DILD and Cirrhosis- Dr. Ochs
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
A liver function test or LFTs includes…
AST
ALT
Alkaline phosphatase (Alk phos, ALP)
bilirubin
albumin
What is a normal INR ratio?
0.9-1.1
What are the 2 types of liver disease?
hepatitis
cirrhosis
What does a MELD Score stand for? What does it assess?
stands for Model for End-Stage Liver Disease
assess likelihood of survival in pts. w/ liver disease and prioritizes pts. for liver transplants
What does a Child-Pugh Score assess? (will not have to calculate on exam)
assess liver function and estimates liver’s ability to metabolize drugs in pts. with decompensated liver disease
How does hepatitis or cirrhosis effect drug metabolism?
hepatitis—> unchanged/slightly decrease
cirrhosis—> significant decrease
What are some risk factors for DILD?
alcohol consumption
age >60
type 2 DM
Rheumatoid arthritis
Liver damage can either be acute hepatocellular or cholestatic. What lab findings would you find for each?
acute hepatocellular- HIGH AST and ALT
cholestatic (gallbladder)- HIGH ALK PHOS
R factor can be calculated to differentiate the type of liver damage present. A R>5, R≤2, and R between 2-5 mean…
R>5 hepatocellular injury
R≤2 cholestatic injury
R 2-5 mixed injury
What drugs cause hepatocellular injury?
acarbose
allopurinol
fluoxetine
losartan
What drugs can cause centrilobular necrosis?
ACETAMINOPHEN
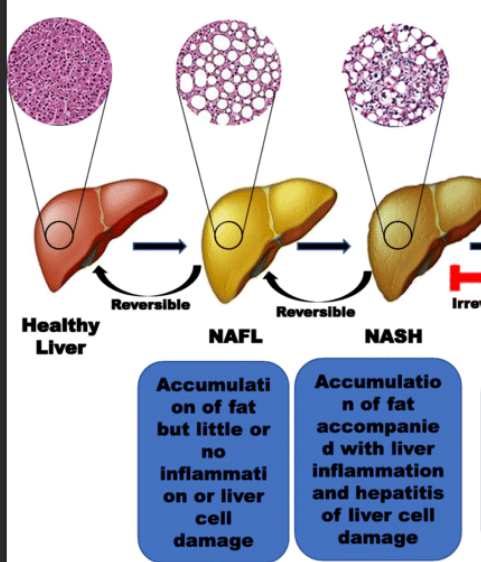
What drugs can cause Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) or Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)?
tetracycline
valproate
What drugs can cause alcoholic steatohepatitis?
alcohol
What drugs can cause phospholipidosis?
amiodarone
What drugs can cause generalized hepatocellular necrosis?
isoniazid
ketoconazole
What drugs can cause toxic cirrhosis?
methotrexate
vitamin A
Cholestatic injury is defined by…
Alk Phos x3 ULN
What drugs can cause cholestatic injury?
erythromycin
amoxicillin-clavulanic acid
carbamazepine
IV vitamin E
Total parental nutrition (TPN)
What drugs can cause mixed hepatocellular and cholestatic injury?
phenytoin
sulfonamides
What is the antidote to APAP toxicity? What is the dose based on?
antidote- N-acetylcysteine
dosed based on Rumack-Mathew Nomogram
What method is used to determine the likelihood of a certain drug causing drug-induced liver injury?
RUCAM
(FYI: this is different from child-pugh because child-pugh focuses on the liver’s ability to metabolize and rucam focuses on the likelihood a drug will cause injury)
PRACTICE:
Significantly elevated Alk Phos is most closely related to which kind of liver damage/injury?
cholestatic
PRACTICE:
What is the MELD score tool used for?
prioritizes liver transplant
PRACTICE
If left undetected, what can NAFLD progress to?
NASH
PRACTICE:
What drugs are associated with steatohepatitis?
tetracycline
valproate
alcohol
PRACTICE:
What drugs are associated with toxic cirrhosis?
methotrexate
Vit A
What are some common causes of cirrhosis?
alcoholism
chronic hepatitis C
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
others: autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis, medications
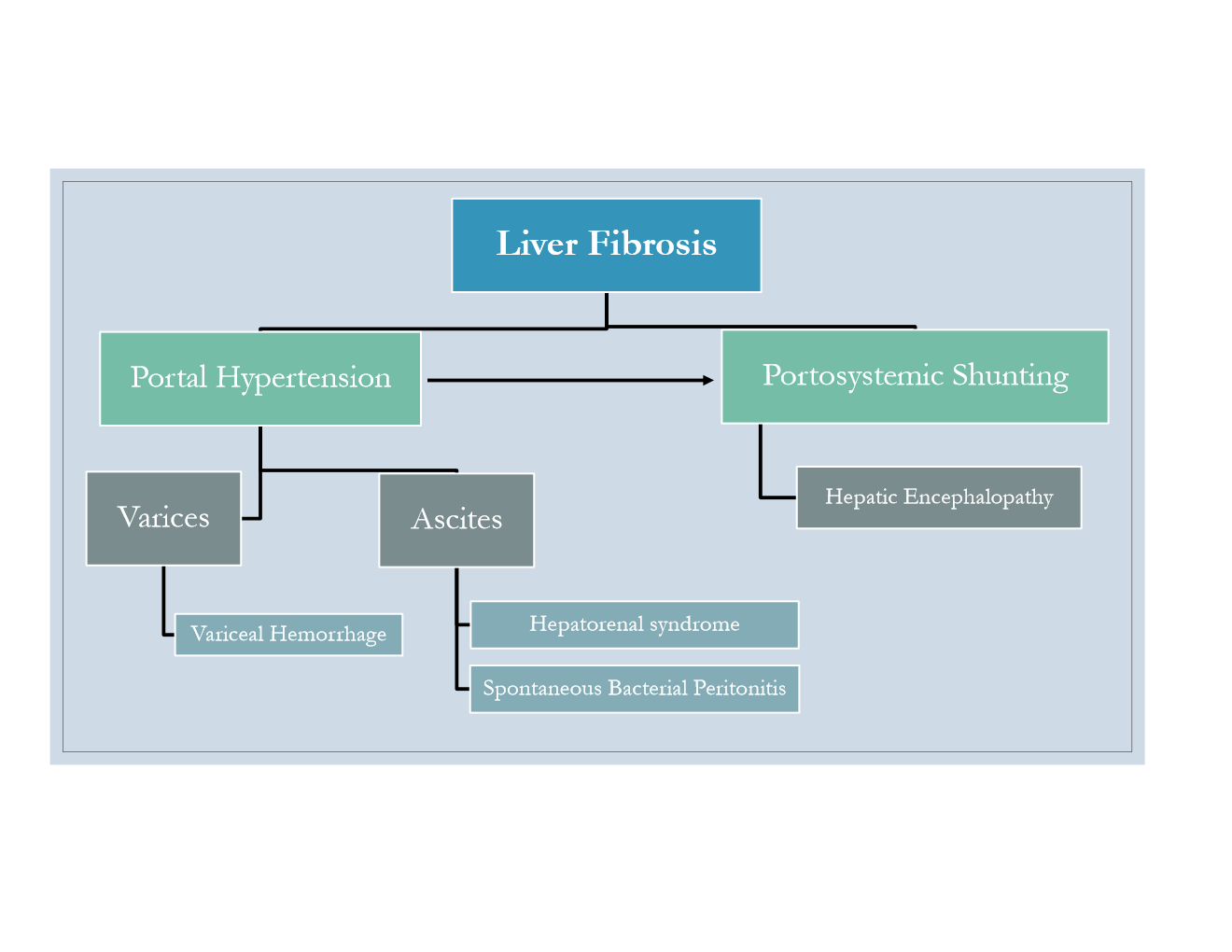
What are signs of decompensated cirrhosis?
variceal bleeding
ascites
encephalopathy
What are some complications of liver fibrosis?
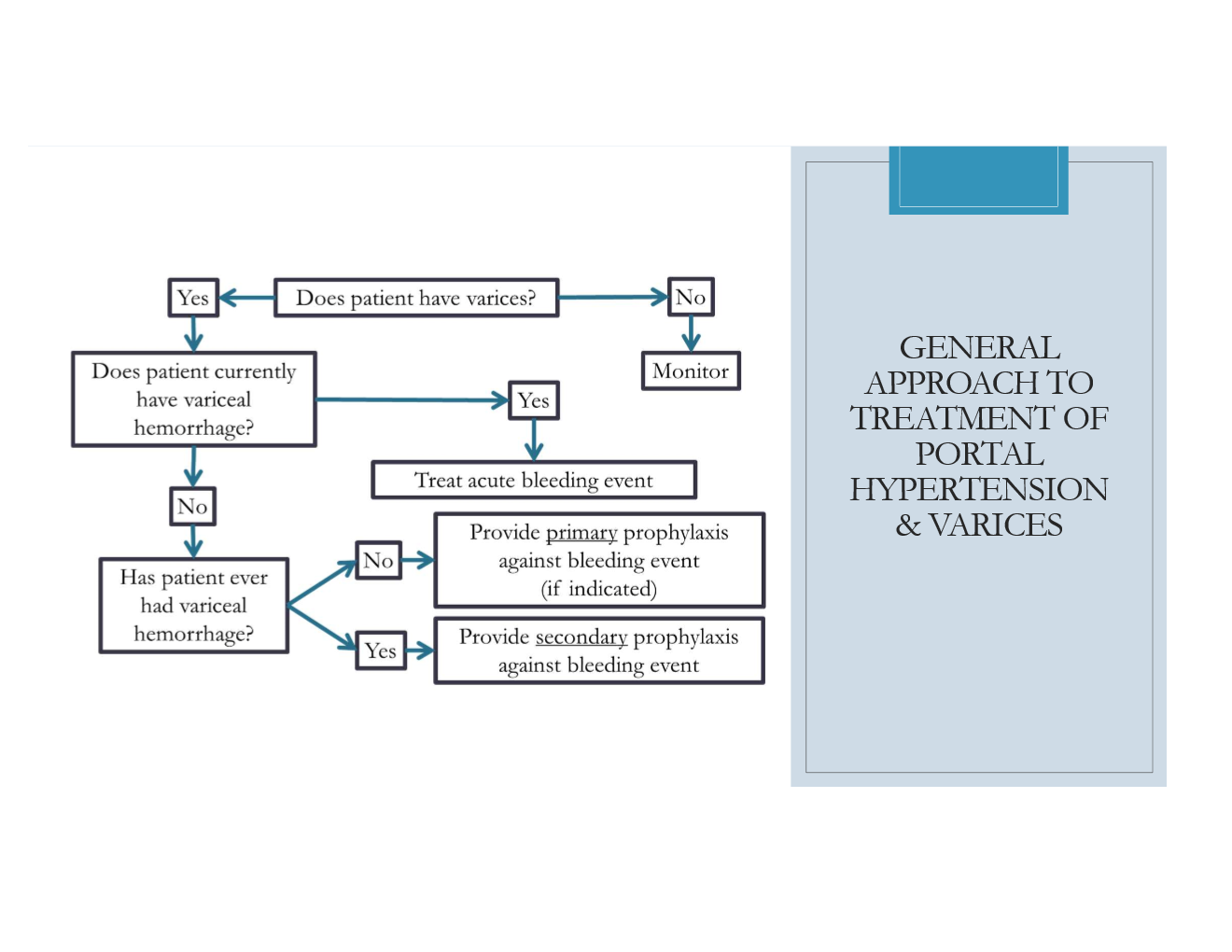
FYI on the general approach to variceal tx
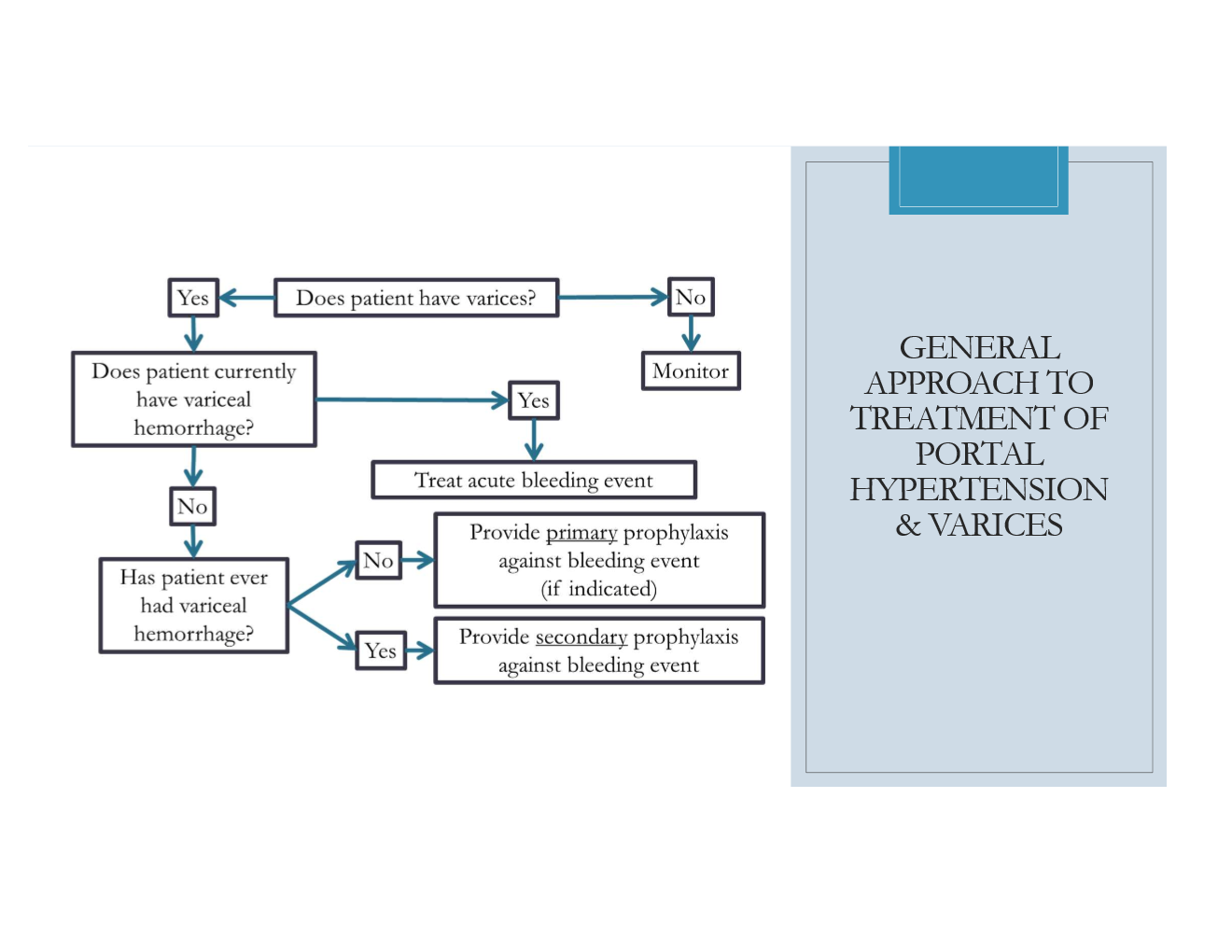
When is primary prophylaxis to prevent variceal hemorrhage indicated?
pts. with SMALL varices AND presence of risk factors
any pt. with medium/large varices
What are the 2 general tx options for prophylaxis of variceal hemmorhage?
Endoscopic variceal ligation (EVL)
non-selective beta-blocker (NSBB)
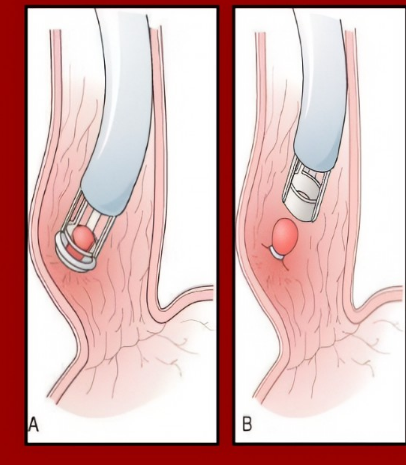
What is Endoscopic variceal ligation? When is it used 1st line for primary prophylaxis?
“banding of varices”
(basically we put a band around the varices, that cuts off the blood flow and then it falls off and dies!)
1st line IF patient cannot tolerate or are contraindicated to NSBBs
not really used for small varices, more for medium/large
What NSBB are used for primary prophylaxis of varices?
propanol
nadalol
carvedilol (has some a-activity)
NSBB should be titrated to goal HR of ____-____ BPM or max tolerated dose.
55-60 BPM
SUMMARY ON PROPHYLAXIS MANAGEMENT OF VARICES:
What prophylaxis tx can be used for the following:
no varices, low risk small varices
small varices with risk factors for bleeding
Medium or large varices
primary prophylaxis NOT recommended
NSBB preferred
NSBB and EVL
An acute variceal hemorrhage is a medical emergency. What are the non-pharm and pharm options for management?
non-pharm (procedures): EVL, sclerotherapy, balloon tamponade, TIPs
PHARM:
Octreotide and antibiotic
vasopressin+nitroglycerin AND antibiotic
Of the pharm tx for acute variceal hemorrhage, which is 1st line, which is 2nd line?
1st- Octreotide
2nd- vasopressin+nitroglycerin
What is the max duration for vasopressin use?
24 hours (in order to reduce ADRs)
Why must nitroglycerin be given with vasopressin?
to decrease risk of ischemia
Why is an antibiotic taken with octreotide or vasopressin+nitroglycerin in acute variceal hemorrhage?
to prevent SBP
What antibiotic is preferred in acute variceal bleeding to prevent SBP?
ceftriaxone
After an acute variceal bleed, what must be initiated?
secondary prophylaxis
In what 2 scenarios is secondary prophylaxis of variceal hemorrhage not needed?
if the pt. had SHUNT surgery or TIPS
What is used for secondary prophylaxis of variceal hemorrhage?
Traditional NSBB—> BUT ONLY NADOLOL OR PROPRANOLOL
NOT CARVEDILOL!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
EVL
How does ascites present?
abdominal bulging
shifting flank dullness
positive fluid wave
What lab value would indicate the ascites is due to portal hypertension?
SAAG ≥1.1 g/dL
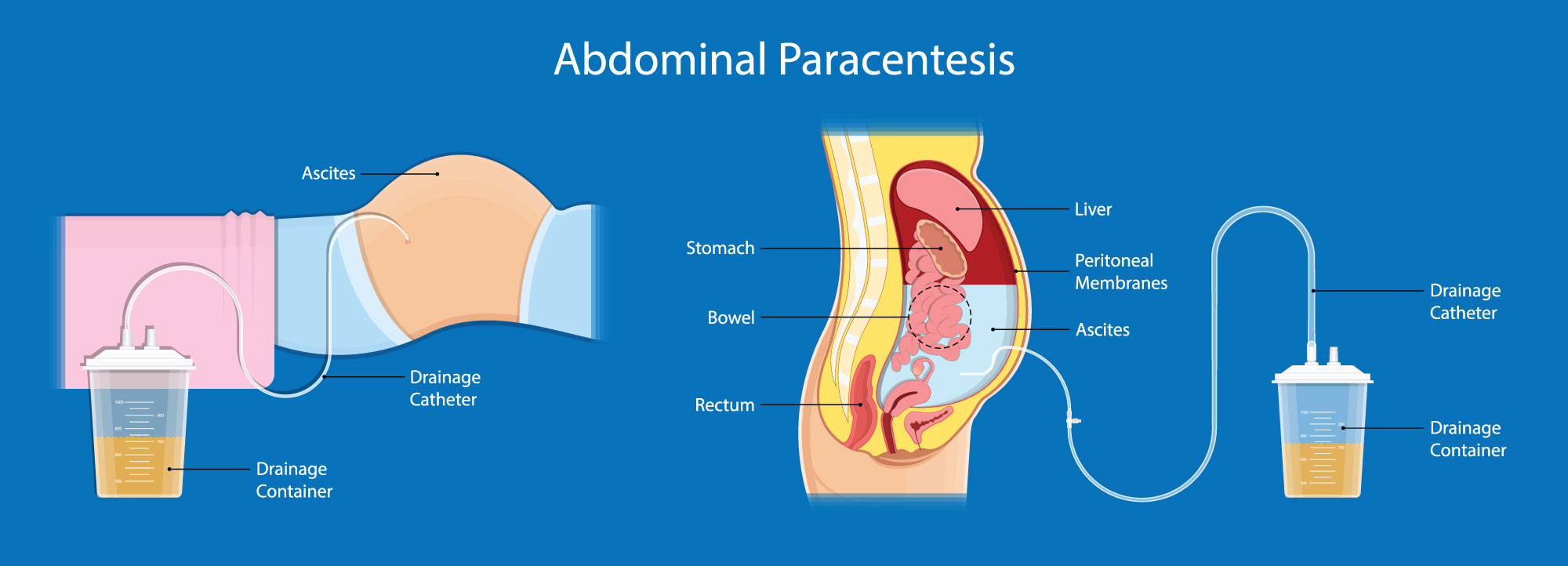
What should be performed on all new-onsets of ascites?
abdominal paracentesis to rule out infection
What are the pharm tx options for ascites? What pharm should be d/c?
tx: diuretics
d/c: anything that may cause Na+/water retention
What electrolyte is important to monitor with the use of diuretics?
potassium (K+)
What is the PREFERRED diuretic regimen for ascites? If a combination of diuretics is not possible, which is preferred?
spironolactone + furosemide (if solo—> spironolactone preferred)
What is the dosing regimen for diuretics in ascites? What is the ratio?
Dosing: ratio of spironolactone 100mg PO daily and furosemide 40mg PO daily
(100:40 mg)
If a paracentesis is performed, what may you consider giving the patient to prevent the fluid from immediately accumulating again?
IV albumin (only given if over >5L removed)
What is SBP? What is it caused by?
SBP is spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and is a bacterial infection OF THE ASCITIC FLUID
caused by bacteria like E. coli, pneumonia, and others
Symptoms of SBP? (not that imp)
fever, abdominal pain and tenderness, confusion (from encephalopathy)
What signs are DIAGNOSTIC of SBP?
positive culture OR
PMNs ≥250 cells/mm3 in ascitic fluid
Long-term SBP prophylaxis is for anyone that is…
high risk
Short-term SBP prophylaxis is for…
acute variceal bleeds
What are the tx options for long-term prophylaxis?
ciprofloxacin
sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim
For TREATMENT (not prophylaxis) of SBP what are the 1st line options? Include the drug, dose, dosage form, and frequency
Cefotaxime 2g IV q8h
Ceftriaxone 2g IV q24h
When is piperacillin-tazobactam+ vancomycin used for tx of SBP?
2nd line (risk of drug-resistance or nosocomial infection)
What is the duration of 3rd gen cephalosporins for tx of SBP?
5-7 days
What are the criteria for albumin to be given with SBP tx?
should be given when the ascitic fluid PMN ≥250 cells/mm3 AND one of the following:
SCr >1mg/dL
BUN >30 mg/dL
Total bilirubin >4 mg/dL
When is secondary SBP prophylaxis indicated? What is the duration of tx?
indicated for ANY patient that survives an episode of SBP
duration: life-long
What are the secondary SBP prophylaxis tx options?
CIPROFLOXACIN
SULFAMETHOXAZOLE/TRIMETHOPRIM
What causes hepatic encephalopathy?
AMMONIA accumulation
What are some symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy?
altered behavior
confusion
loss of consciousness
disoriented
What is the name of the criteria that grades hepatic encephalopathy?
West Haven Criteria
What are some non-pharm ways to correct hepatic encephalopathy?
reduce protein intake (choose veggie/dairy protein> meat)
What are the pharm options for hepatic encephalopathy? say which is 1st line.
Lactulose- 1st LINE
antibiotics
zinc
What is the MECHANISM of lactulose?
enhances diffusion of ammonia from blood to gut
ACIDICFICATION results in conversion of ammonia into ammonium
ammonium is then excreted
What is dose is lactulose available as? What is the dosing for episodic or persistent hepatic encephalopathy?
available as 10g/15 ml solution
episodic: initiate 16.7 PO q1-2h until BM
reduce to 10-30g PO q8-12h, and titrate to 2-3 soft BM
persistent: titrate to 2-3 soft BM
What is used in combination with lactulose as a SECOND LINE AGENT for hepatic encephalopathy? (Include drug, dose, route, and frequency)
Rifaximin 550mg PO BID
Rifaximin is preferred over _____________ or ________________ in hepatic encephalopathy.
neomycin or metronidazole
what is the mechanism for rifaximin and zinc?
rifaximin- reduces gut bacteria
zinc- aids in conversion of ammonia to urea