ap psych c10--testing and individual differences
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
split-half reliability
randomly dividing a test into two different sections and then correlating people’s performances on the two halves. the closer the correlation coefficient is to +1, the greater its reliability
test-retest reliability
the correlation between a person’s score on one administration of the test with the same person’s score on a subsequent administration of the test
test validity terms
accuracy of a test. a test cannot be valid if it is not reliable
predictive validity is a measure of future performance based on a test
construct validity: if an independent measure already exists that has been established to identify those who will make fine chefs and love their work, we can correlate prospective chefs’ performance on this measure with their performance on any new measure. the higher the correlation, the more construct validity the new measure has
aptitude tests
measure ability or potential (career quiz)
achievement tests
achievement tests measure what one has learned or accomplish (bio tests)
speed test vs. power tests
speed tests ask many questions in a short period of time (apush mcq)
power tests measure the difficulty of questions you can answer (SAT math section 1 vs. math section 2)
intelligence
a loose term, but we call it the ability to gather and use information in productive ways
fluid intelligence
our ability to pick up new skills, while crystallized intelligence is the ability to use knowledge accumulated over time
spearman’s theory, gardner’s theory, and sternberg’s theory
spearman’s theory: intelligence can be measured by a single ability
gardner’s theory: multiple intelligences in different sectors (mathematical, musical, verbal, etc.)
sternberg’s theory: people can be evidence analytic (being good in school), creative intelligence, and practical intelligence (street-smart)
stanford-binet test
pioneered by alfred binet, who came up with the concept of “mental age” (how old you are mentally) to identify what children were lagging behind their peers so they could close the achievement gap
stanford professor lewis terman officialized the IQ test (intelligence quotient) which divides a person’s mental age by their chronological age and multiplying by 100
adults are all an arbitrary age of 20
wechsler IQ test
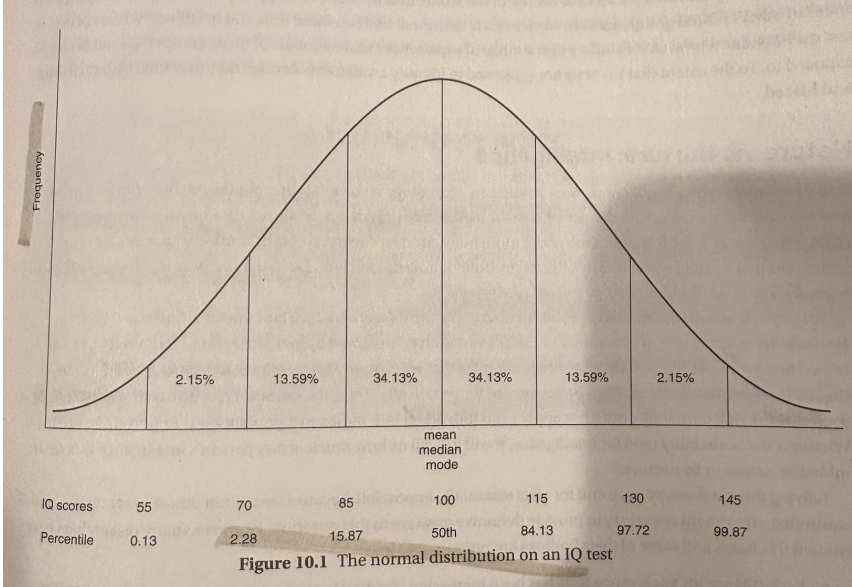
(pic pg. 83) is pretty similar to stanford-binet test but is standardized to create a normal distribution to see where people fall
wechsler tests multiple subcategories for both verbal and math, like vocab, etc. which can also help identify learning disabilities
nature vs. nurture, how it relates to intelligence
looking to see how heritable intelligence is has created some findings, and scientists suggest both genetic and environmental factors play a role
flyn effect: performance on intelligence tests has been increasing through the century
ok ok findings
identical twins score more similarly on intelligence tests than fraternal twins do
racial differences in IQ scores are because of environment
heritability
a measure of how much a trait’s variation is explained by genetic factors, and can range from 0 to 1, where 0 indicates it is fully the environment and 1 indicates it is fully genes