ch03 rg astro 1 phases, eclipses,
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
geller
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
If you were standing in Quito, Ecuador (on the Earth’s equator), which of the following points in the sky would pass directly over your head at some time during a 24-hour period?
A) The summer solstice
B) The winter solstice
C) The vernal equinox
D) The north celestial pole
E) More than one of these
C) The vernal equinox
TRUE OR FALSE:
The phases of the moon are caused by the shadow of the Earth on the Moon.
FALSE
What causes the PHASES of the moon?
due to changing illumination from the Sun.
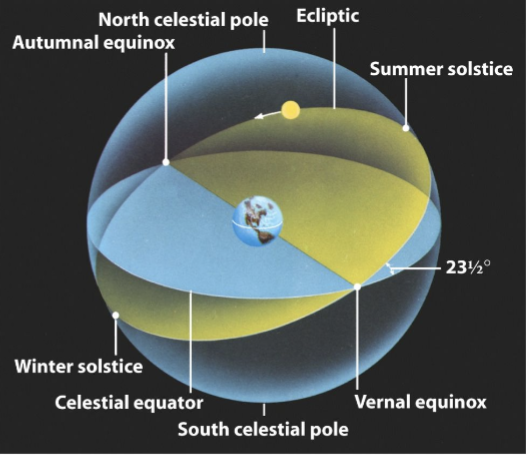
One year on the first day of spring in Santa Barbara, there is a full moon. On this date, where on the celestial sphere is the Moon located?
A) At the summer solstice
B) At the winter solstice
C) At the vernal equinox
D) At the autumnal equinox
E) It is not near any solstice or equinox
D) At the autumnal equinox
New Moon
The phase of the Moon when the dark hemisphere of the Moon faces Earth
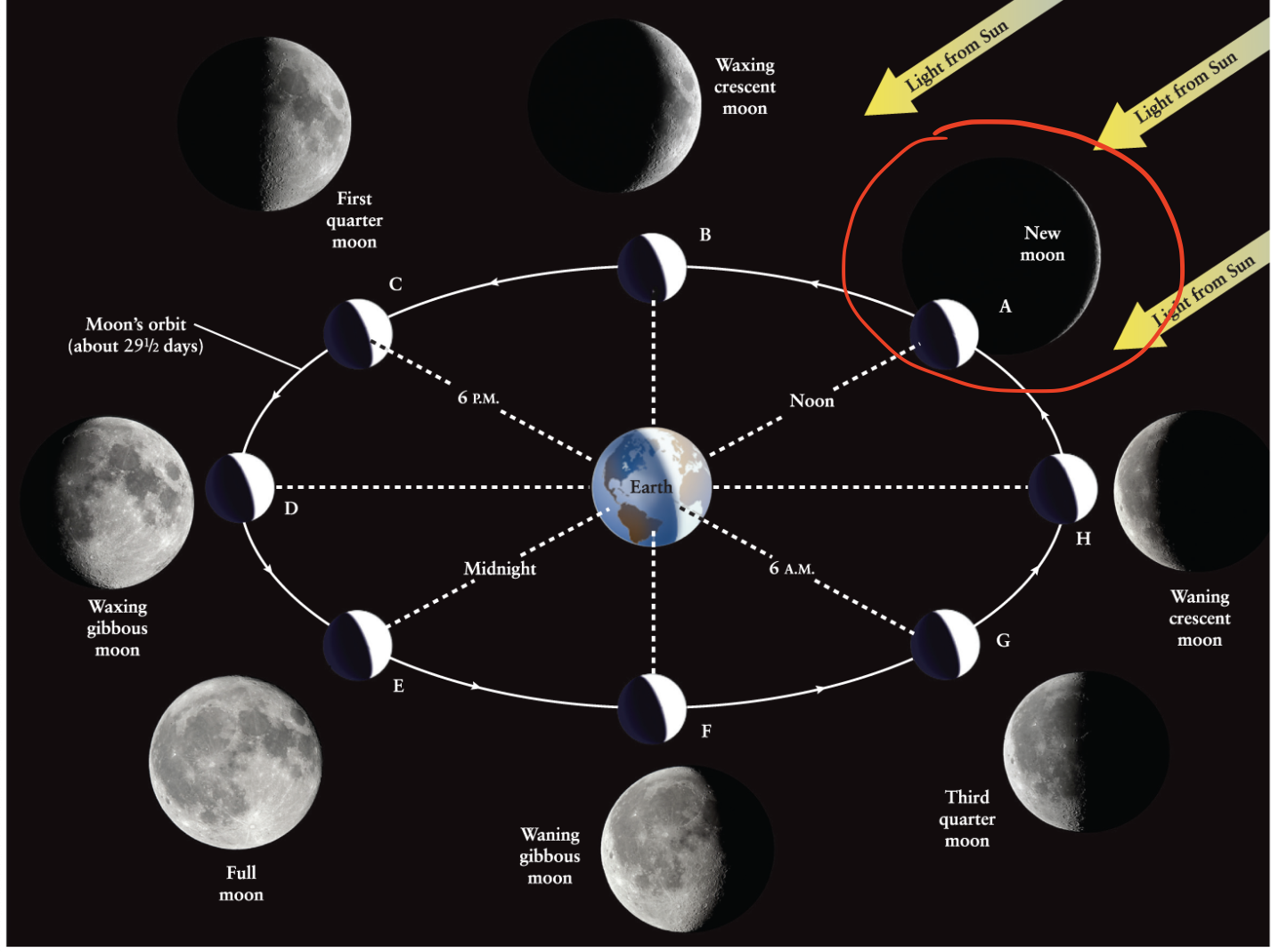
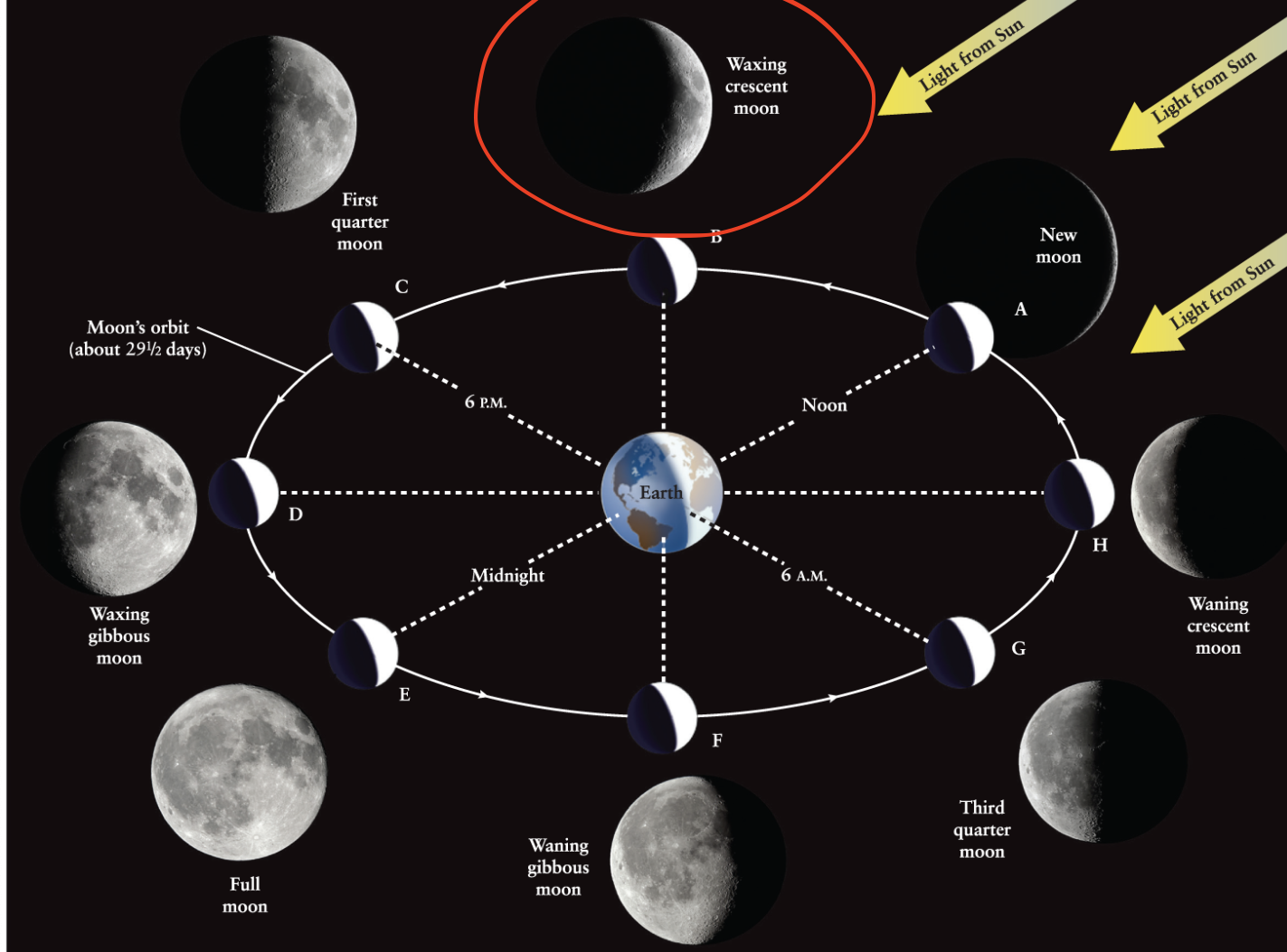
Waxing crescent moon
The phase of the Moon that occurs between new moon and first quarter.
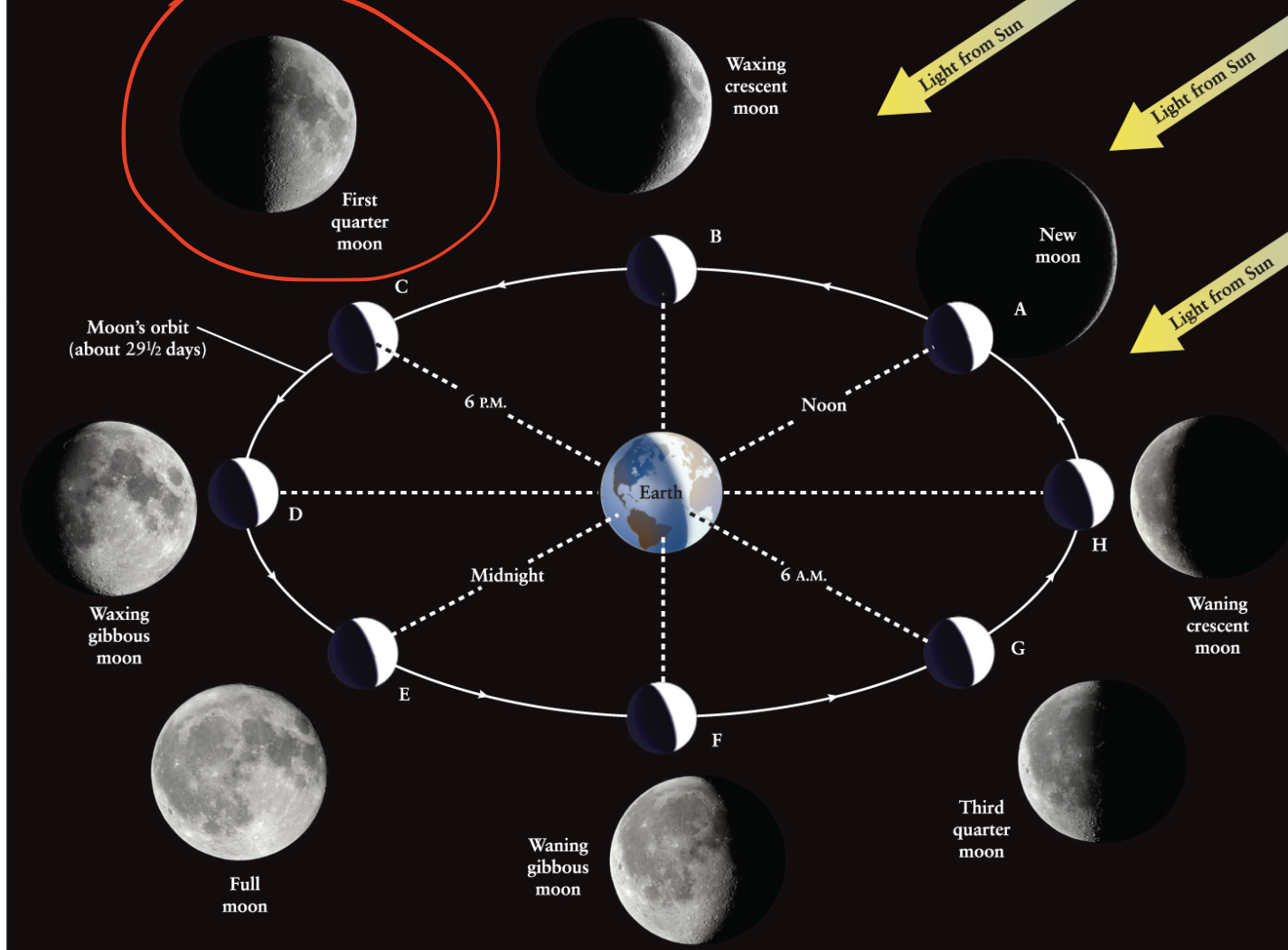
First quarter moon
The phase of the Moon that occurs when the Moon is 90 degrees East of the Sun.
Waxing gibbous moon
The phase of the Moon that occurs between first quarter and full moon
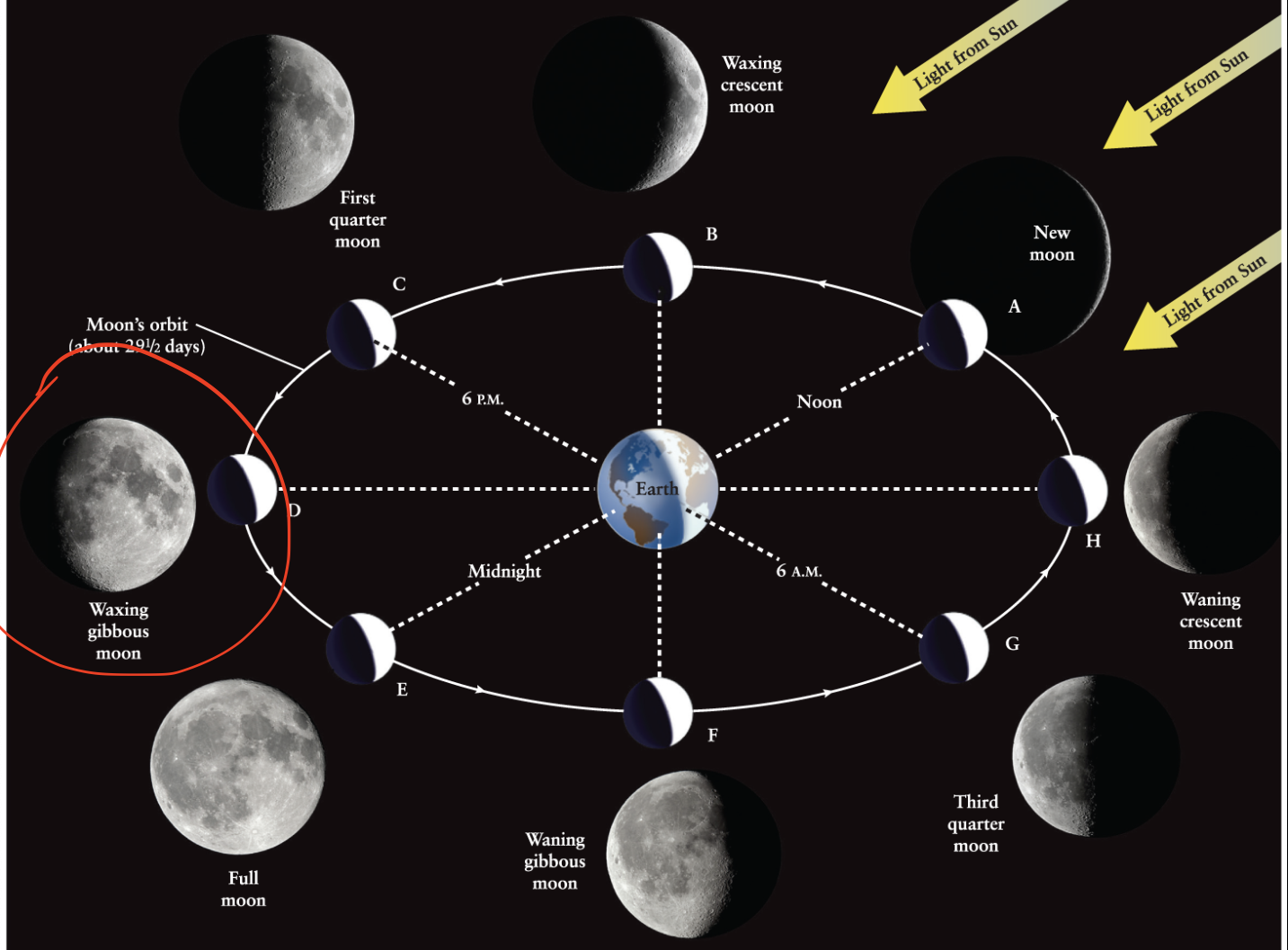
Full moon
A phase of the Moon during which its fully lit hemisphere can be seen from Earth.

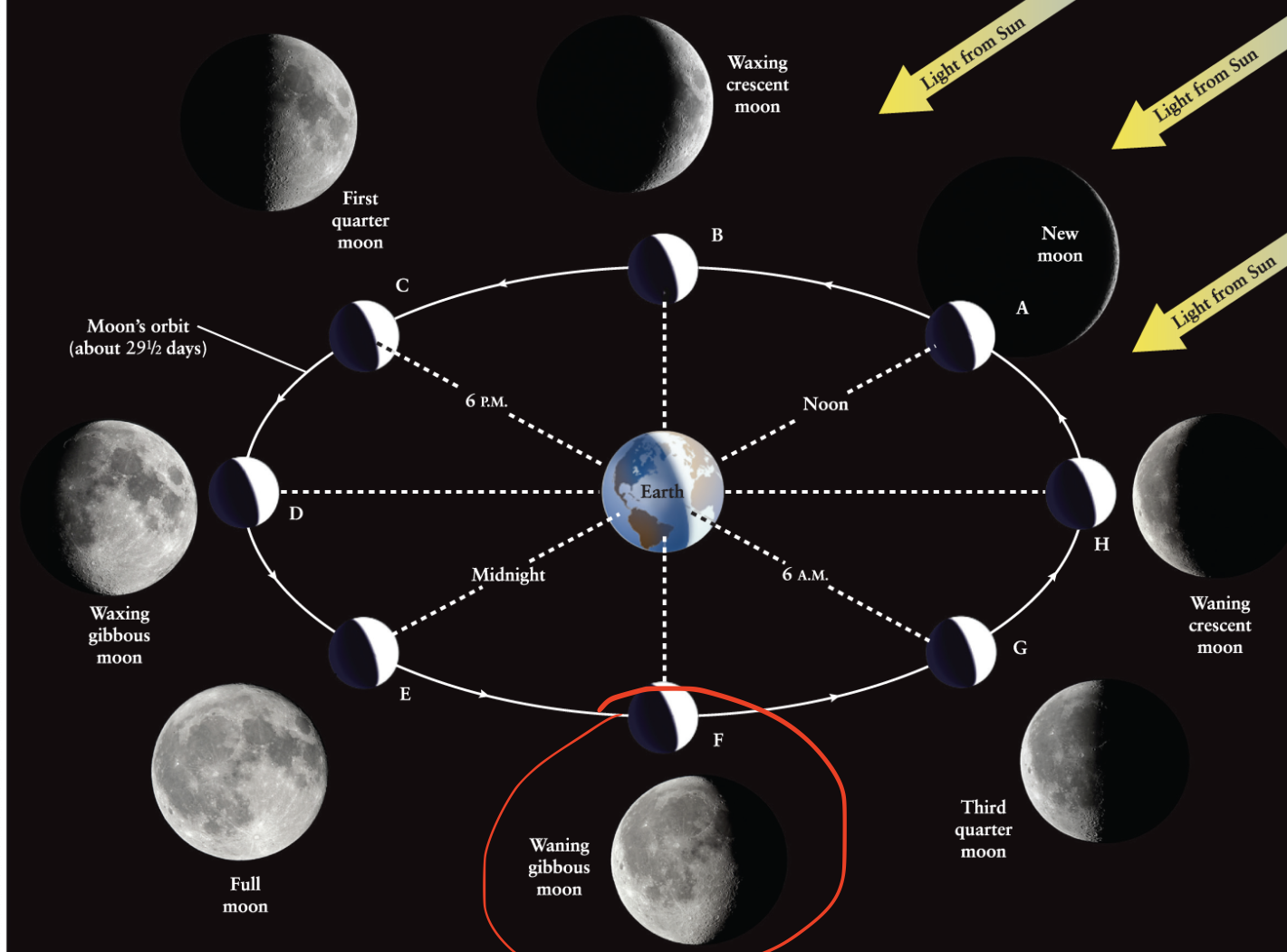
Waning gibbous moon
The phase of the Moon that occurs between full moon and third quarter
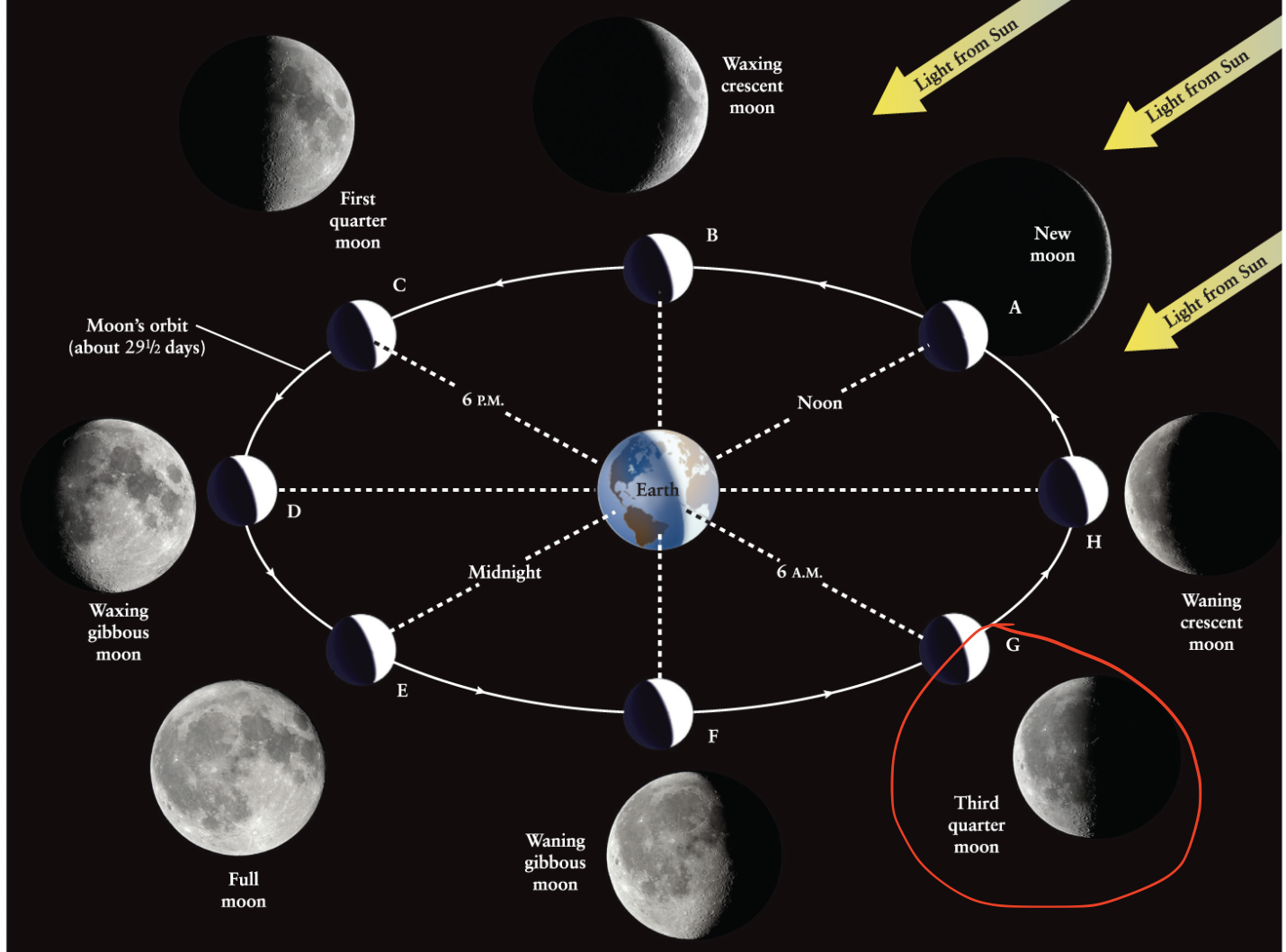
Third quarter moon
The phase of the Moon that occurs when the Moon is 90 degrees West of the Sun.
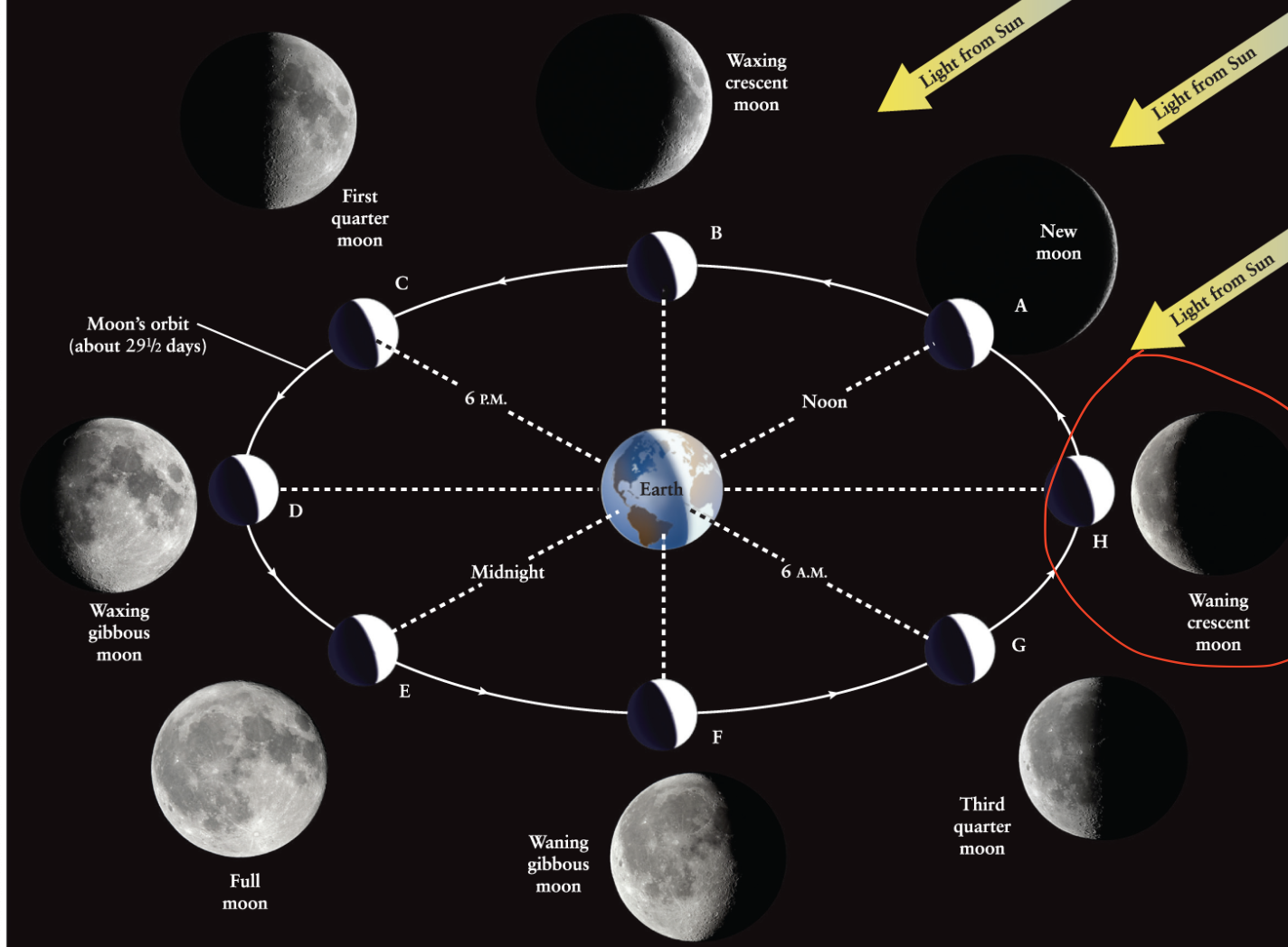
Waning crescent moon
The phase of the Moon that occurs between third quarter and new moon.
How long does it take the Moon to complete one orbit around Earth?
4 weeks
On average, the Moon rises and sets…
About an hour later each night.
Phases are a result of us seeing…
The illuminated half of the Moon at different angles as the Moon moves around its orbit.
Synchronous rotation (example)
It takes exactly as long for the Moon to rotate on its axis as it does to make one orbit around Earth.
Sidereal month VERSUS synodic month
Sidereal month is the time it takes the Moon to complete one full orbit of Earth, as measured with respect to the STARS
Synodic month is the time it takes the Moon to complete one cycle of phases, as measured with respect to the SUN
The synodic month is LONGER than the sidereal month
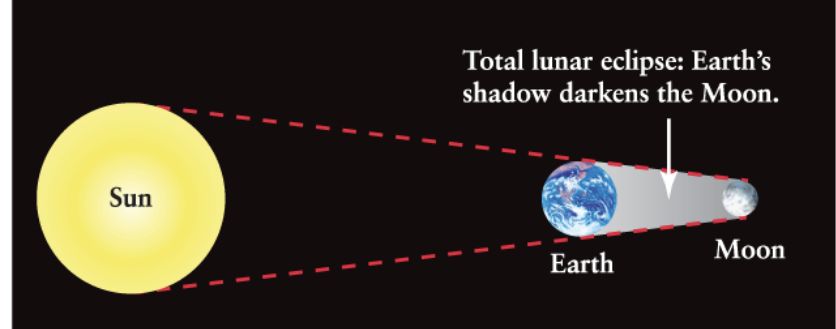
Lunar eclipse
Occurs when the Moon passes through Earth’s shadow
The Earth MUST be between the Sun and the Moon
Occurs only at FULL MOON
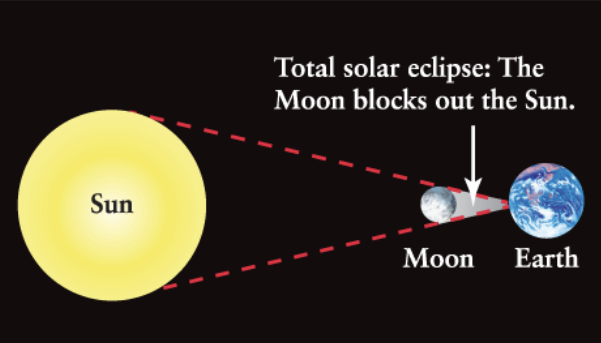
Solar eclipse
Occurs when the Moon casts a shadow on Earth
The Moon MUST be between Earth and the Sun
Occurs only at NEW MOON
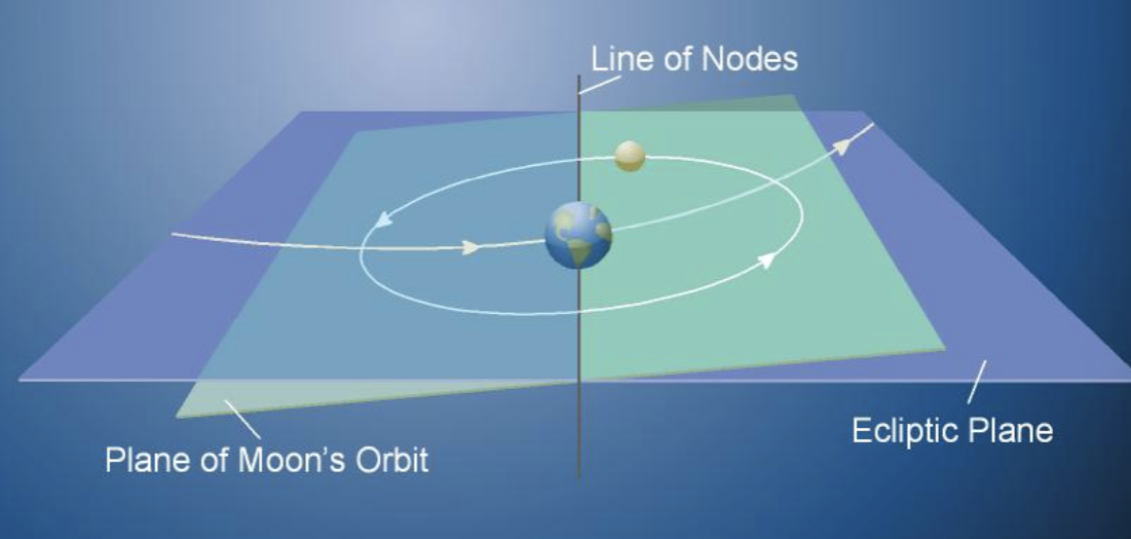
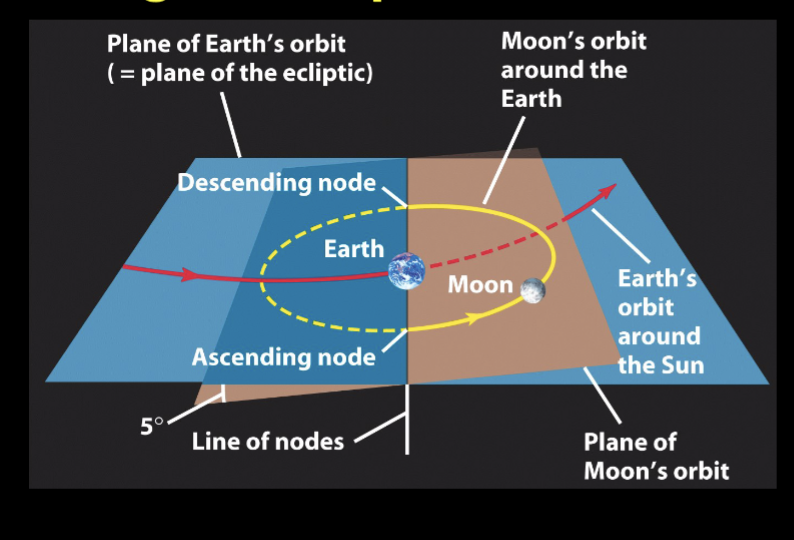
Line of Nodes definition
The plane of moon’s orbit is tilted by about 5 degrees from the ecliptic.
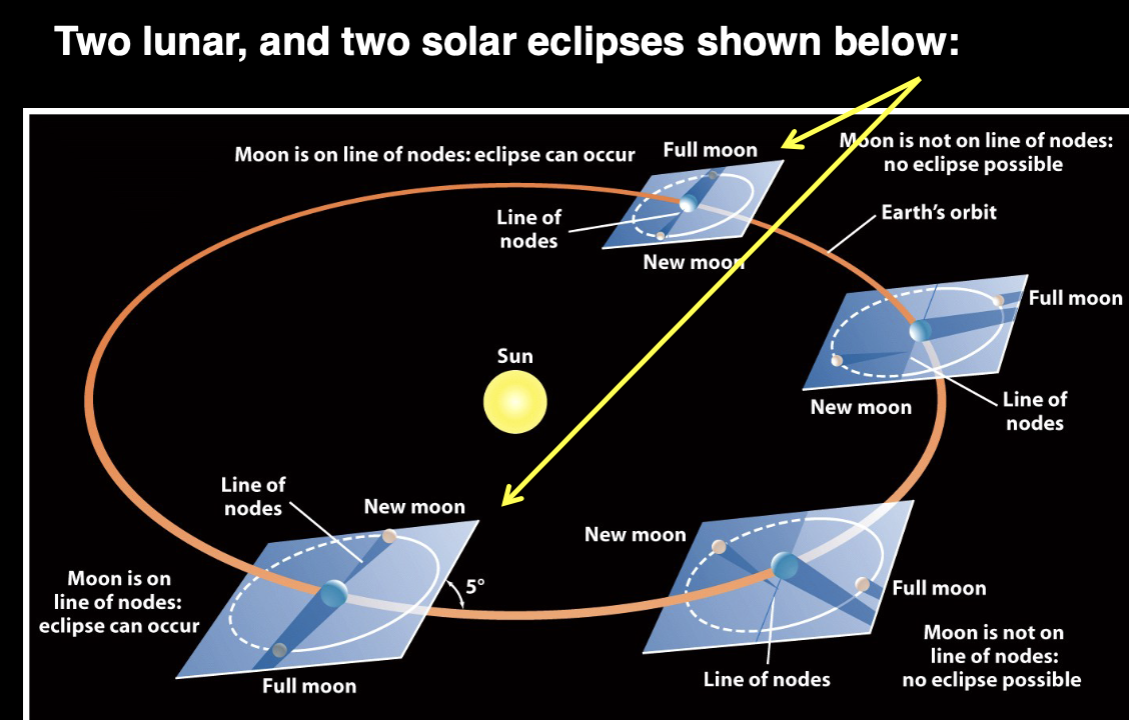
Eclipses can occur ONLY IF…
When the Line of Nodes is pointed at the Sun and all three objects (Sun, Earth, Moon) are in a line.
This also means there has to be a FULL or NEW moon
When does the alignment for Solar or Lunar eclipses occur?
Alignment occurs every 346.6 days
TRUE OR FALSE:
Alignment for eclipses is NOT related to the solstices or the equinoxes
TRUE
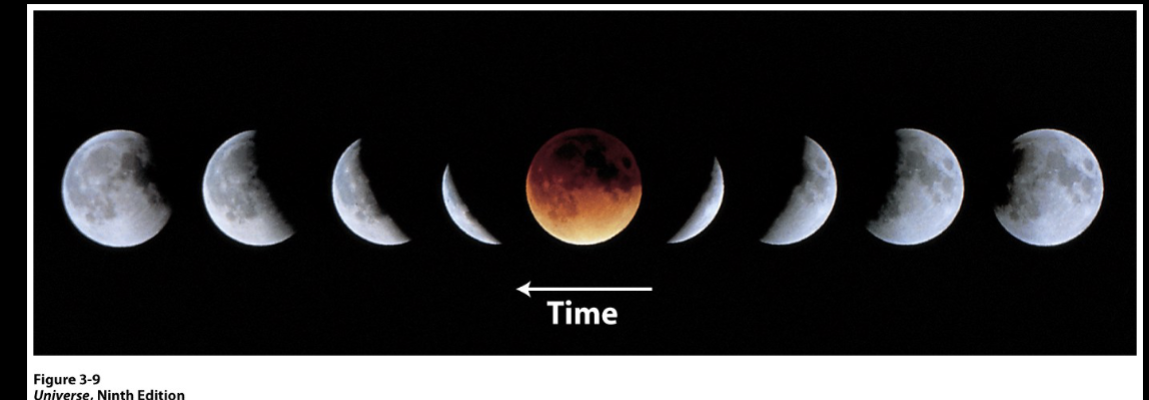
Color of an eclipse
Blue light gets scattered more than red in Earth’s atmosphere
The shadow of a lunar eclipse COMPARED TO the shadow of a solar eclipse
Lunar eclipse— entire Earth can be in shadow
Solar eclipse— only a small, fast moving shadow!
Why isn’t there a lunar eclipse every full moon and a solar eclipse every new moon?
The plane of the Moon’s orbit is NOT along the ecliptic
How many solar eclipses each year?
At least 2—but never more than five
How many lunar eclipses each year?
On average, two or three
Umbra
The central, completely dark portion of a shadow (the DARKER one)
Penumbra
The portion of a shadow in which only part of the light source is covered by an opaque body. (the LIGHTER one)
Total lunar eclipse
The Moon is completely immersed in Earth’s umbra
Partial lunar eclipse
The Moon does not appear completely covered
Penumbral eclipse
The Moon passes only through Earth’s penumbra
Totality
The moment or duration of total blockage of the sun OR the moon during an eclipse
(Can last as long as 1 hour and 42 minutes)
What happens during a total solar eclipse?
The sky begins to darken, the air temperature falls, winds increase, and nature goes quiet.
Solar corona
Hot, faintly glowing gases seen around the Sun during a total solar eclipse; the uppermost regions of the solar atmosphere
When is the only time it is safe to look at the sun during a SOLAR eclipse?
During totality
Eclipse path
The track of the tip of the Moon’s shadow along Earth’s surface during a total or annular solar eclipse
Perigee
The point in Earth’s orbit in a satellite or the Moon is NEAREST Earth.
Apogee
The point in Earth’s orbit where a satellite or the Moon is FARTHEST away.
Annular eclipse
An eclipse of the Sun in which the Moon is too distant to cover the Sun completely; a ring of sunlight is seen around the Moon at mid-eclipse.