Urinalysis
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
What are two methods for acquiring a urine sample
Midstream "Clean Catch" acquisition; Catheter acquisition.
Which cells form the visceral layer of Bowman's capsule, what shouldn’t be able to filter thrpugh the kidneys capillary (glomeruli)
Podocytes
cells, proteins, glucose.
What is needed for a Midstream "Clean Catch" Urine Acquisition
A sterile container; sterile wipes.
Pee for a small void (count to three, then give sample)
A voided urine sample shows a colony count near 10^5 bacteria/mL. What type of infection does this count range typically suggest
Cystitis
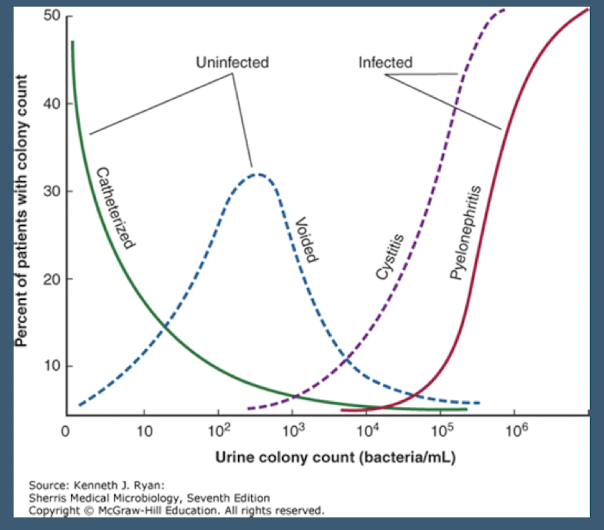
A urine sample obtained via catheterization shows a low bacterial count. Is this sample likely infected or uninfected according to the source diagram
Uninfected.
What is the normal range for Urine Specific Gravity
1.009 – 1.030.
What is the normal pH range for urine
5.0 – 7.5.
According to the normal range table; what are the expected results for Bilirubin; Urobilinogen; Blood; Protein; Glucose; Ketones; Nitrite; and Leukocyte Esterase in urine analysis
Negative.
What is the normal range for WBCs and RBCs found per high power field (HPF) in urine microscopy
0 – 5 Cells/HPF.
How should Bacteria; Urine Casts; and Urine Crystals be reported in a normal urinalysis microscopy result
Bacteria: None/Few; Urine Casts: None; Urine Crystals: None.
What color is urine if the volume is replete and the patient is hydrated
Pale yellow.
What color might urine be if the volume is depleted or there is hyperbilirubinemia
Dark yellow

If urine is red and the sediment is red; what condition is suggested
Gross Hematuria.
If urine is red with a red supernatant; what conditions might be indicated
Hemoglobinuria (RBC are lysed) or Myoglobinuria. (muscle breakdown, kidney injury)
Diet-Related: Beets, Rhubarb, Blackberries

What are potential causes of orange colored urine
Medication-induced; Rifampin (TB med) ; Azo (Phenazopyridine, cystitis med).
What condition might cause urine to appear blue-green
P. aeruginosa Urinary Tract Infection.
What finding is suggested if urine is cloudy or turbid
Pyuria – Infection. WBC content
What finding is suggested if urine is foam/frothy
Proteinuria.
What is Specific Gravity a measure of
Urine Concentration; Density of Urine Relative to the Density of Water.'
How much is just water vs ion etc. solutes.
What is the normal range for Specific Gravity measured by dipstick
1.009 – 1.030
What causes the specific gravity assessment to be invalidated; requiring the use of urine osmolality instead
Presence of urinary glucose; protein; or RBCs.
Osmolality can only be measured through a lab (Concentration of particles per kilogram of a solution)
What concentration range is normal for Urine Osmolality
50 – 1200 mOsmol/kg.
Does concentrated urine have a higher or lower specific gravity or osmolality
Higher specific gravity or osmolality.
What is another name for Arginine Vasopressin (AVP)
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH).
What is the action of ADH on the renal tubules
Acts on Renal Tubules to increase Water Retention; Increases the Concentration of the Urine.
Takes water from tubule back into systemic circulation
What is the underlying cause of Central Diabetes Insipidus? What clinical manifestations are seen with Diabetes Insipidus
Inadequate AVP Production.
NOT DIABETES MELLITUS
Polyuria; Polydipsia (drinking a lot) ; Large Urine Output; Hypernatremia; Low Urine Specific Gravity.
What causes and what are the key features of the Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH)
Excessive Production of AVP; Secondary to cancers(neoplasms), CNS disorders, medications, or infections)
Clinical Manifestations including H/A; Confusion; N/V; Coma; Hyponatremia; Elevated Urine Specific Gravity.
A patient presents with hyponatremia; confusion; and an elevated urine specific gravity. Which condition is strongly suggested
Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH).
What is the typical pH range for Acidotic Urine
Urinary pH < 5.
What is a common condition associated with Acidotic Urine
Metabolic Acidosis.
What is the typical pH range for Alkalotic Urine
Urinary pH > 7.
Name three common conditions associated with Alkalotic Urine
Metabolic Alkalosis; Infection with Urea Causing Organisms (Proteus spp.); Standing Urine Samples (Delayed Analysis).
What are the two forms of bilirubin? In what forms can bilirubin be found in the blood ?
Direct (conjugated) or indirect (unconjugated).
Unconjugated or conjugated.
Why is unconjugated bilirubin typically NOT filtered by the kidney? What happens to conjugated bilirubin after it is filtered by the kidney?
It is bound to albumin. It is filtered; but most is reabsorbed within the proximal tubules.
What form of bilirubin is always present when bilirubin is detected in the urine? The presence of bilirubin in the urine is typically indicative of what major pathology? What clinical sign may accompany the presence of bilirubin in the urine?
Conjugated bilirubin. Hepatocellular Disease Jaundice
How is urobilinogen formed
Conjugated Bilirubin is catabolized by Gut Bacteria and leads to the formation and absorption of urobilinogen.
Most is excreted via the Liver
Small amounts are excreted by the kidneys
What pathological condition causes increased levels of urinary urobilinogen excretion
Liver Failure or significant hemolysis; where the liver is unable to clear urobilinogen.
What do urine dipsticks assess for regarding blood
Heme-molecules within urine.
What finding is suggested by a Positive Heme dipstick result and Positive Microscopic RBCs
Gross Hematuria or Microscopic Hematuria.
If a urine dipstick is Positive for Heme; but microscopic analysis is Negative for RBCs; what two conditions might be indicated
Hemoglobinuria (i.e.; Hemolysis) or Myoglobinuria (i.e.; Rhabdomyolysis).
Describe the key urinalysis findings for Obstructive Jaundice (Color, bilirubin, urobilinogen, blood, microscopy)
Unrinalysis Color: Dark Yellow; Bilirubin: Positive; Urobilinogen: Variable Depending on degree of obstruction; Blood: Negative.
A patient presents with dark yellow urine; a positive bilirubin result; and urobilinogen is variable on the dipstick. Blood is negative. What hepatobiliary condition is suggested?
Obstructive Jaundice
If complete OBSTRUCTION → You only see urobilonogen if it passes the liver and gets to your gut so uribilinogen woud be negative
Describe the key urinalysis and microscopy findings for Hemolysis (Color, bilirubin, urobilinogen, blood, microscopy)
Urinalysis: Color: Red; Bilirubin: Negative; Urobilinogen: Positive; Blood: Positive; Microscopy: RBC: None (Hemoglobinuria).
A patient's urinalysis shows positive blood on dipstick; red urine color; positive urobilinogen; but microscopy reveals no RBCs. What condition is strongly suspected
Hemolysis (Hemoglobinuria).
Why should protein theoretically be absent from urine
Protein molecules are too large to pass through the glomeruli.
What specific protein can urine dipsticks detect; and at what concentration range
Albumin concentrations from 200 to 300 mg/L.
How are urine dipsticks used in relation to protein
Used as a screening tool for Renal Disease.
Urine Dipsticks typically are insensitive for non-albumin proteins
Semi-Quantitative
Measure as Negative, 1+, 2+, 3+, 4+
What process normally handles glucose after it is filtered by the glomeruli
It is continuously reabsorbed within the renal tubules.
What condition describes the presence of glucose in the urine
Glucosuria.
Glucosuria typically occurs when serum glucose levels exceed what threshold
180 mg/dL.
Besides Diabetes Mellitus; what class of medications can cause glucosuria by increasing urinary output of glucose
Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporters 2 (SGLT2)-Inhibitors (i.e.; Invokana: Canagliflozin).
What are ketones a byproduct of
Fatty acid metabolism (Lipolysis).
Theoretically, ketones should not be present in the urine (unless you’re doing keto lol)
What are common causes of Ketonuria
Uncontrolled Diabetes Mellitus; Ketogenic Diet; Starvation.
Ketonuria can be associated with what acid-base disorder
Metabolic acidosis.
What are nitrites a byproduct of
Certain species of Gram-Negative Nitrate metabolism.
Name common causative agents that produce nitrites in urine
E. coli and other Enterobacteriaceae (Includes Klebsiella spp. and Proteus spp.).
Will Gram-Positive Organisms typically produce nitrites
No.
typically.
What is Leukocyte Esterase
An enzyme within WBCs.
When will Leukocyte Esterase be positive in urine
In cases of infection or possibly inflammation.
Where do urinary casts form
Distal Tubules and Collecting Ducts.
What is Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN) and what does it result in
Renal Tubular Damage which results in Acute Kidney Injury (AKI).
What are the major causes and signs/symptoms of Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN)
Major Causes: Ischemia, Nephrotoxins, Sepsis
AKI + Reduced Urine Output.
What is Glomerulonephritis
Inflammation of the Renal Glomeruli.
What are causes and signs/symptoms of Glomerulonephritis
Major Causes: Autoimmune process, infection related
Hematuria; AKI; Edema; Proteinuria; HTN.
Nephrotic Disease is defined as a spectrum of glomerular disease resulting in alterations of what
Basement membrane permeability.
What are causes and the signs/symptoms of Nephrotic Disease
Some Major Causes: Diabetes Mellitus, Amyloidosis Proteinuria (>3 g/24 Hours); Hypoalbuminemia; Edema; HLD.
Describe Hyaline Casts
Faint; colorless; concentration of mucoproteins secreted from renal tubules
Are Hyaline Casts specific to renal disease
No; they are Non-specific; Present in normal/non-renal disease patients.
Describe Granular Casts
Broad; fine or coarse; composed of degraded cellular products and serum proteins (Albumin; IgG; Transferrin; etc.)
Granular Casts are indicative of what condition
Non-specific; Indicative of Renal Parenchymal Disease; Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN.)
What are Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Casts associated with
Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN)
What are Fatty Casts and what are they associated with
Hyaline Casts which contain lipid droplets and can be overserved in patients with lipuria
Nephrotic Syndromes.
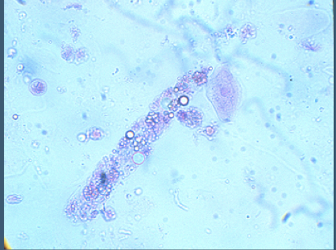
Red Blood Cell Casts occur in which specific kidney condition
Glomerulonephritis; resulting from grouped RBCs leaking through damage of the glomerular basement membrane
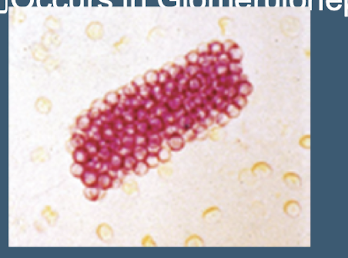
White Blood Cell Casts typically occur in what type of infection
Upper urinary tract infections (i.e.; Pyelonephritis)
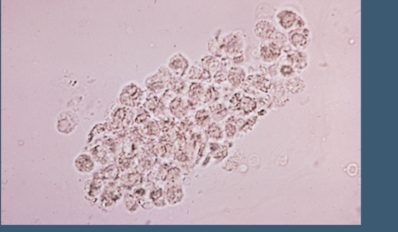
Besides quantifying RBCs and WBCs; what initial step using microscopy can guide treatment choice for bacteria
Initial Gram Staining. followed by subsequent culture and sensitivity
Name several conditions included in the differential diagnosis for Hematuria
UTI; Bladder CA; Renal Cell CA; Interstitial Cystitis; Radiation Cystitis; Chemotherapeutic Cystitis; Glomerulonephritis; etc..
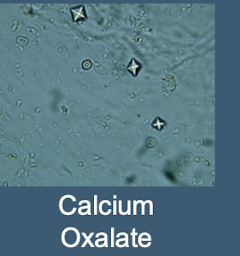
What is the most common stone type; appearing as small square crystals with a central cross
Calcium Oxalate
Uric Acid crystals are often seen in what condition and associated with what pH of urine
Rhomboids, hexagons, or squares
Gout; Acidic Urine

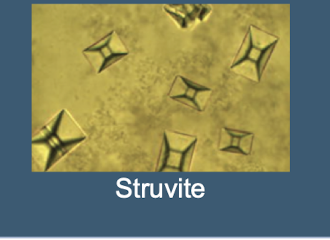
What are Struvite crystals often called; and what type of urine are they associated with
Staghorn “coffin-lids”– Triple Phosphate; Alkaline Urine
associated with proteus mirabilis produces urease
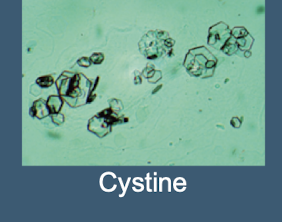
Cystine crystals (Colorless Hexagons) are seen in patients with what genetic disorder
Cystinuria
A urine culture is positive for E. coli (>100;000 colony forming units per mL). The susceptibility report shows Ampicillin as 'R' and Ciprofloxacin as 'S'. Which antibiotic should theoretically be used for treatment
Ciprofloxacin.
List the four steps of the 24 hour urine collection procedure
First Urine is voided and discarded; The time is recorded; This is the beginning of the 24 hour urine study;
Each subsequent urine is collected in a container;
Urinate one last time at the end of the 24 hour period; This is the end of the 24 hour urine collection;
Urine is then analyzed for various electrolytes; proteins; catecholamines; etc..
What are common pathologies associated with increased Calcium excretion in a 24-hour urine collection. Decreased?
Hyperparathyroidism; Sarcoidosis; Hyperthyroidism.
Hypothyroidism or renal failure
Increased Catecholamines found via a 24-hour urine collection indicates what pathology
Pheochromocytoma
Decreased Creatinine clearance found via a 24-hour urine collection indicates what pathology
Renal Disease.
A 24-hour urine collection showing increased Free Cortisol is the screening test of choice for which syndrome
Cushing Syndrome.
Increased protein clearance found via a 24-hour urine collection indicates what pathology
Nephrotic syndromes - Preeclampsia
Urine Microalbumin testing is used as a screening tool for diabetic patients to determine the risk of developing what condition
Nephropathy.
Define Macroalbuminuria based on 24-hour urine collection results
>300 mg/24 Hr.
Define Microalbuminuria based on the Albumin/Creatinine Ratio (Spot Urine)
30 – 299 mcg/g Cr (Spot Urine).
what is normoalbuminuria
<30 mg/24 hr
What therapy is typically given to those diagnosed with microalbuminuria
ACE Inhibitor or ARB Therapy.
If Urine Sodium is < 10 mEq; what two clinical states are suggested
Hyponatremia; Volume Depletion.
If Urine Sodium is > 20 mEq; what kidney/hormonal conditions might be indicated
SIADH; ATN.
Urine Potassium < 10 mEq suggests what clinical manifestations
Hypokalemia; Potassium Depletion; Extrarenal Loss.
Urine sodium > 40 mEq suggests what clinical manifestations
Acute Tubular Necrosis ATN