D and F block
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is the Deacon’s process for chlorine preparation, and what catalyst is used?
The Deacon's process is a chemical reaction that converts hydrochloric acid and oxygen into chlorine gas using copper(II) chloride as a catalyst. This process is typically carried out at temperatures between 400 and 450 degrees Celsius.
Which lanthanoid is naturally radioactive?
Promethium (Pm) is the only naturally radioactive lanthanoid. It has no stable isotopes and is typically found in trace amounts in uranium ores.
In which medium does KMnO₄ exhibit the strongest oxidizing power?
KMnO₄ has the strongest oxidizing power in acidic medium, not neutral.
What happens when potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) reacts with hydrogen peroxide in an acidic medium?
Blue Chromium Pentoxide (CrO5)(CrO_5)(CrO5) is formed.
Why are KMnO₄ (Potassium Permanganate) and K₂Cr₂O₇ (Potassium Dichromate) colored?
Their colors arise due to charge transfer transitions.
(Due to Ligand-to-Metal Charge Transfer (LMCT).)
What is the most stable oxidation state of titanium (Ti), and why?
+4 is the most stable oxidation state of Titanium (Ti).It is due to the stability of the electronic configuration with fully filled d-orbitals, making it less reactive.
Which transition metal among Fe, Cu, Zn, and V can show the highest oxidation state?
Vanadium (V) with the electron configuration (Ar)3d³4s² has the highest oxidation state of +5.
What is the electronic configuration of the d-block element that shows the highest oxidation state?
The d-block element with the highest oxidation state is Osmium (Os) and Ruthenium (Ru) in +8 oxidation state (seen in OsO₄ and RuO₄).
The electronic configuration of Osmium (Os) is [Xe] 4f^{14} 5d^{6} 6s^{2} and for Ruthenium (Ru) is [Kr] 4d^{7} 5s^{1}. Both can exhibit the highest oxidation state of +8.
Among La³⁺, Lu³⁺, Gd³⁺, and Ce³⁺, which has the maximum tendency to form complexes and why?
Ce³⁺ (Cerium) has the maximum tendency to form complexes. This is because it has a larger ionic radius and lower charge density compared to other lanthanides, facilitating coordination with ligands.
Which lanthanoids exhibit a +4 oxidation state?
Ce, Pr, Tb, and Dy can show a +4 oxidation state.
What happens when CuSO₄ reacts with excess KCN?
It forms K₃[Cu(CN)₄] (Potassium tetracyanocuprate(I)) and K₂SO₄. This reaction occurs through complexation, where copper(II) ions are reduced and coordinate with cyanide ions to form a stable complex.
What happens when pyrolusite (MnO₂) is fused with KOH in the presence of air?
It forms potassium permanganate (K₂MnO₄).
Among CrO, VO, TiO, and FeO, which is the most basic and which is the least basic?
Most Basic: FeO
Least Basic: TiO
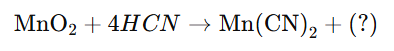
In the reaction:
what is true about the missing substance?
It is a pseudohalogen (CN)2
When excess KI is added to aqueous CuSO₄, the solution acquires a dark brown coloration. This is due to the formation of:
I₃⁻ (aq)