3. Physical Chemistry
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
what are exothermic and endothermic reactions?
exothermic - reactions that release thermal energy
endothermic - reactions that take in thermal energy
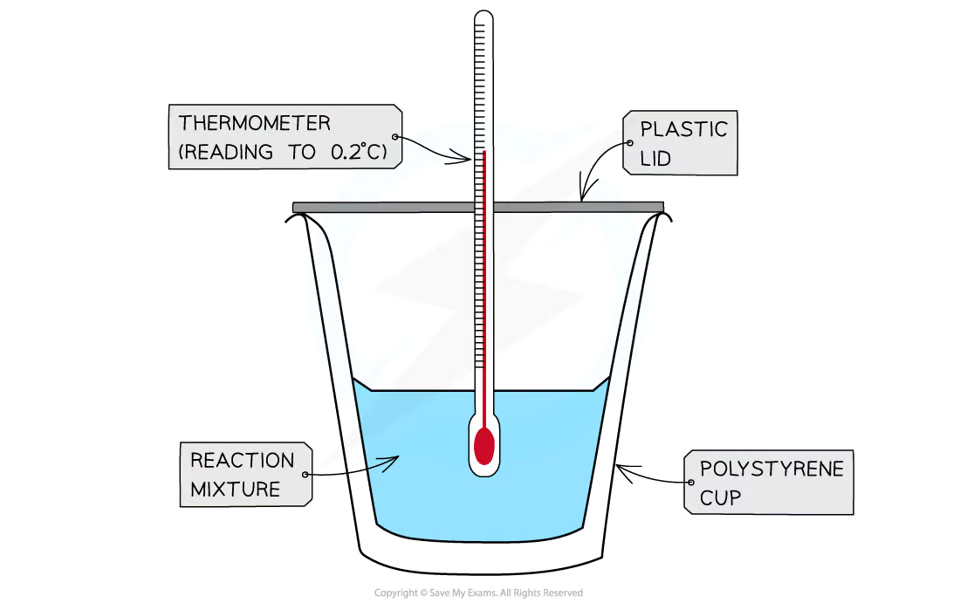
how would you do a calorimetry experiment to find the enthalpy change of a reaction in solution?
METHOD:
set a calorimeter with a polystyrene cup, plastic lid, and thermometer
add a fixed volume of one reagent to it and take the initial temperature
add an excess amount of the second reagent and stir continuously
record the maximum temperature and calculate the temperature change
calculate the energy released using:
Q = mcΔT
Q = the heat energy change, J
m = the mass of the substance being heated, g
c = the specific heat capacity, J/g/°C (4.18 J/g/°C)
ΔT = the temperature change, °C
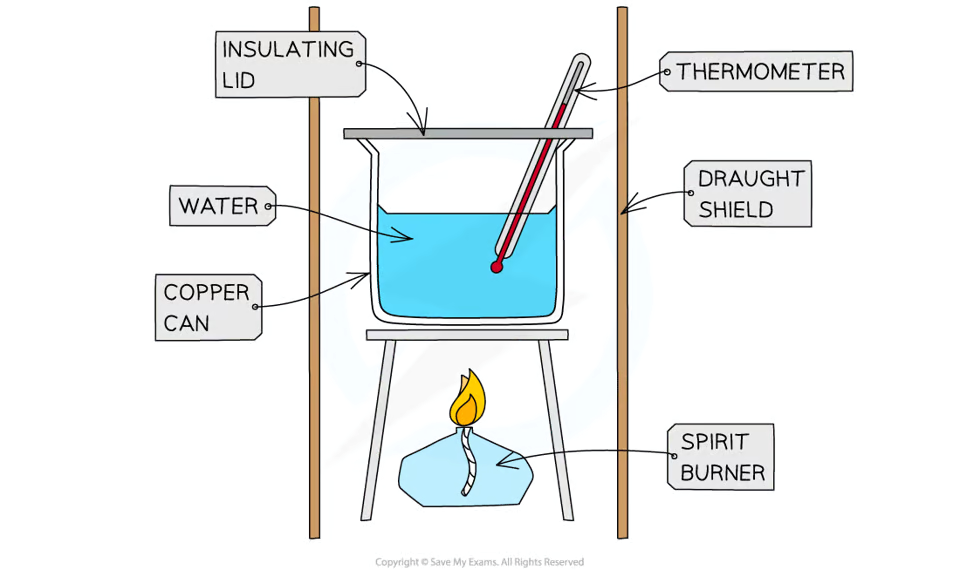
how would you do a calorimetry experiment to find the enthalpy change of a combustion reaction?
what errors could there be?
METHOD:
measure a fixed volume of water into a copper can
weigh the spirit burner using a balance
measure the initial temperature of the water
burn the fuel and stir the water
wait until the temperature has risen by approximately 20 oC and extinguish the flame
record the final temperature of the water and re-weigh the spirit burner
calculate the energy released using:
Q = mcΔT
ERRORS
not all of the heat produced by the combustion reaction heats the water
some is lost to the surroundings
some is absorbed by the calorimeter
to minimise heat losses, the calorimeter should not be too far above the flame and have a lid
shielding can be used to reduce draughts
the main errors are:
heat losses
incomplete combustion
what is the equation for heat energy changes?
Q = mcΔT
Where:
Q = the heat energy change, J
m = the mass of the substance being heated, g
c = the specific heat capacity, J/g/°C
ΔT = the temperature change, °C
which is positive and negative in exothermic and endothermic reactions?
exothermic is negative
endothermic is positive
what is the equation for energy released per mol of fuel?
ΔH = Q/n
units are kJ/mol
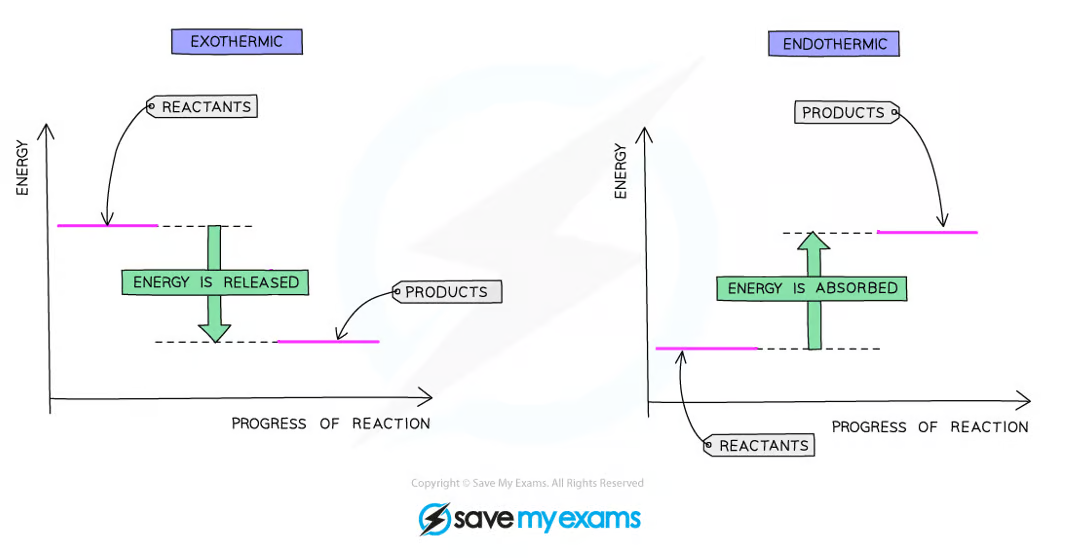
how would you draw an energy level diagrams for both exothermic and endothermic reactions?
do exothermic and endothermic reactions involve making or breaking bonds?
MEXO-BENDO
Exothermic: making
Endothermic: breaking
During reactions, energy must be taken in to break bonds and energy is released when new bonds are formed. Whether a reaction is endothermic or exothermic overall depends on the difference between the energy needed to break existing bonds and the energy released when new bonds are formed.
what are the energy levels in exothermic reactions?
the energy released when new bonds are formed is greater than the energy taken in to break bonds
the change in energy is negative since the reactants have more energy than the products
therefore an exothermic reaction has a negative ΔH value
what are the energy levels in endothermic reactions?
the energy needed to break existing bonds is greater than the energy released when new bonds are formed
the change in energy is positive since the products have more energy than the reactants
therefore an endothermic reaction has a positive ΔH value
what is the equation for enthalpy change in terms of bonds?
Enthalpy change (ΔH) = Energy taken in - Energy given out
PRACTICAL: Investigating Temperature Changes
METHOD
using a measuring cylinder, place 25 cm3 of the NaOH solution into the calorimeter
measure and record the temperature of the solution
add 5 cm3 of the dilute HCl and stir
measure and record the highest temperature reached by the mixture
repeat steps 1 – 4 increasing the amount of acid added by 5 cm3 each time
RESULTS
record your results in a table with volume of acid and temperature
the larger the difference in temperature, the more energy is absorbed or released