HRM L3
1/33
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Human Resource Managers
forefront of the worldwide war for competitive advantage
3 Keys to effectively utilizing Labor Markets to one’s Competitive Advantage
Companies must have a clear idea of their current configuration of human resources (know strengths and weaknesses of their employees)
Organizations must know where they are going in the future and be aware of how their present configuration of human resources relates to the configuration that will be needed
Organizations need programs that will address the discrepancies between the present configuration and the configuration required for the future
Forecasting
the first step in the planning process where the HR manager attempts to determine the supply of and demand for various types of human resources to predict areas within the organization where there will be future labor shortages or surpluses
Overview of the Human Resource Planning Process
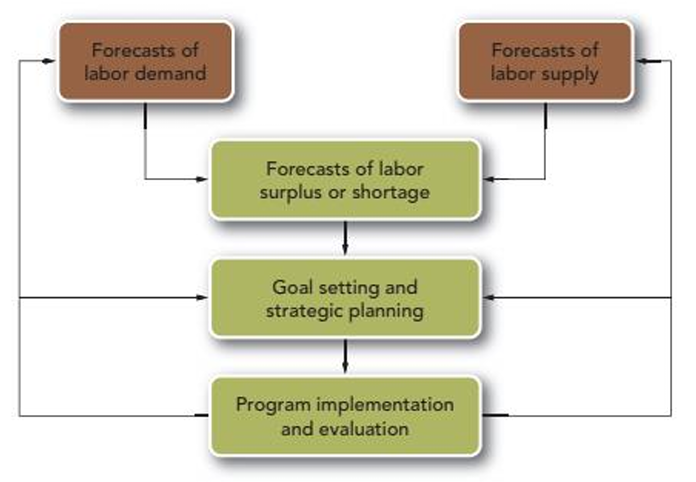
Determining Labor Demand
demand forecasts are developed around specific job or skills relevant to organization’s current & future state
when job or skills are identified, planner needs to seek information to predict whether the need for people with those skills or job will increase or decrease in future
in sophisticated level, organization might have statistical models that predict labor demand, given relatively objective statistics on leading indicators from previous year
Leading Indicator - objective measure that accurately predicts future labor demand
Determining Labor Supply
when company has projected labor demand, it needs to get an indicator of their labor supply
this calls for a detailed analysis of how many people are currently in various job categories or skills within the company
then, this analysis is modified to reflect changes in the near future caused by retirements, promotions, transfers, voluntary turnover, and terminations
labor supply’s projections can be derived either from historical statistical models or judgmental techniques
Transitional Matrices - a statistical procedure and matrix which shows the proportion of employees in different job categories at different times
matrices are useful for charting historical trends in the company’s supply of labor
if conditions remain constant, they can be used to plan for the for future
historical precedents for labor supply may not always be reliable indicators of future trends
Determining Labor Surplus or Shortage
when forecasts are known, the planner can compare the figures to ascertain whether there’ll be labor shortage or surplus for the respective job categories
when this is determined, organization can determine what is going to do about these potential problems
Goal Setting and Strategic Planning
second step in human resource planning
purpose of setting quantitative goals is to focus attention on the problem and provide a benchmark for determining the relative success of any programs aimed at redressing a pending labor shortage or surplus
these goals should come directly from the analysis of labor supply & demand
this should also include a specific timetable (when results should be achieved) and specific figure (what should happen with the job category or skills)
this stage is critical as the many options available to the planner differ widely in their expense, speed, effectiveness, amount of human suffering, and revocability (how easily the change can be undone)
Human Suffering & Revocability
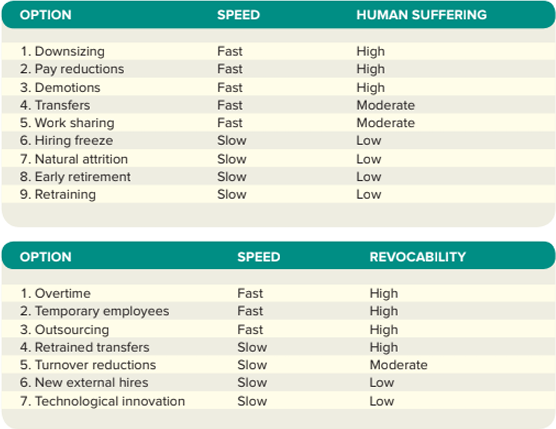
Human Suffering
caused by downsizing
immediate and long-term element
lack of pay, benefits, & meaningful work has negative implications for financial, physical, & psychological aspects of individuals
this cause bankruptcies, illnesses, & depression
Downsizing
typical response of a firm to labor surplus
planned elimination of large numbers of personnel designed to enhance organizational effectiveness
companies do this due to recession, poor performance, or strategic reasons
to avoid indiscriminant across-the-board reductions, they should perform surgical strategic cuts that not only reduce costs but improve their competitive position
Early Retirement Programs and Buyouts
another means to reduce labor surplus
older workforce has advantages in terms of experience & stability
older workers are more costly than younger workers due to their higher seniority, medical costs, and pension contributions
several forces fuel the drawing out of older workers:
improved health of older people, in combination with the decreased physical labor
attractive for many workers as they fear social security will be cut and sponsored pensions may not cover their expenses
age discrimination legislation & outlawing of mandatory retirement ages have created constraints on firm’s ability to unilaterally deal with an aging workforce
employers are concerned about losing the wealth of experience of older workers
Employing Temporary Workers
most widespread means of eliminating a labor shortage
Temporary Employment - offers flexibility needed to operate efficiently in the face of swings in the demand for goods & services
This often preceded in permanent hiring and often a leading indicator of economy expansion
Advantages of Temporary Workers
Frees the firm from many administrative tasks & financial burdens associated with being the employer of record
Small companies that can’t afford their own testing programs often get employees who have been tested by a temporary agency
Reduces training costs and eases the transition for both the temporary worker and company
As temporary worker has little experience in the host firm, the person brings an objective perspective to the organization’s problems & procedures that is sometimes valuable
Disadvantages of Temporary Workers
need to be overcome to effectively use this source of labor
low levels of commitment and customers on the part of temporary employees often spills over, which reduces the level of customer loyalty
Outsourcing
organization‘s use of an outside organization for a broad set of services
logical choice when a firm simply doesn’t have certain expertise & is not willing to invest time and effort into developing it
companies increasingly outsource their HRM tasks to outside vendors who specialize in efficiently performing many of the more routine administrative tasks associated with this function
Offshoring (1)
special case of outsourcing where the jobs that move actually leave one country and go to another
this kind of job migration has always taken place, however, rapid technological changes have made the current trends in this area historically unprecedented
organizations should consider several critical factors when making the decision to offshore some product or service
those who failed to look before they leaped onto the offshoring bandwagon have been disappointed by their results
quality control problems, security violations, and poor customer service experiences wiped out all the cost savings attributed to lower wages and more
Offshoring (2)
if one can’t take the work overseas but still wishes to tap into less-expensive global talent to fill a labor shortage, then one might simply bring foreign workers into the country
Immigration is a vital part of the American economy, and many foreign workers are happy to leave their home and pursue their own American dream
entrance of foreign workers into US to fill jobs is federally regulated, so there are limits to what can be accomplished
employers wishing to hire foreign workers need to help them secure work visas and show that there are no qualified Americans who could do the same work
Altering Pay and Hours
companies facing labor shortage may be reluctant to hire new full-time or part-time
they may have the option of trying to garner more hours out of the existing labor force, which makes the workers enjoy the added compensation
but over extended periods, employees experience stress and frustration from being overworked in this manner
In labor surplus, organizations can sometimes avoid layoffs if they can get their employees to take pay cuts
Program Implementation and Evaluation
programs developed in the strategic-choice stage of the process are put into practice in the program-implementation stage
critical aspect of program implementation is to make sure that one is held accountable for achieving the stated goals and has the necessary authority and resources to accomplish this goal
it’s important to have regular progress reports on the implementation to be sure that all programs are in place by specified times and that the early returns from these programs are in line with projections
final step in the planning process is to evaluate the results.
Human Resource Recruitment
practice or activity carried on by the organization with the primary purpose of identifying and attracting potential employees
role of HR recruitment is to build a supply of potential new hires that the firm can draw on if the need arises
goal of the recruiting is NOT simply to generate large numbers of applicants
if the process generates a sea of unqualified applicants, firm will incur great expense in personnel selection, but few vacancies will actually be filled
this problem of generating too many applicants is often promulgated by the use of wide-reaching technologies like the Internet to reach people.
Personnel Policies
generic term used to refer to organizational decisions that affect the nature of the vacancies for which people are recruited
characteristics of the vacancy are more important than recruiters or recruiting sources when it comes to predicting job choice
Internal VS External Recruiting: Job Security
desirable feature of vacancy is it provides ample opportunity for advancement and promotion
one organizational policy that affects this is the degree to which the company ―promotes from within—that is, recruits for upper-level vacancies internally rather than externally
perceptions of job security and long-term commitment to the organization are also promoted by due process policies
Employment-at-Will Policies
policies which state that either an employer or an employee can terminate the employment relationship at any time, regardless of cause
companies that don’t have this typically have extensive due process policies
Due Process Policies
policies by which a company formally lays out the steps an employee can take to appeal a termination decision
Extrinsic and Intrinsic Rewards
companies take a lead-the-market approach to pay (a policy of paying higher-than-current-market wages) to have a distinct advantage in recruiting
pay can make up for a job‘s less desirable features—for example, paying higher wages to employees who have to work midnight shifts. These kinds of specific shift differentials and other forms of more generic compensating differentials will be discussed in more detail in later chapters that focus on compensation strategies. We merely note here that ―lead‖ policies make any given vacancy more attractive to applicants.