Protein Structure pt 1
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
linear sequence of a.a. is referred to as a protein’s - structure
primary
>40 a.a are -
<40 a.a. are -
proteins
peptides
40 a.a. is the minimum length that a polypeptide can fold into a protein with a - or -
2D, 3D structure
polypeptides rarely exceed - a.a.
1000
- reaction between a.a. reflects what is happening in vitro
in vivo, a ribozyme is required
condensation
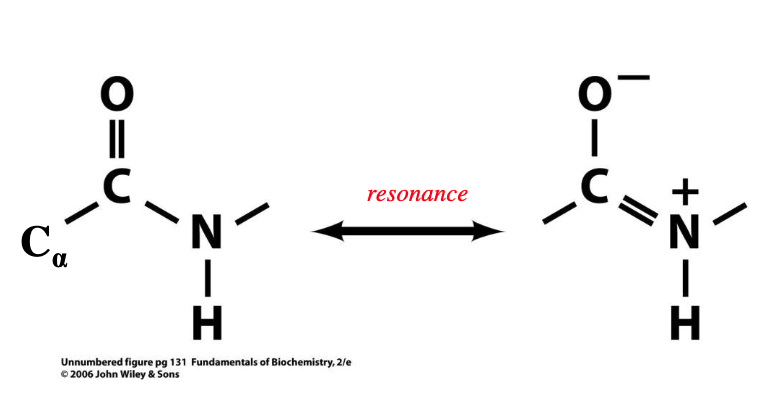
resonance between the carbonyl double bond and peptide bond gives the peptide bond -
this resonance makes peptide bond - and C-N atoms are not able to - freely
~40% double bond character
rigid, rotate
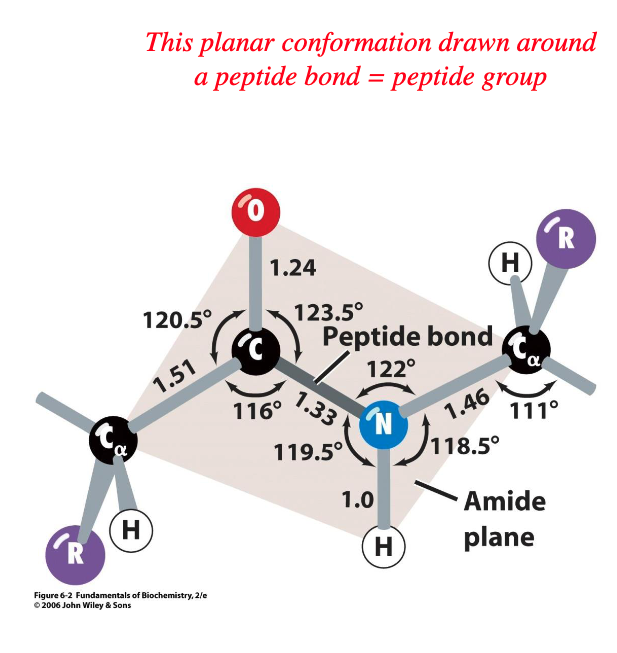
in majority of proteins, peptide groups are in - configuration
trans
rotations occur about the Φ and the Ψ
phi and psi
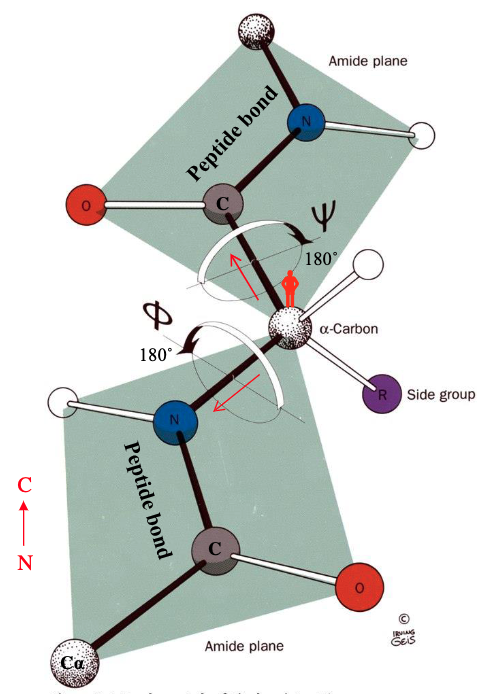
Φ bond refers to the - bond
Ψ bond refers to the - bond
C represents a - around which peptide groups rotate
C-N
C-CO
pivot
Φ and Ψ angles that place atoms of adjacent or nearby peptide groups too close to each other aren’t permitted, this is called - and it defined by the - radii of neighbouring atoms
large R groups will impose even greater - on permissible bond rotations
steric hindrance, VDW
restrictions
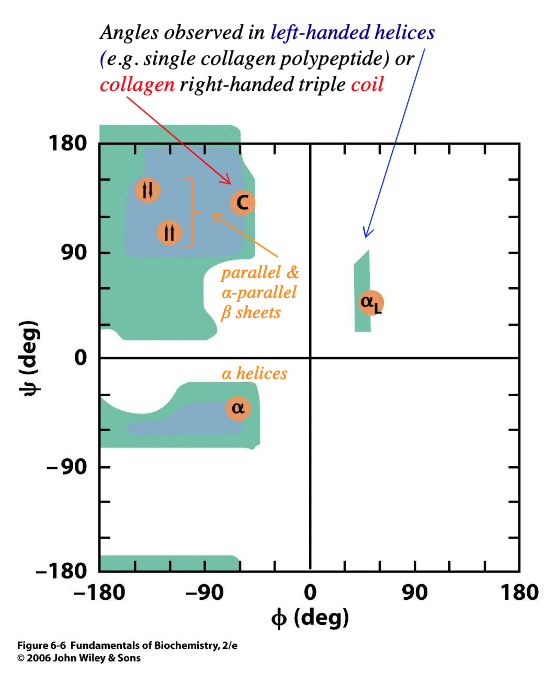
permissible phi and psi bond rotations for each amino acid can be calculated and represented in a - plot
blue areas show typical limits for all amino acids except - and -
Ramachandran
glycine, proline
glycine is much less constrained because the R group is a -
rotations about the phi and psi bond are much less likely to - with carbonyl O or amino H
small H
collide
proline is much more constrained because its cyclic side chain is - back to its amino acid group in the pp chain
repeating proline residues form the -
covalently bonded
left-handed helix
secondary structure of proteins refers to the local spatial arrangement of the - without contribution from, but still constrained by, the -
polypeptide backbone, side chains
tertiary structure of proteins refers to the unique - of the entire polypeptide, mainly due to the arrangement of its -
3D structure
side chains
quaternary structure of proteins refers to proteins composed of - that have a specific - of subunits
2 or more polypeptide chains
spatial arrangement
H bonds between - and - groups in the polypeptide backbone and between - a.a. residues
amino, carbonyl, polar
ionic bonds between charged groups in - and - a.a. residues
acidic, basic
disulfide bonds between - groups in cysteine a.a. residues
thiol/sulfhydryl
VDW bonds between - groups in - a.a. residues
hydrophobic, nonpolar
the only helical structure that allows both intra-helical H-bonding and permissible Ramachandran phi and psi angles is the - helix
carbonyl O of residue ‘n’ is H-bonded to amino ‘H’ of the ‘-’ distal residue
creates a regular right-handed rotation around helical axis with - a.a. residues per turn
R groups are pointed -, avoiding interference
right-handed alpha
n+4
3.6
outwards
adjacent beta strands of the same polypeptide chain from a kinky linear alignment, which allows optimal H-bonds to form with permissible - and - bond rotations
H-bonding occurs between - strands, creating beta sheets of 2-22 strands with a highly - structure
phi, psi
adjacent, rigid
optimal H bonds between beta strands are -
polypeptide backbone forms - to accommodate optimal H-bonding between strands and results in beta sheets with a pleated edge
R groups in the same beta strand - project to - sides of the sheet
R groups on adjacent beta strands project in the - direction
straight
kinks
alternately, opposite
same
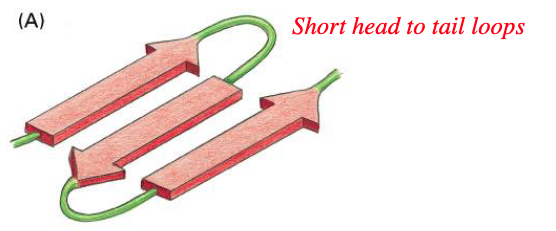
what type of beta strand is this
anti-parallel
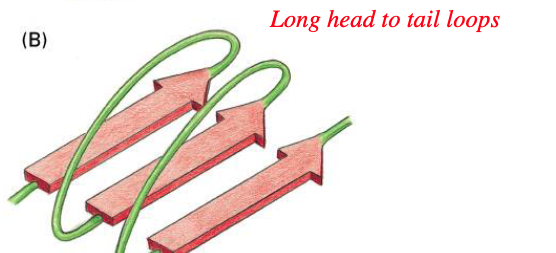
what type of beta strand is this
parallel
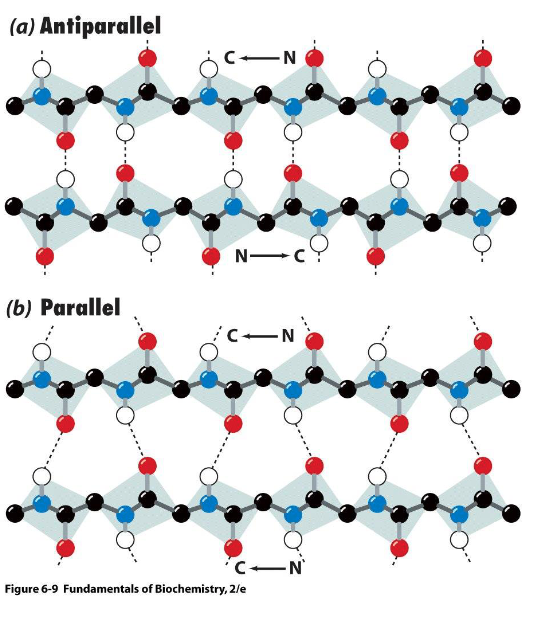
in anti-parallel beta sheets, adjacent beta strands line up so that H bonds are - and -
in parallel beta sheets, beta strands are not lined up perfectly, so H bonds are not -, which likely explains the - (less/more) stable structure compared to anti-parallel beta sheets
short, stable
straight, less
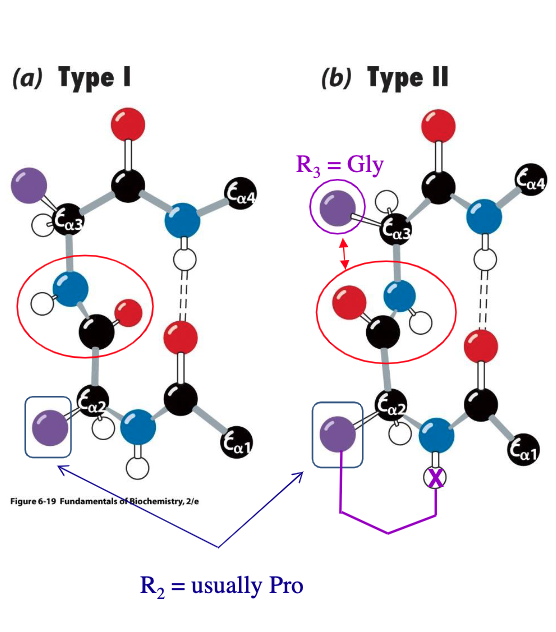
reverse turns or beta bends involve - (how many?) successive a.a. residues in a type I or II arrangement
residue 2 is often -
residue 3 is often - in type II to deal with steric hindrance
4
proline
glycine
fibrous proteins are - and are usually higher order - structures formed from regular repeating - structures
globular proteins are functional and are usually unique - structures formed by combinations of common - structures plus - structures
structural, quaternary, secondary
tertiary/quaternary, secondary, irregular or unique
collagen is most - vertebrate protein
involved in --bearing components of - tissues, such as bone, teeth, cartilage, tendon and the matrices of skin and blood vessels
abundant
stress, connective
collagen fibre contains 3-polypeptide chains, derived from many different genes
typical collagen chain has ~1000 residues in repeating triplets of -, X is often - and Y is often -
proline residues cannot participate in a classic -, so instead, individual collagen chains form a very - with 3 residues/turn
- (how many) left-handed helices wind around each other, forming a - to form a -, collagen fiber
every third residue of an individual left-handed helix passes through the - of the triple helix, which is why glycine is - in the collagen sequence, only glycine can fit
- between all three chains holds triple helix together
Gly-X-Y, proline, Hyp
right-handed alpha-helical structure, tight left-handed helix
3, right-handed rope-like twist, triple helix
centre, invariant
H bonds
beta bulges are strands of beta sheet containing an - that is not - to its neighbouring strand
extra residue, H bonded
helix caps are ends of alpha helical strands often contain - or -, whose R groups can bend back to - with 1 of 4 terminal residues
Asn, Gln, H bond
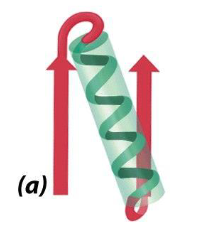
what is this
beta-alpha-beta motif
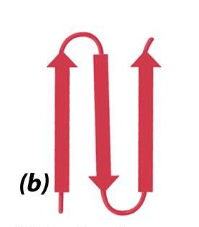
what is this
beta hairpin
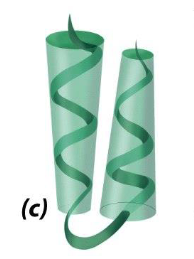
what is this
alpha alpha motif
two successive antiparallel alpha helices packed against each other
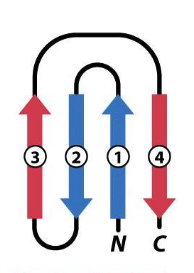
what is this
greek key, a beta hairpin is folded over to form a 4 stranded antiparallel beta sheet