FW370 Exam Study Set
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This is the study set for CSU's FW370 from Spring 2025 taught by Dr. Lise Aubry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Manipulative experiment
direct alteration of the predictor variables in a lab or field setting, can answer causative questions
Natural experiment
measurements or observations of biological systems in the absence of manipulations by the investigator, often answer descriptive questions
two-tailed t-test
What kind of model do you use to show the investigator if there is a difference between two population means, but not the direction of the difference?
One-tailed t-test
a statistical test that compares whether the mean of one population is more, or less, than that of the other population it is being compared to
inductive reasoning
This type of reasoning moves from Specific to general is its line of thought and draws conclusions from large bodies of observations BUT does not test hypotheses
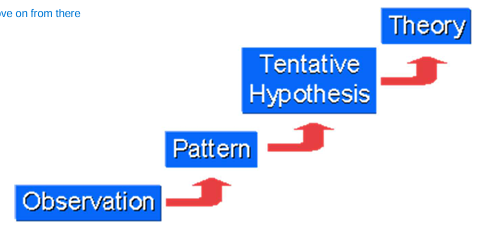
deductive reasoning
This is the type of reasoning where you start with a general idea and work down to the more specific (less commonly utilized today)
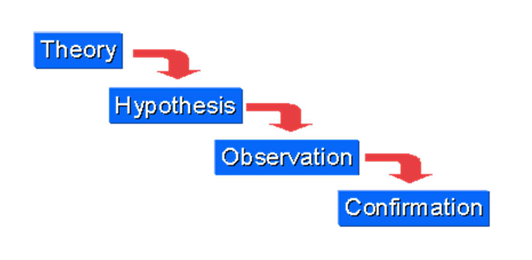
Hypotherico-deductive
This type of reasoning gains support for a hypothesis by testing the predictions and by utilizing falsification and repeatability
Plausibility Generality Specificity Testability Feasibility
What are the five features of a good hypothesis
hypothesis predictions testing Strong support theory
What are the steps of the scientific methods simply put
methodical repeatable verifiable
What are the three main components of scientific research
Null hypothesis
What is the hypothesis of no change that is often abbreviated as H0
Alternate hypothesis
What is the hypothesis that must be mutually exclusive and is abbreviated as Ha
the observed difference was so great it is unlikely to have been caused by chance alone
What does it mean when we reject an null hypothesis?
prediction
a statement about what you expect to find from your experiment
probability of commiting a type one error called alpha
Define level of signifigance
area under the standard deviation curve inside t critical representing probability of the sample statistic occurring if the null hypothesis is true
Define P-value
each sampling unit in the population has an equal chance of being selected
Define simple random sampling
divides the population into groups called strata and a sample is taken from each using other types of sampling
define stratified sampling
a spatial grid is used to generate equally sized sampling regions and sampled within each grid cell either randomly or aligned to the cells center
define systematic sampling
Primary sampling areas are located at random within an overall study area first then sampling units are located at random within each primary sampling area
define cluster sampling
observations within a single unit or treatment not independent of one another
What are pseudo replicates?
an aggregate of subjects which we wish to describe adn draw conclusions about
Define population
a collection of subjects selected within the study population representative of the target population
define sample
measurement unit
define sample unit/observation
qualitative or quantitative measured or recorded for each subject in the sample
define variable
a set of values for all variables of interest measured across all individuals in the study
define dataset
Variables can only be integers
define discrete data
any real number
define continuous data
unordered categories like eye color
define and give an example of nominal data
order categories like behavior
define ordinal data and give an example
mean median mode
What are measures of center
standard deviation, varience, quartiles
what are measures of dispersion
an estimate of a population parameter derived from a sample
define statistic
the difference between the sample and the population tha tis due solely to the incomplete enumeration of all elements of the population
define sampling error
tendency to favor the selection of units having particular characteristics
define sampling bias
how close is the measured value to the true value
define accuracy
how close are repeated measures to each other
define precision
accuracy precise
Sampling bias induces a lack of ______ even when the data is ____
precision
Sampling error induces a lack of _____ and decreases as sample size increases
resutls when most convinient units are chosen from a population
Define Convenience sample
obtained at the discretion of someone who is familiar with the relevant characteristics of a population
define judgement sample
all units within the population have a known or estimable probability of being choses
defien probability or random sample
straight-line segments laid out in the area to be sampled
What are transects?
measurements are taken from a set of points established throughout a target population
define points (point counts)
small geographic areas used to sample habitat characteristics or count animals
define plots( quadrats) sampling units
unbiased estimate of parameters, independence of samples, precise estimates of parameters, reliable inference of treatment effects
what are the 4 main important reasons for proper sampling
The result of a random experiment
Define probability outcome
the set of possible outcomes
define probability sample space
the long-run relative frequency of occurence of each possible event
define probability
the occurrence of a phenomenon of interest
define event in terms of probability
the number of events
Define Trial in terms of probability
P(A and B)= P(A)*P(B*A)
what is the equation for a dependent shared probability event between A and B
P(A and B)= P(A) *P(B)
what is the probability equation for an independent shared event
an event in relation to another event is the probability that the event happens given the other event has already happened
what is conditional probability
a discrete frequency distribution which gives the probability of a number of independent events occurring in a fixed time
what is a Poisson distribution
Bell-shaped and symmetrical asymptoting at the x axis described by mean and standard deviation
What is a normal distribution?
68
In a normal distribution one standard deviation from the mean in both directions yields what percentage of the distribution
describe patterns in population like means and standard deviations
What are descriptive statistics
Make inference about populations like t-tests ANOVA and regerssions
What are inferential statistics
the unpaired compares two pop means and the paired compares means from same sample two times
What is the difference between a two sample paired t-test and a two-sample unpaired t-test
bird abundance before and after a burn
what is an example of a two sample paired t test
the variation between populations
what does treatment effect refer to?
the natural variation within a population
what does error refer to in statistical testing
the difference is larger that what we would expect due to chance alone
How do you phrase an alternative hypothesis your believe to be greater than the null
what we are measuring
what is the response in ANOVA
the interaction of factors
If One-way ANOVA is an extension of the t-test to 3 or more samples than what is the two-way ANOVA
the value of one observation does not influence or affect the value or other observations
what is the independence of observation assumption of ANOVA
ANOVA tests
what is this a graph of
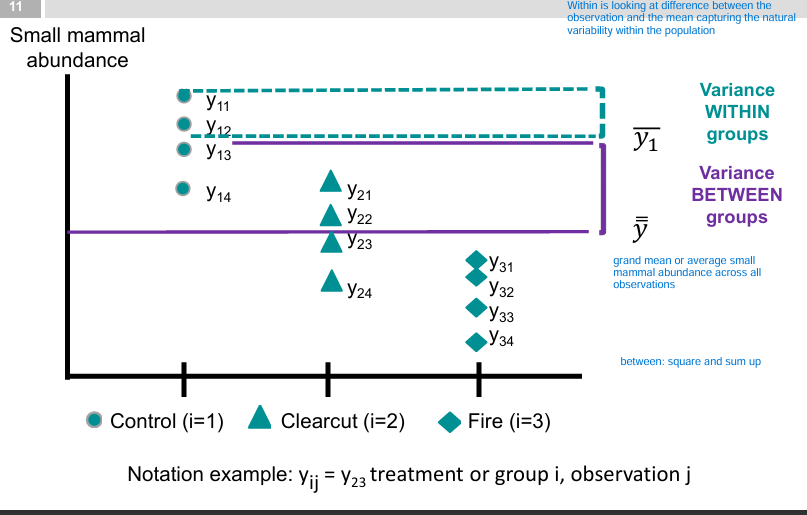
sums of squared normal random variables
What is Chi square random variables?
the ratio of two independent chi square random variables divided by their repective degrees of freedom
What is an F random variable
when the variation between groups is large compared to variation within groups
In terms of f test what tells us that the treatment effect is stong?
when the f statistic is less than the f critical
when is there no treatment effect in terms of the F test?
The minimum calculated amount of difference between groups for there to be an honest difference between groups
What is Honest significant difference
a variable of interest
What is a factor in terms of a two way anova
a particular value or state of a factor
what is a level in terms of a two way anova
ANOVAs with two or more outcome (dependent) variables, correlated, and in the same analysis
what is a MANOVA
any of the ANOVAs and also trying to control for an external influence to the dependetn variable
what is a ANCOVA
the analysis of covarience used to compare two or more regression lines
What is another definition for ANCOVA