Hypernatremia and the Kalemias
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
My new band name for real
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
loss of water, hypertonic IV solution, rarely excessive oral intake
Hypernatremia (Na+ over 145) is usually due to the
Hypothalamus (leads to ADH release)
What organ senses osmolarity to trigger the thirst reflex?
Oliguric (no pee) vs non-oliguric (pee)
Since all hypernatremic conditions are hypertonic (295+ mOsm/kg) what do we need to determine?
cell death by shrinkage
Acute symptoms of hypernatremia are due to
orthostatic hypotension, lethargy, irritability, weakness, hyperthermia, delirium, seizures, coma, oliguria, osmotic cerebral myelination (RARE)
Symptoms of severe hypernatremia (Na 160+)
reduced water (lack of access, burns), nonrenal losses, water shifts into cells (rare)
Causes of oliguric hypernatremia (300+ mOsm/kg (osmolality))
central and nephrogenic DI (give ADH to determine which one)
Causes of non-oliguric hypernatremia (under 250 mOsm/kg (osmolality))
osmotic diuresis (mannitol, urea)
Causes of non-oliguric hypernatremia (300+ mOsm/kg (osmolality))
if mild Hypotonic fluids (orally or D5W); NS 0.9% followed by D5W (severe)
Treatment plan for hypovolemic hypernatremia
SLAM D5W until Na gets to 145, after that go slower; DDVAP (central DI), Dialysis (extreme cases)
Treatment plan for acute hypovolemic hypernatremia (rare)
D5W based on weight and Na level (goal is 140)
Treatment plan for chronic hypovolemic hypernatremia
12 mEq/L in 24 hours
What is the limit for correcting hypernatremia
INSIDE THE CELL
Where does potassium live?
Sodium/potassium pump (intracellular), dietary intake (extracellular)
How is K+ balanced?
metabolic alkalosis, hyperglycemia/insulin, beta-2 adrenergic agonist, hypothermia
Internal losses of K is due to
Diarrhea (most common), medications (thiazides, loop), adrenal tumors (hella aldosterone), sweat, low Mg (refractory), inadequate intake
External causes of hypokalemia
3.0-3.5 (mild), 2.5-3.0 (moderate), <2.5 (severe)
What are the levels for hypokalemia?
polyuria/polydipsia (short term), tubulointerstitial nephritis (long term), arrhythmias, cardiac arrest, smooth muscle contraction (constipation), skeletal muscle cramps, flaccid paralysis, respiratory depression, fatigue, hallucinations, delirium, psychosis
Signs and Symptoms of hypokalemia
BMP, ABG, Renin, aldosterone, cortisol, TSH, 24 hour urine, spot K/Cr ratio, EKG, imaging (look for adrenal adenoma, pituitary tumor, RAAS)
Work up for hypokalemia
under 25 (not the kidneys), over 40 (kidneys NOT working)
24 hr urine findings for hypokalemia
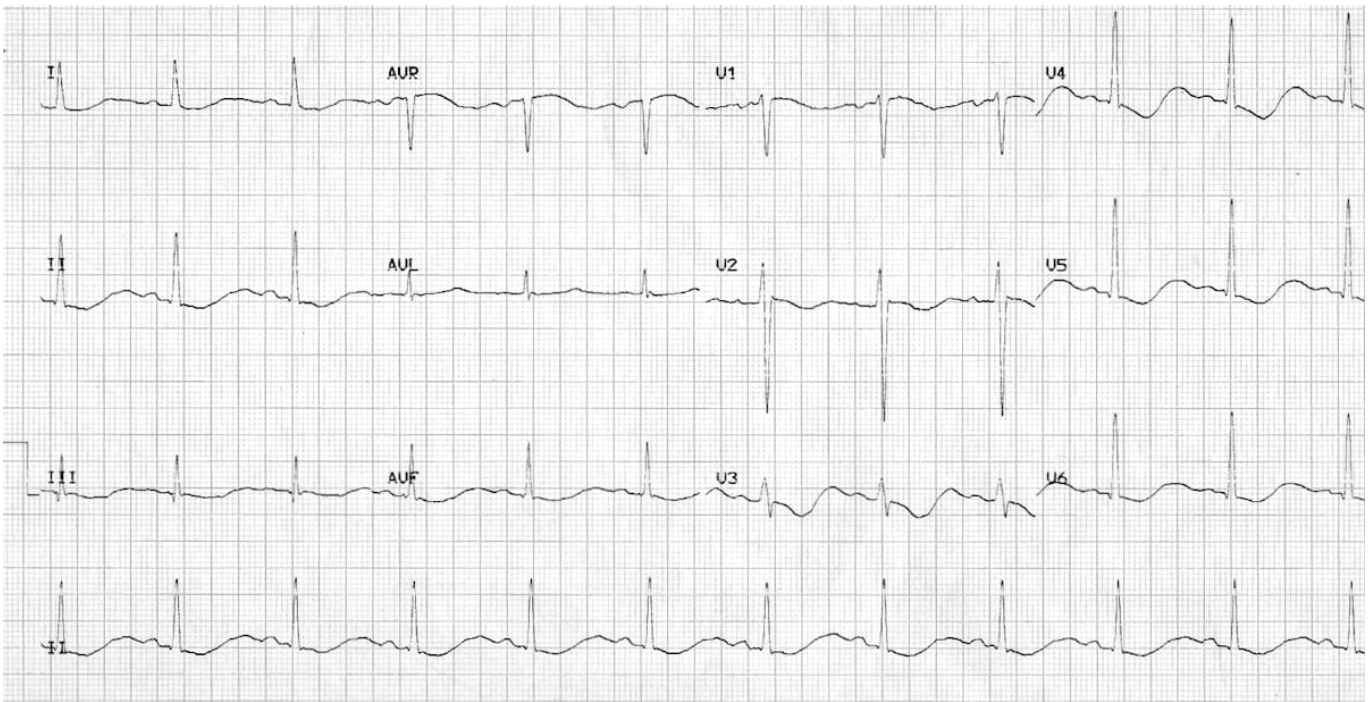
T wave flattening → ST depression and inverted Ts, prolonged QT → U waves
EKG findings for HYPOkalemia
Treat the underlying (like the metabolic acidosis), Oral K 20-40 mEq/day (mild-moderate), IV K (if under 3 or serious symptoms), Cardiac monitoring, K sparing diuretic PRN, Mg (if refractory)
Treatment plan for hypokalemia
K under 2.5, severe symptoms
When should hypokalemia peeps be referred or admitted
Pseudo (MOST COMMON - tourniquet on too long when drawing blood, small bore needles, clenched fist), tissue breakdown (rhabdo, tumor lysis syndrome, hemolysis), Hyperglycemia, Metabolic acidosis, AKI, CKD, hyporeniemic/hypoaldosteronism, excessive intake with renal disease, ACEi/ARB, beta blockers, K sparing, aldosterone antagonists, NSAIDs
Causes of HYPERkalemia
Asymptomatic (if mild), arrhythmias, palpitations, SOB, hyperventilation, flaccid paralysis, worsens any metabolic acidosis
Signs and symptoms of HYPERkalemia
CBC, CMP, ABG, aldosterone, renin, cortisol, EKG (Occurs at 5.5, deadly at 7.0 normal EKG does not mean normal K)
Diagnostics for HYPERkalemia
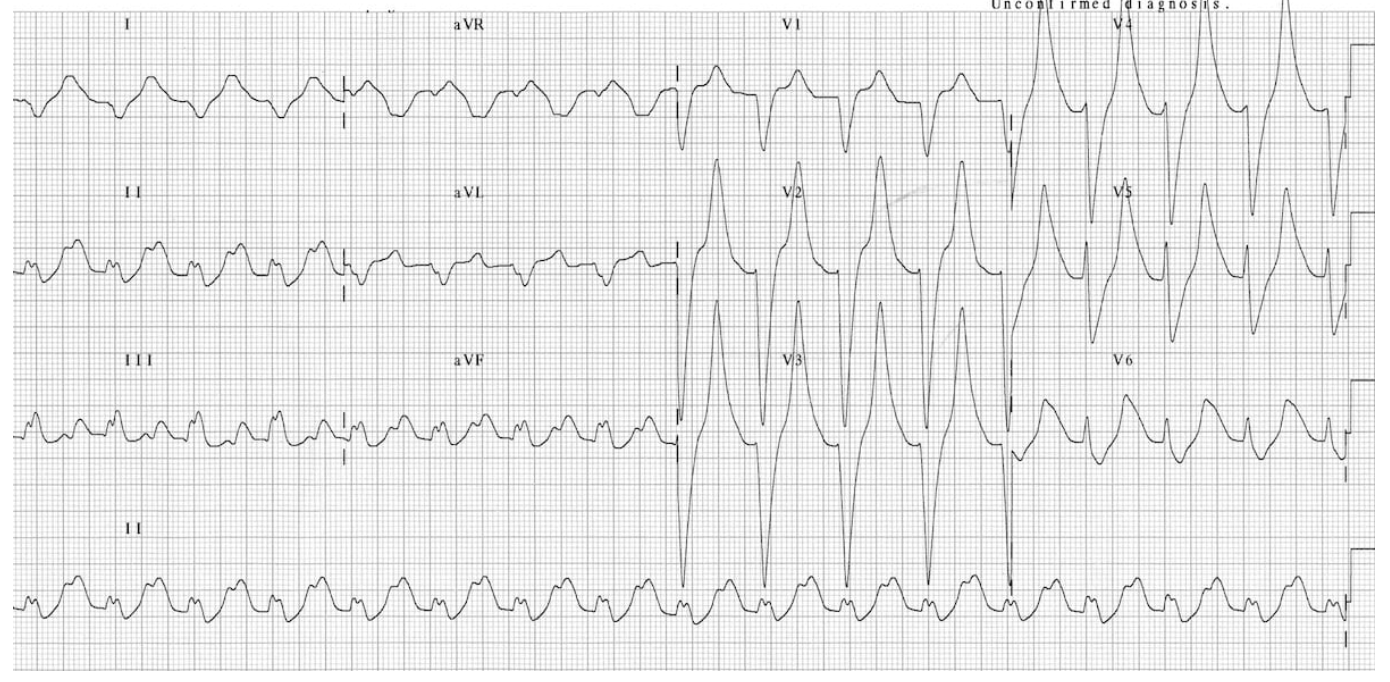
Peak Ts → prolonged PR interval and QRS → loss of P waves → sine waves → V.fib/asystole
EKG findings in HYPERkalemia
IV Calcium gluconate, K+ shift (insulin/glucose or beta agonist), loop diurectics, hemodialysis (AKI, CKD, life-threatening, refractory), Sodium polystyrene (kayexalate - only if life threatening and dialysis is not available; RISK OF NECROSIS)
Emergent treatment of HYPERkalemia (6.5+ or EKG changes)
Repeat blood work and ECG, fix underlying issues, remove the source, stop any offending meds, Loop/thiazides, Potassium binders (patiromer, sodium zirconium Cyclosilicate), Dialysis, Sodium polystyrene, SGLT-2 for chronic prevention
Non-emergent/excretory treatment of HYPERkalemia
kidney disease/transplant, Severe or life threatening hyperkalemia
When should HYPERkalemia homies be referred/admitted?