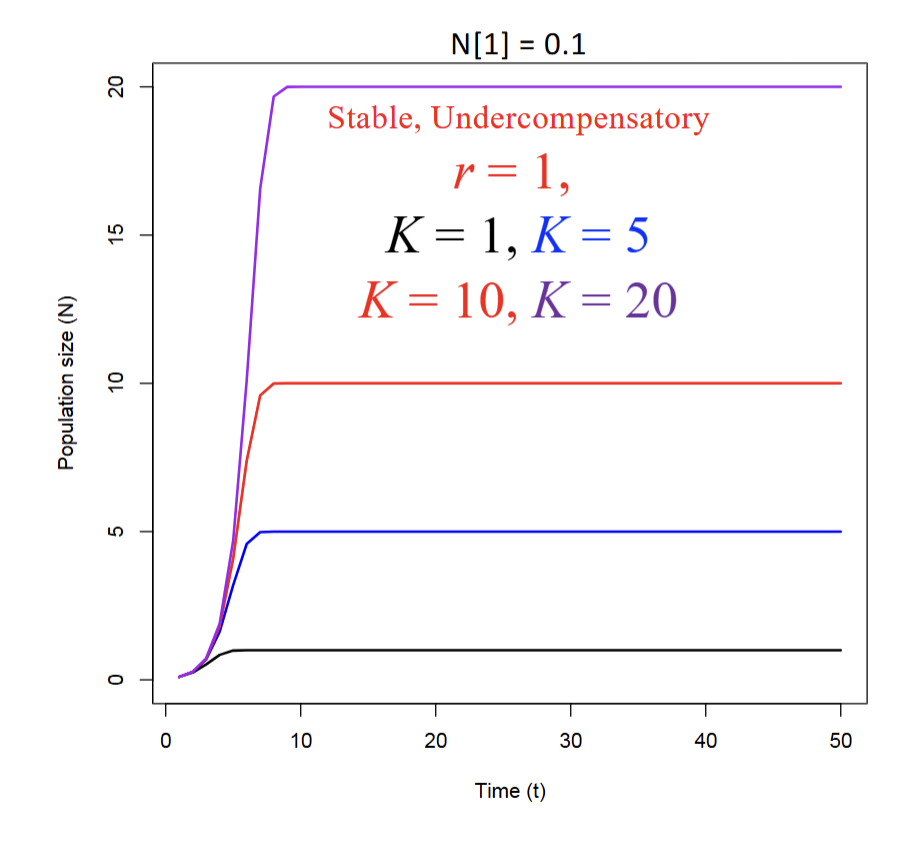
How does discrete time dynamics get affected when there is a varying initial conditions N1?
There will be either gradual increases or gradual decreases
-N1<K=gradual increase
-N1>K=gradual decrease
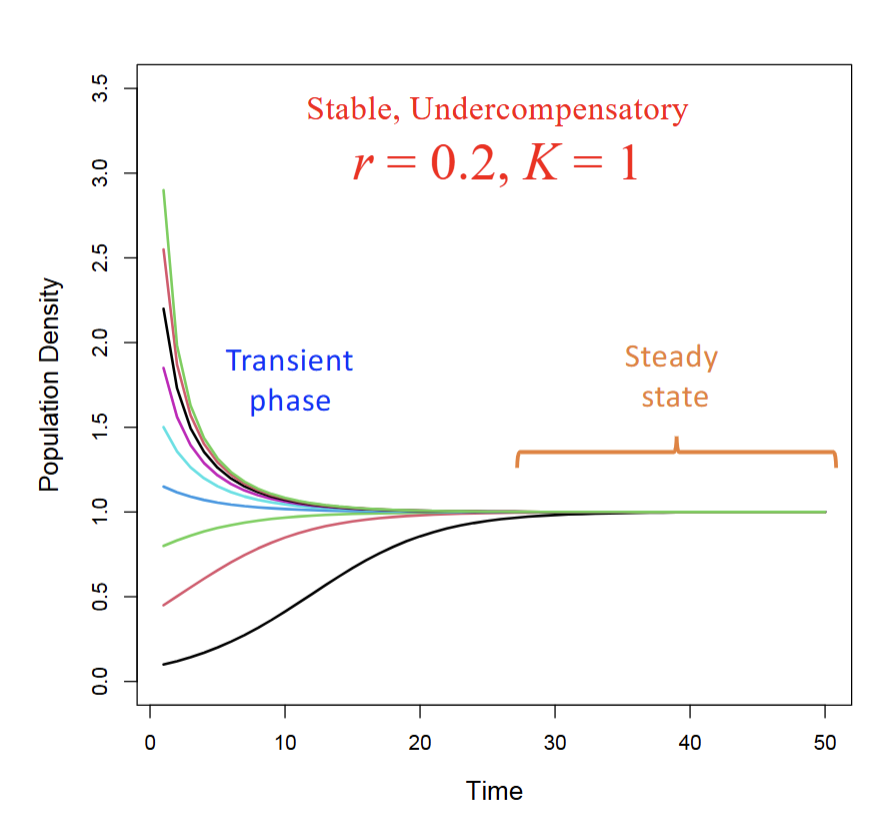
How does discrete time dynamics get affected when intrinsic growth rate {r} increases?
Allows steady state to be reached faster, furthermore controls stability
How does continuous time dynamics get affected when intrinsic growth rate {r} increases?
Approach steady state faster, and no change in steady state dynamics with r
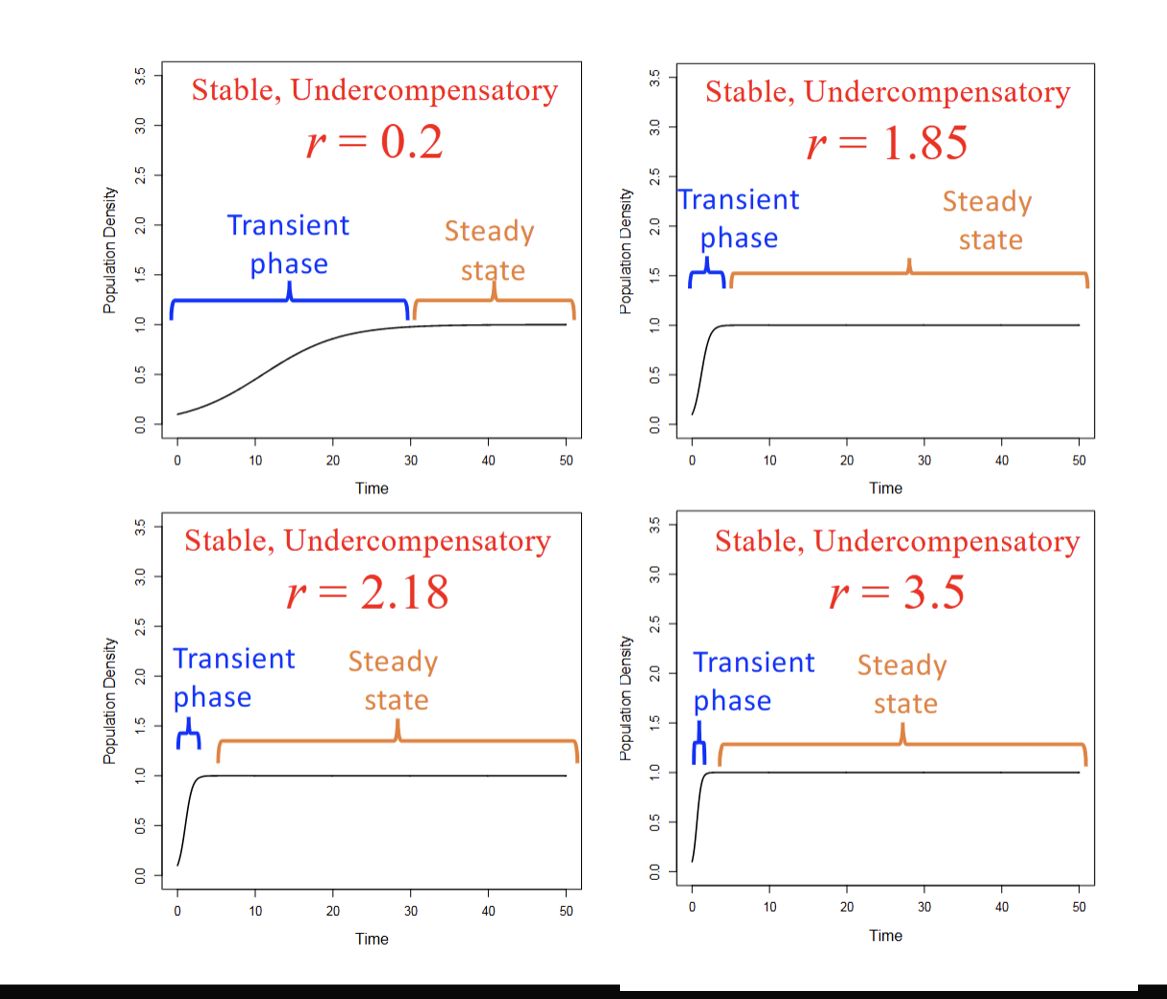
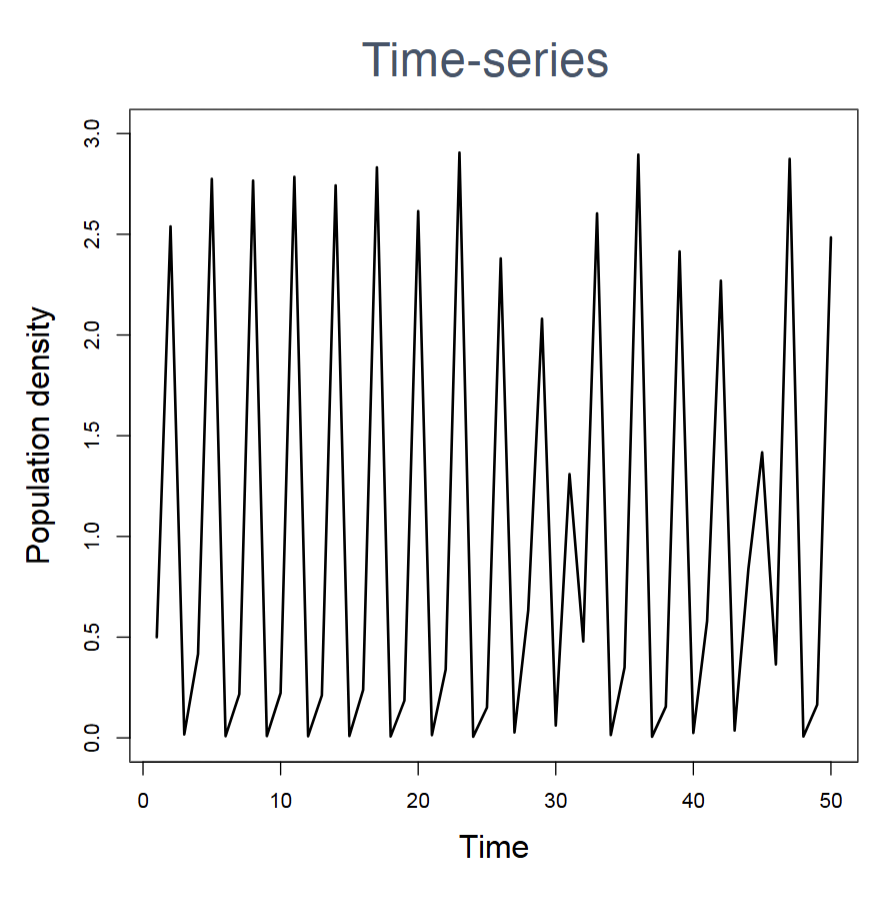
How to plot a time series?
X-axis=Time
Y-axis=Population density
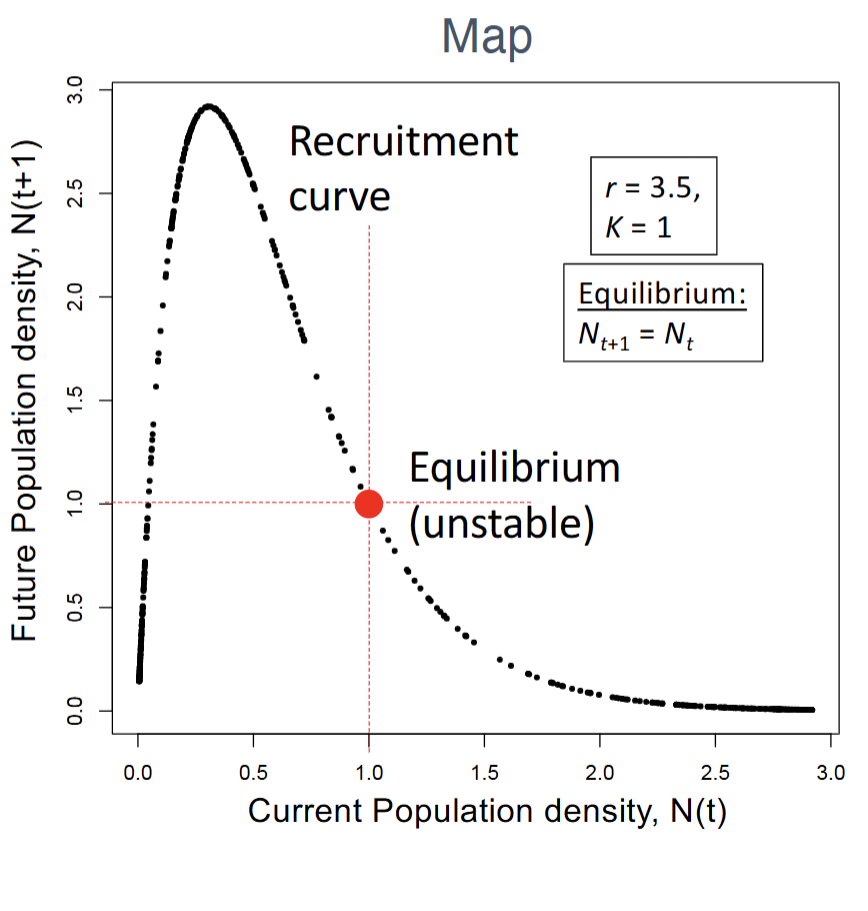
How to plot a map?
X-axis=Current population density, N(t)
Y-axis=Future population density, N(t+1)
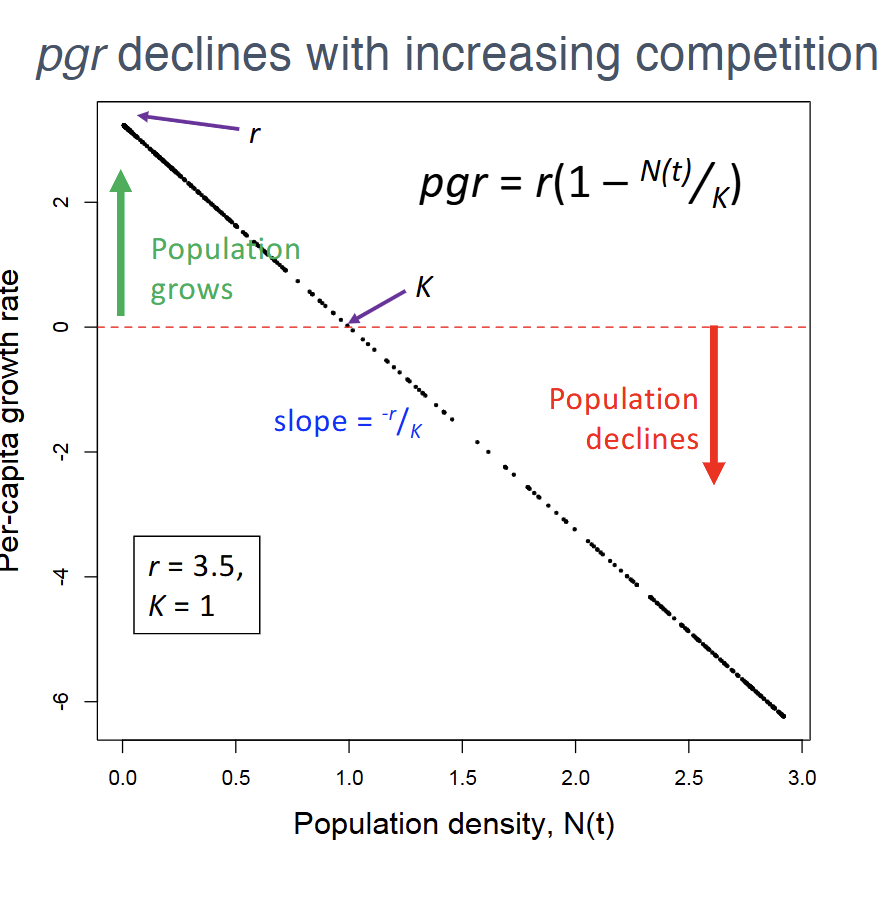
How to plot per-capita growth rate?
X-axis=Population density, N(t)
Y-axis=Per-capita growth rate
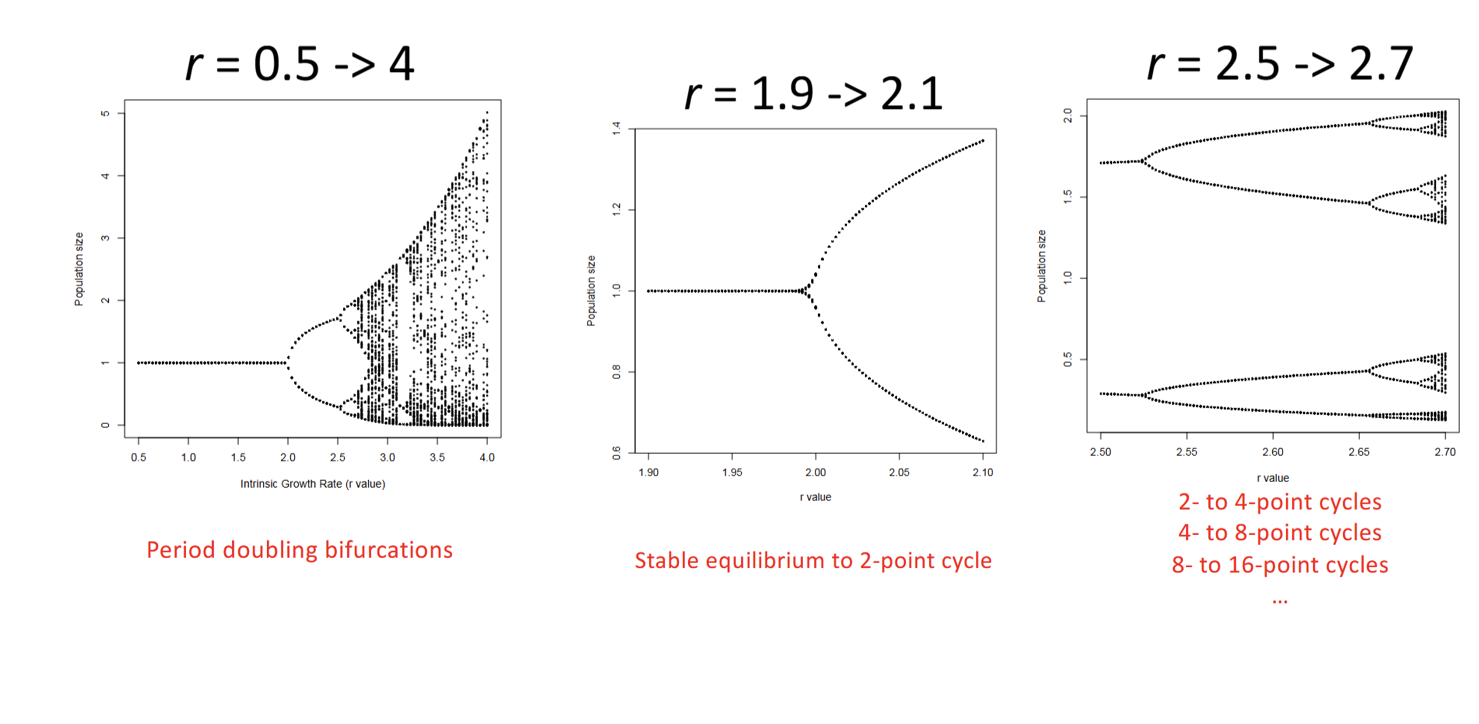
What are the different bifurcation plots?
→Period doubling bifurcations (r=0.5→4)
→Stable equilibrium to 2-point cycle (r=1.9→2.1)
→2 to 4 point cycles (r=2.5→2.7)
→4 to 8 point cycles (r=2.5→2.7)
→8 to 16 point cycles (r=2.5→2.7)