Physics Mirrors and Reflection
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
light
A form of energy that travels away from the source
Reflection
The bouncing back of a wave when it hits a surface through which it cannot pass.
Luminous object
Something that emits light.
Non-luminous object
An object that does not give out it's own light.
Real image
a copy of an object formed at the point where light rays actually meet
Virtual image
An image formed by the apparent intersection of rays
Lateral inversion
The apparent reversal of an image.
Diffuse reflection
When light hits off an object and scatters.
Regular reflection
When something is reflected off a silvered flat surface.
2 types of spherical mirrors
concave(caves in) and convex(bulges out)
Formula for a concave mirror / convex lens
Real: 1/f = 1/u + 1/v, Virtual: 1/f = 1/u - 1/v
Formula for a convex mirror / concave lens
1/u - 1/v = -1/f (f=focal point
Formula for magnification
Magnification = image size / real size M = v/u
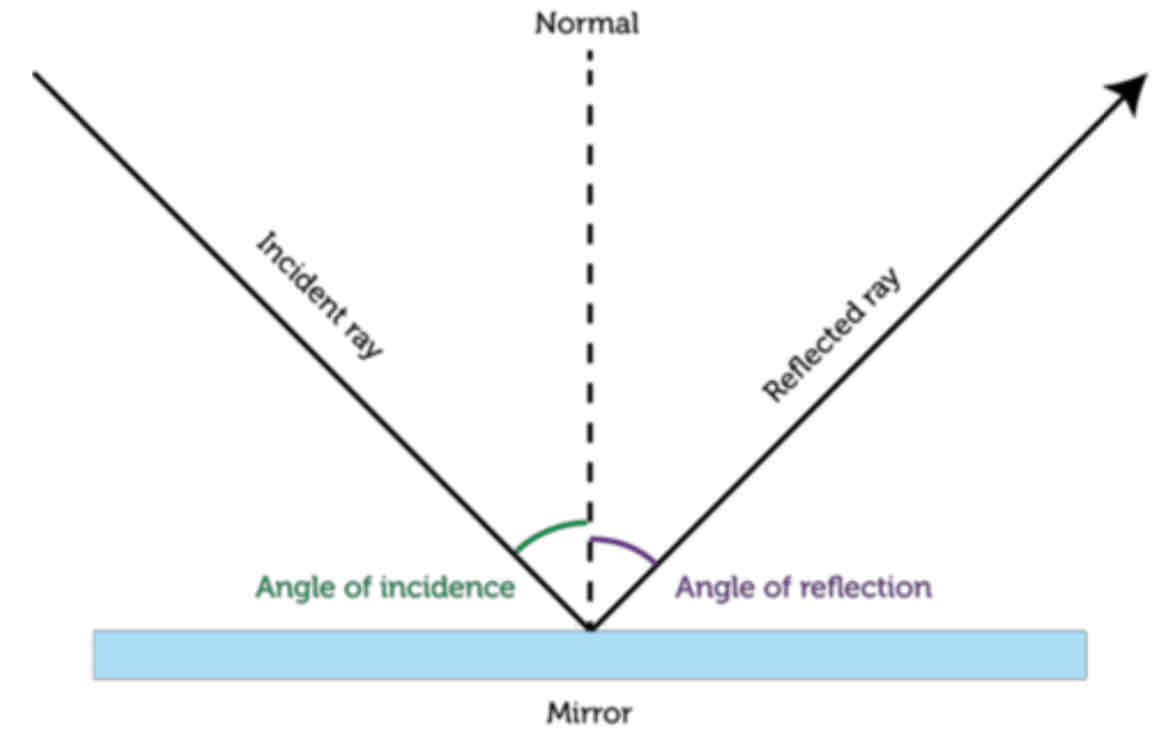
Laws of reflection
The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
The incident ray, the normal and the ray of reflection all lie on the same plane
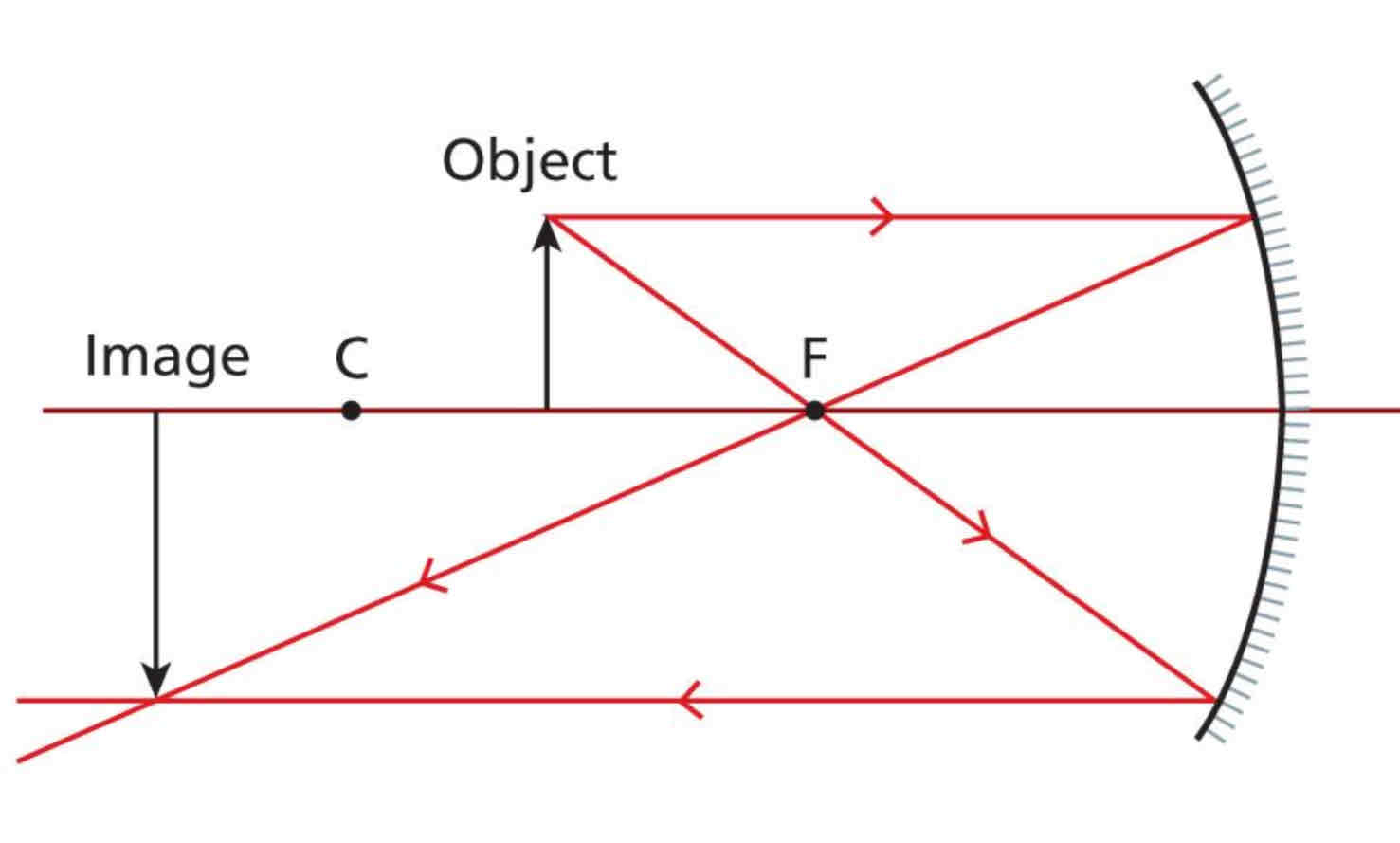
Object placed outside the focus of a concave mirror
Image is real and inverted and magnified
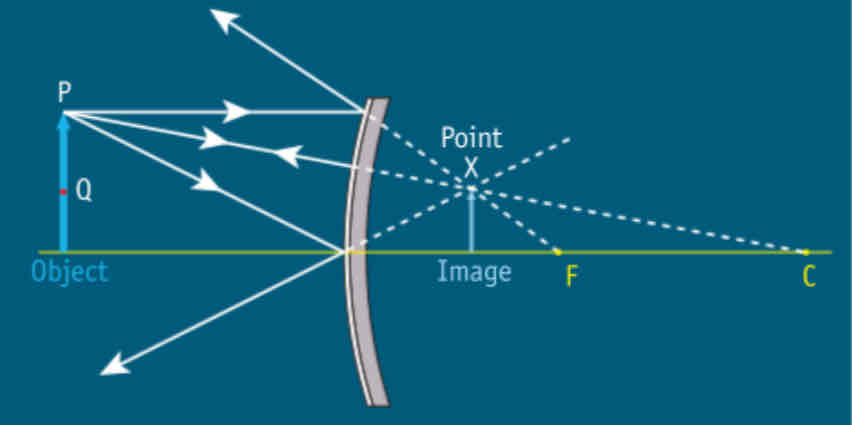
Object placed inside the focus in a concave mirror (draw diagram)
Image is virtual and upright
Special Shoes: Object placed at focus in a concave mirror (draw diagram)
Image is at infinity
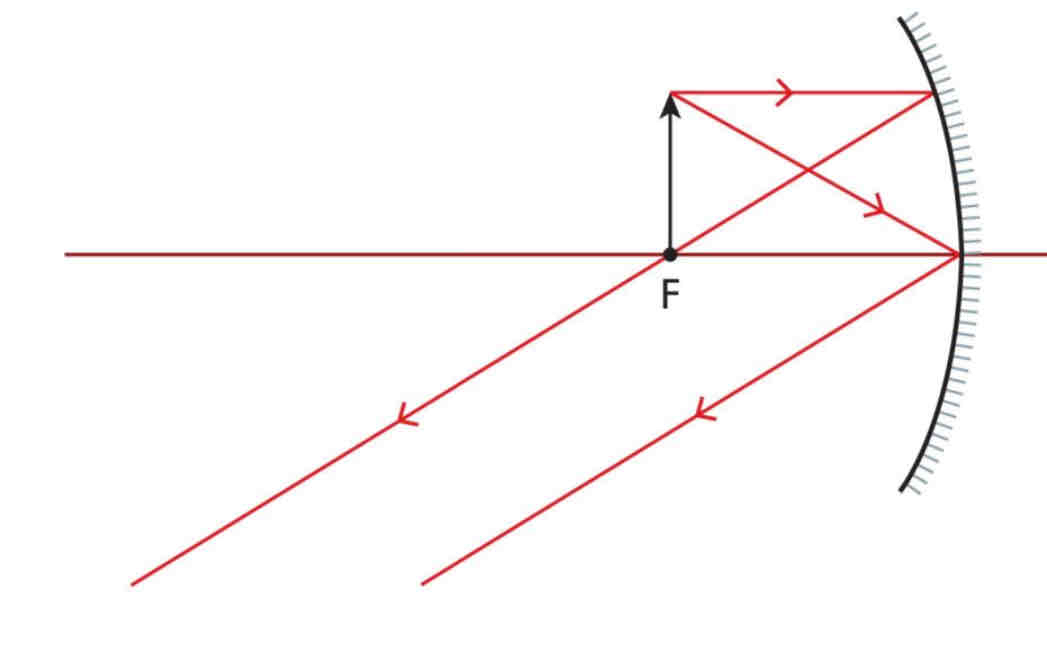
Diagram of an object in a plane mirror (relationship between Angle of incidence and reflection)
Angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
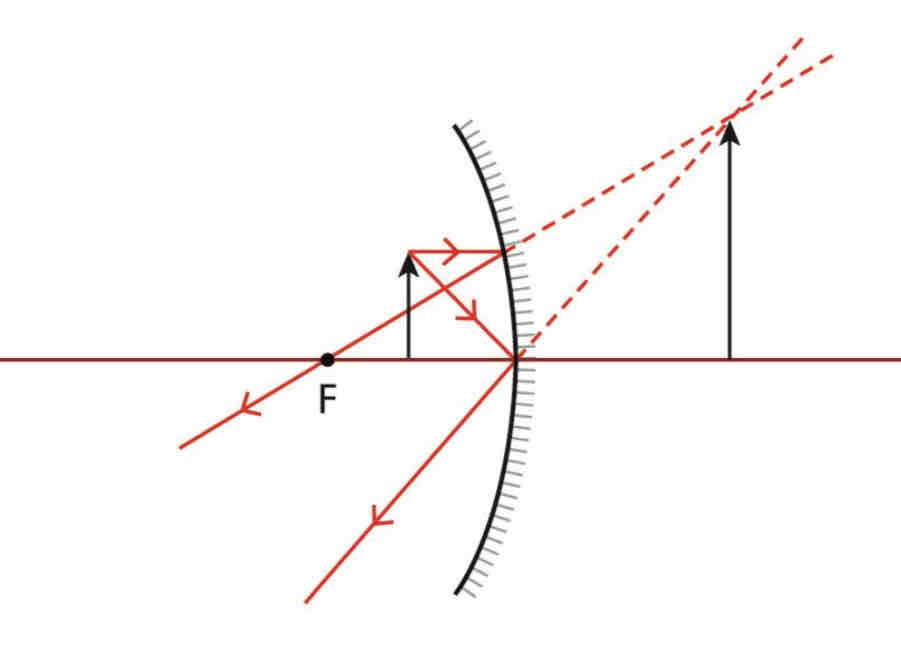
Rules of a convex mirror
from top of an object to mirror parallel to principle axis; back up as if coming from the focus on the other side.
From top of object hitting the mirror on the principle axis and back out at same angle on the other side.
Diagram of convex mirror.
No matter where the object is placed the rays appear to intersect behind the mirror - Virtual image.
How tall should a mirror be to see the full image of a person?
Half of the height of the person (Because the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of refraction)
Centre of Curvature
Centre/radius of the sphere from which the mirror is made of (Double the focal point)
Pole
The centre of a spherical mirror
Principal axis
A line running through the pole of a mirror or the optic centre of a lens
Focus/Focal point of a mirror
Halfway between the pole and the centre of curvature
Focal length of a mirror
The distance from the pole to the focus of a mirror