Identifying Aquatic Insect Order & Families
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms

Identify, Name ecology and feeding type
Order: Trichoptera
→ has cases
Ecology: varies
Feeding: varies
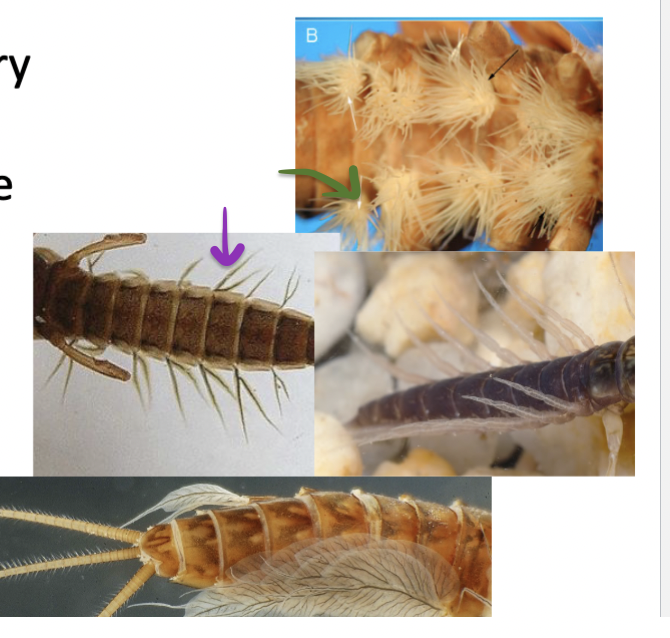
What features are these?
Gills
What are tarsi? And how are they used in the identification of bugs
Tarsi are the legs of an insect.
They can help with identification through counting the segments of the Tarsi, the pairs of Tarsi along the thorax and the number of claws each Tarsi has.
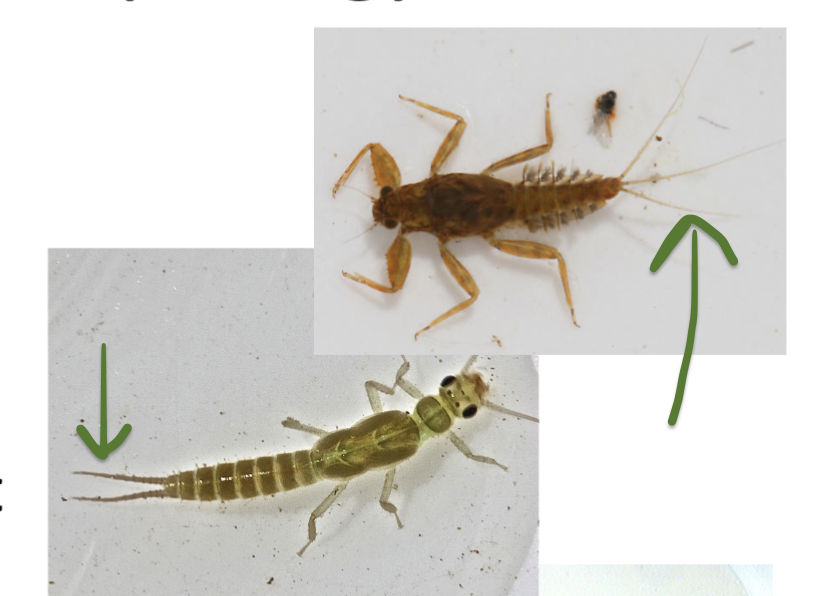

What is the feature in the photo?
Once you think you have identified them, do they have claws, hooks or hairs?
Cerci
has hair

What are these features called? Once you think you have identified them, do they have claws, hooks or hairs?
Prolegs, they have claws and hairs
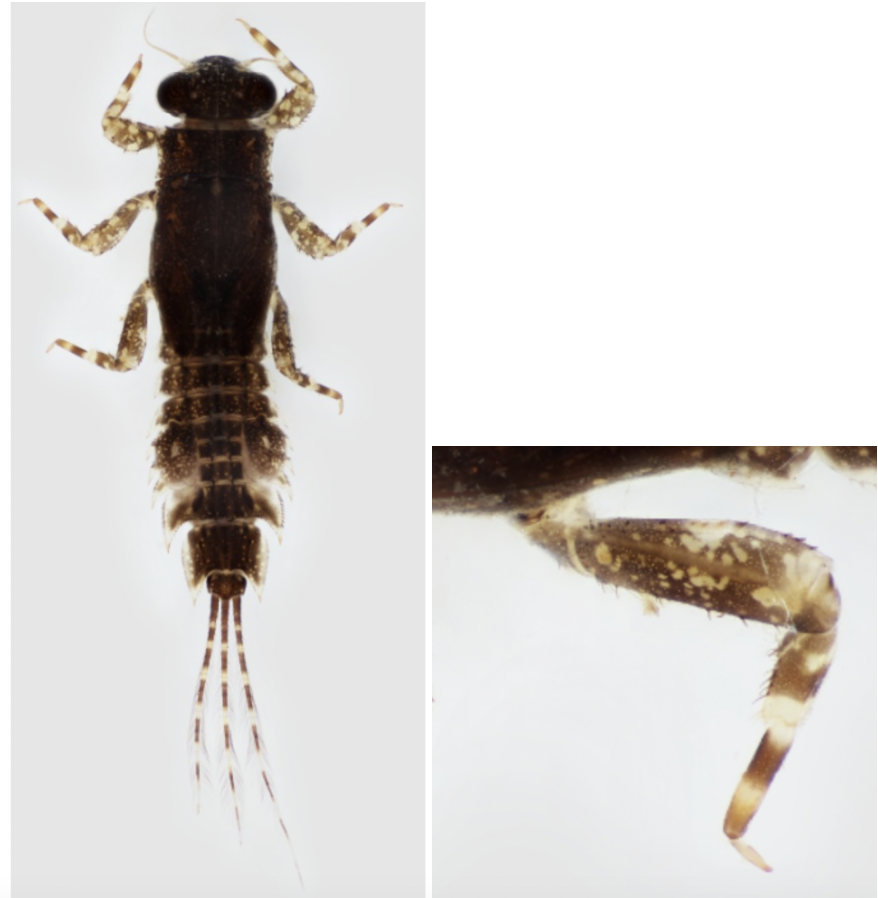

Ephemeroptera:
- 2 or 3 cerci
- 3 pairs of tarsi, and one claw on each tarsi
- abdominal gills
- Ecology - varied
- Feeding - varied

Order: Ephemeroptera
- 2 or 3 cerci
- 3 pairs of tarsi, and one claw on each tarsi
- Ecology: varied
- Feeding: varied
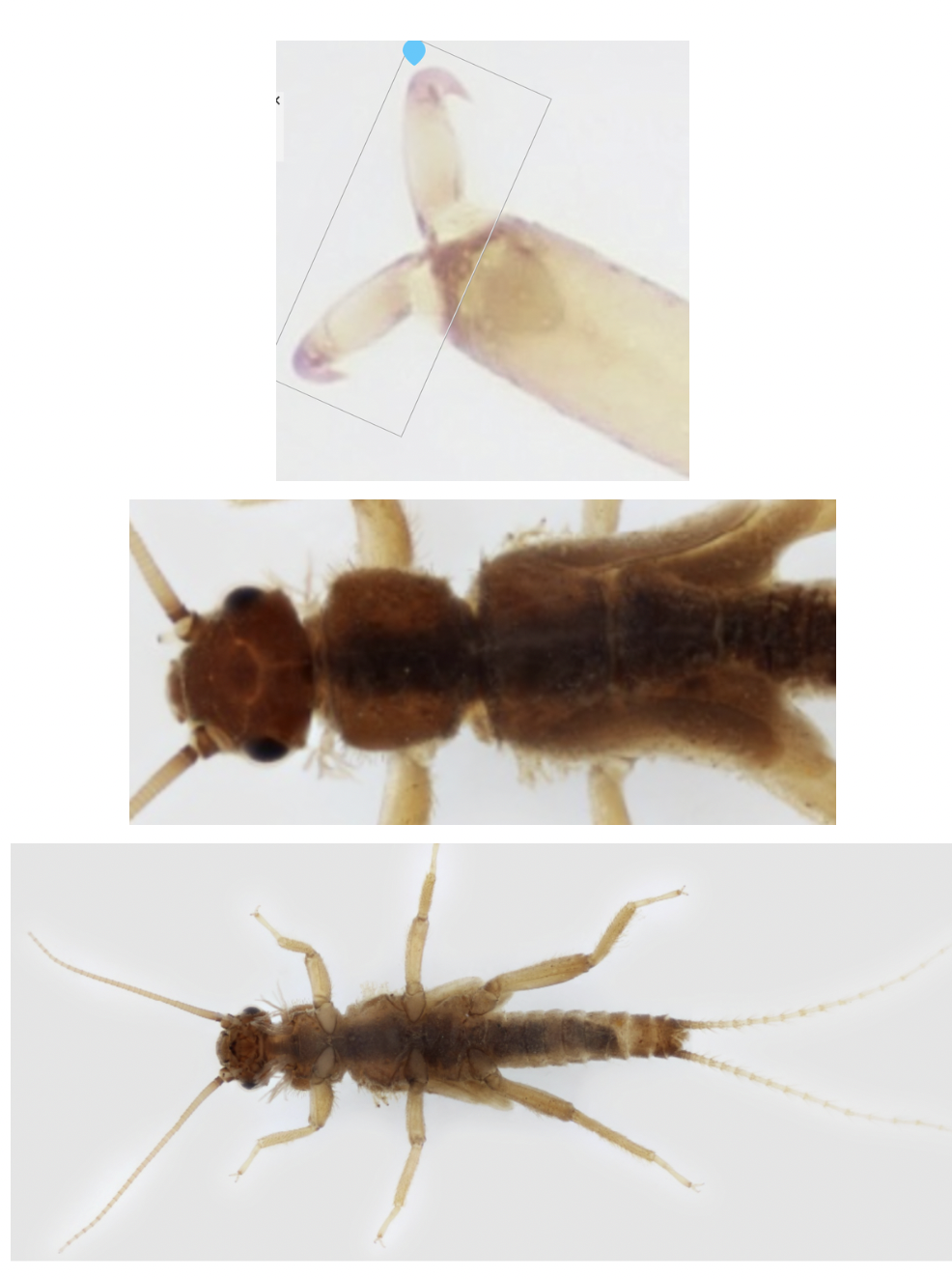

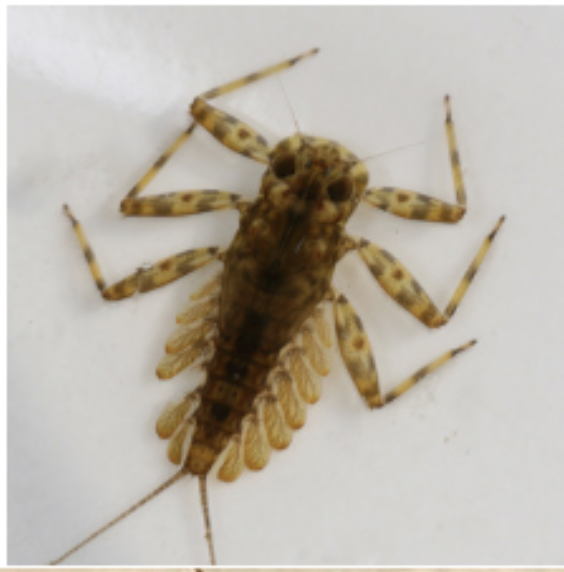
Order: Plecoptera
- 2 cerci
- 3 pairs of tarsi, with 2 claws on each tarsi
- gills on head or thorax
- Ecology: Varied
- Feeding: Varied
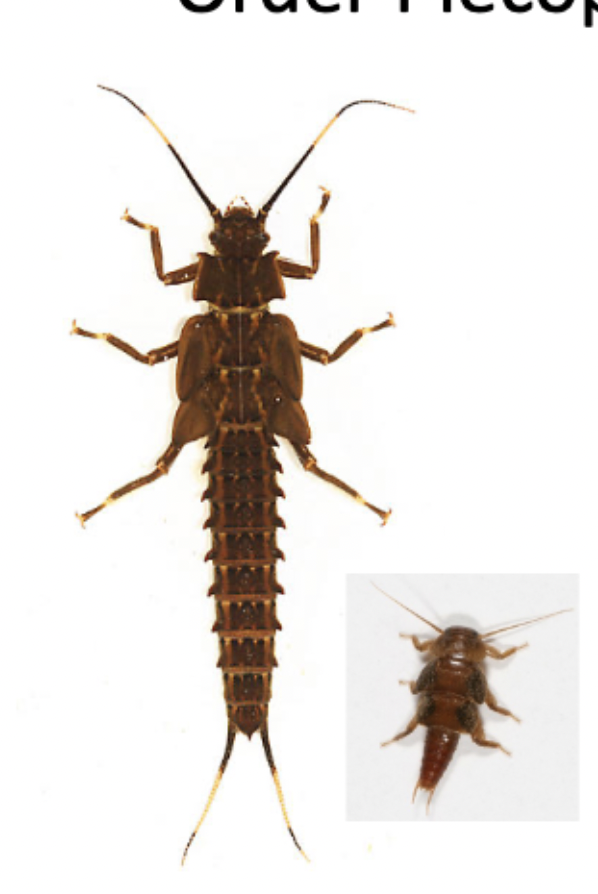

Order: plecoptera
- has three pairs of tarsi, with 2 claws on each tarsi
- has 2 cerci
- ecology: varied
- feeding: varied

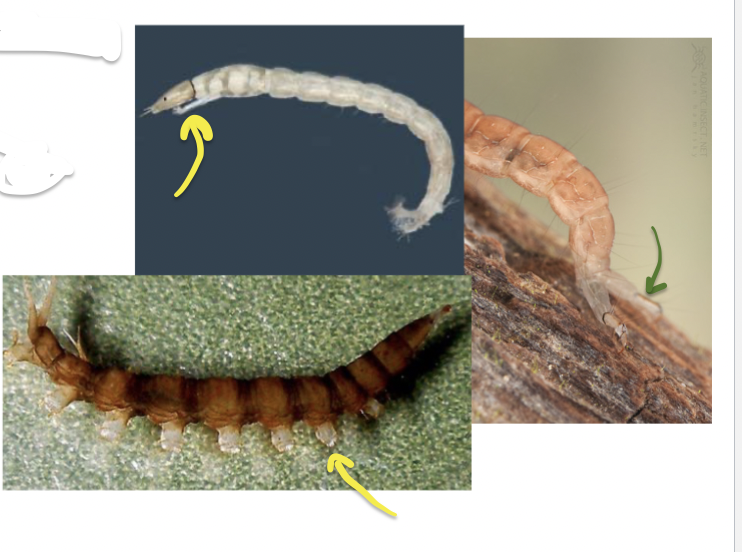
Order: Coleoptera ; Family: Elmidae
- cone shaped body
- feather-like anal gills
Ecology: riffles
Feeding: scrapers
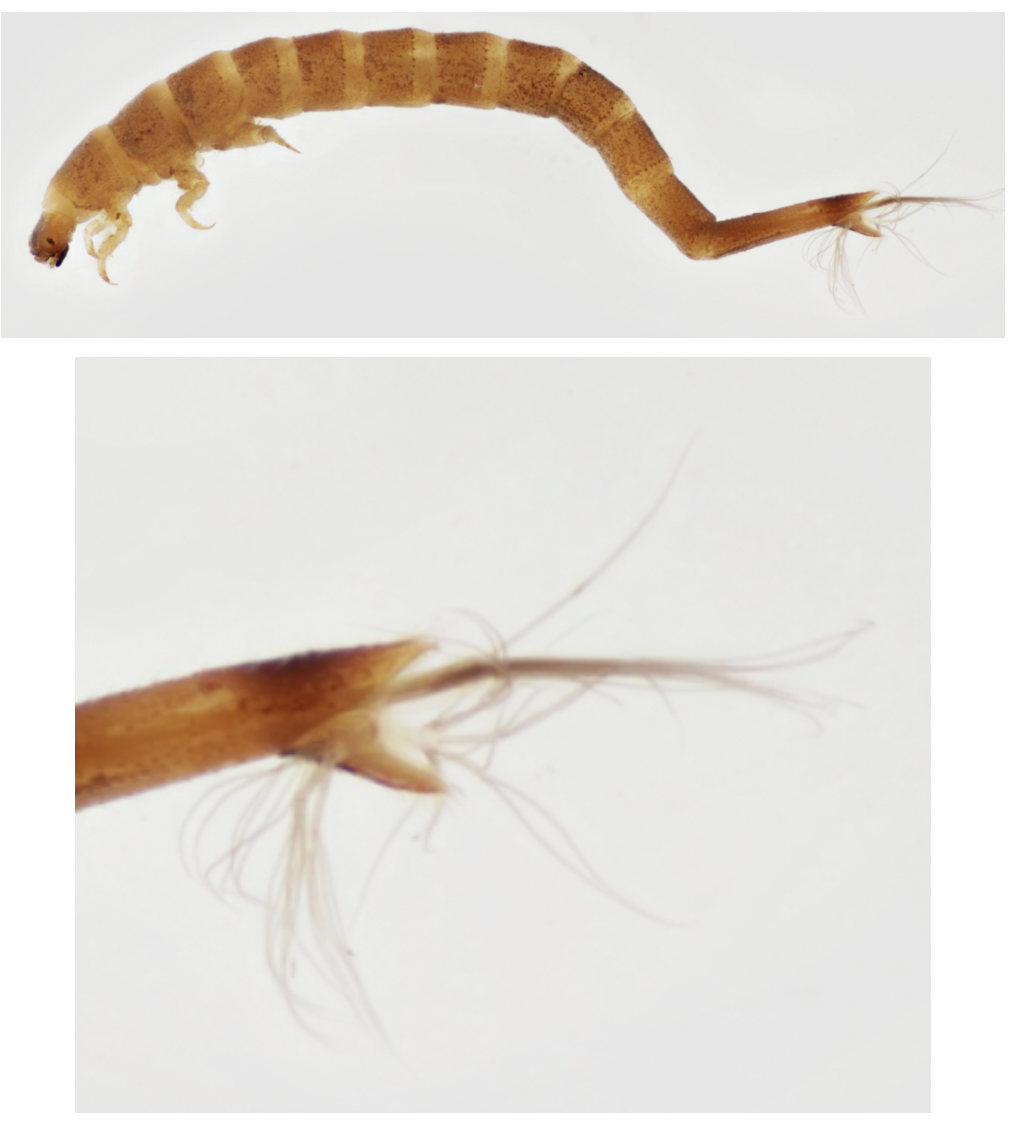

Order: Coleoptera Family: Elmidae
→ feather like anal-gills
→ Cone-shaped body
Ecology: riffles
Feeding: scrapers
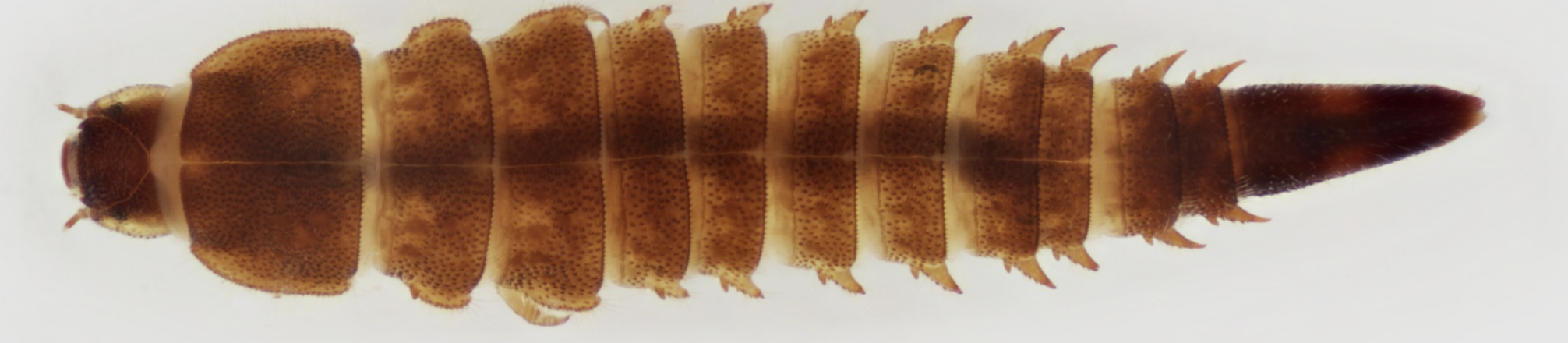
Order: Coleoptera ; Family: Elmidae
→ Feather like anal-gills
→ cone-shaped body
Ecology: ripples
Feeding: scrapers
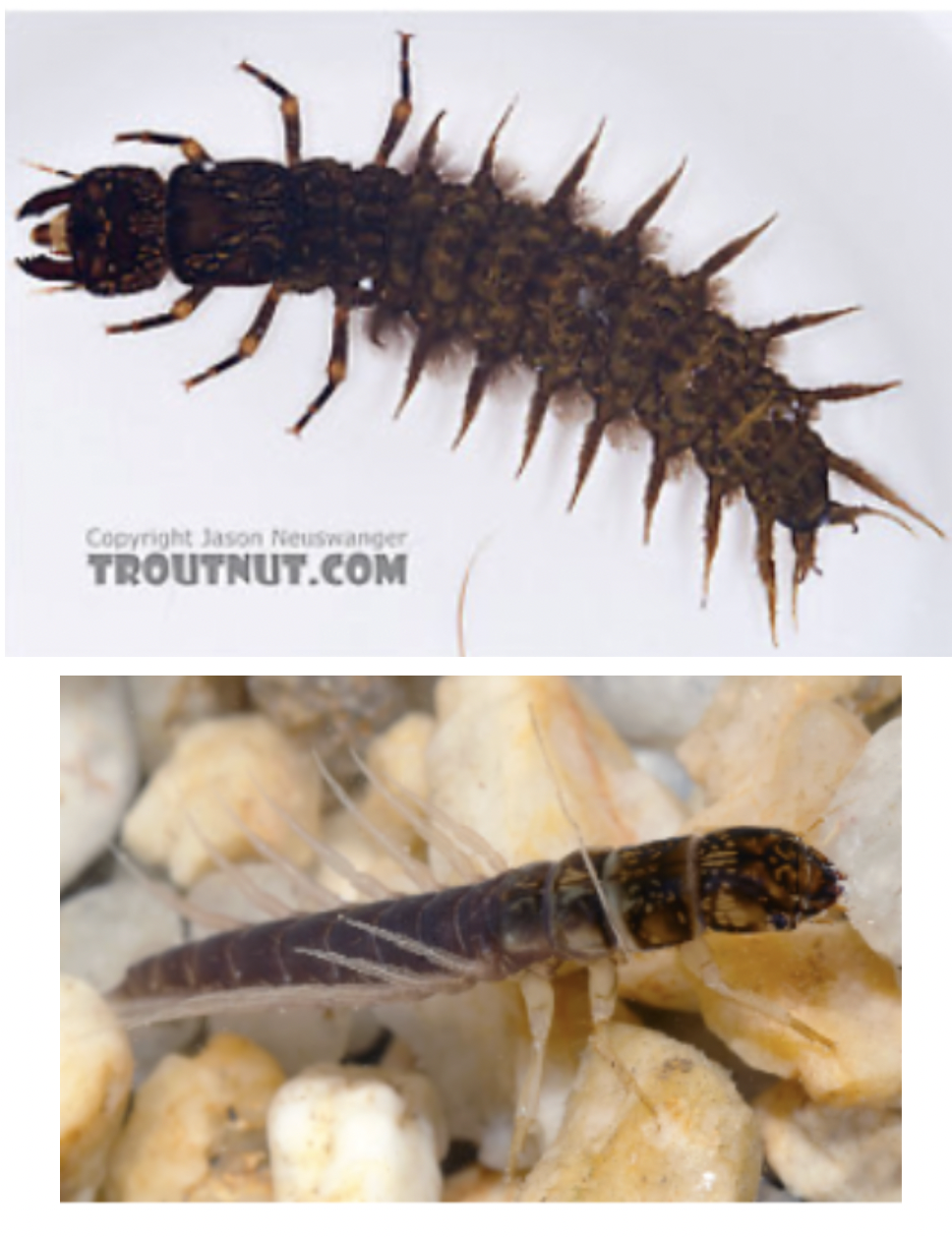

Order: Megaloptera
→ abdomen has a pair of finger-like gills from each segment
→ piercing mouthparts

Order: Megaloptera Family: Coryalidae
→ abdomen has a pair of finger-like gills from each segment
→ piercing mouthparts
→ 2 terminal prolegs with hooks on the end

Order: Megaloptera Family: Sialidae
→ has finger-like gills along the abdomenan
→ piercing mouthparts on larvae
→ a single long terminal cercus

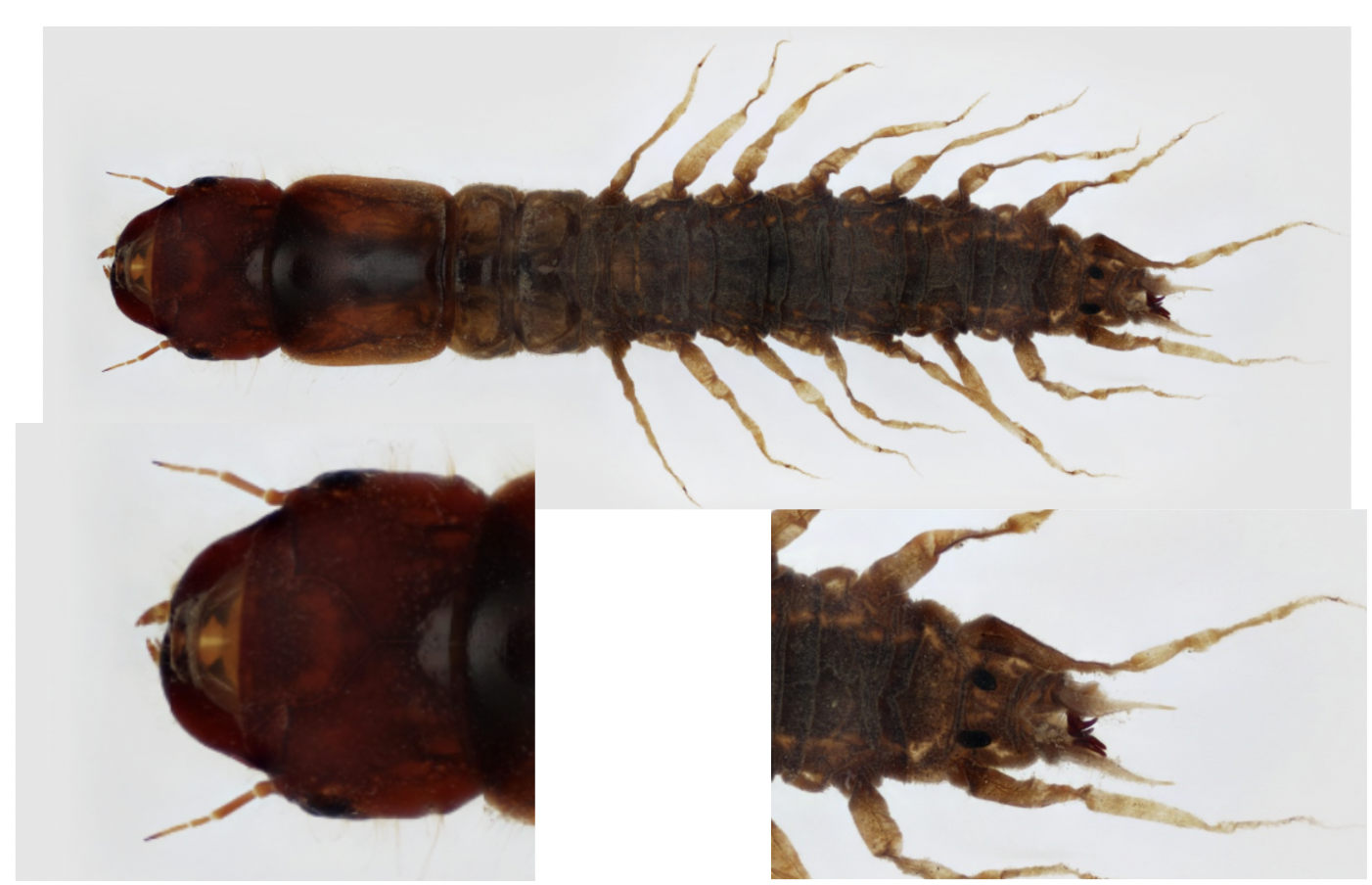
Order: Trichoptera
→ terminal prolegs with single hook
→ abdominal gills ( feather)
→ ecology: varies
→ Feeding: varies

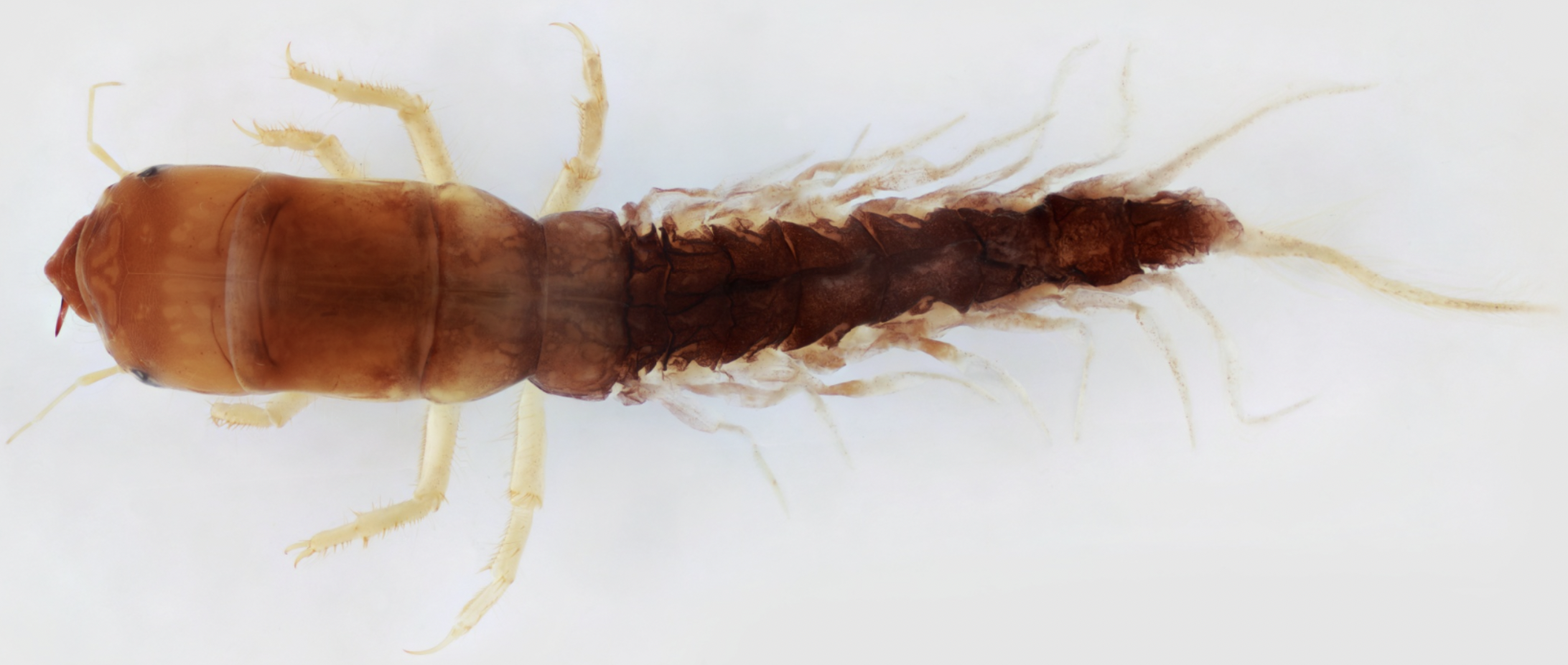
Identify, Name ecology and feeding type
Order: Trichoptera
→ two perminal prolegs, one hook on each
→ feathery abdominal gills
→ a case (yellow in the photo)
Ecology: varies
Feeding: varies
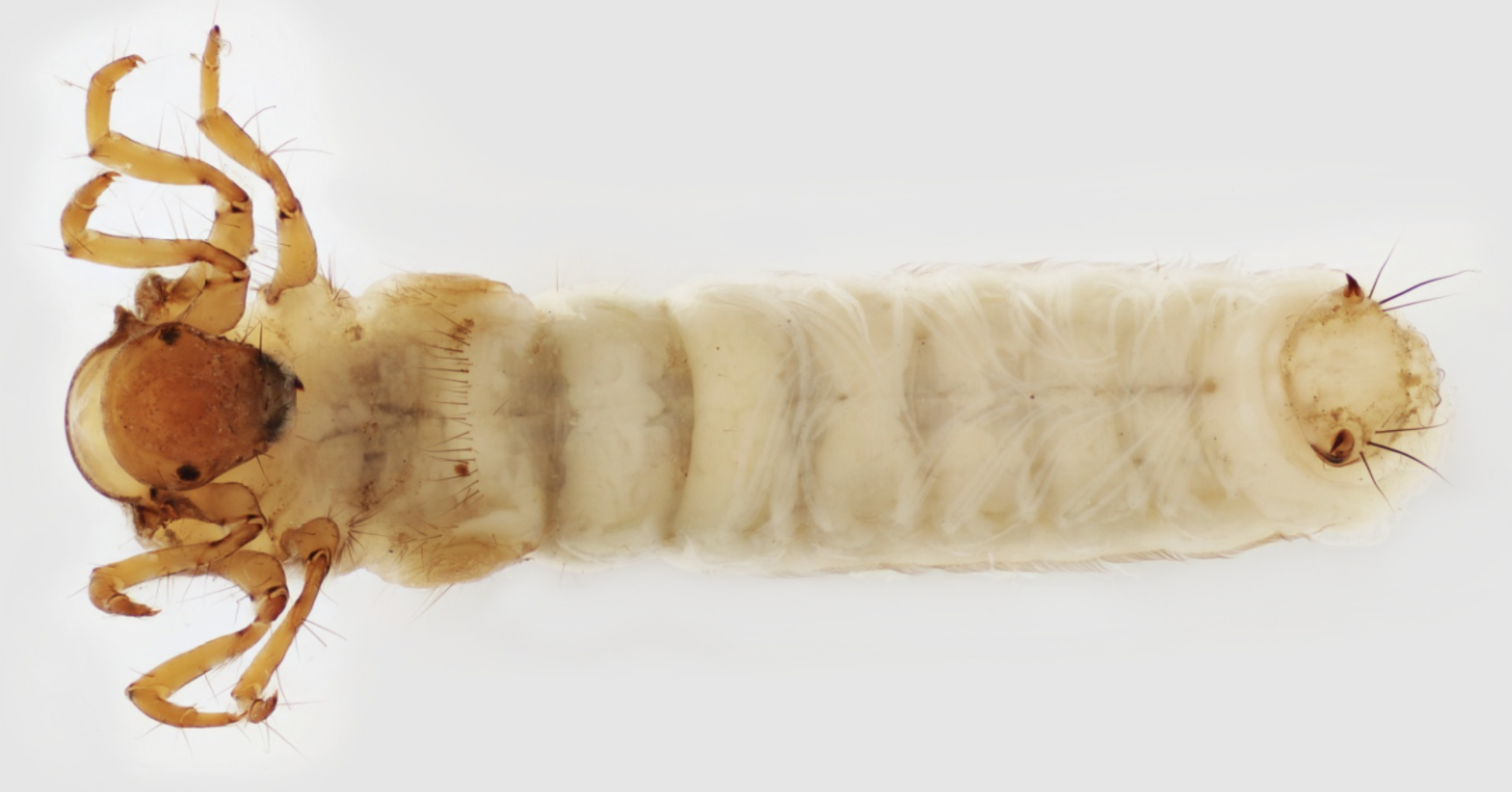

Order: Trichoptera
→ terminal prolegs with single hook
→ abdominal gills ( feather)
→ can have cases or an abdominal hump
→ ecology: varies
→ Feeding: varies
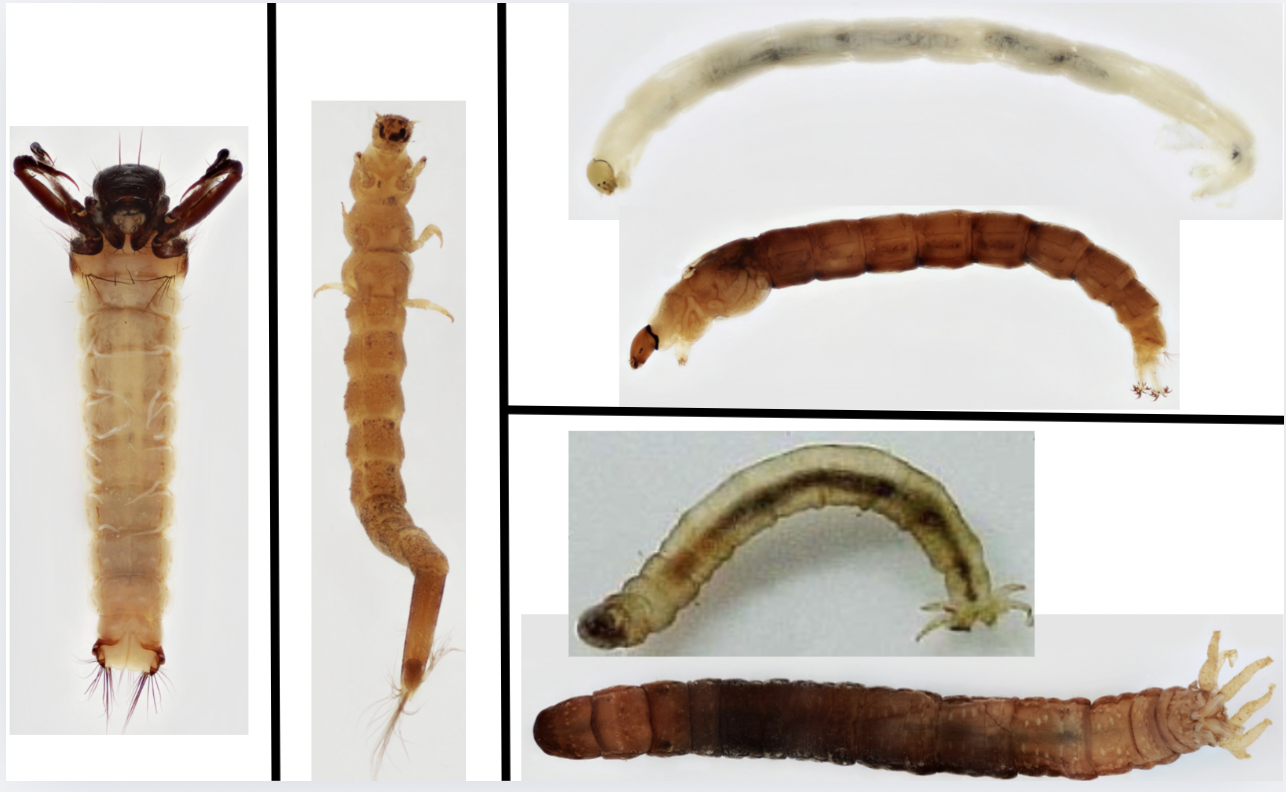

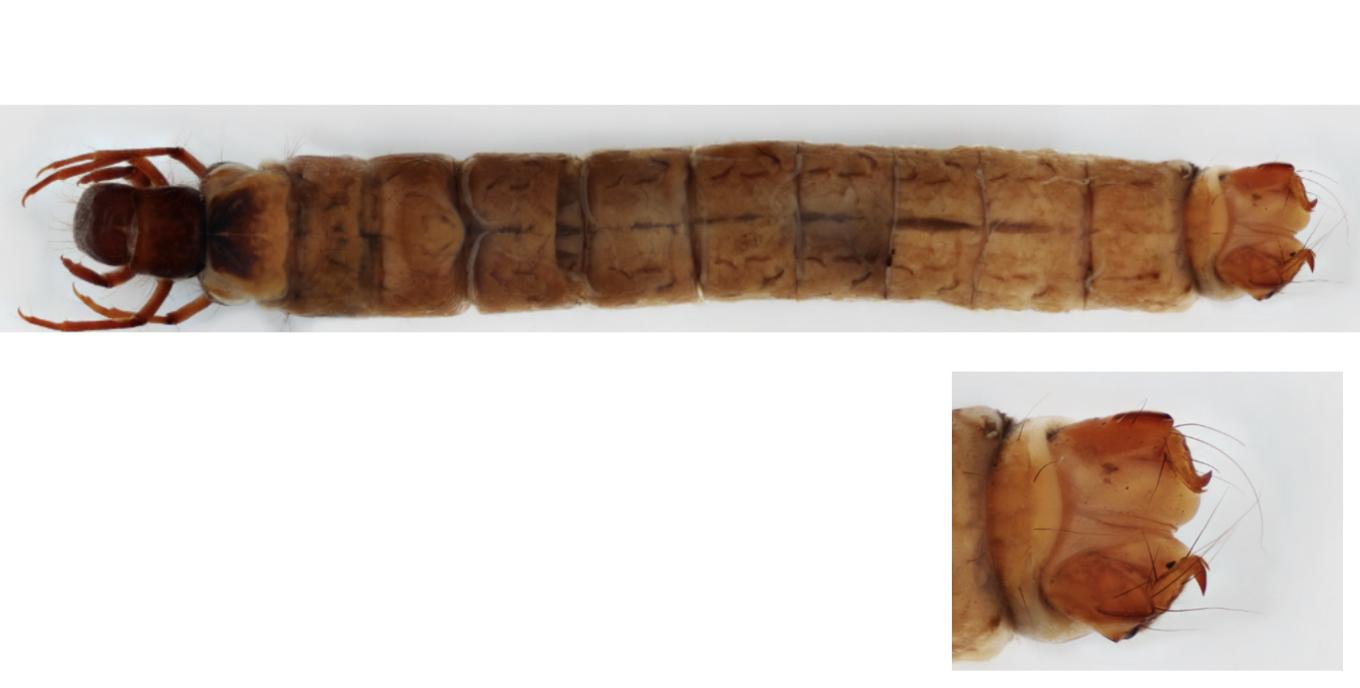
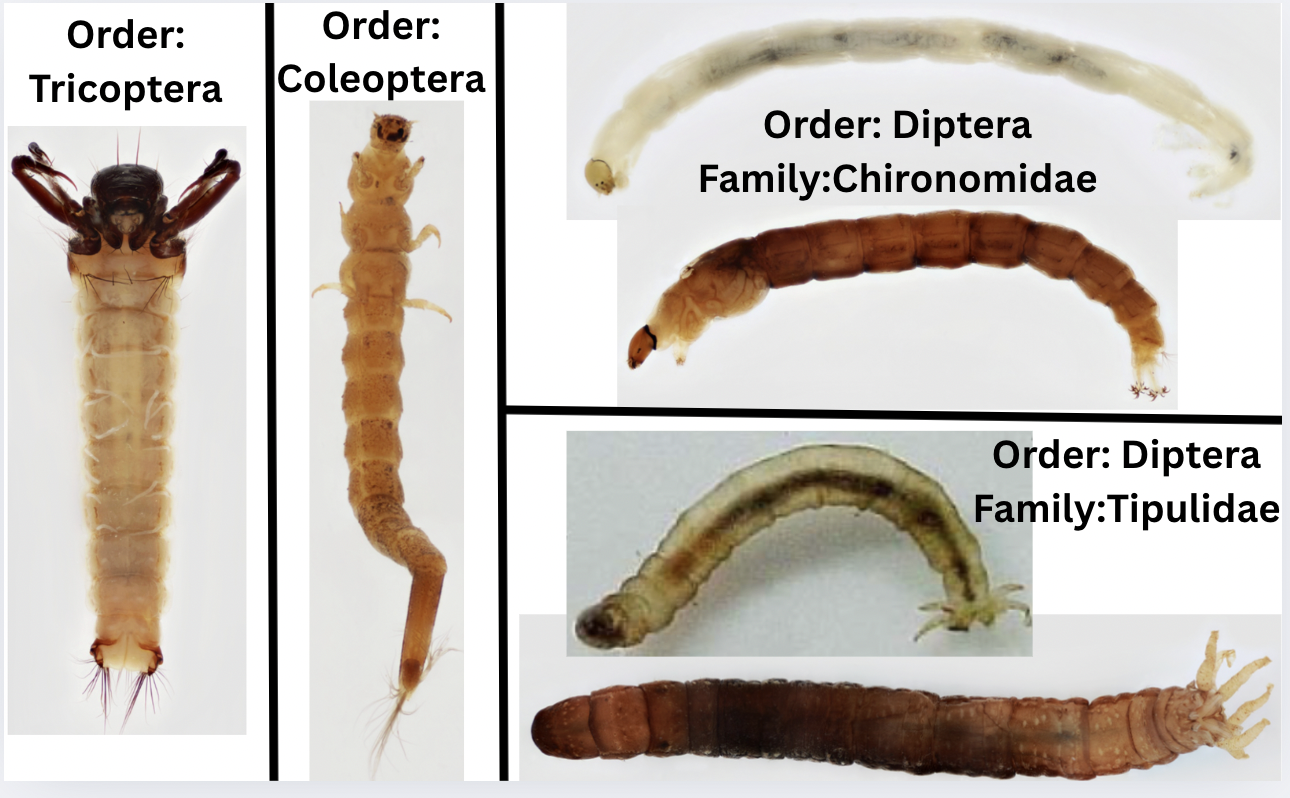
Order: Coleoptera
→ cone-shaped body
→ feather-like anal gills
Order: Tichoptera
→ Abdominal gills
→ Terminal prolegs with hooks
Order: Diptera ; Family: Chironomidae
→ head relatively smaller than body
→ Two prolegs at anterior & posterior
→ Can be red coloured
Order: Diptera ; Family: Tipulidae
→ finger-like anal gills
→ brownish clear body


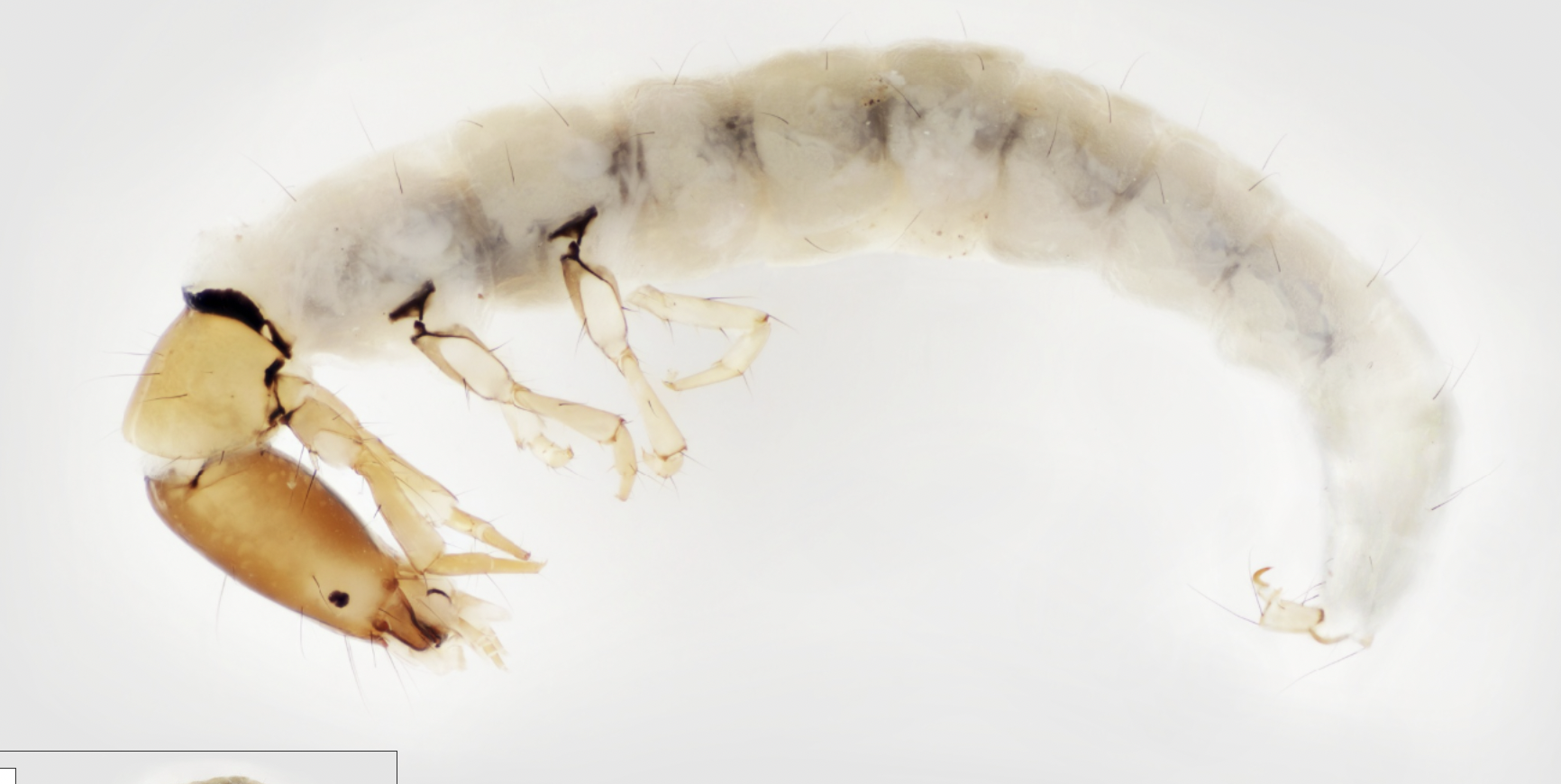
Identify, Name ecology and feeding type
Order: trichoptera
- has a hump on the back
- has two prolegs at the anterior and posterior with hooks ( not present on this one)
- usually has abdominal gills although not present in this one
Ecology: varied
Feeding:varied
What are the three families in order, diptera?
Simuliidae
Chironomidae
Tipulidae
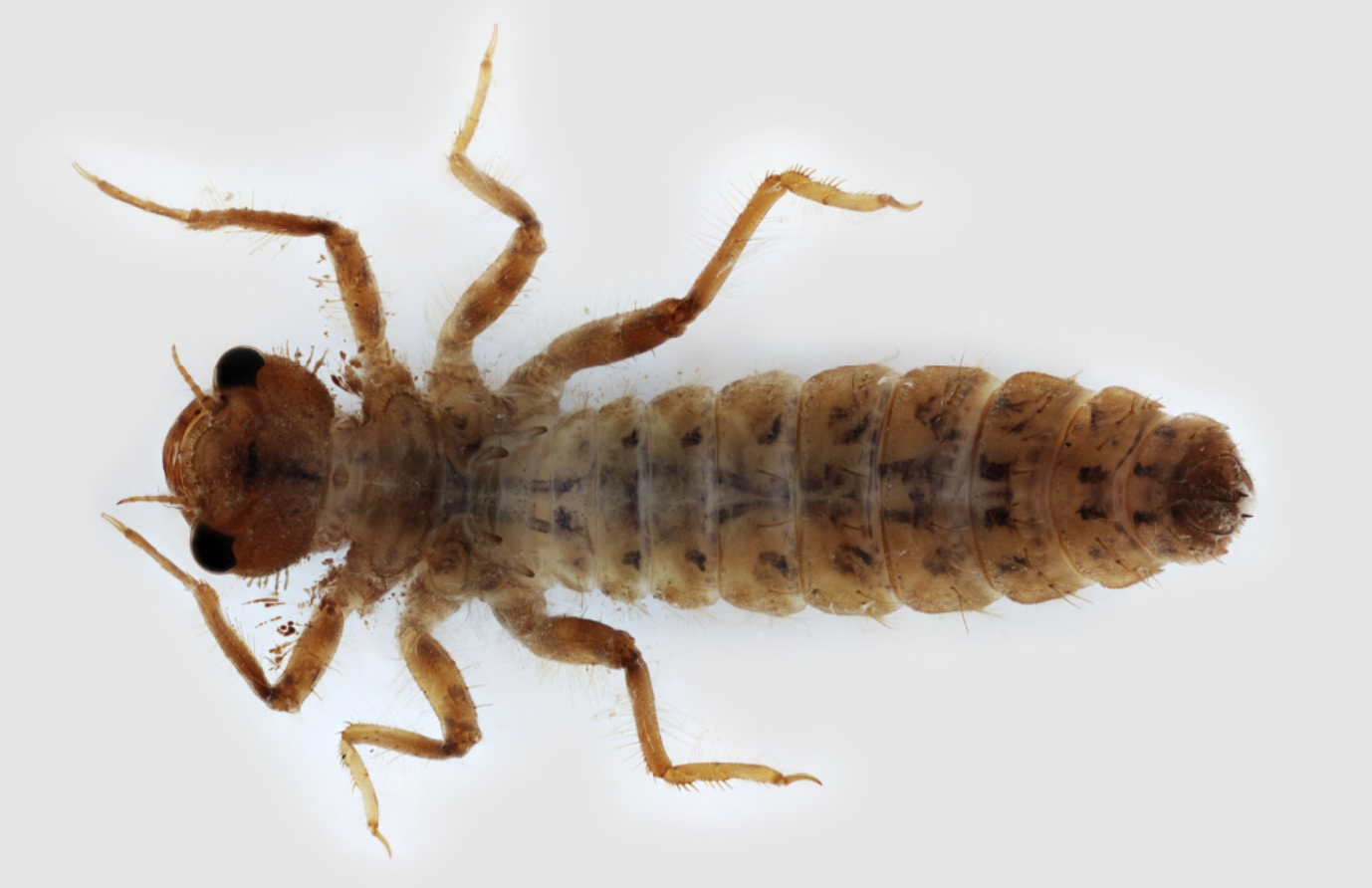

Order: Odonata
→ squiggly legs
→ big eyes
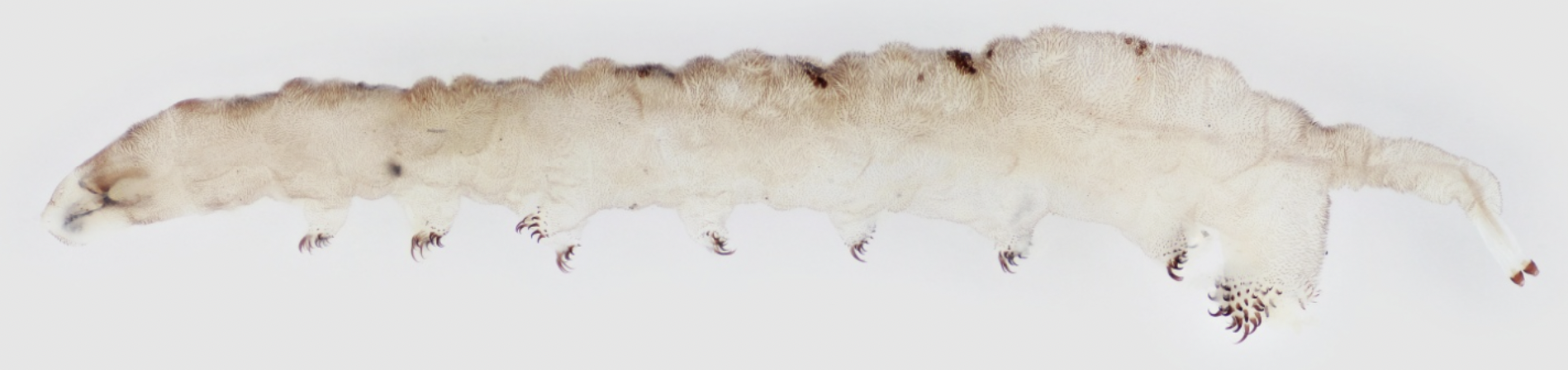

Identify Order, Name ecology and feeding type
Order: Diptera
- no tarsi but prolegs are present.
- relatively small head
- Ecology: benthic to lotic
feeding: varied
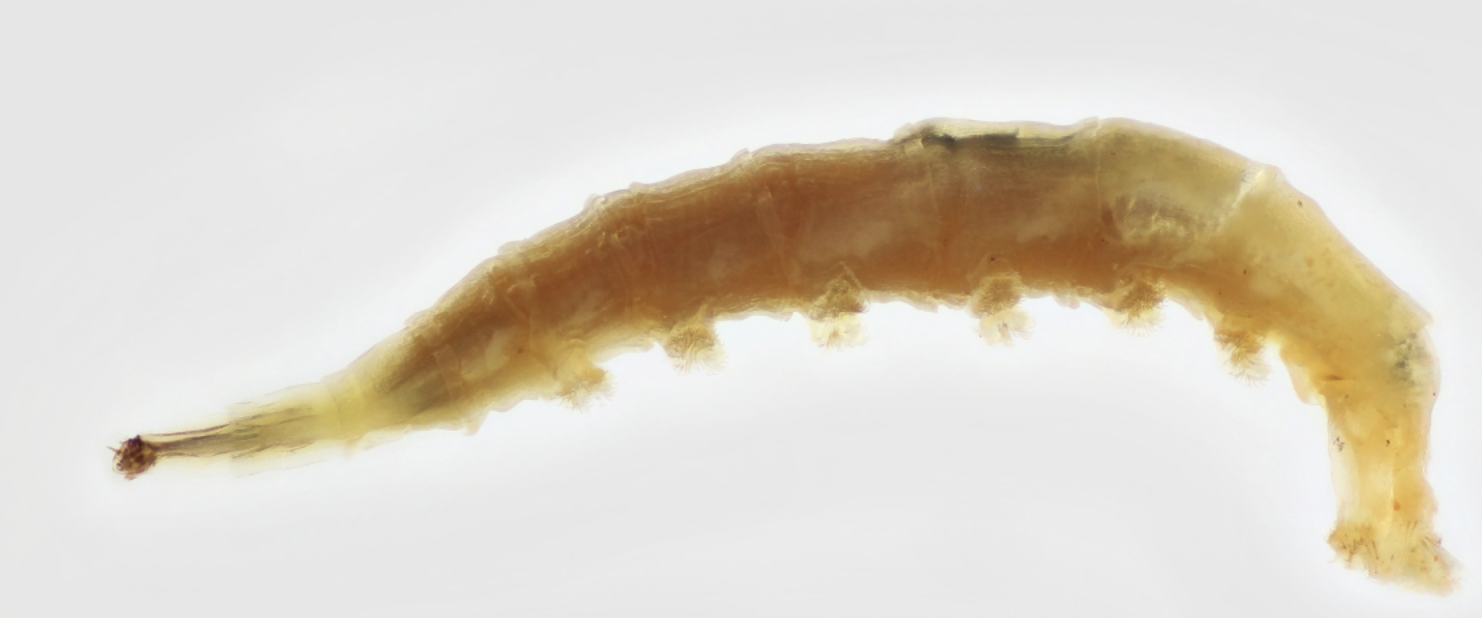

Identify to order, Name ecology and feeding type
Order: Diptera
→ no legs and there are prolegs (sometimes diptera doe snot have prolegs)
→ relatively smal head compared to body
Ecology: benthic to lotic
Feeding: varied
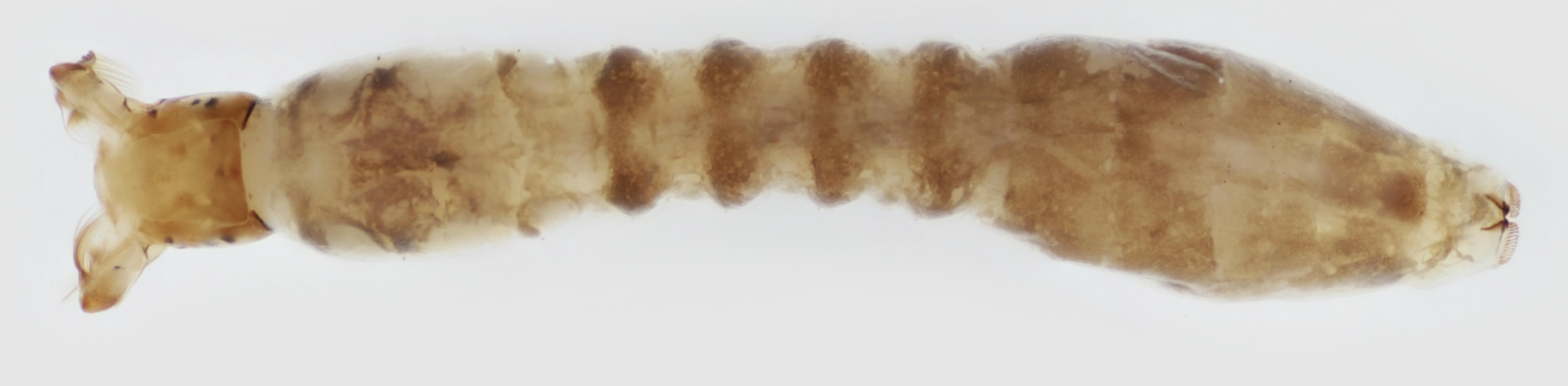
Identify, order and family.
List feeding and ecology type
Order: Diptera
Family: Simuliidae
→ has gills by protusions close to head
→ no legs
→ head is relatively smaller than body ( in this photo it is smaller than the abdomonen
Ecology: benthic to lotic
Feeding: Simuliidae are usually filter feeder of fine-particulate organic matter and converts it to fecal pellet
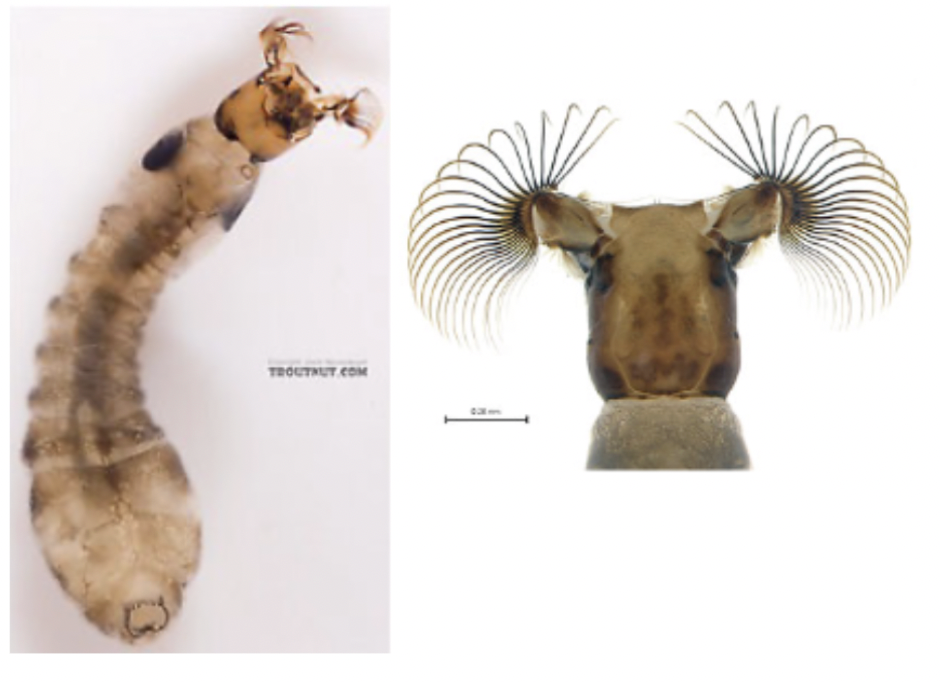

Order: Diptera
Family: Simuliidae
→ feathery gills on the head
→ no legs
→ small head compared to body
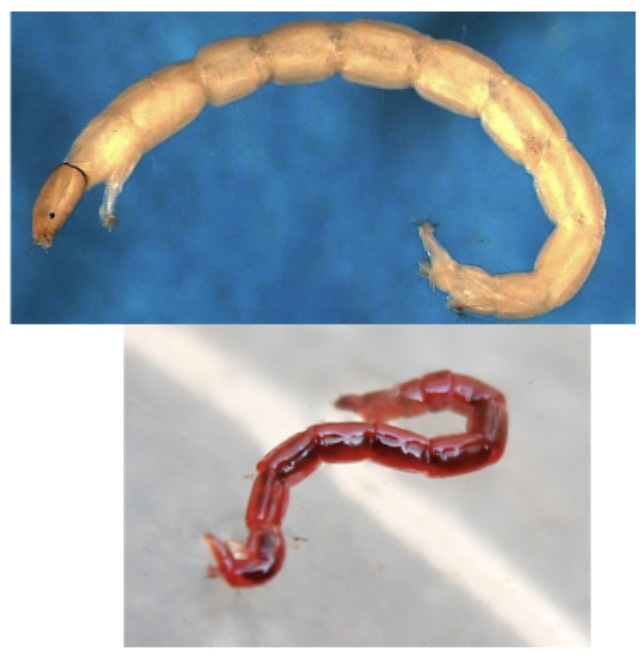
Order: Diptera
Family: Chironomidae
→ two gripping prolegs at anterior and posterior
→ extremely small head
→ may be bright red (hemoglobin)
→ Ecology: Chironomidae mostly benthic
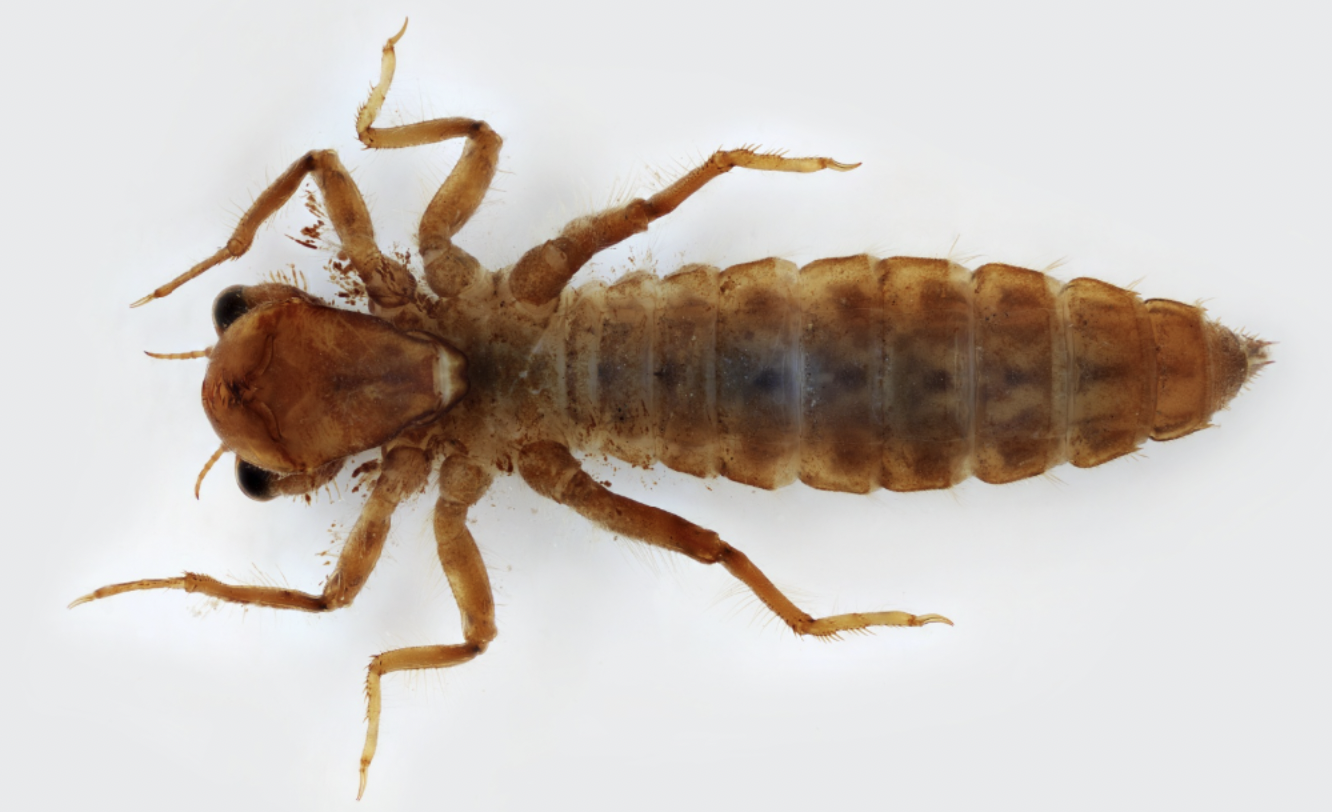

Order: Odonata
→ squiggly legs
→ big eyes

Name order and family
Order: Diptera
Family: Chironomidae
→ Bright red
→ worm like
→ two-gripping pro-legs at posterior and anterior
What are the different feeding groups?
Predators:
→ highly mobile; mouthparts modified for piercing and are usually directed forwards
→ feed on detritus
Gathering collectors:
→ Highly mobile, mouthparts may be modified or generalized
→ may feed on detritus
Filtering collectors:
→ Sessile or semi-mobile ; mouthparts highly modified for silk-spinning or fans
→ feed on detritus
Shredders:
→ Highly mobile
→ mouthparts are strong and modified for chewing detritus
Scrapers:
→ semi-mobile; have hard mouthparts like radulas or modified mandibles directed downwards
→ feed on algae bacteria or fungi growing on rocks of the biotic substrata