Bio "Cells" Unit Test Part 1- Cell functions, Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic, Microscope
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
The Cell Theory states that…?
All living organisms (things) are composed of cells
Cells are the basic unit of life
All cells come from other, pre-existing cells
What are the differences plant cells have compared to animal cells?
They contain a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a central vacuole, things animal cells do not have.
What are some similarities between plant and animals cells?
They are both Eukaryotic
Both have a cell membrane, a nucleus, cytoplasm, ribosomes, golgi, mitochondria, and ER
What are the differences animal cells have compared to plant cell?
Animal cells have centrioles and lysosomes which plant cells do not.
How are Eukaryotic Cells Similar to Prokaryotic cells?
They both have…
A cell membrane
Ribosomes
DNA
Cytoplasm
How are eukaryotic cells different compared to prokaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells
Have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Typically larger than prokaryotic cells
More complex
Cell Membrane Function
Membrane that separates and protects the interior of the cell. It only lets certain things in and out of the cell which keeps the cell stable (homeostasis).
Cell Wall Function
Layer that provides additional protection to cell
Nucleus Function
The control center of the cell, holds DNA
Cytoplasm Function
Surrounds cell structures and supports organelles
Ribosome Function
Turns RNA into chains of proteins (makes proteins)
ER (Rough and smooth) Function
Makes and moves proteins and lipids around the cell
Golgi Function
Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to other organelles.
Mitochondria Function
Produces energy and powers the cell through cellular respiration.
Chloroplast Function
Makes glucose (energy) using light energy aka photosynthesis
Vacuole Function
Stores nutrients and waste products.
Centrioles Function
Help with cell division by organizing the microtubules that separate chromosomes and are vital to the formation of cilia and flagella.
Lysosomes Function
Break down cellular waste and debris.
Cytoskeleton Function
Provides structural support, maintains cell shape, and anchors organelles
Vesicle Function
Package created by the golgi that transport materials within the cell

Lightest green
Cell Membrane
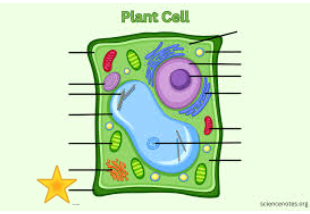
Outermost Border
Cell Wall
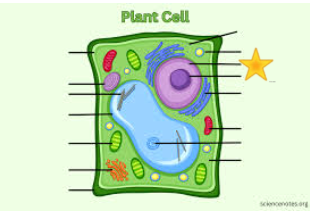
Light Purple
Nucleus
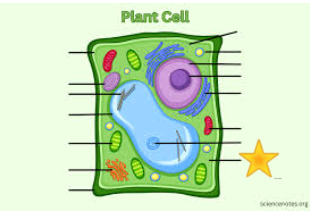
Cytoplasm
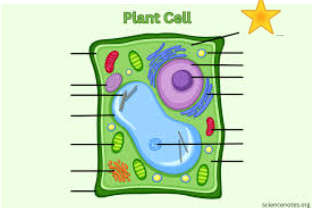
Small dots throughout and on rough ER
Ribosomes
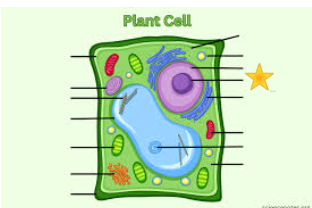
Dark Purple
Nucleolus
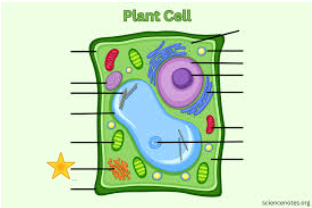
Orange
Golgi

Blue
ER (Rough and smooth)
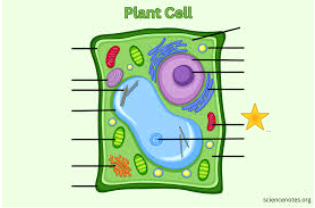
Red
Mitocondria
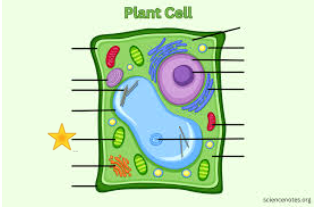
Chloroplast

Vacoule

Lysosomes

Centroiles
Nucleolus Function
Produces and assembles ribosomes, which are essential for protein synthesis in the cell
What form(s) of life are Prokaryotic cells?
(Eu) bacteria
Archaea
What form(s) of life are Eukaryotic Cells?
Plants
Animals
Fungi
Protists
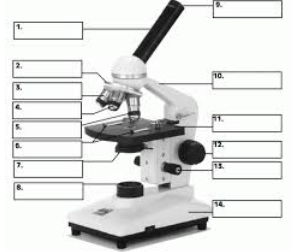
#1
Body Tube
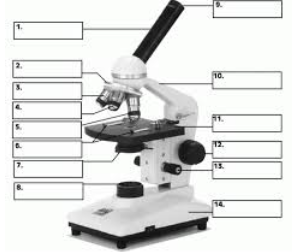
#9
Eyepiece
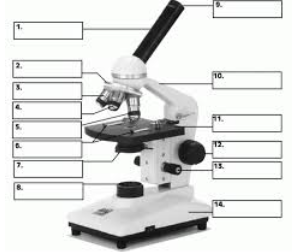
#12
Coarse Focus adjustment
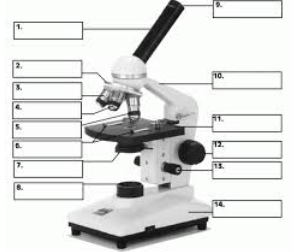
#13
Fine Focus Adjustment
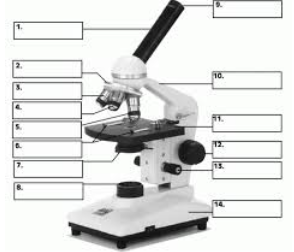
#2
Revolving Nosepiece
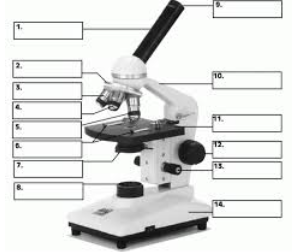
#11
Stage
Eyepiece Function
Lens you look through
Coarse Focus Adjustment Function
Moves the stage in large increments
Body Tube Function
Tube that supports the eyepiece
Fine Focus Adjustment Function
Moves the stage in small increments
Revolving Nosepiece Function
Rotating device that holds and changes the objective lenses
(a) High, (b) medium and (c ) low power Objectives Function
Magnification lenses with the (a) highest, (b) median, (c ) lowest power
Arm Function
Attaches body tube to the base
Stage Function
Holds the specimen (slide)
Stage Clips Function
Clips that keep the slide from moving on the stage
Diaphragm Function
Controls the amount of light entering the stage
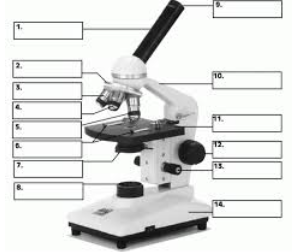
#7
Diaphragm
Base Function
Supports the microscope
Cilia Characteristics
Short, hair like, lots in one cell, oar-like motion, found only in eukaryotic cells
Flagella Characteristics
Long, whip-like appendages, few in one cell (1-8), wave-like motion, found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells