Intro + Amino Acids
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
What did Anfinsen demonstrate using RNase A?
He demonstrated that the primary amino acid sequence of a protein contains all the information necessary to determine its 3D folded structure.
Can you define a "diffusion-limited" enzyme?
An enzyme that’s so efficient it catalyzes a reaction every time it encounters a substrate molecule (it works as fast as the molecules can diffuse).
By what factor does RNase A accelerate the hydrolysis of RNA compared to the uncatalyzed reaction in water?
By a factor of 1015 (one quadrillion).
What is the specific biological role of a ribonuclease inhibitor?
A large protein that binds tightly to RNase A, wrapping around it to prevent it from indiscriminately cleaving RNA, which would be toxic to the cell.
What is Hund’s Rule?
The lowest energy configuration is the one with the maximum number of unpaired electrons allowed by the Pauli exclusion principle (electrons fill empty degenerate orbitals before pairing up).
What is the physical shape and directionality of p-orbitals?
Dumbbell-shaped and possess directionality along the x, y and z axes.
In CO2, what is the hybridization of the C atom, and what is the resulting bond angle?
The C is sp-hybridized, resulting in a linear geometry with a 180° bond angle.
Can you describe the orbital composition of an sp2-hybridized atom?
Consists of 3 sp2-hybrid orbitals (trigonal planar arrangement) and one remaining unhybridized p-orbital.
What are the 4 most abundant elements in the human body by dry weight?
Carbon: 61.7%
Nitrogen: 11%
Oxygen: 9.3%
Hydrogen: 5.7%
Why does carbon in methane (CH4) adopt a tetrahedral geometry instead of using its raw 2s and 2p orbitals?
It undergoes sp3 hybridization, blending the s and p orbitals to create 4 equivalent hybrid orbitals that maximize distance from each other (minimizing repulsion).
In a CO2 molecule, what type of bond results from the side-to-side overlap of "pure" p orbitals?
A pi-bond.
Can you define the difference between a Formal Charge and a Partial Charge?
formal: a full +1 or -1 charge resulting from a gain or loss of electrons
partial: δ+ or δ-, a slight charge imbalance caused by EN differences in a covalent bond
Can you arrange these common bio-elements in order of increasing electronegativity: C, H, O, N?
H < C < N < O
What are the 4 groups attached to the α-carbon of an amino acid?
amino group (-NH3+)
carboxylate group (-COO-)
hydrogen (-H)
variable R-group (side chain)
In a Fischer projection of an amino acid, what direction are the bonds represented by the horizontal lines pointing?
They project forward, out of the page toward the viewer.
Which stereoisomer of amino acids is predominantly used to build proteins in living organisms?
The L-isomer.
What is the specific name for a sulfur-sulfur bond (R—S—S—R)?
Disulfide bridge/linkage.
What characterizes a "peptide" in terms of charge distribution
It contains formal charges at the N-terminus (+1) and C-terminus (-1), but also internal partial charges (O is δ-, N and H are δ+) due to the polarity of the amide/peptide bonds.
What is the weighted average mass of an amino acid residue and why is it different from the free amino acid average?
110 Da
lower than the free average (128 Da) because a water molecule (18 Da) is removed during peptide bond formation
Can you explain the "CORN" mnemonic for L-stereochemistry?
Looking down the H-Cδ bond, if the groups CO ➡ R ➡ N appear in a clockwise direction, the amino acid is in the L-configuration.
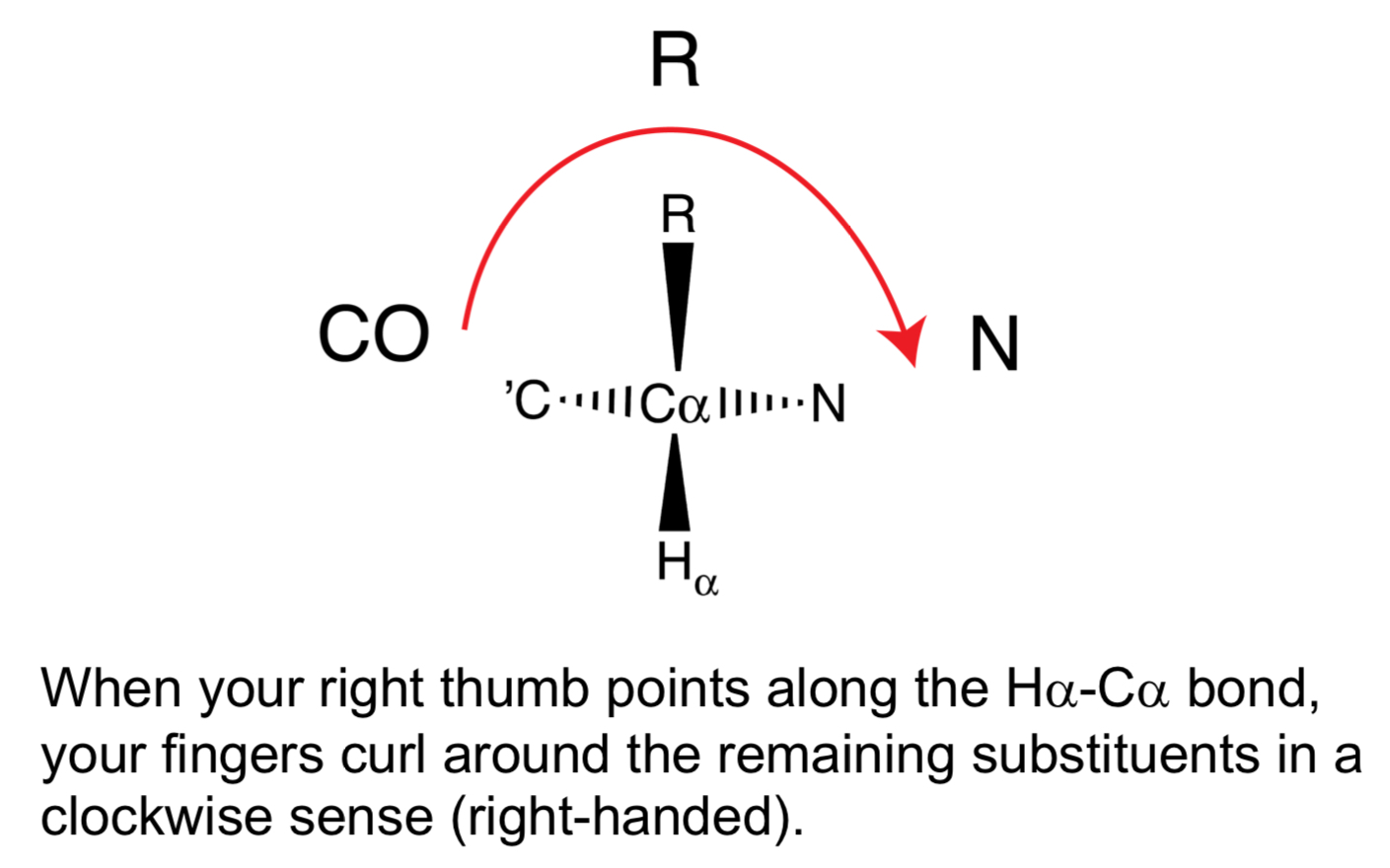
Which amino acid is an exception to the rule that L-amino acids have an "S" configuration in the RS system?
Cysteine: has an "R" configuration because the sulfur atom in its side chain gives the R-group higher priority than the carboxyl group.
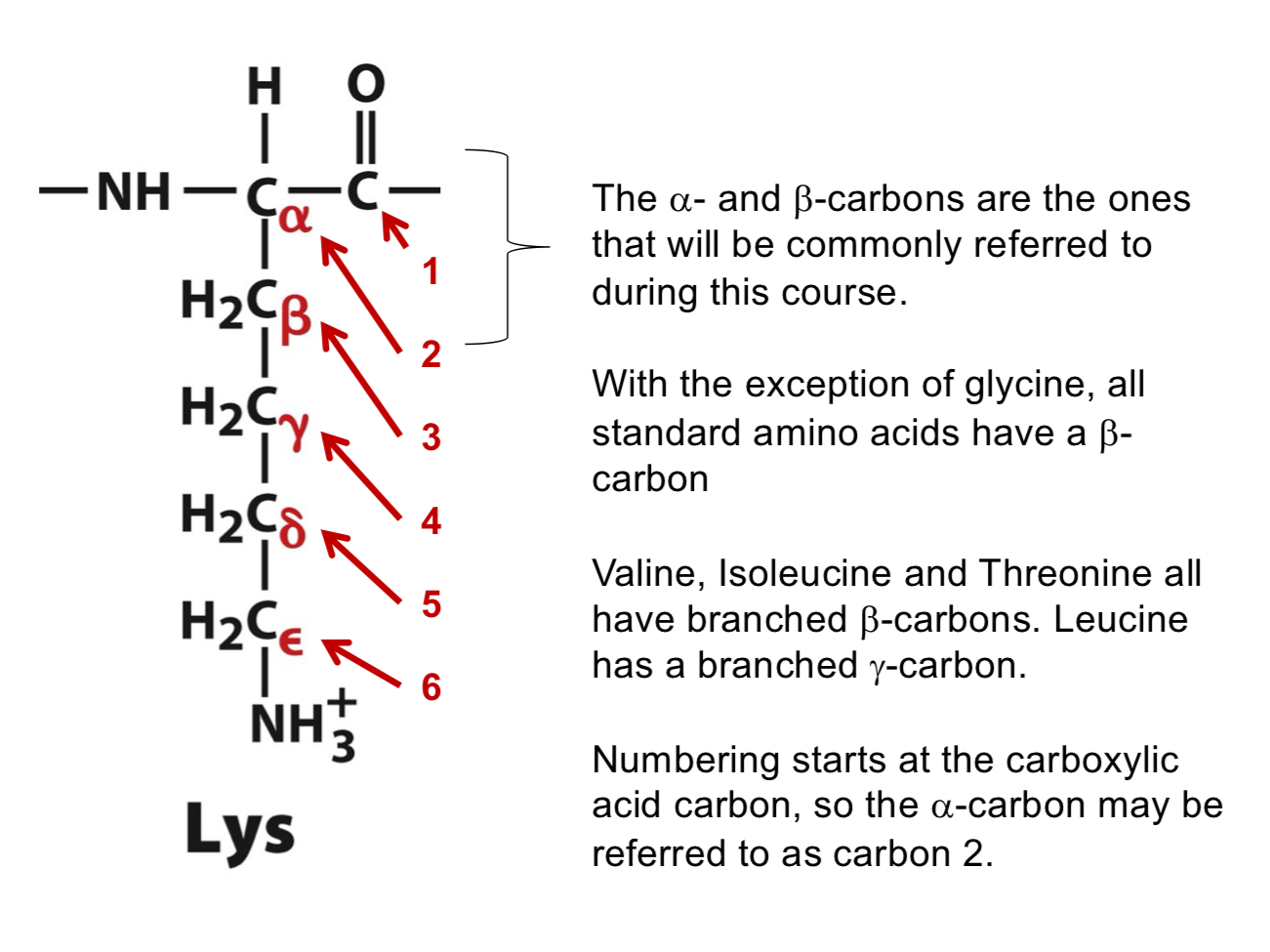
Can you list the 3 amino acids that have branched β-carbons?
valine (V)
isoleucine (I)
threonine (T)
What is the pKR of Histidine, and why is this biologically significant?
pKR: ~6.0
since this is close to physiological pH (7.4), Histidine can easily shift between protonated (charged) and deprotonated (neutral) states, making it a versatile catalyst
Can you define 1 Dalton (Da) in terms of atomic mass?
1 Dalton is 1/12 the mass of a 12C atom.
Which amino acid is the only one without a β-carbon?
Glycine (its side chain is just a Hydrogen atom).
According to the IUPAC numbering system for amino acids, which carbon is designated as "Carbon 1?”
The carbonyl/carboxylic acid carbon. (The α-carbon is Carbon 2).
Which amino acids fall under the "Charged Polar" category with a negative charge at pH 7.0?
Aspartic acid (D) and Glutamic acid (E).
What are the 2 sulfur-containing amino acids?
Methionine (M) and Cysteine (C).
What is Alanine?
Ala, A
non-polar
What is Valine?
Val, V
non-polar
What is Leucine?
Leu, L
non-polar
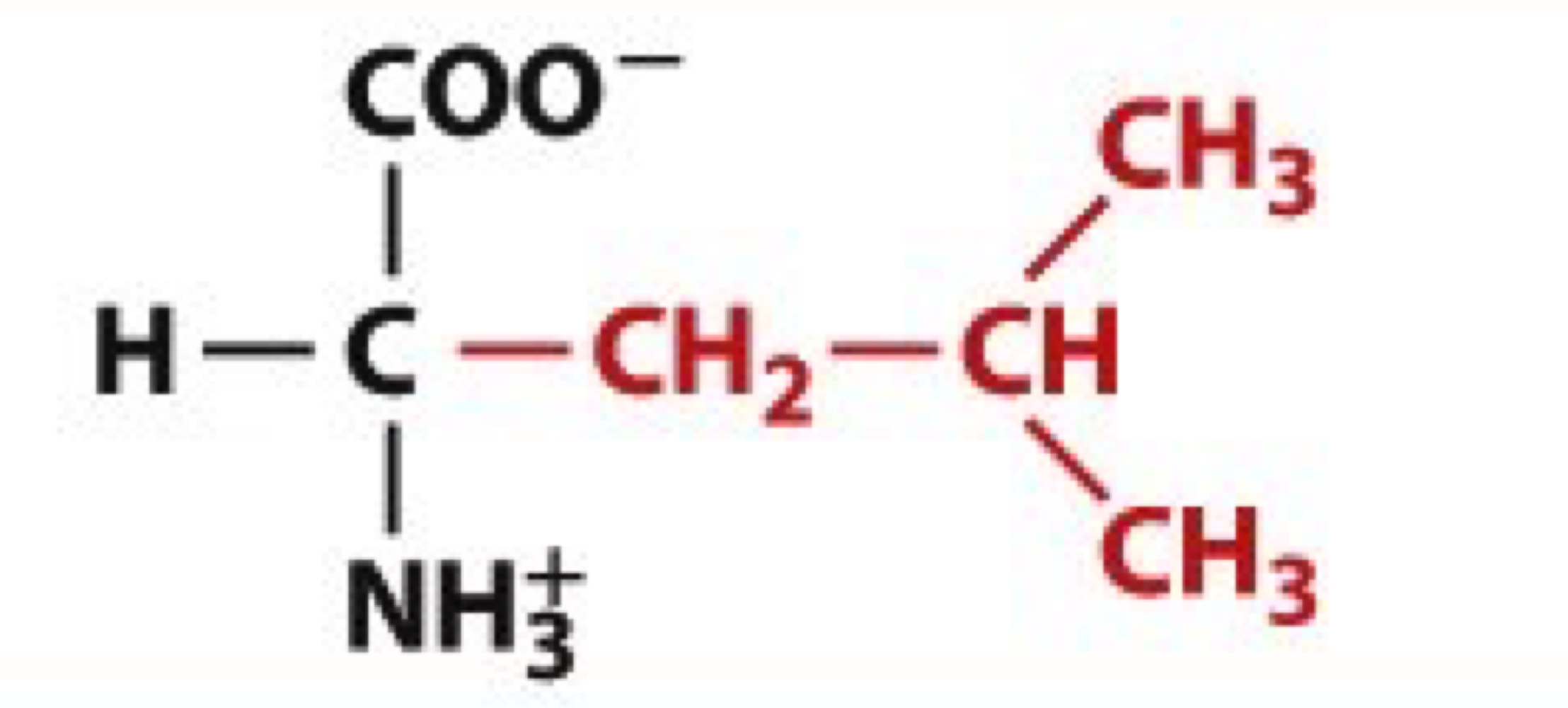
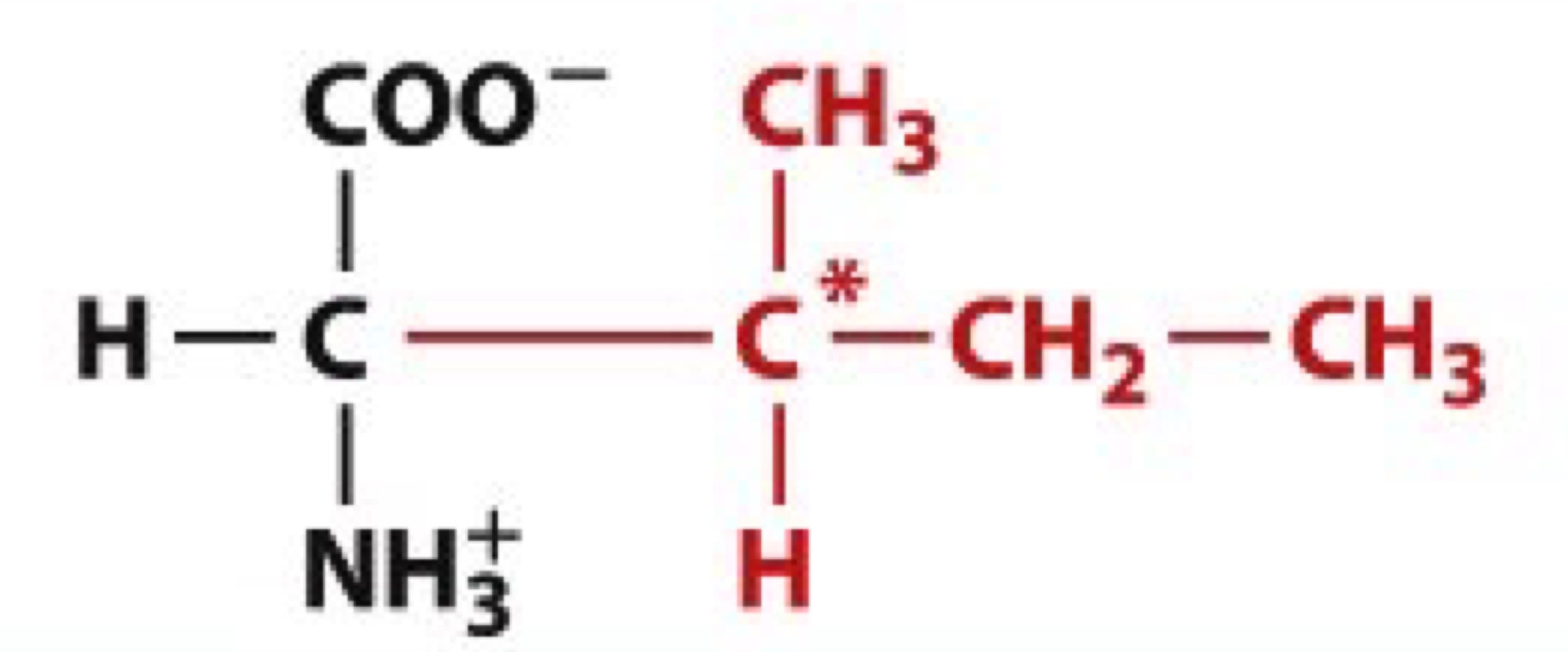
What is Isoleucine?
Ile, L
non-polar
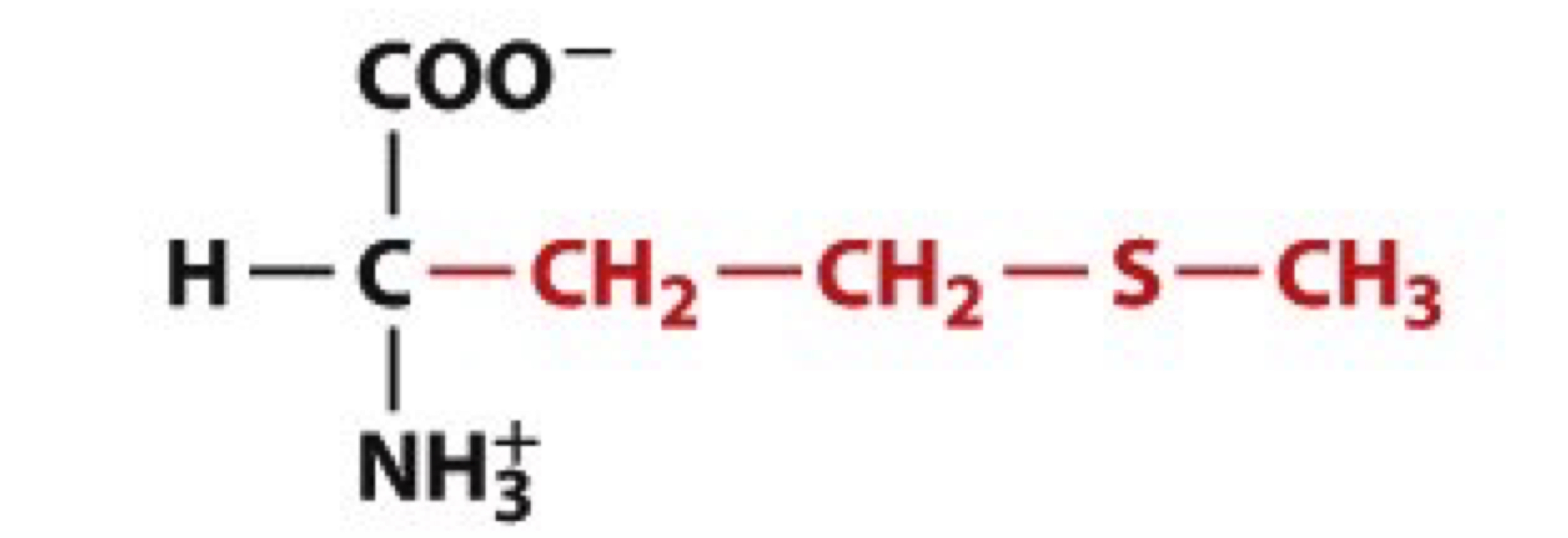
What is Methionine?
Met, M
non-polar
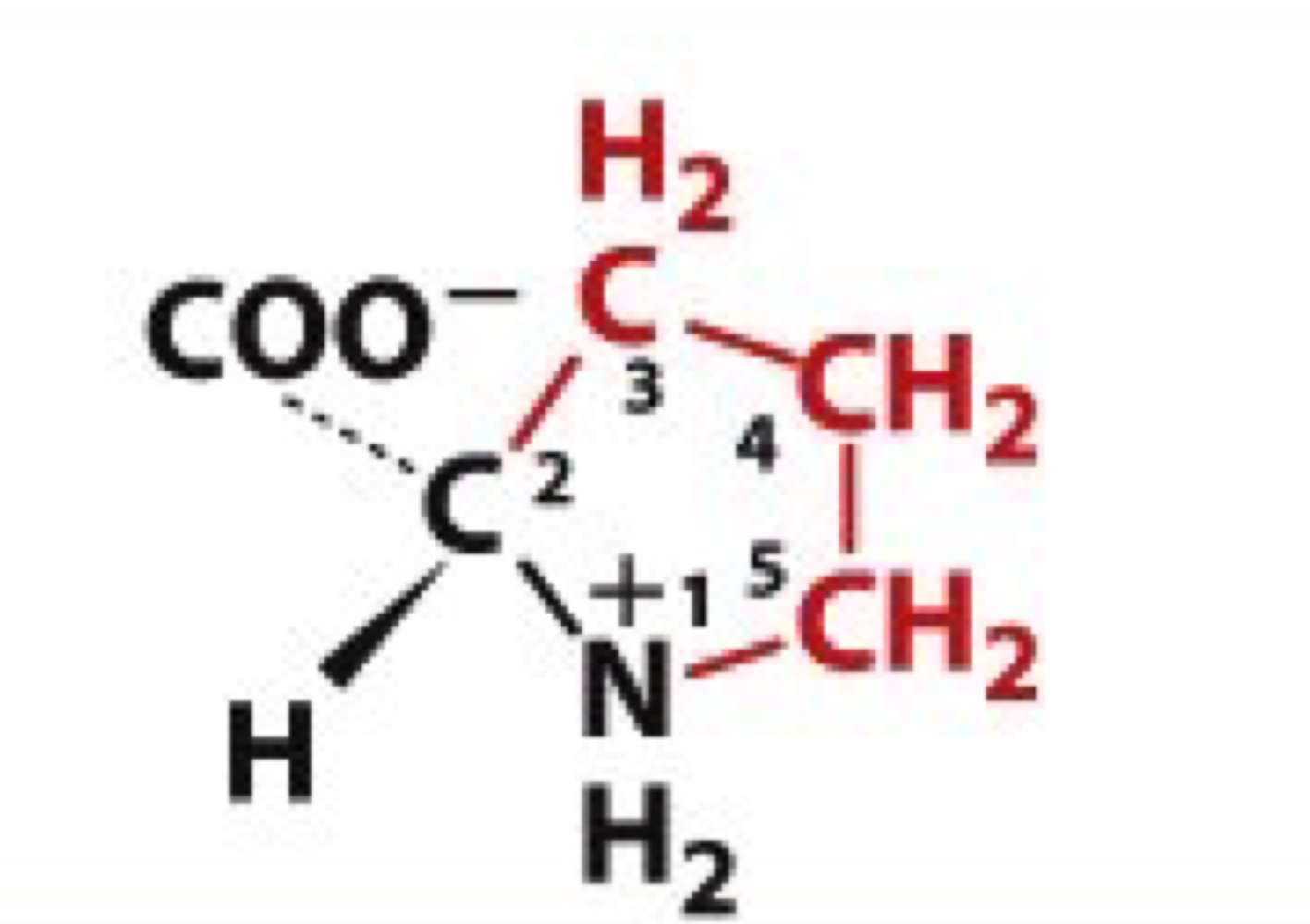
What is Proline?
Pro, P
non-polar
What is Phenylalanine?
Phe, F
non-polar
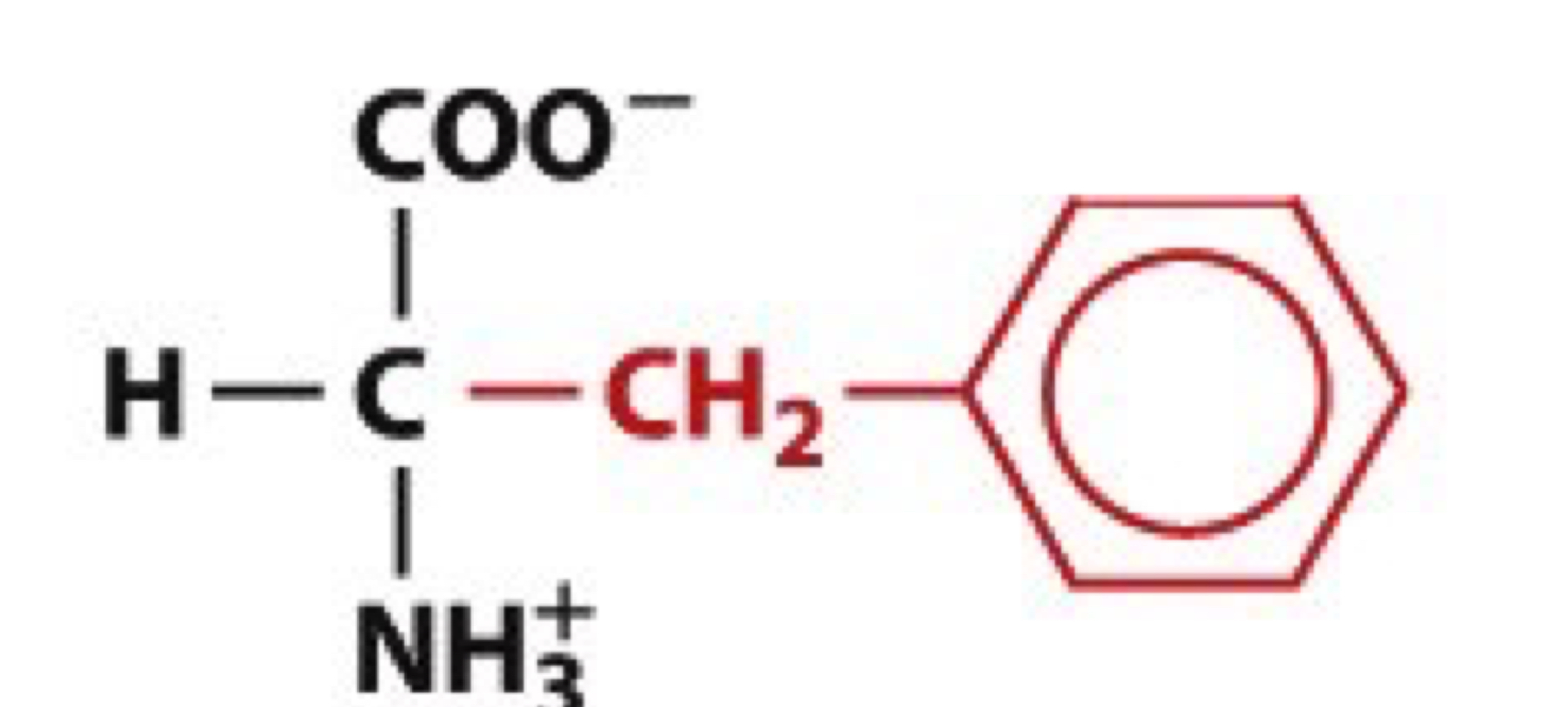
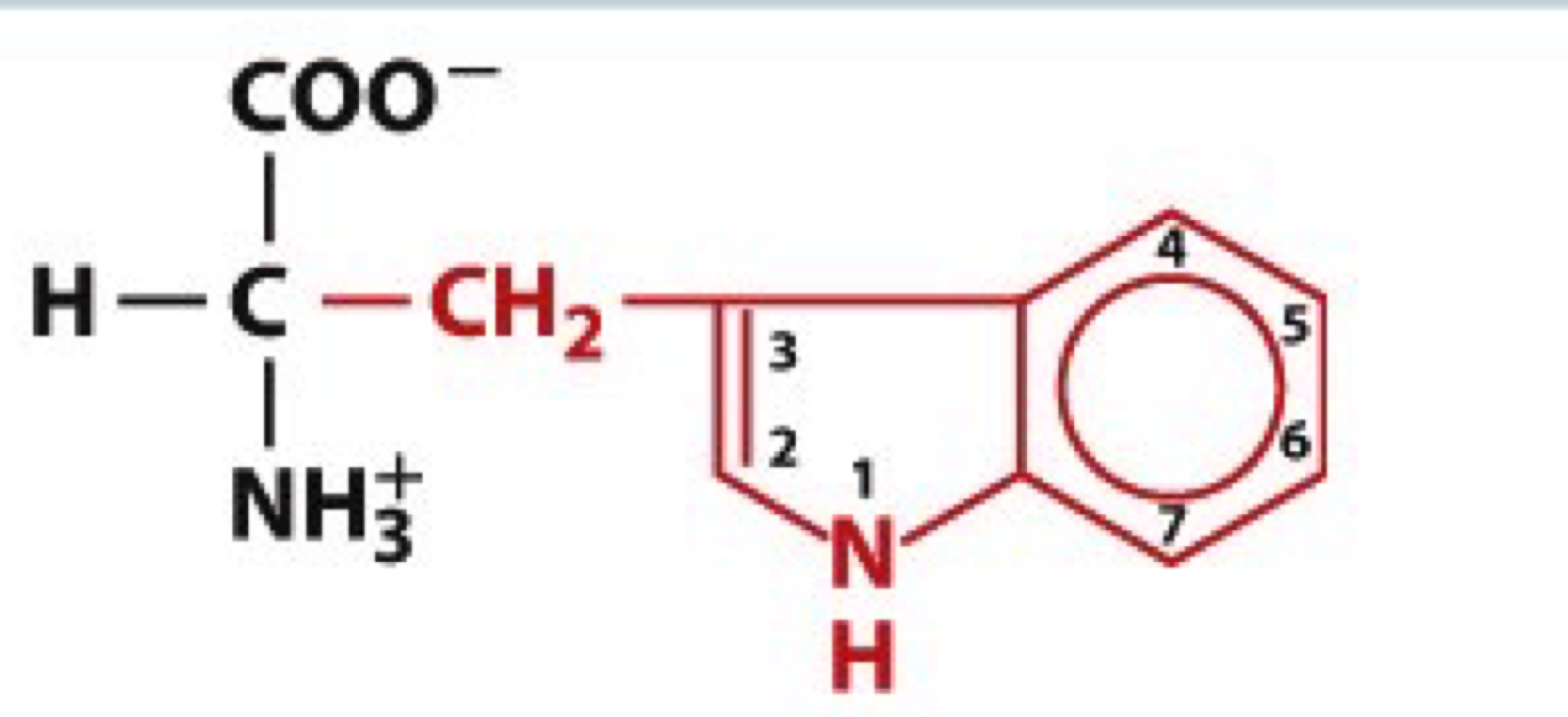
What is Tryptophan?
Trp, W
non-polar
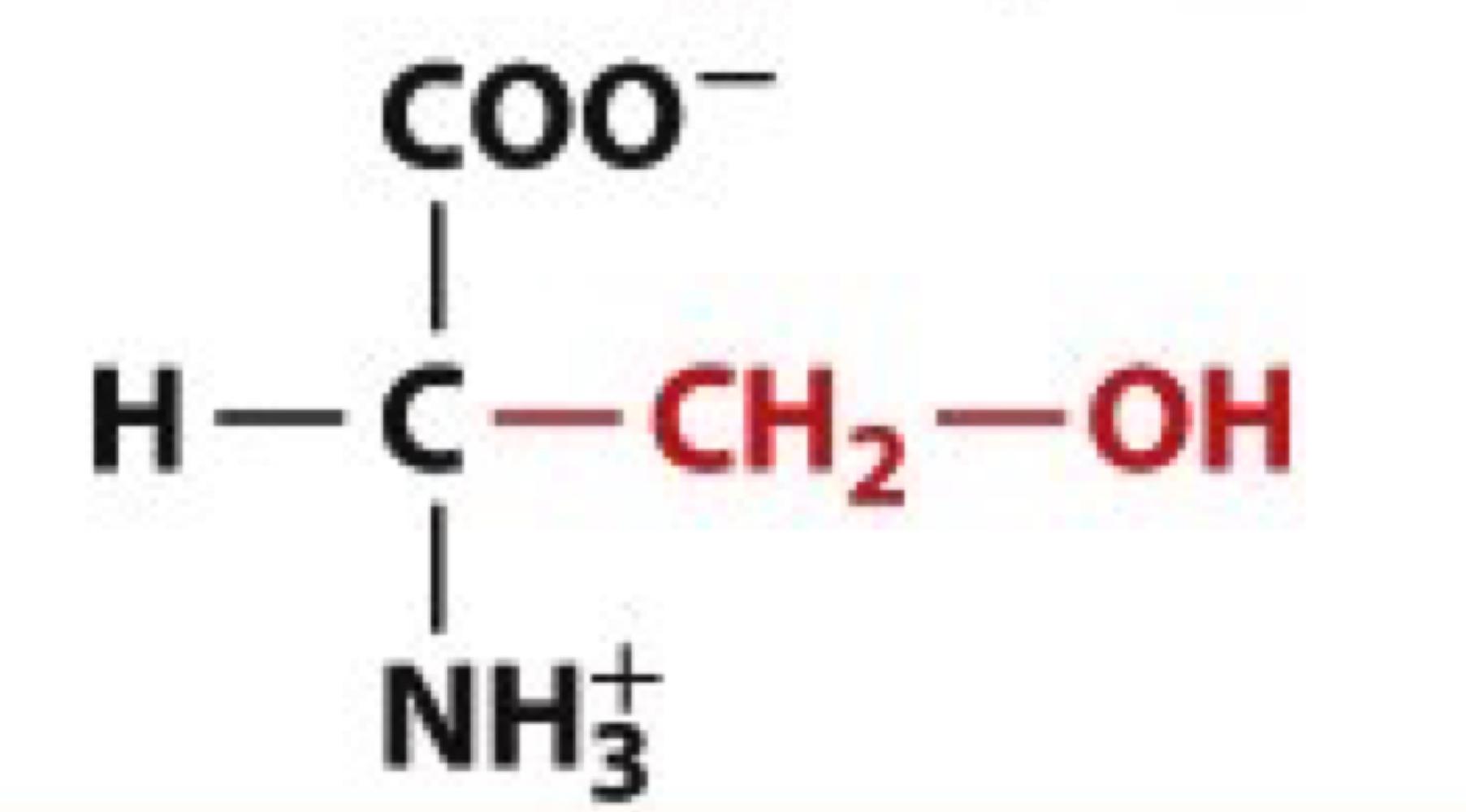
What is Serine?
Ser, S
uncharged
What is Threonine?
Thr, T
uncharged

What is Asparagine?
Asn, N
uncharged
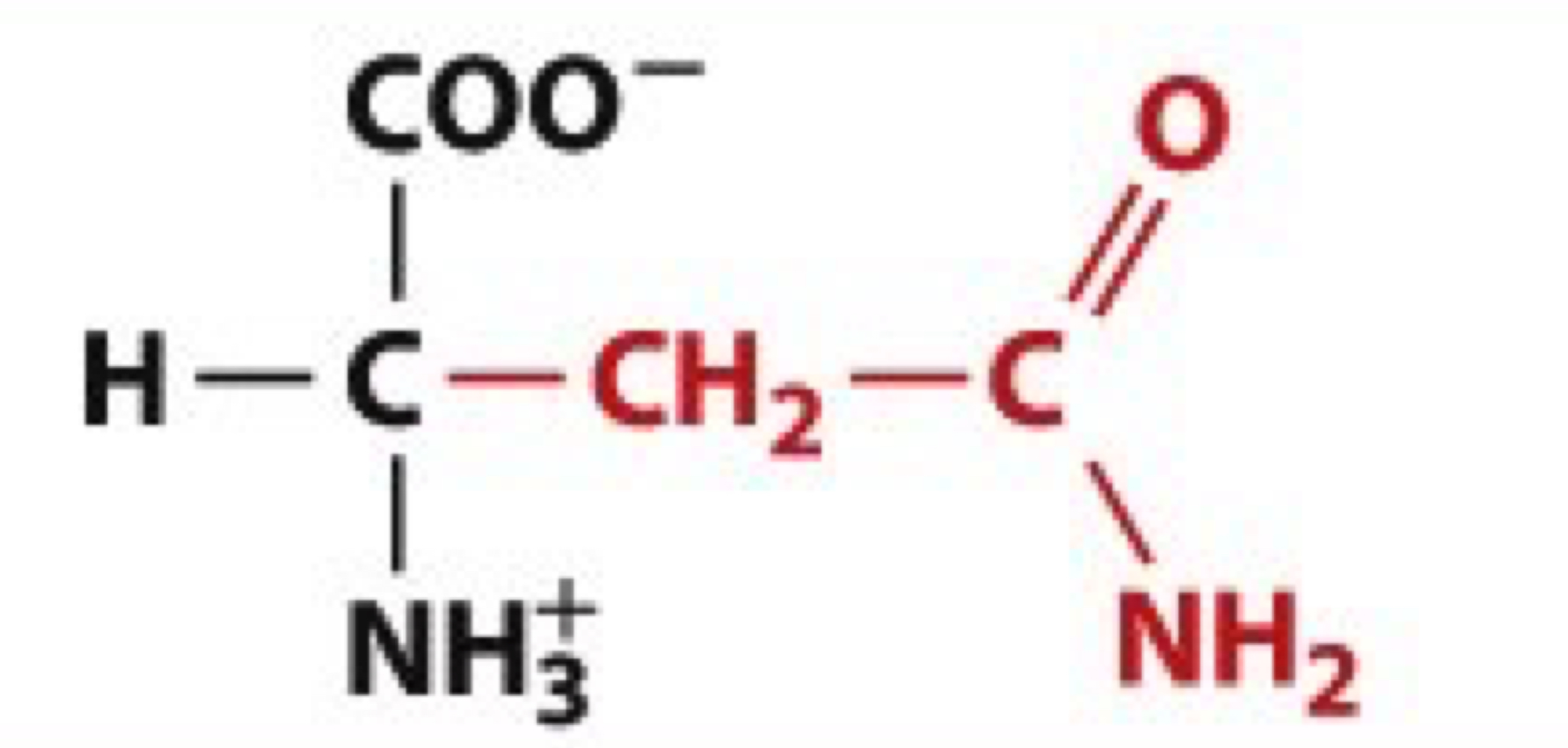
What is Glutamine?
Gln, Q
uncharged
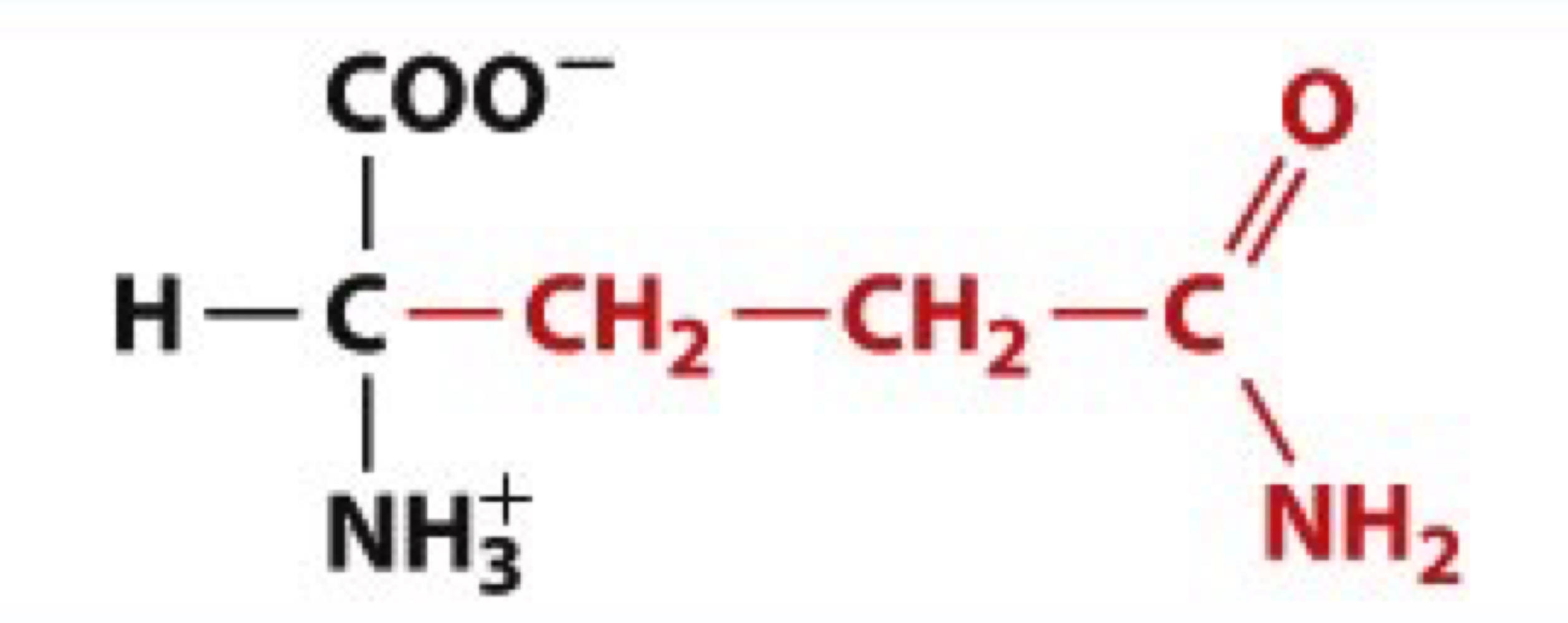
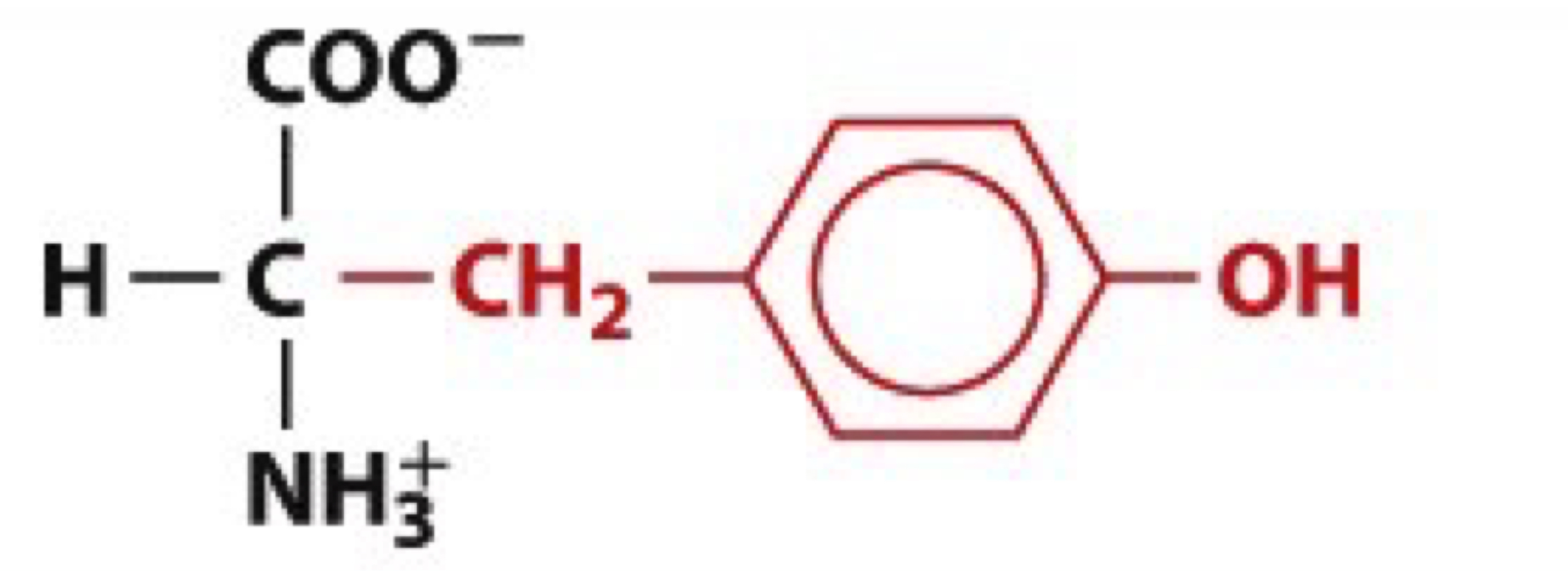
What is Tyrosine?
Tyr, Y
uncharged
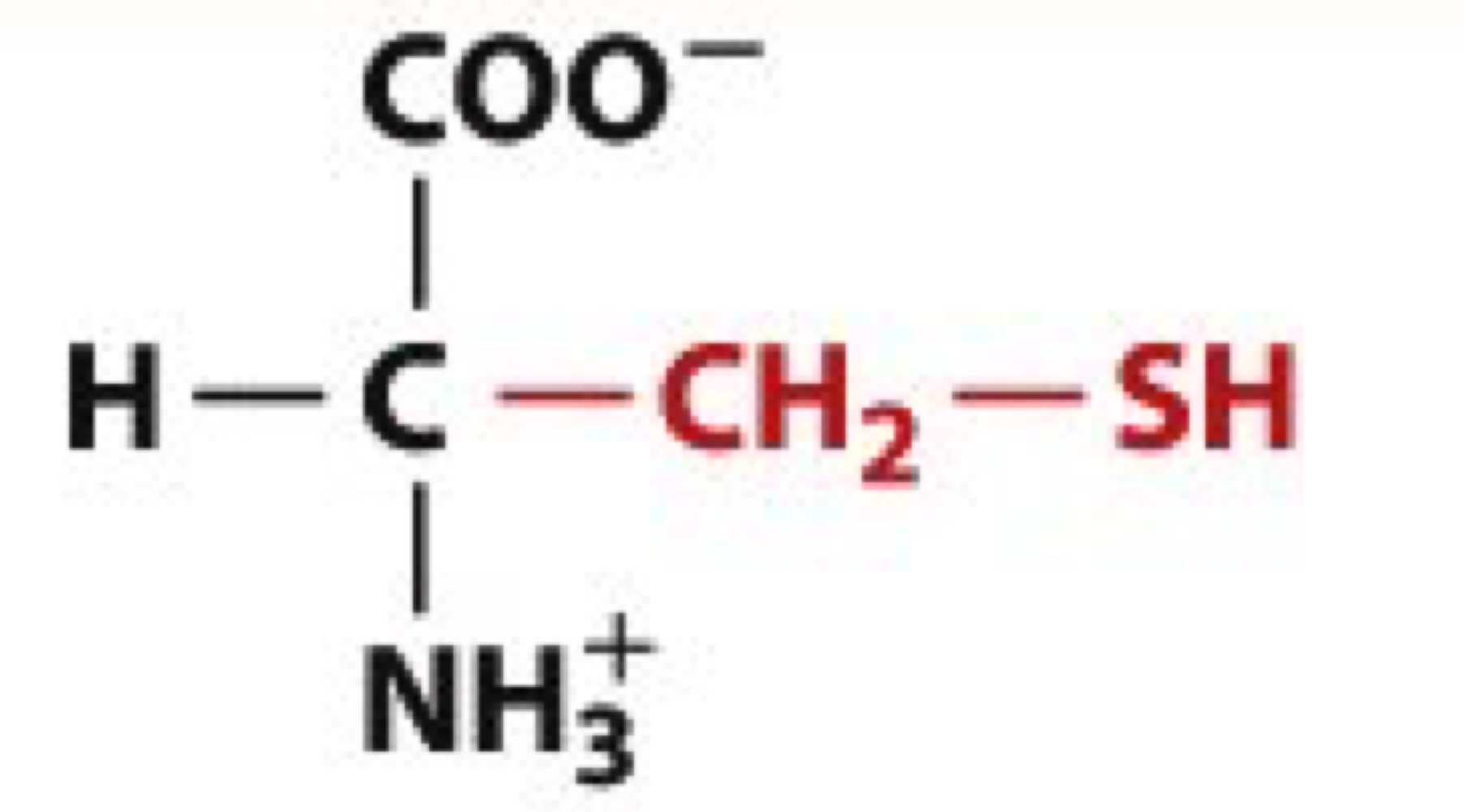
What is Cysteine?
Cys, C
uncharged
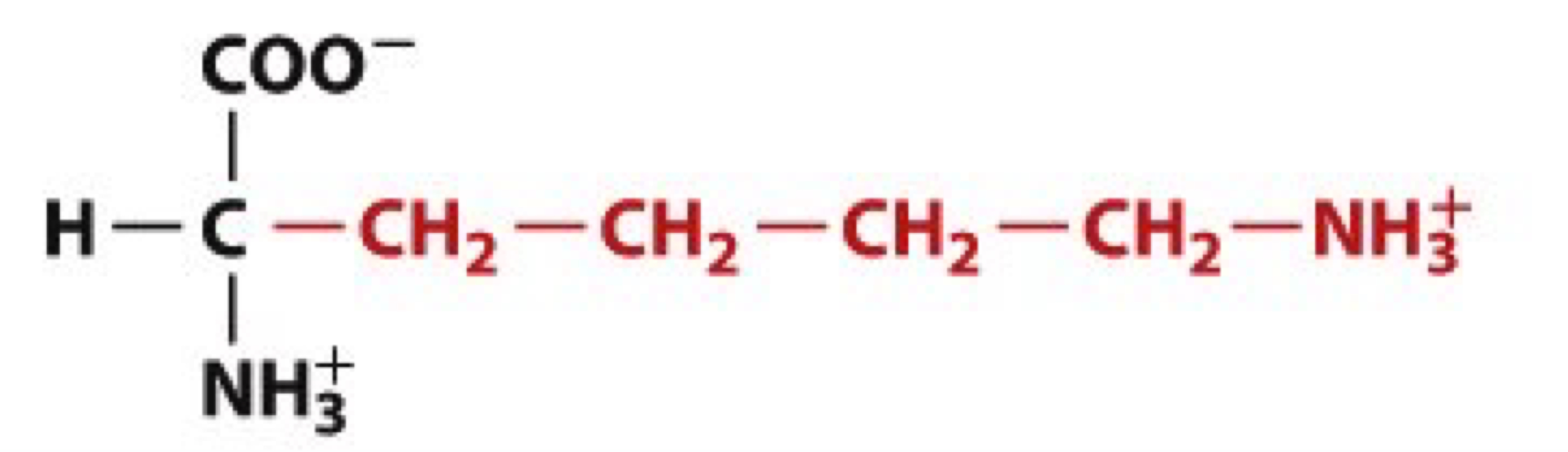
What is Lysine?
Lys, L
charged polar
What is Arginine?
Arg, R
charged polar
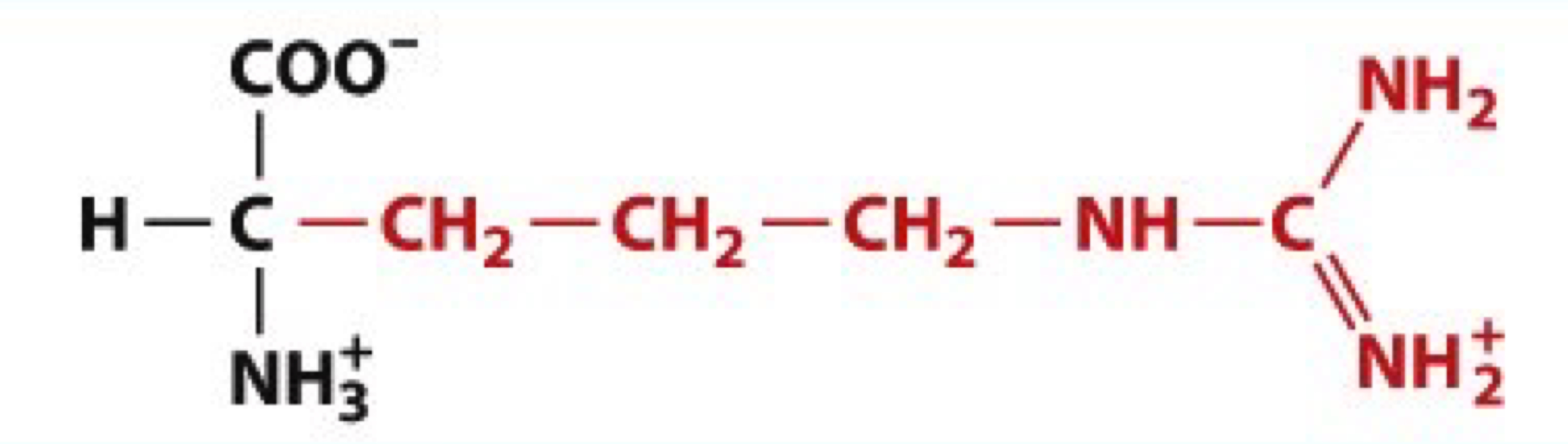
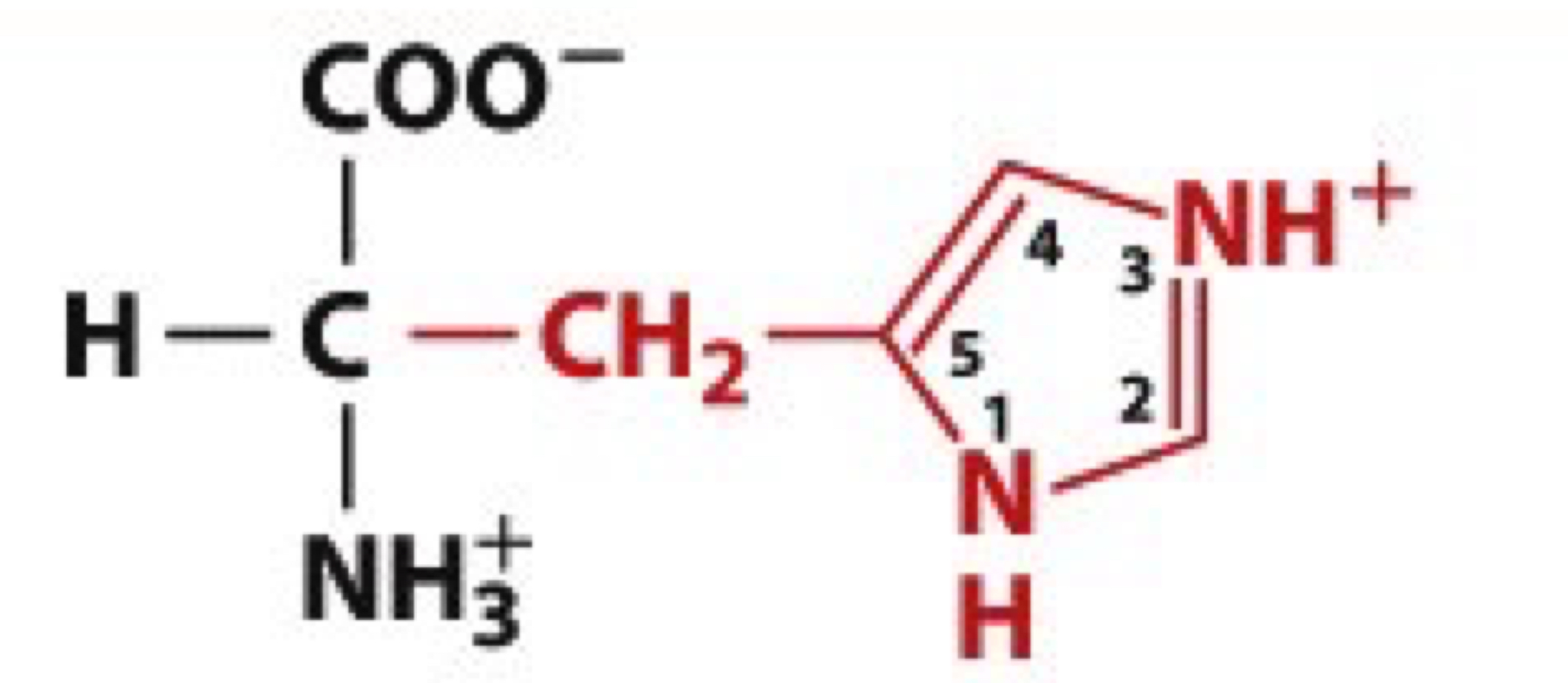
What is Histidine?
His, H
charged polar
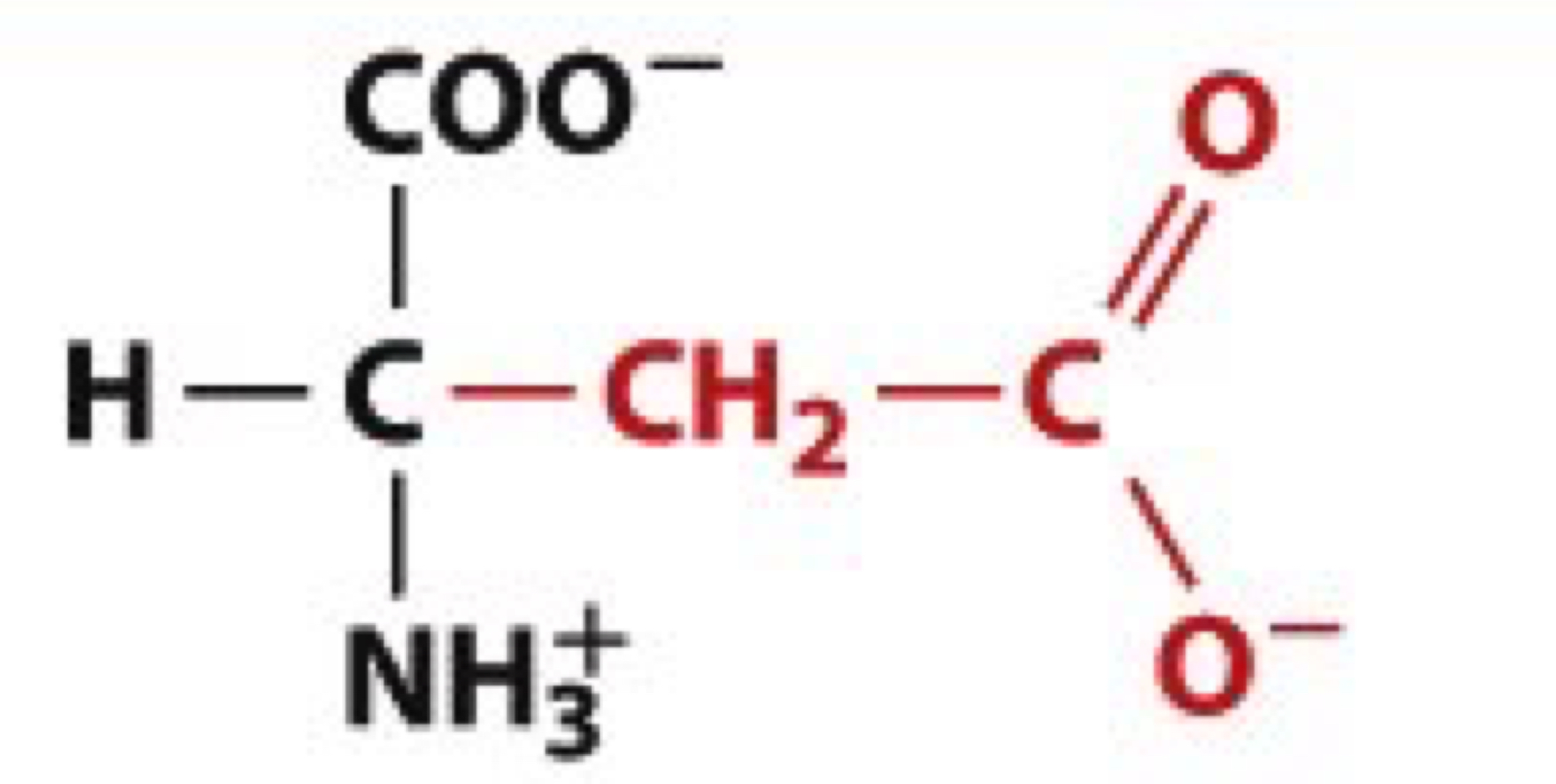
What is Aspartic acid?
Asp, D
charged polar
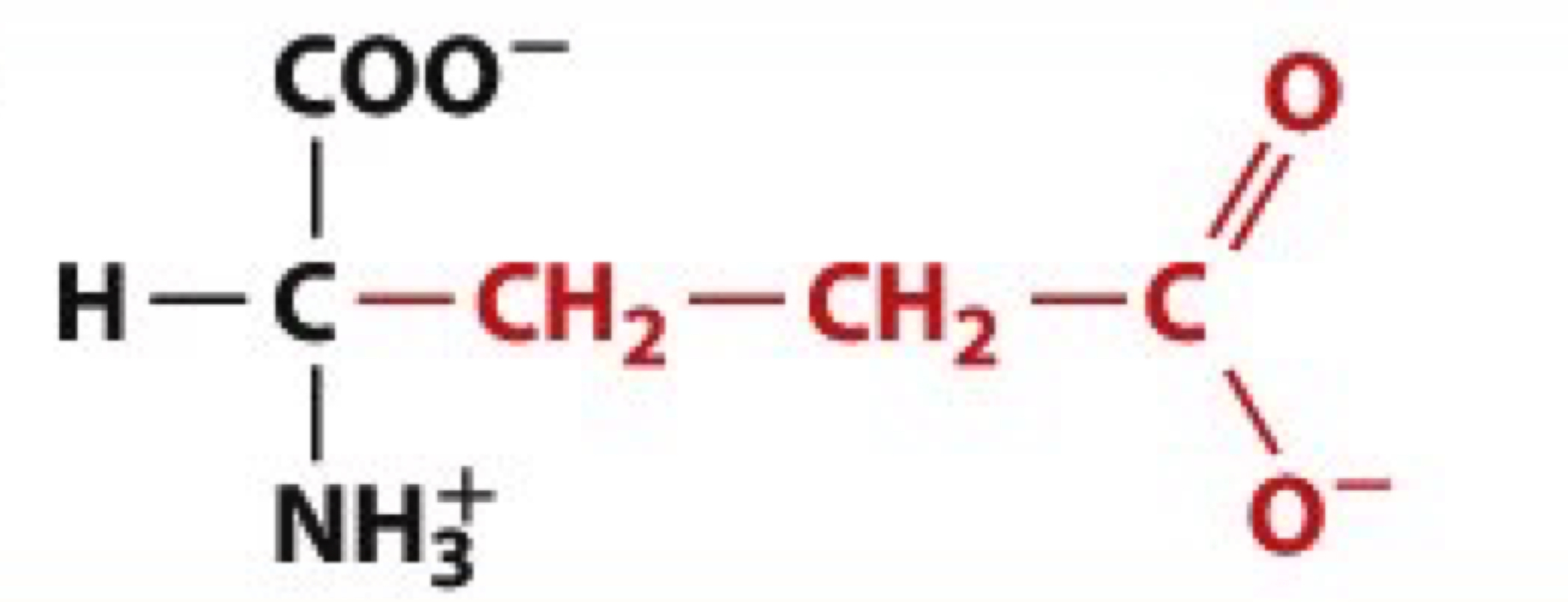
What is Glutamic acid?
Glu, E
charged polar
Which 3 codes are used for "ambiguous" amino acid analyses, and what does each represent?
Xaa (X): any or unknown amino acid
Asx (B): Asparagine (N) or Aspartate (D)
Glx (Z): Glutamine (Q) or Glutamate (E)
Which amino acids are frequently listed in parentheses, and why?
Glycine (G) and Histidine (H)
their properties are context-dependent:
Gly is borderline non-polar/polar, His’ charge depends on pH
In the Taylor Venn Diagram, which amino acids are categorized as "tiny?”
Glycine (G), Serine (S), and Cysteine (C).
Can you arrange the aromatic amino acids in order of decreasing polarity?
Histidine ➡ Tyrosine ➡ Tryptophan ➡ Phenylalanine
At what wavelength do Tryptophan and Tyrosine absorb UV light strongly, and what is the practical use of this?
~280 nm: allows for spectroscopic studies to quantify protein preparations and distinguish them from nucleic acids.
Which aromatic amino acid has the highest molar absorptivity at 280 nm?
Tryptophan (Trp).
Which 5 descriptors apply to Tyrosine's sidechain?
potential H-bond acceptor and donor
aromatic
polar
charged
large
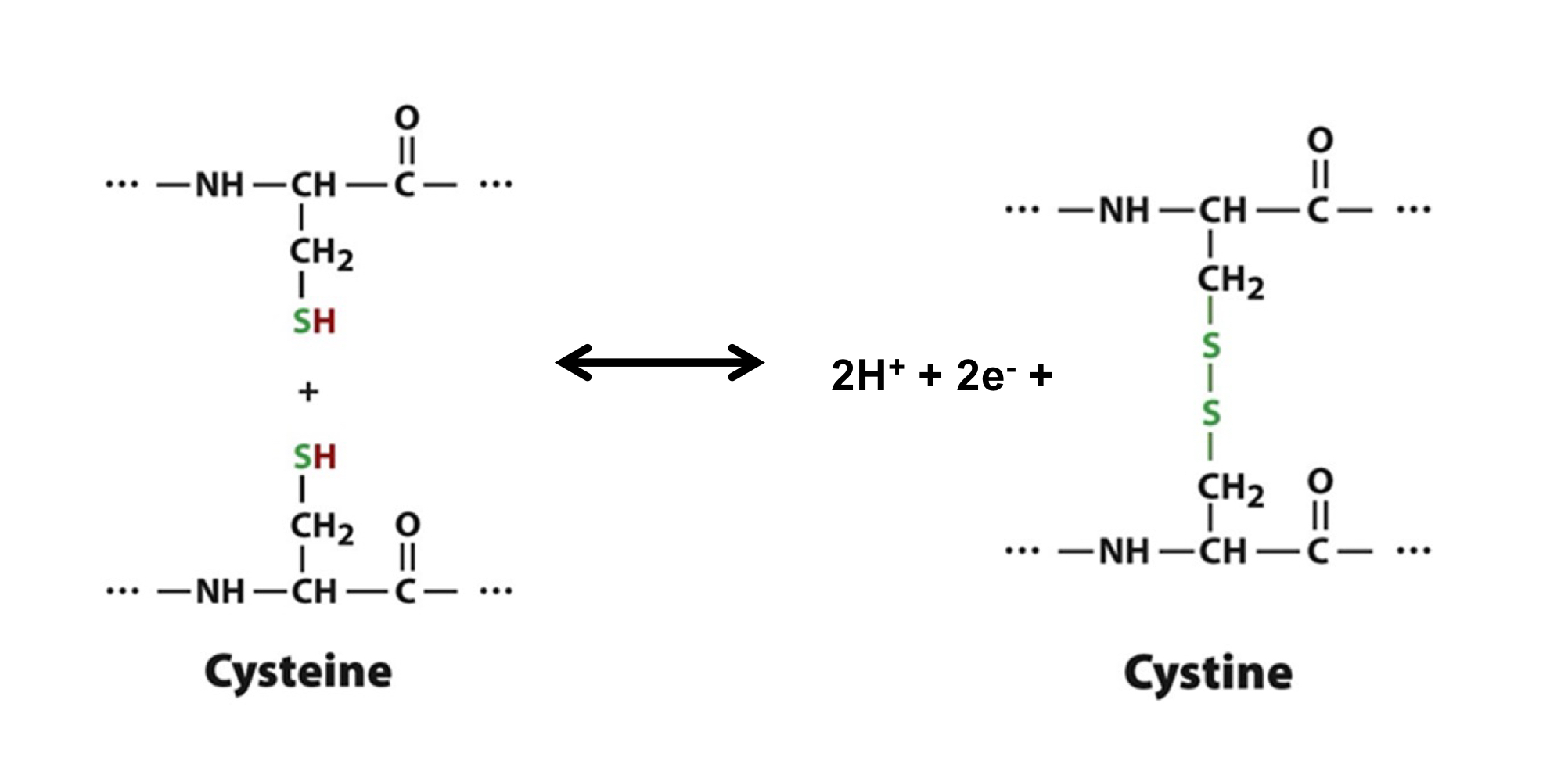
Can you describe the chemical shift that happens when Cysteine becomes Cystine?
oxidation of two Cysteine molecules forms a covalent disulfide bond (releasing 2H+ and 2e-)
occurs in oxidizing environments
ex. extracellular space, lumen of organelles
What is the pKa of the Histidine imidazole ring, and why is this biologically significant?
pKa: ~6.0
allows it to easily switch between protonated and neutral forms at physiological pH, making it a versatile catalyst
Aside from the Indole ring of Tryptophan, what other two sidechain systems show nitrogen delocalization?
Amides (Asn/Gln)
Guanido group (Arginine)
What is Selenocysteine (Sec, U) derived from, and what is its biological function?
derived from Serine
found in selenoproteins that break down peroxides (antioxidant properties) to prevent damage to tissues and DNA
What is the 22nd proteinogenic amino acid, and where is it found?
Pyrrolysine (Pyl, O)
found in methyltransferases of methanogenic archaea and bacteria
How are Selenocysteine and Pyrrolysine incorporated into proteins if they aren't "standard"?
Incorporated using variant codons; they aren’t "hard-coded" in the standard genome DNA in the same way the primary 20 are.
What is the bond angle of a water molecule, and what causes its polarity?
104.9°
polarity is caused by the difference in EN between oxygen (more negative) and hydrogen (more positive), creating a dipole
Can you define the ion product of water (Kw) and its value at 25°C?
Kw: [H+][OH-] = 1 x 10-14 M2
Can you match these substances to their pH: Blood, Milk, Household Ammonia, Vinegar, Gastric Juice?
Blood: 7.4
Milk: 4
Ammonia: 12
Vinegar: 3
Gastric Juice: 1.5
What is the "Water Paradox" in the context of the origin of life?
water is essential for life, but free movement of water must be controlled
wet-dry cycles (like on land) were likely necessary for polymers to form
Why is pH control critical for enzyme function?
enzyme activity is sensitive to pH (bell-shaped curve)
changes in pH affect the protonation/deprotonation of amino acids, which changes the enzyme's structure and catalytic ability
At what point is a buffer system most effective at resisting pH changes?
at the midpoint, where the concentration of the acid (HA) equals the concentration of the conjugate base (A-)
at this point, pH = pKa
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation?
pH = pKa + log [A-]/[HA]
What is the Zwitterionic form of an animo acid?
where the carboxyl group is deprotonated (COO-) and the amino group is protonated (NH3+)
net charge of zero and predominates at neutral pH
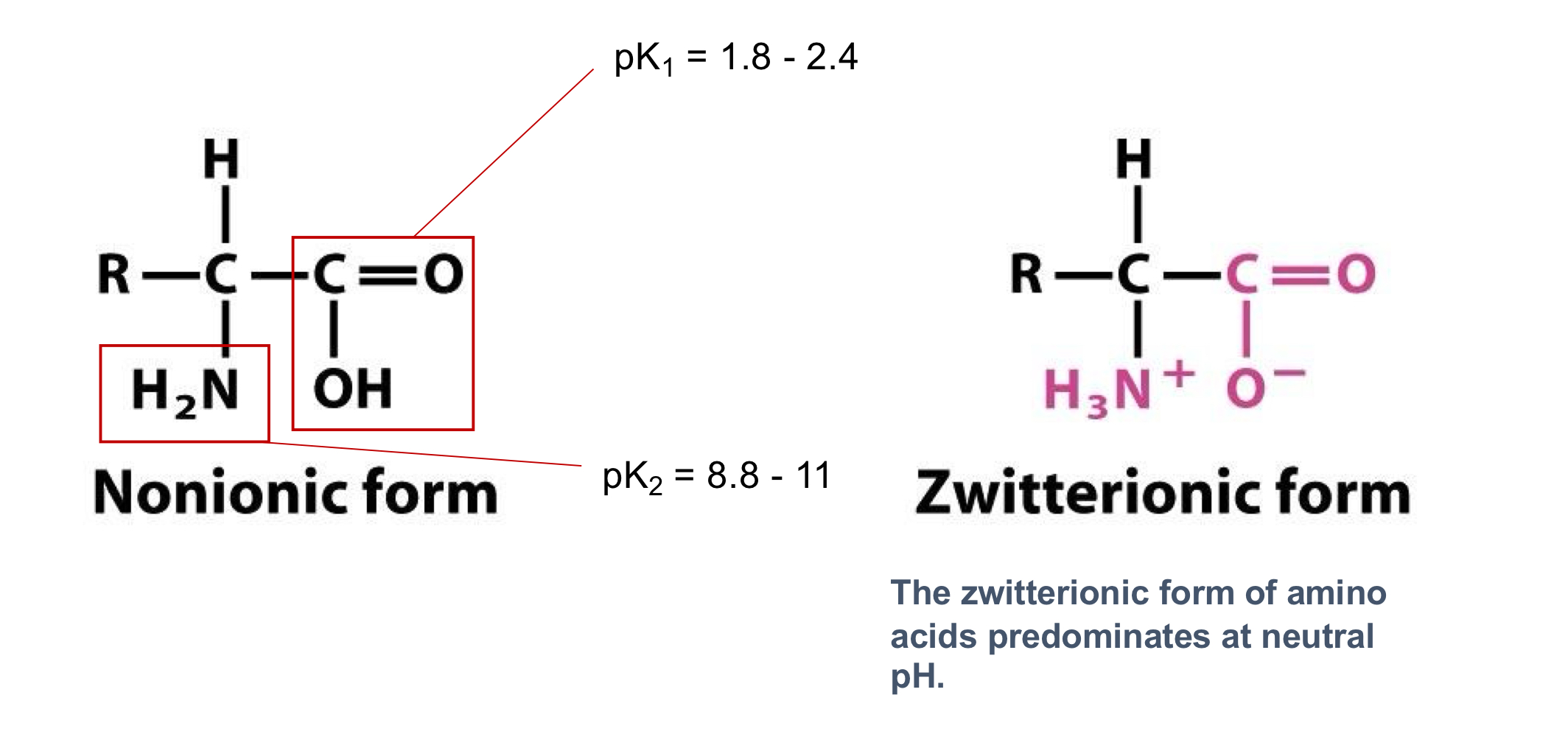
What are the typical pKa ranges for the α-carboxyl and α-amino groups of amino acids?
α-carboxyl (pK1): 1.8-2.4
α-amino (pK2): 8.8-11
What is the difference between reversible and irreversible post-translational modifications?
reversible modifications can be added and removed to signal/regulate
ex. O-Phosphoserine)
irreversible modifications are permanent changes to the structure
ex. 4-Hydroxyproline in collagen
How does Acetyl-lysine influence epigenetics?
It modifies the interaction between histones and DNA, changing how genes are accessed and expressed.
Can you name 2 amino acids that are metabolic intermediates but are NOT "coded" into proteins?
Ornithine and Citrulline (both part of the urea cycle).
Can you list 3 general roles of non-proteinogenic amino acids?
intermediates in biosynthesis/metabolism
neurotransmitters
components of bacterial cell walls
What does the pKa value specifically tell us about a functional group?
The pH at which the group is 50% protonated and 50% deprotonated (acidic properties).
Can you define the "Buffer Region" on a titration curve?
The flat region around the pKa where [HA] = [A-] and pH changes slowly.
In the Henderson-Hasselbalch rearrangement, what does a ratio of 101 mean?
There is 10x more Conjugate Base (A-) than Acid (HA).
What is the formula for the fraction of base?

Why is Histidine's side chain (pKR = 6.0) biologically significant?
Its pKa is near physiological pH, allowing it to switch states easily in the body.
How do nearby negative charges affect a pKa value?
They raise the pKa (it becomes harder to remove the proton).
How do nearby positive charges affect a pKa value?
They lower the pKa (it becomes easier to remove the proton).
Why does Hydroxylamine (NH2OH) have a lower pKa than Ammonia (NH3)?
The Oxygen is electron-withdrawing, which polarizes the N-H bond and makes the proton easier to remove.
What is the Isoelectric Point?
The pH at which a molecule carries no net charge (charge = 0).
Can you calculate the pI for Glycine using pKa1 = 2.3$ and pKa2 = 9.78?
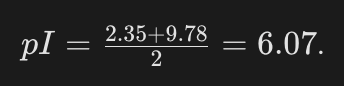
How does the pKa1 of Alanine change as you increase the peptide chain length (ex. Ala to Ala-Ala)?
The pKa1 increases (from 2.34 to 3.12, etc.) as the carboxyl group is moved further from the positively charged amino group.
What is the net charge of a diprotic amino acid like Glycine at a very low pH (pH < 2)?
+1 (Both the carboxyl and amino groups are protonated).
On a titration curve, what is physically occurring at the point where pH = pKa?
this is the midpoint of titration where the concentration of the protonated species equals the concentration of the deprotonated species
ex. [COOH] = [COO-]
What is the formula for the isoelectric point (pI) of basic amino acids like Histidine, Arginine, and Lysine?
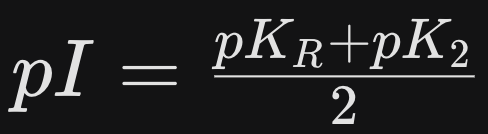
How many buffering regions (plateaus) would you expect to see on a titration curve for Histidine, and why?
3
Histidine is triprotic: has 3 ionizable groups (α-carboxyl, imidazole side chain, and α-amino), each with its own pKa
In the Histidine titration curve, what is the net charge of the species existing between pKa1 (carboxyl) and pKa2 (side chain)?
+1
Based on the class notes, if Histidine has a pKR of 6.04 and a pK2 of 9.3, what is its pI, and what is its charge at that pH?
the pI is 7.69 (or 7.67 depending on rounding)
at this pH, its net charge is 0 (neutral)
Why does the titration curve for amino acids "flatten out" at the $pKa$ values?
Because the amino acid is acting as a buffer at those points, resisting changes in pH as protons are added or removed.
Which amino acid requires more nNaOH/n (base) to reach a net charge of -1: Glycine or Histidine?
Histidine: it requires roughly 3 equivalents of base to reach the -1 state
Glycine only requires 2, because Histidine has an extra ionizable proton on its side chain