Immunology Quiz 4
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Define vaccine.
Product that stimulates person’s immune system to produce immunity to a specific disease.
Goal is to protect against severe disease & death.
Vaccine typically used for prevention. This makes them function as _____________.
Prophylactics.
What are the 4 vaccine characteristics?
SPSP:
Safe: minimal side effects
Protective: against illness caused by live pathogen exposure
Sustained Protection: several years
Practical: Low cost-per-dose, stable, easy administration
Give an example of an eradicated disease.
Smallpox (Variola virus)
What is variolation?
Old practice where pus from infected person was injected into live human.
Improved outcomes rate, but not safe enough to be approved today.
Describe the heterologous vaccine class.
Closely related microorganism.
Attenuated vaccine class.
Weakened microorganism.
Inactivated vaccine class
Killed microorganism.
Toxoid vaccine class.
Inactivated bacterial toxin.
Subunit vaccine class.
One or multiple antigens from infectious agent.
Conjugate vaccine class.
Weakly immunogenic polysaccharide antigen attached to immunogenic carrier protein.
Allows for cells to uptake and present (heightened immune response).
What are the limitations of live attenuated vaccines?
Reactogenic: causes strong reactions.
Possible reversion to active virus → infection of unvaccinated through fecal transmission
What are the limitations of inactivated vaccines?
Reactogenic: causes strong reactions.
What are the limitations of subunit vaccines?
Reduced efficacy compared to other vaccine types.
What are the limitations of toxoid vaccines?
Potentially reactogenic
Single antigen only.
Which vaccine class commonly uses adjuvants?
Subunit vaccines.
What is the function of an adjuvant? (5)
Increases immunogenicity of weak antigens.
Enhances speed & response of immune.
Stims production of antigen specific antibodies and T cells.
Enhances immune response in immunologically immature patients (ie. infants).
Decreases dose of antigen required for protection.
What is one of the limits of COVID vaccines in developing countries (besides cost)?
Must be kept at very low temperatures.
What is a facultative intracellular pathogen?
Give 3 examples.
Can survive in and out of cell.
Salmonella, Shigella, Yersinia
What are obligate intracellular pathogens?
Give 3 examples.
Hard to grow in lab, in cell only.
Rickettsia, Chlamydia, Coxiella
Give 4 examples of extracellular pathogens.
Vibrio cholerae, Pseudomonas, enterotoxigenic E. coli, Bordetella pertussis.
What are commensals?
Microbes that reside in or on the body without harming health.
Overgrowth can cause disease.
What are transient flora?
Colonize for hours to weeks, no permanent association.
May cause disease.
What are primary/overt pathogens?
Capable of causing disease in healthy individuals.
What are the steps in the infectious cycle of extracellular pathogens?
Entry/attachment
Local or general spread
Multiplication
Evasion of host defenses
Damage
Shedding from body/transmission
What are 5 common portals of entry for pathogenic microorganisms?
Respiratory tract
Gastrointestinal tract
Skin and mucous membranes
Genitourinary tract
Direct inoculation
Vector
Cuts/scrapes
Surgery/indwelling device
Describe the first stage of bacterial attachment.
Nonspecific (locking)
Hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions
Usually low affinity
Reversible transient binding to surfaces
Describe the second stage of bacterial attachment.
Specific (anchoring/locking)
Reversible specific binding to surfaces
“Lock & key” bonds b/w complementary molecules on each cell surface
Usually high affinity interactions
What are the two main strategies for bacterial attachment?
Direct adhesin-receptor interaction
Indirect via a bridging molecule
What is tropism in regards to bacteria?
Tissue specificity which is determined by adhesion-receptor interactions.
What host factors and bacterial factors contribute to dissemination (spread) of bacteria?
Host:
Fluid movement
Localized inflammation
Cellular trafficking
Bacterial:
Motility
Localized production of enzymes
Type-IV pilus mediate what kind of motility? What is this motility type best suited for?
Twitching motility. Allows for movement along solid and mucosal surfaces.
Like inchworm.
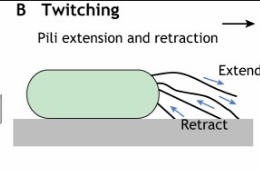
List 3 types of evasion strategies for each category: stealth, frontal attack.
Stealth:
Hide (capsules, biofilms)
Run (antigenic variation, modify surface)
Molecular mimicry
Frontal attack:
Kill (toxins)
Disarm (toxins, proteases, peptidase)
Invade
Give 4 ways bacterial toxins may target host cells?
Damage membranes (pore forming)
Cleave host surface components
Modulate signal transduction pathways
Protein synthesis inhibition
What are cytotonic toxins?
Alter cellular pathways but don’t kill cells.
Define sporadic disease.
Groups of cases that occur infrequently or irregularly.
Define an epidemic/outbreak.
Disease occurrence higher than normal but contained in small population.
Ie. When COVID was in china only.
Define a pandemic.
Disease or condition that spreads across regions, large-scale disruption.
Ie. COVID during lockdown.
Define an endemic.
Disease/conditions present among population at all times.
Ie. Maybe COVID now.
What is disease incidence?
Rate of new cases over period.
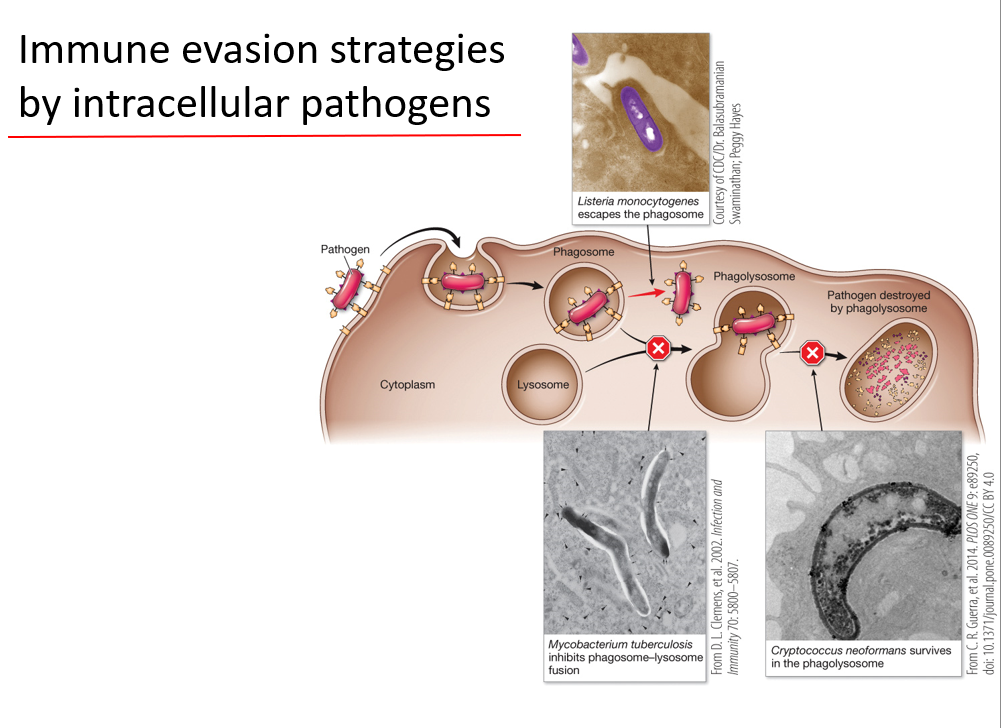
What are some ways intracellular pathogens evade the immune system?
Intra:
Escape phagosome and survive in cytosol of phagocyte
Prevent phagosome-lysosome fusion
Survive in phagolysosome w/o being digested
What are some immune evasion strats by extracellular pathogens?
Genetic variation
Toxins & proteases
What are 3 mechanisms for genetic variation in bacteria?
Multiple varied gene copies that contain own on/off switch
Have one expression locus with many silent gene copies. Copies can be switched into locus via gene rearrangement when necessary.
Highly variable region in gene product that can change when needed.
Briefly describe the gonorrhoeae pilin mechanism for antigenic variation.
Homologous recombination between expressed locus and silent locus in variable region only (adhesion region conserved).
What are the categories of bacterial toxins?
Endotoxins: pathogen component
Exotoxins: pathogen secreted
How do toxins disrupt phagocytosis?
Phagocytosis require remodeling the actin cytoskeleton. Some toxins can inhibit the actin cytoskeleton.
Ex. Yersinia pestis (plague)
What is an injectosome?
Delivers toxin into host cell.
In which 2 ways can extracellular pathogens evade antibodies?
Proteases inactivate/cleave IgA
Binds protein to Fc region of Ab so it can no longer bind to host (competes)
Give the 3 biofilm locations.
Tissue surface
Foreign body surface
Within secretions and tissues
What is the difference between an antibiotic and antimicrobial agent?
Antibiotics are produced by microorganisms. Antimicrobial agents are chemicals.
What is the difference between bacteriostatic and bactericidal?
Cidal causes cell death while static only prevent growth.
What is the old way of measuring efficacy of antibiotics/agents? What about the new way?
Old:
Minimal inhibitory concentration
Takes long time in individual tubes
New:
E test
Non-porous plastic strip with gradient placed on plate
Mult. per plate = less sample needed
What is empiric therapy?
Infection treatment when infectious agent is unknown.
Uses broad-spectrum.
What is tolerance? What affects it?
Host reaction to antibiotic.
Toxicity (antifungals more)
Probability of allergic rxns
Effects on normal flora
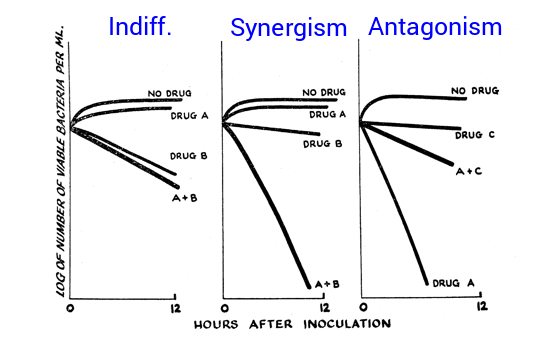
What are the three types of antibiotic interactions when multiple are used in combination?
Indifference: no effect
Synergism: combined effect greater than additive of each individually.
Antagonism: combined effect worse than additive of each individually.
Define efficacy.
How a bacteria responds to an antibiotic.
Which antibiotics target cell wall biosynthesis?
B-lactams
Penicillin’s
Cephalosporins
Carbapenem’s
Monobactams
Glycopeptides
Polypeptides
How are some bacteria resistant to B-lactams??
B-lactamase breaks B-lactam ring.
What is the basic mechanism for B-lactam and glycopeptide antibiotics?
Prevent cross-linking of peptidoglycan strands.
What is the basic mechanism of polypeptide antibiotics?
Halt synthesis of cell wall components.
Which antibiotic family targets DNA synthesis? What to they target specifically?
Quinolones → DNA gyrase.
Which antibiotic targets RNA synthesis? What is its specific target?
Rifampicin → B subunit of RNA polymerase
Which antibiotics target protein synthesis? Give each’s specific target.
Aminoglycosides → cause mRNA codon to be misread
Tetracyclines → interfere w/ binding of tRNA
Macrolides → block exit tunnel, prevent peptide chain elongation
Linezolid → prevent formation of 50/30s ribosomal complex
What are the anti-metabolite antibiotics? Which metabolic pathway do they target?
Sulfamethoxazole, trimethoprim → folic acid synthesis (major source of building blocks for nucleic acids).
Give 3 mechanisms of acquired antibiotic resistance.
Reduced accumulation (efflux, permeability changes)
Antibiotic inactivation (acetylation, cleavage)
Altered target (mutation selected for)
What does the ESCAPE acronym stand for?
Most problematic pathogens:
Enterococcus faecium (device biofilms)
Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
Clostridium difficile (gram neg)
Acinetobacter baumanii (hospital issue, intrinsic immunity)
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (common in compromise immune population, intrinsic immunity)
Enterobacteriaceae (E. coli, etc.)