Human Anatomy/Physiology Lab Practical 2- Articulations/Joints
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
151 Terms
Fibrous Joints
Cartilaginous Joints
Synovial Joints
What are the 3 structural classes of joints?
Articulations
sites where two or more bones meet
–hold the skeleton together
–give skeleton mobility
–joints are the weakest parts of the skeleton
Structural classification of articulations
–material binding the bones together
–presence of a joint cavity
–types
•fibrous
•cartilaginous
•synovial joints
Functional classifications of articulations
–amount of movement allowed at the joint
–types:
•synarthroses (immovable)
•amphiarthroses (slightly movable)
•diarthroses (freely movable)
Son
means together- tied together
Amphi
both- immoveable and moveable
Synarthroses
Amphiarthroses
Diarthroses
Name the 3 functional classes of joints
Because of the joint cavity
Why is synovial joints always diarthroses/freely mobile
Fibrous Joints
•Bones are connected by fibrous tissue with no joint cavity
• Amount of movement allowed depends on the length of connective tissue fibers uniting the bones
•Dense regular connective tissue holds together the ends of bones and bone parts; no joint cavity
Gomphosis
Suture
Syndesmosis
What are the 3 structural categories of fibrous joints
Gomphosis
Suture
What 2 structural categories of fibrous joints are synarthrosis aka immobile
Sydesmosis
Which structural category of fibrous joints are amphiarthrosis aka slightly mobile?
Gomphoses
Periodontal membranes hold tooth and bony jaw
ex: tooth to jaw
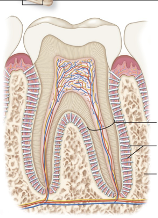
Suture
Dense regular connective tissue connects skull bones
ex: lambdoidal suture (connects occipital and parietal bones)
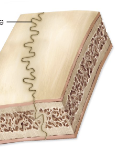
Sydemoses
Dense regular connective tissue fibers (interosseous membrane) between bones
ex: articulations between radius and ulna and between tibia and fibula
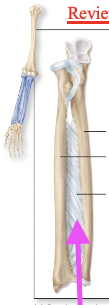
Ampharthrosis (slightly mobile)
Articulation between radius and ulna, and between tibia and fibula
Pubic symphysis; intervertebral disc articulation
Synarthrosis (immobile)
Tooth to jaw
Lamboidal suture
Epiphyseal plates in growing bones; costochondral joints
Diarthrosis (freely mobile)
Intercarpal joints
intermareal joints
elbow joint
knee joint
Interphalangeal joints
MP joints
Glenohumeral joint
Hip joint
Joint cavities
These have synovial fluid, which are fluid filled spaces between two bones
Syndesmosis Interosseous membrane
Dense regular connective tissues between bones - this is ampharthroses
Length of connective tissues
Amount of movement is based on
Cartilaginous Joints
Cartilaginous joints have cartilage connecting the articulating bones
These joints are either immobile, or slightly mobile
Connecting cartilage can be either hyaline or fibrocartilage
Pad of cartilage is wedged between the ends of bones; no joint cavity
THESE ARE FOR COMPRESSION
Synchondrosis
Symphysis
What are the two types of structural categories for cartilaginous joints?
Synchondrosis
Which cartilaginous joint category is synarthrosis (immobile)?
Symphysis
Which cartilaginous joint category is amphairthrosis (slightly mobile)?
Sychondrosis
Hyaline cartilage between bones
ex: epiphyseal plates in growing bones; costochondral joints
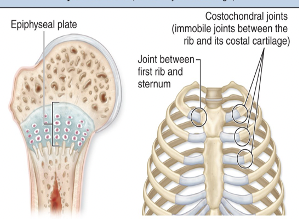
Symphysis
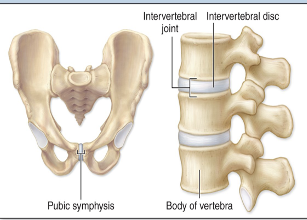
Fibrocartilage pad between bones (this word means growing together)
ex: pubic symphysis; intervertebral disc articulations
Hyaline
Shiny
ex: chicken bone
Fibrocartilage
Tough
Compression
Cartilage
Chon= _______
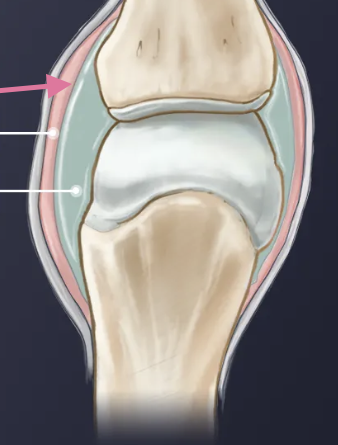
Synovial Joint
•Articulating bones are separated by fluid-containing joint cavity
•This arrangement permits substantial freedom of movement
•Ends of bones covered with articular cartilage; joint cavity separates the articulating bones; joint enclosed by an articular capsule, lined by a synovial membrane; contains synovial fluid
Articular Capsule
made of a fibrous layer and a synovial membrane – synovial membrane (epi that makes fluid) wraps entire joint – saran wrap
–Fibrous capsule:dense regular CT
–Synovial membrane: lines all internal joint surfaces that are not hyaline cartilage
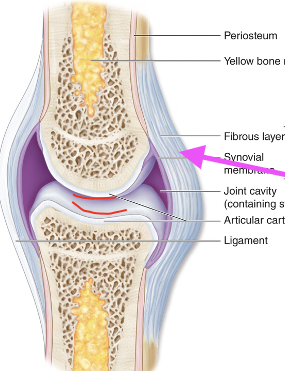
Lubricate, reduce friction, shock absorption, nutrient waste removal (bc no blood supply)
What does synovial fluid do for us?
Articular Cartilage
–Absorbs compression
–No perichondrium
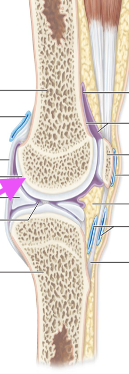
Joint Cavity
Synovial Fluid is aka…
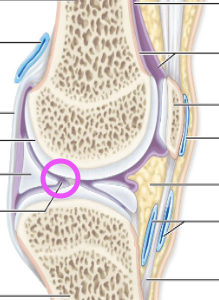
Synovial Fluid
–a filtrate of plasma
–lubrication – reduces friction between articular cartilages
–nourishment of chondrocytes
–Shock absorber
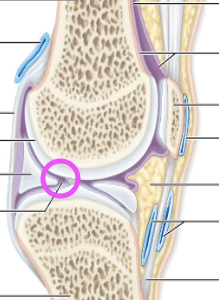
Strengthening Ligaments
–Intrinsic or capsular ligaments
–Extrinsic ligaments
•Extracapsular ligaments
•Intracapsular ligaments
Fatty Pads
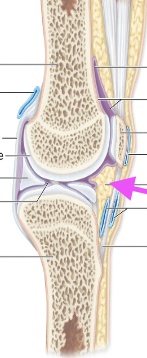
Menisci
CT pads
Structure for mobile joints
(Model explained in class)
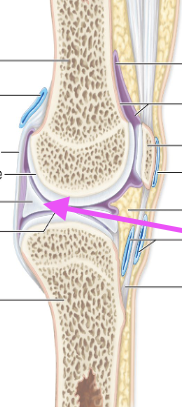
Bursae
Fluid pocket
Synovial
Where Rubbing occurs
(Water balloon story)
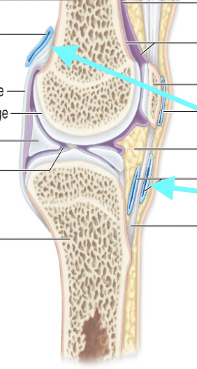
Intrinsic Ligaments
Thick bands of fibrous connective tissue that help thicken and reinforce the joint capsule
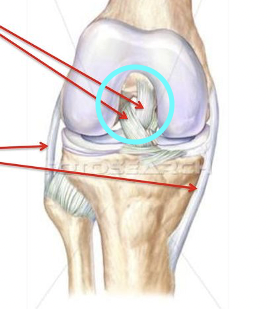
Extrinsic Ligaments
Separate from the joint capsule and help to reinforce the joint by attaching the bones together
These include BOTH extra scapular and intrascapular
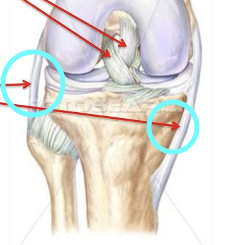
Extracapsular Ligament
Tibial and fibular collateral ligament, patellar ligament
Intracapsular Ligament
Anterior/posterior cruciate
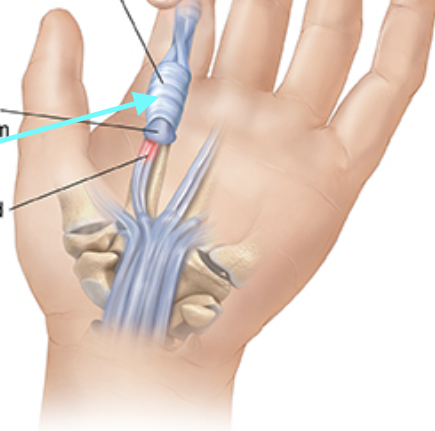
Tendon Sheaths
A thin layer of tissue, surrounds each tendon in the body.
Can also be called synovial lining or fibrous sheath.
Help protect tendons from abrasive damage as they move.
Synovial Membrane
Gliding Joint
Pivot Joint
Hinge Joint
What are the 3 uniaxial synovial joints?
Elliposoid Joint
Saddle Joint
What are the two biaxial joints?
Ball and Socket Joint
What is the only multiracial synovial joint?
Plane joint
Gliding joints are also known as…
Gliding or planar joints
Flattened or slightly curved surfaces that slide across one another, but the amount of movement is very slight
LINEAR MOVEMENT
Gliding Joint
Examples of which synovial joint type?
Intercarpal joints
Intertarsal joints
Sternoclavicular and acromioclavicular joints
Vertebrocostal joints
Sacro-iliac joints

Pivot Joint
Bone with a rounded surface fits into a ring formed by a ligament and another bone permitting rotation only
ROTATIONAL
Pivot Joint
Examples of which joint type?
Atlantoaxial Joint
Proximal Radioulnar Joint

Hinge Joint
Convex feature of one bone fits into concave depression of another bone
Permits angular motion in a single plane, like the opening and closing of a door
ANGULAR
Hinge Joint
Examples of which type of synovial joint?
Elbow joint
Knee Joint
Ankle Joint
Interphalangeal Joint

Saddle Joint
Saddle-shaped articular surface on one bone closely interfaces with a saddle-shaped surface of another bone
Concave of one axis and convex on the other
ANGULAR MOTION
Saddle Joint
Examples of which synovial joint?
THUMB
First carpometacarpal Joint (articulations between carpal and first metacarpal)
TRAPEZIUM

Ellipsoid Joint
An oval articular face nestles within a depression on the opposing surface
Oval articular surface on one bone closely interfaces with a depressed oval surface on another bone
ANGULAR MOTION
Condylar Joint
Ellipsoid Joint is aka….
Ellipsoid Joint
Examples of which synovial joint?
KNUCKLES
Metacarpophalangeal joints 2-5
metatarsaophalangeal joints
Radiocarpal joint

Ball-and-socket Joint
The round head of one bone rests within a cup-shaped depression of another
ANGULAR, CIRCUMDUCTION, AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
Ball-and-Socket Joint
Examples of which synovial joint?
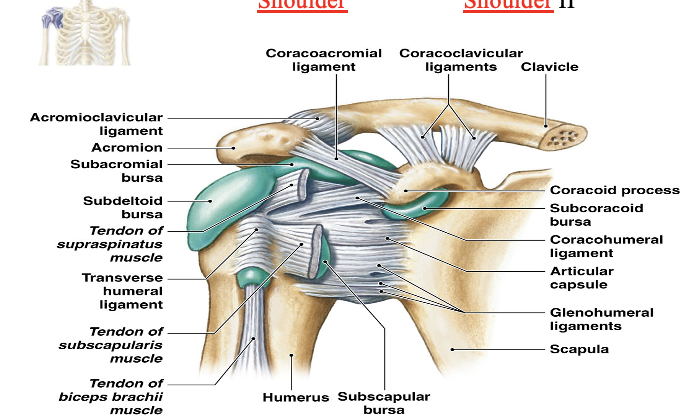
Shoulder Joint aka Glenohumeral
Hip Joint

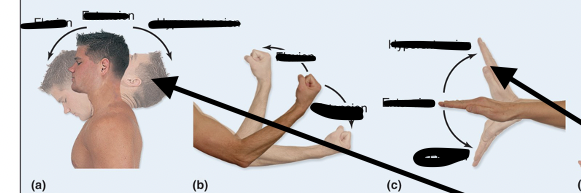
Flexion
Decreases angle between joints
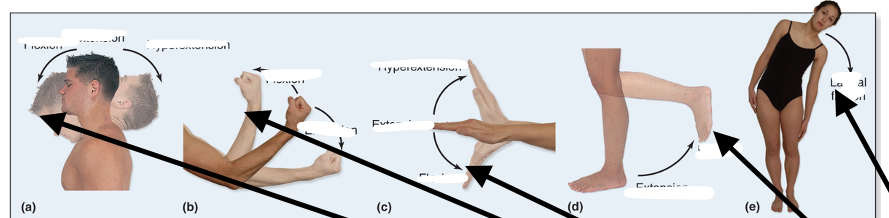
Extension
Increases angle between joints
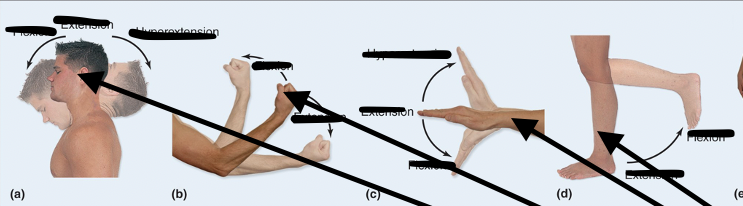
Hypertension
Overextending/flexing
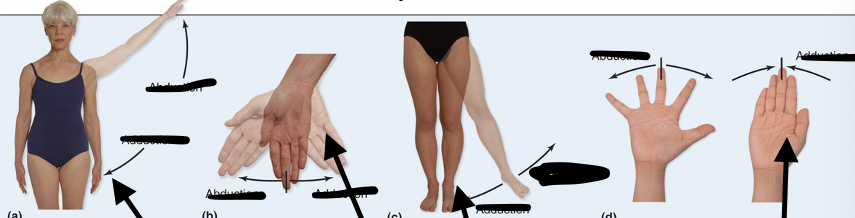
Abduction
Moves AWAY from midline or is TAKEN AWAY from the body
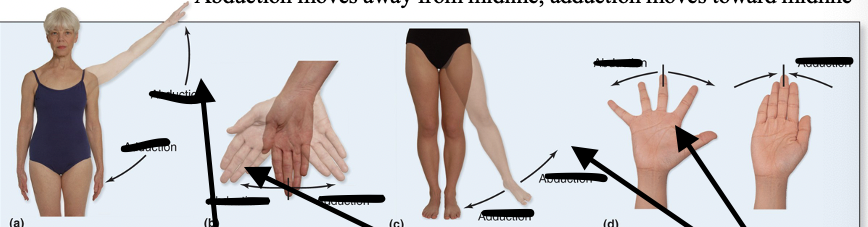
Adduction
Moves TOWARD midline or it is ADDED to the body
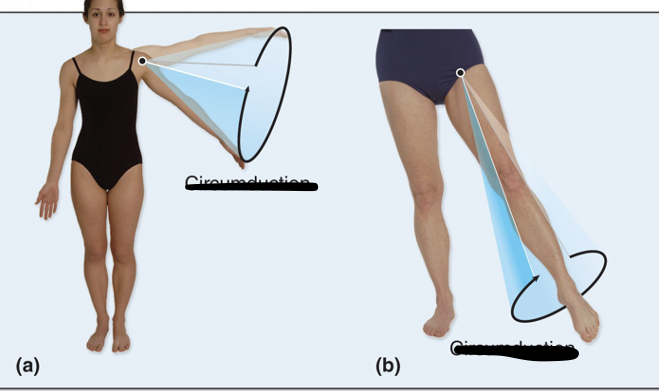
Circumduction
Proximal end of appendage remains stationary, distal end traces a circle
Involves combination of flexion, abduction, extension, and adduction
(Draw circle on board-forms cone-circumference)
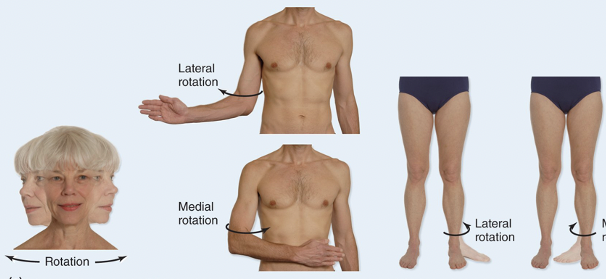
Rotational Movements
Involves turning a bone around its own long axis
Common at hip and shoulder joint
Examples: medial and lateral rotation of thigh
Supination Rotation
Palm is up

Pronation Rotation
Back or top is exposed

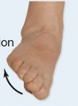
Inversion
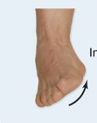
Eversion
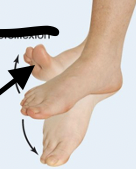
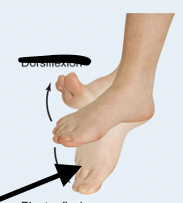
Dorsiflexion
Dorsal fin on back-lifts back up
Plantar Flexion
Plant your toes
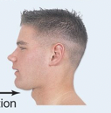
Protaction
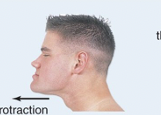
Retraction
Double Chin
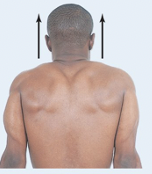
Elevation
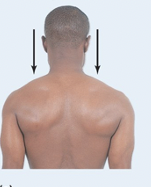
Depression
Opposition
Two structures cross over
Only happens at thumb and pinky finger
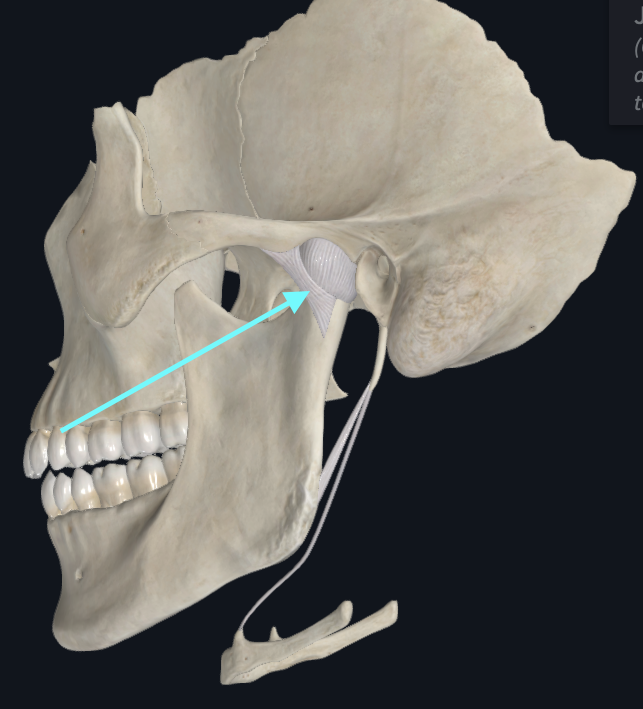
Temporamandibular Joint (TMJ)
A modified hinge type of synovial joint
Head of Mandible
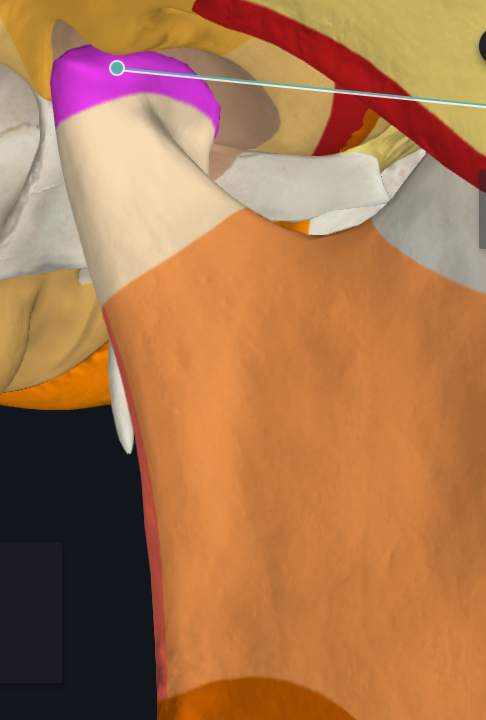

Mandibular Fossa
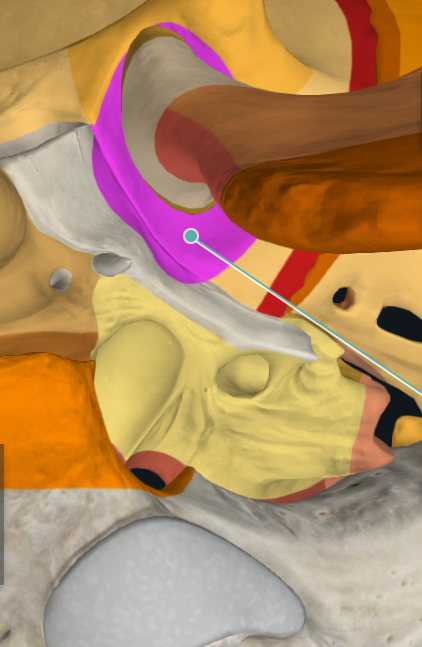
Sphenomandibular Ligament
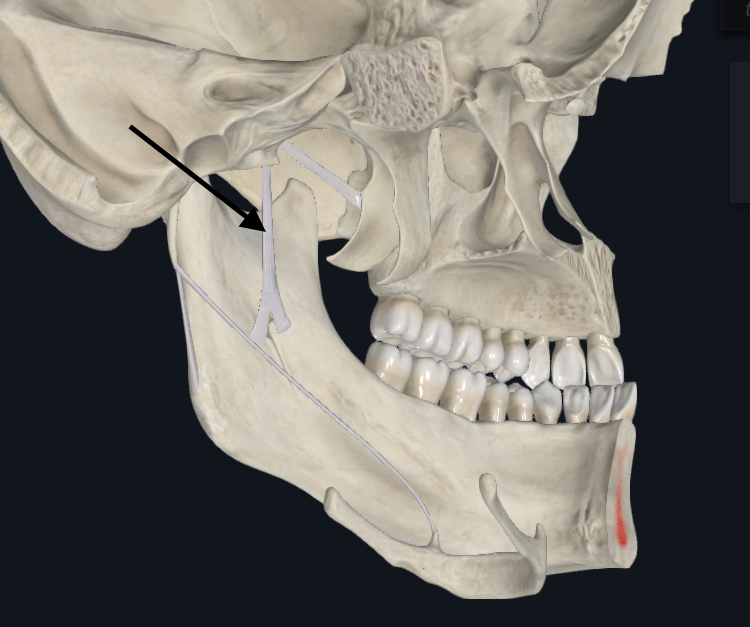
Stylomandibular Ligament
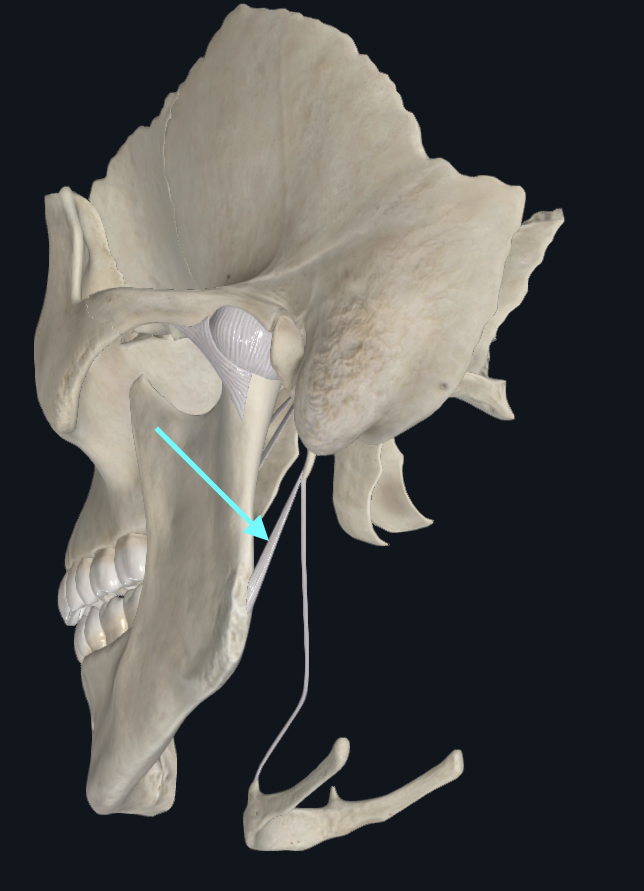
Lateral Ligament of TMJ
Intervertebral Articulations
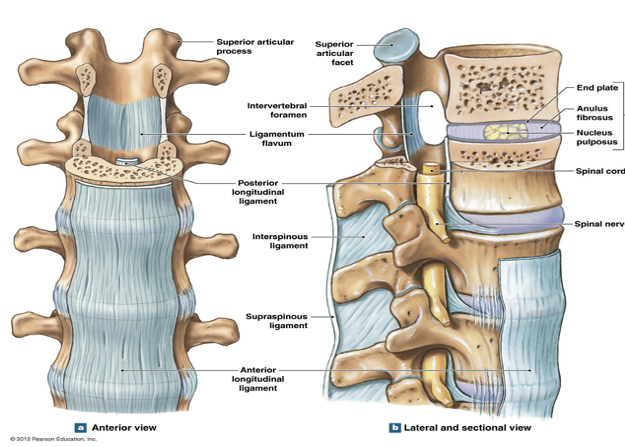
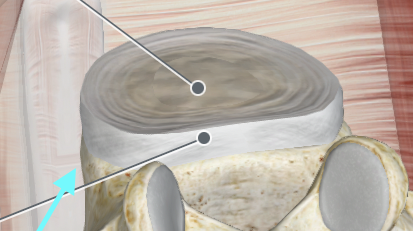
Intervertebral Discs
Nucleus Polposus of Intervertebral Discs
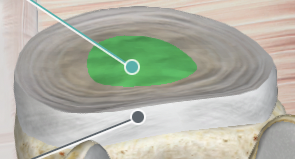
Anulus Fibrosus of Intervertebral Discs
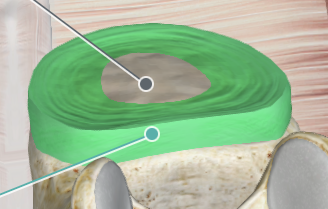
Anterior Longitudinal Ligament
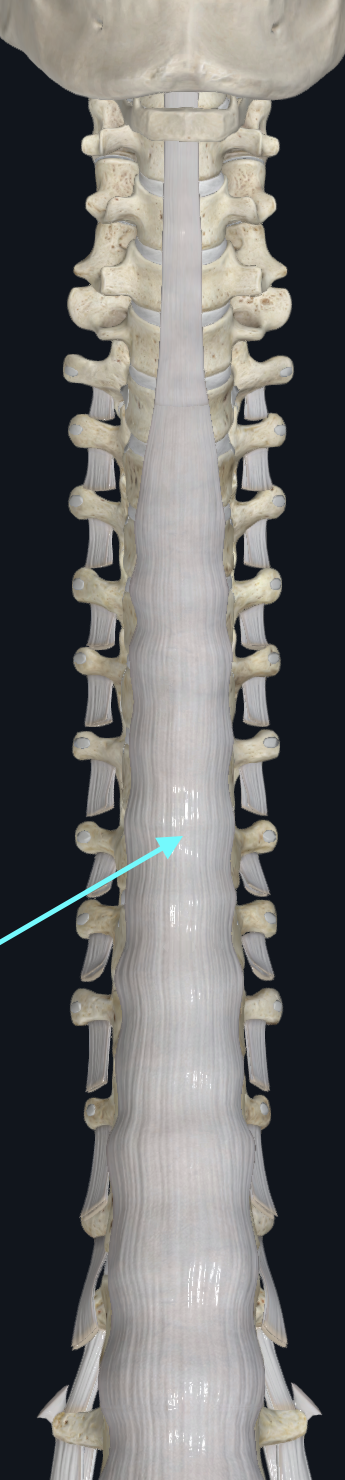
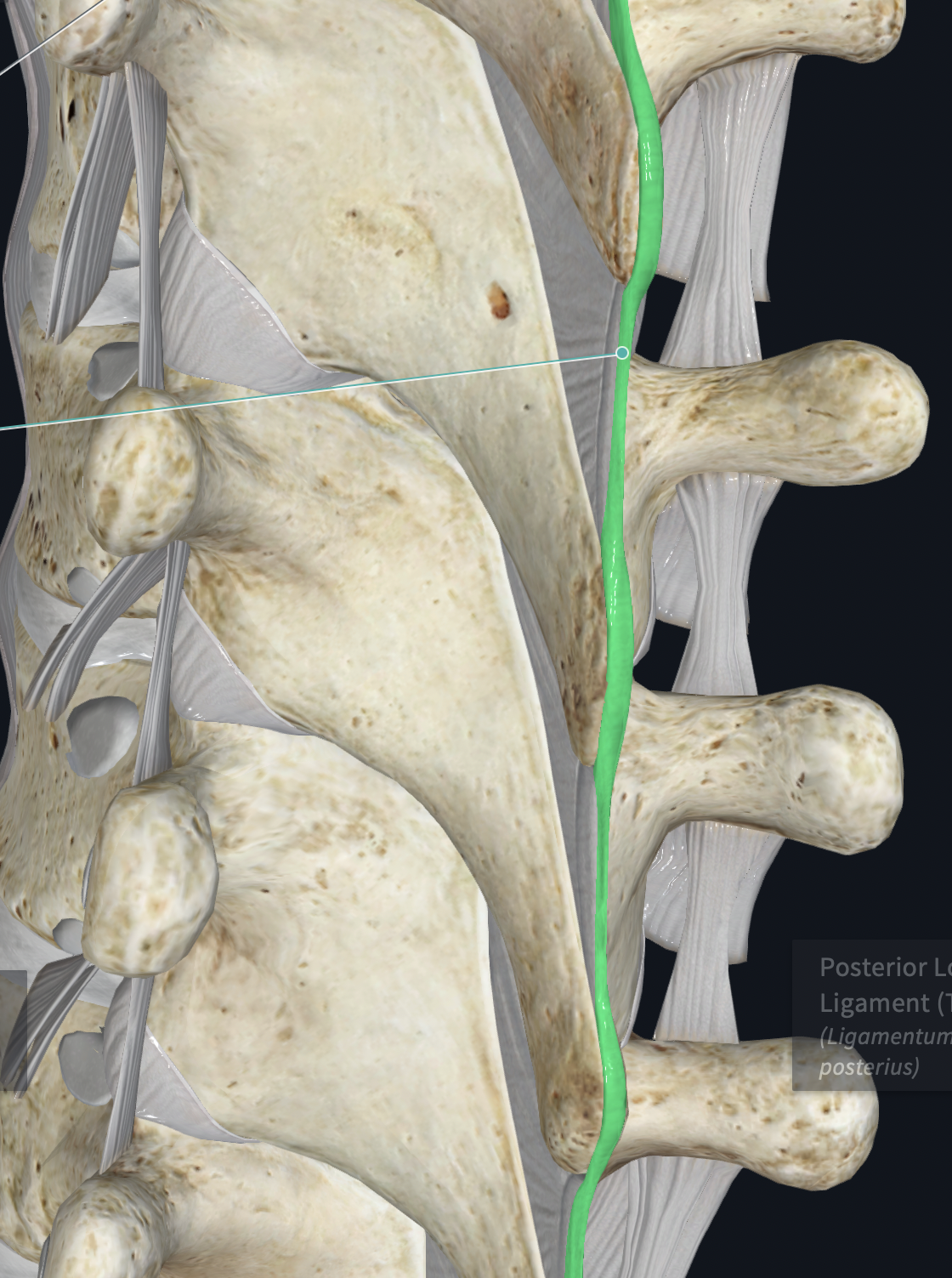
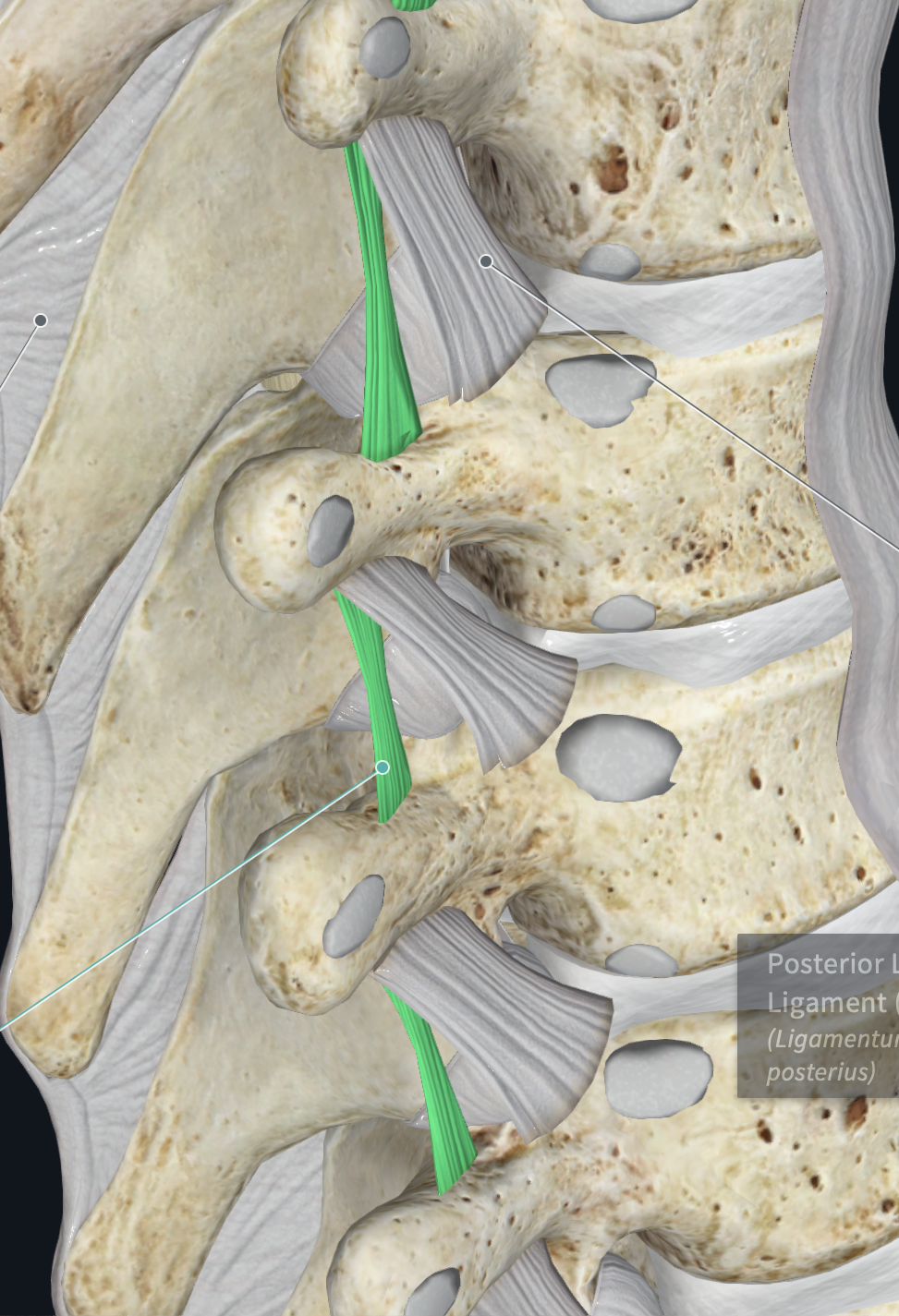
Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
behind body of vertebrae, runs up and down
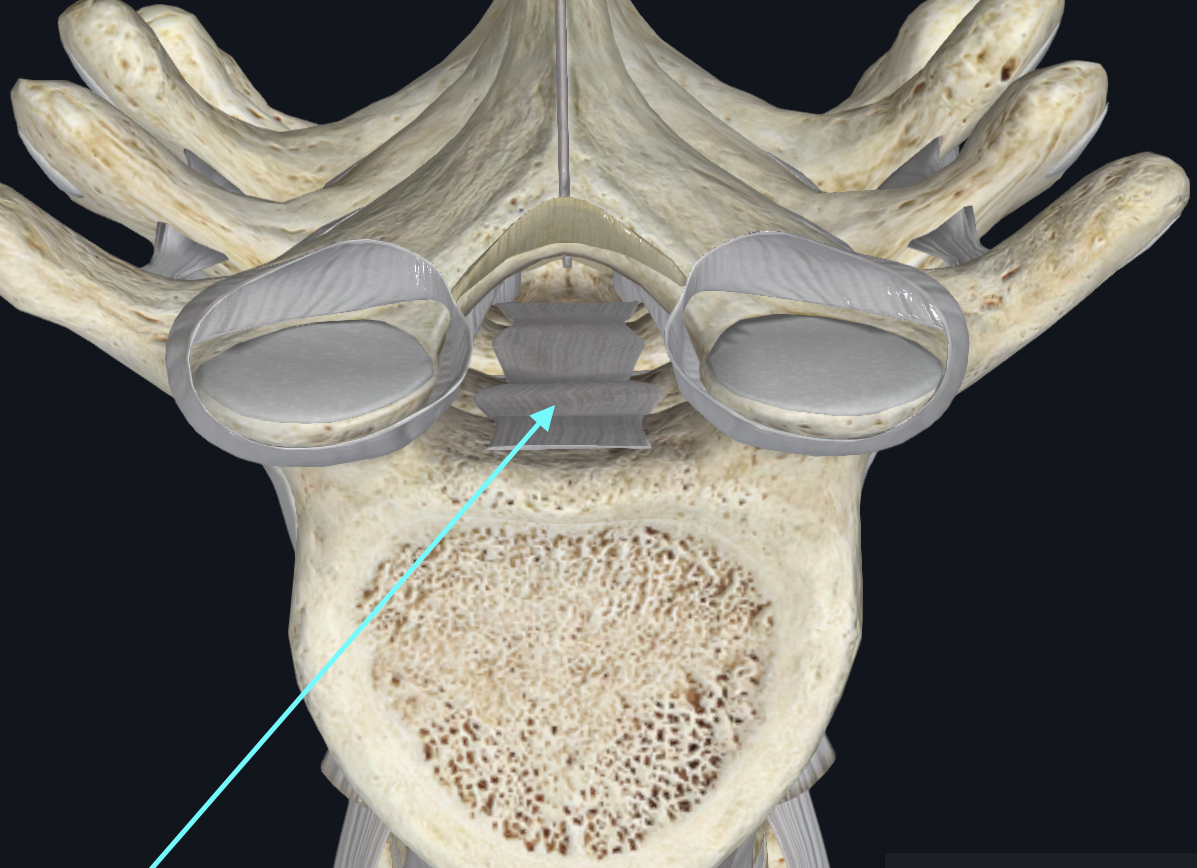
Ligament Flavum
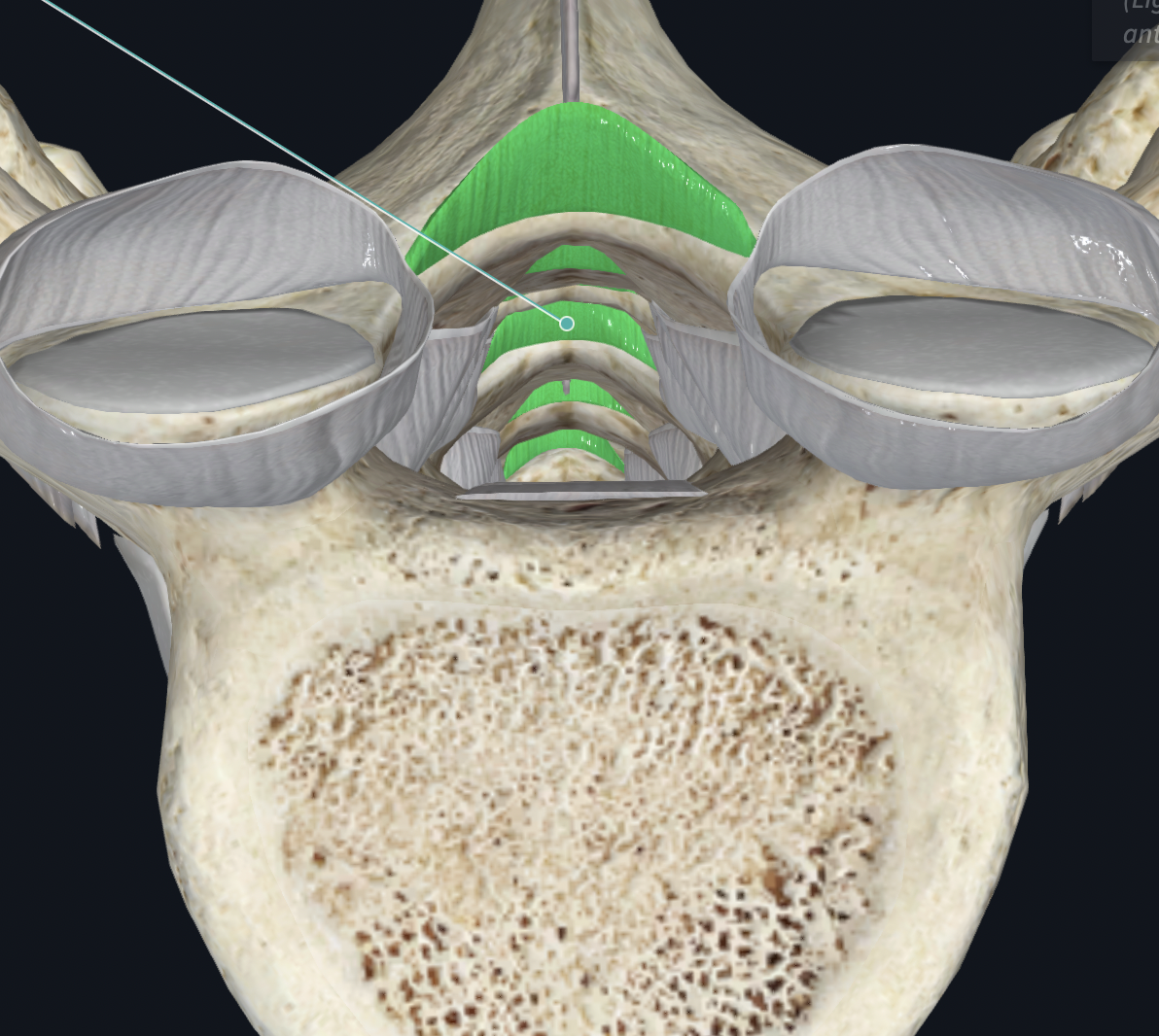
Interspinous Ligament
between (between spinous processes of vert)
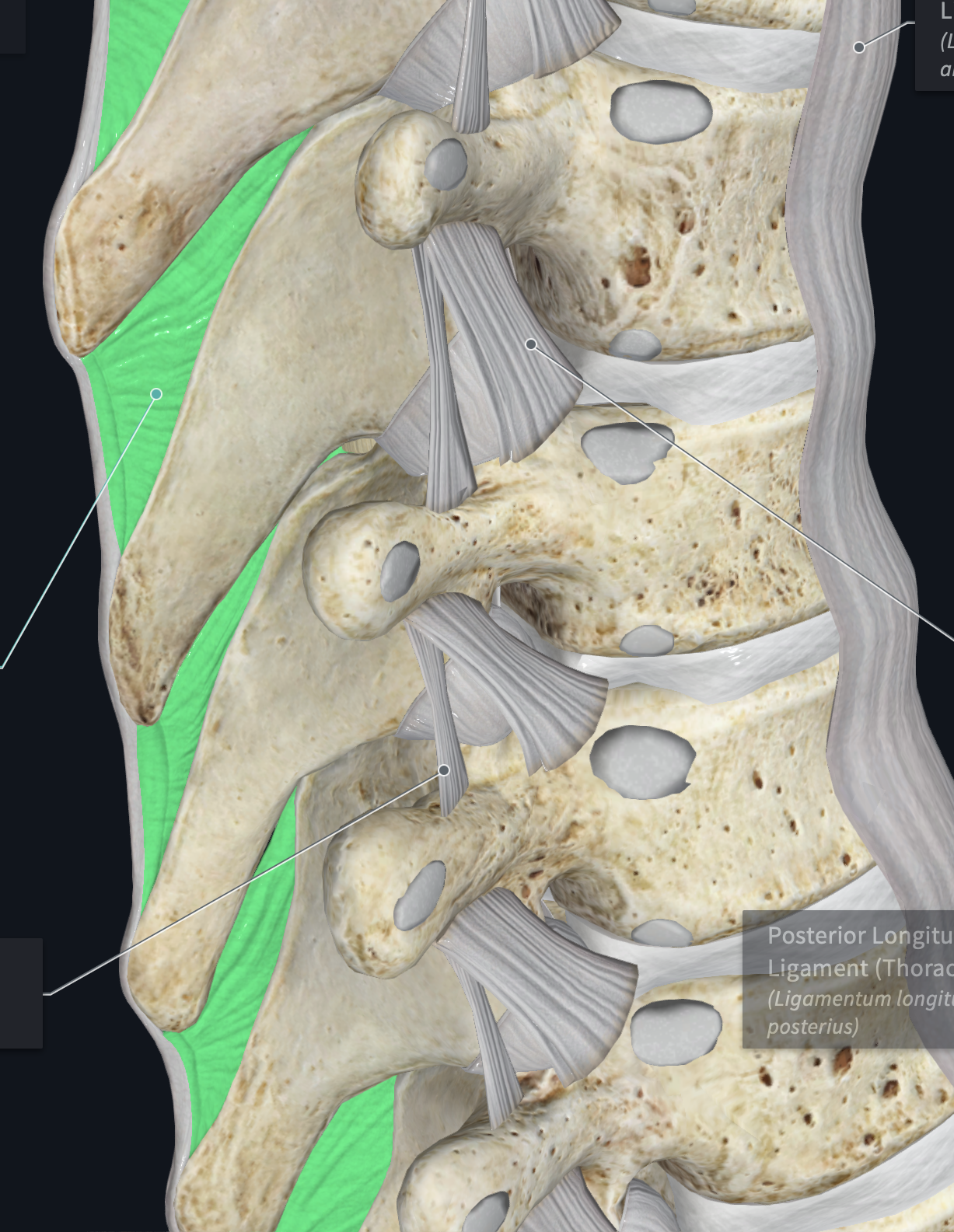
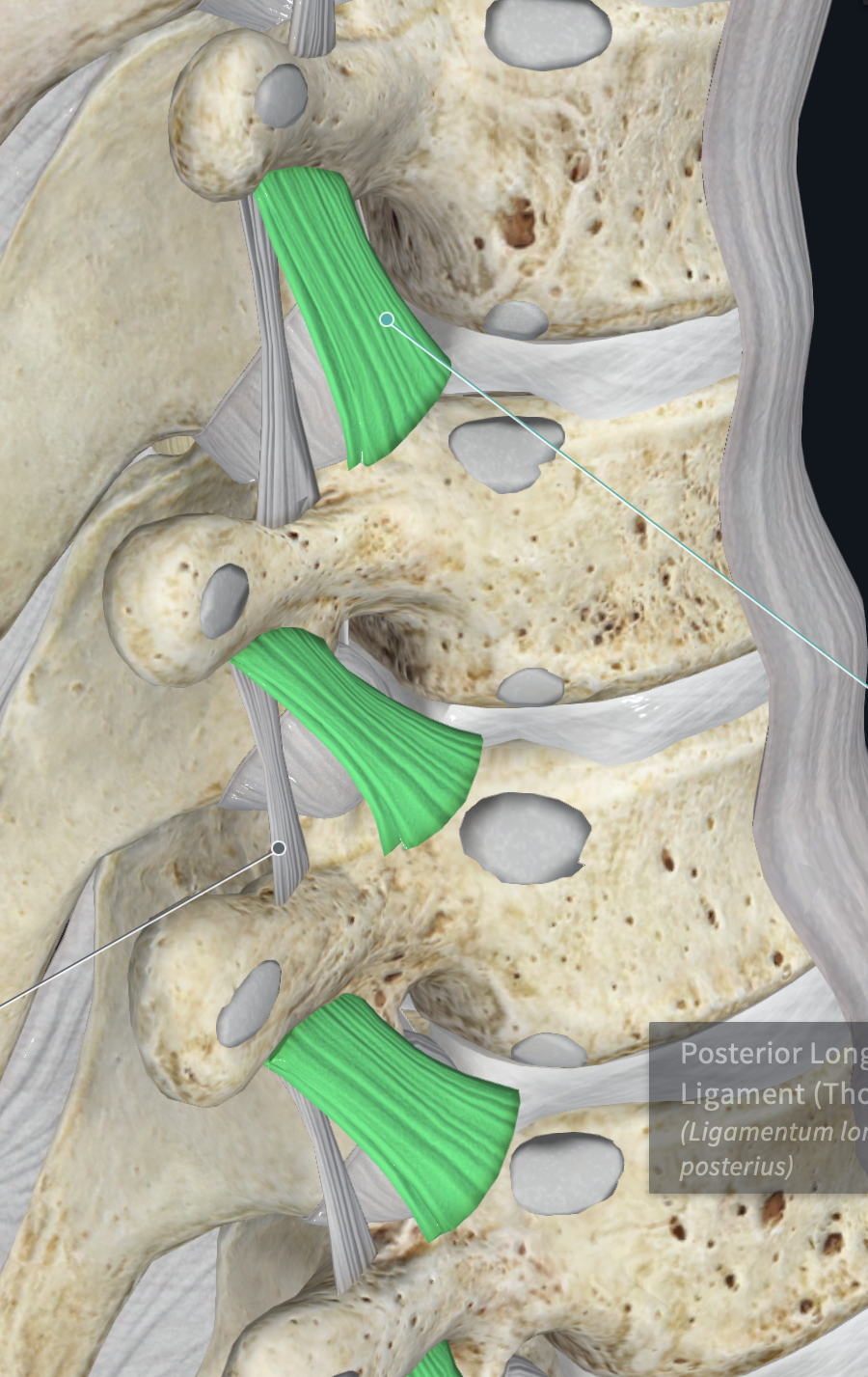
Thoracic zygapophyseal Capsules
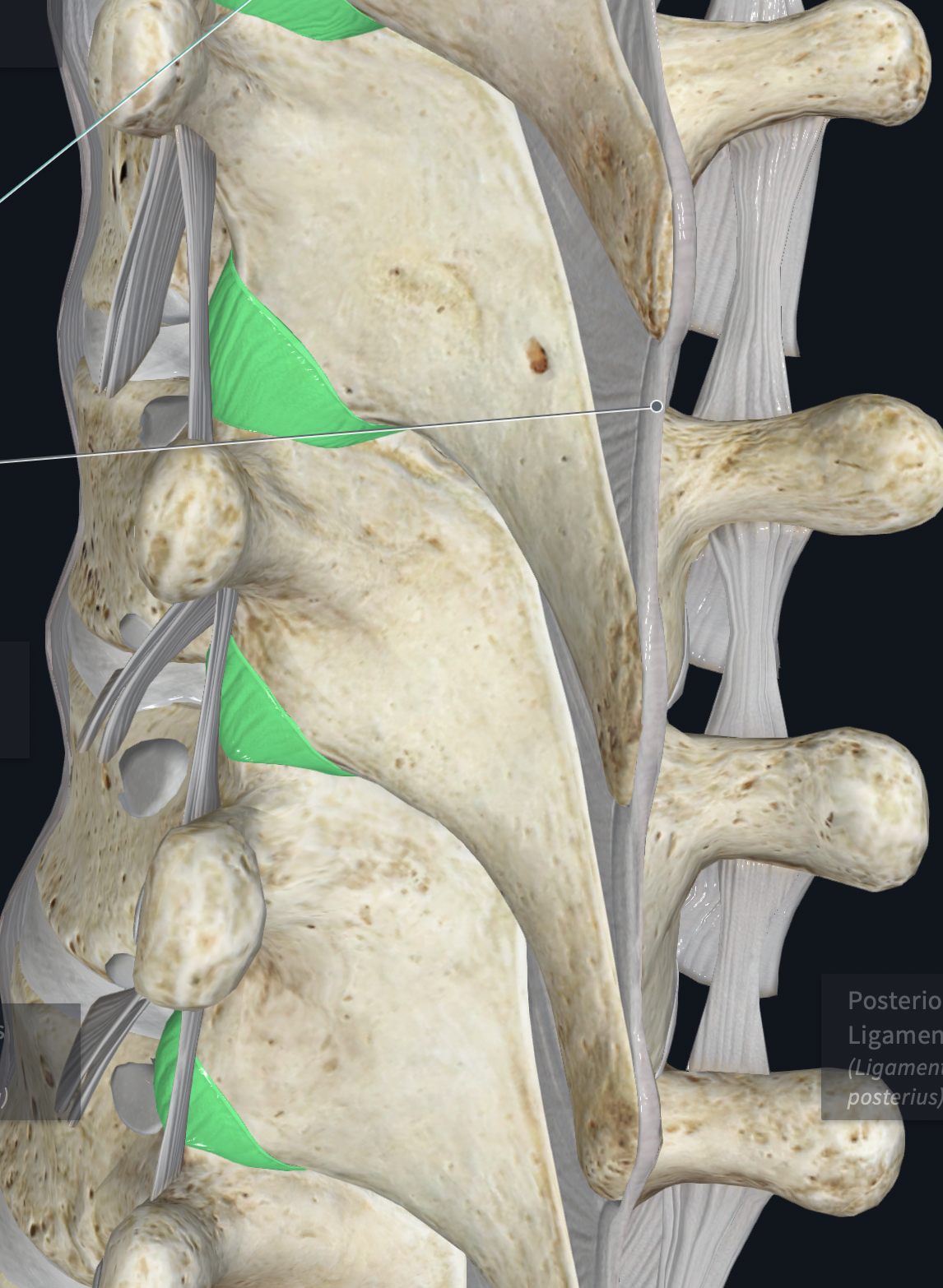
Supraspinous Ligament
Costotransverse Ligaments
Intertransverse Ligaments
Shoulder Joint