burn care & management
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
164 Terms
true or false: burn centers treat soft tissue infections in addition to burn injury
true
criteria for burn center referral
-partial thickness burns greater than >10% TBSA
-full thickness any size any age (more critical >5% TBSA)
-burns on face, hands, feet, genitalia, perineum, or major joints OR any burn that is circumferential
-any third degree burns-high voltage electrical burns, including lightning injury
-chemical burns or inhalation injury-burn injury in those with preexisting medical disorders that could complicate management, prolong recovery, or affect mortality
-burns and concomitant trauma in which the burn injury poses the greatest risk of morbidity or mortality
-burn injury in clients who will require special social, emotional, or rehabilitative intervention
how long does it take for a burn to declare itself?
48-72 hours
what are the three zones of injury?
coagulation stasis hyperemia
zone of ________ = area of burned tissue that is irreversible and no longer viable
coagulation
zone of ________ = potentially reversible if appropriate burn intervention is administered
stasis
the zone of hyperemia (zone 3) is completely reversible UNLESS there is an infection in which zone?
zone 2 - stasis
zone of ________ = area of unburned tissues around zone 2 (stasis)
hyperemia
which zone of injury is where burn care tries to mitigate due to it being the most damaged zone?
zone 1 - coagulation
after a burn, it is important to run the area under ______ water for 20 minutes to restore normal temperature
cool
what are the two main concerns associated with burn injury?
infection control, fluid replacement
burns are classified based on _______ and ______
depth; severity/SA
what are the four terms defining the depth of penetration or thickness of skin injured?
- superficial
- superficial partial thickness
- deep partial thickness
- full thickness
which type of burn is not included in TBSA calculations since it does not involve the dermis?
Superficial
which type of burn affects the epidermis only and involves erythema of the skin that may be warm to the touch and dry?
Superficial
superficial burns usually heal within ____ days
3-4
the ________ is the tough outer layer of the skin composed of epithelial tissue
epidermis
the epidermis is _________ which means the nutrients need to come from the dermis
avascular
in "thin" skin (legs, back, forearms, etc), there are ____ layers; however, "thick" skin is comprised of an extra layer known as the ________ _______
4; stratum lucidum
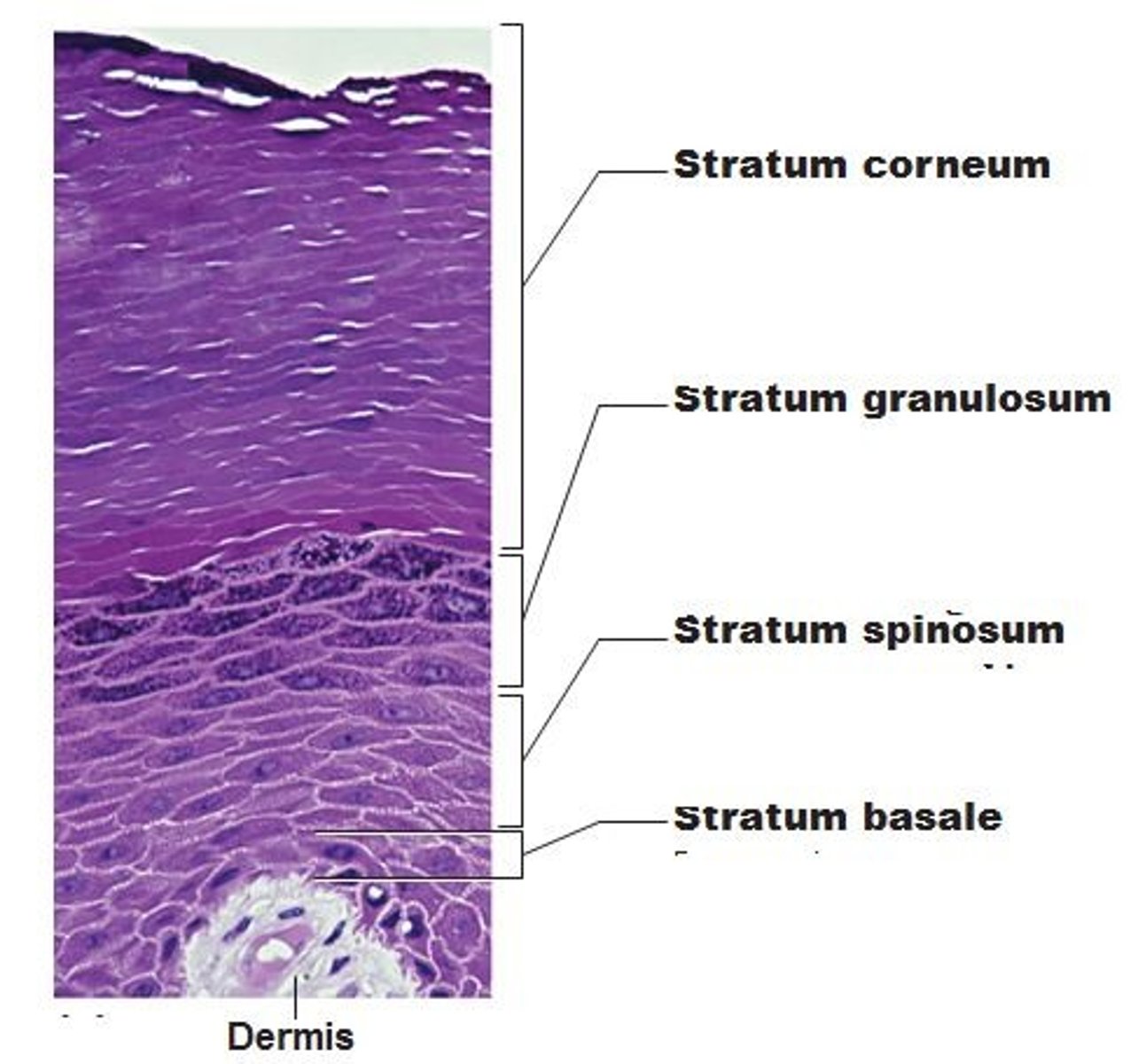
layers of the epidermis
- stratum corneum (superficial)
- statrum lucidum (thick skin ONLY)
- stratum granulosum
- stratum spinosum
- stratum basale (deepest)
superficial partial thickness burn injuries extend into the ________ ________ and can be referred to as "second degree burn"
papillary dermis
presentation of superficial partial thickness burns
- severe pain & swelling
- sensation is present
- blanching with pressure
- blistering
- moist/pink
superficial partial thickness burns usually occur due to ________ which can be associated with hot liquid or steam
scalding
which type of burn injury heals within 2-3 weeks by re-epithelization from dermal appendages and rarely forms a hypertrophic scarring or contracture?
superficial partial thickness
______ is a term referring to a healing process where the top layer of skin sheds off
Slough
the _______ _________ ________ is composed of dermal papillae and epidermal pegs that create a bond in order to withstand friction and shear forces of the skin
dermal epidermal junction
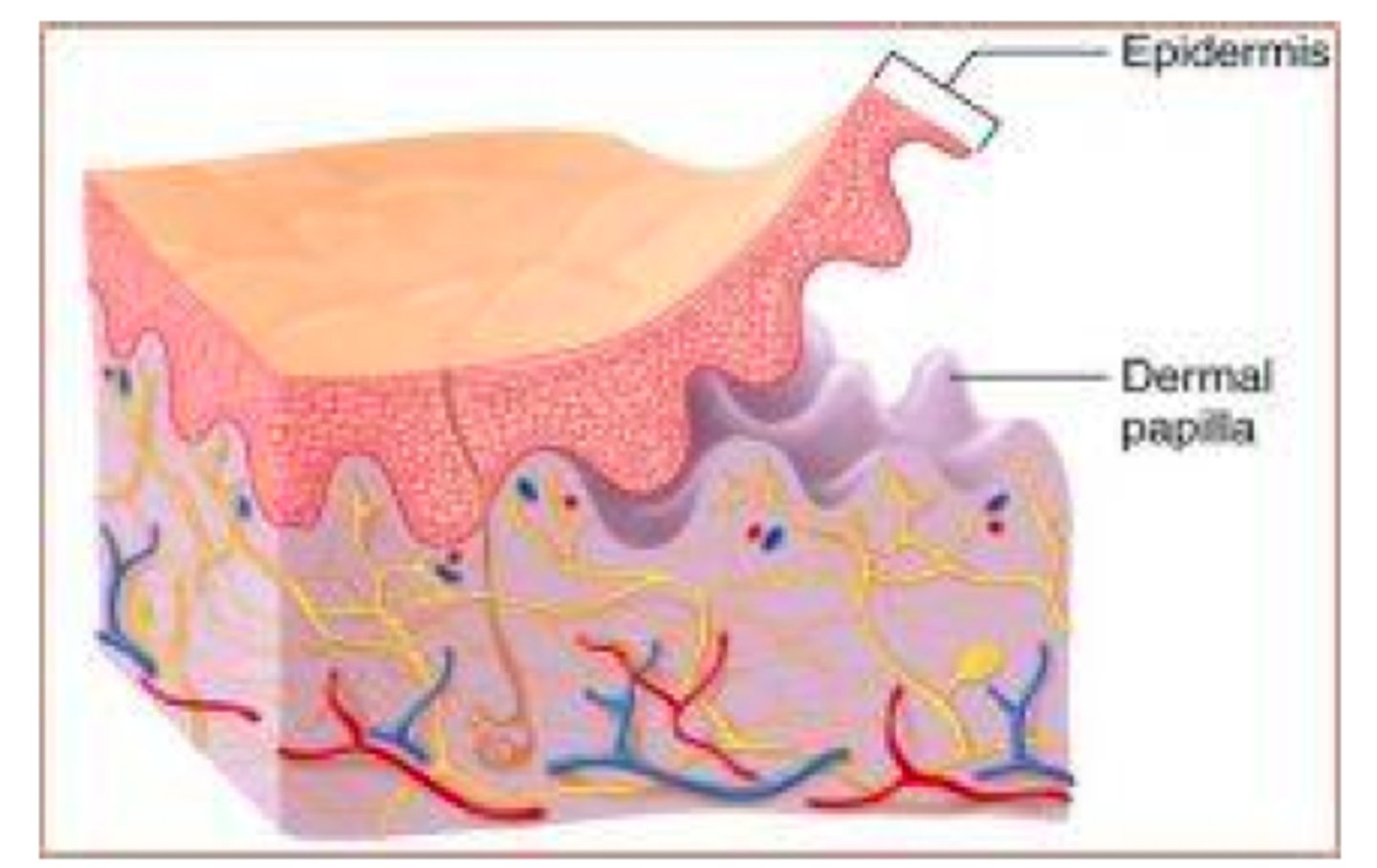
the dermal epidermal junction flattens with age which makes geriatric skin more susceptible to skin _______ and affects the healing process
tearing
which part of the dermal epidermal junction allows the nutrients from the dermal vasculature to pass through the avascular epidermis and permits re-epithelialization?
basement membrane
deep partial thickness burn injuries extend into the _________ ________ and are formerly known as "third degree burns"
reticular dermis
deep partial thickness burns lack nociceptive sensation but can still feel
- vibration
- rapid pressure
- stretch
- light touch
- sustained pressure
which type of burn injury has the following characteristics?- mottled white appearance
- does not blanch with pressure
- impaired capillary refill
deep partial thickness
deep partial thickness burns can cause permanent damage to
- hair follicles
- sebaceous glands
- epidermal cells responsible for re-epithelialization
deep partial thickness burn injuries heal within 3-9 weeks by _________ and requires surgery since re-epithelialization cannot occur
contraction
which type of burn injury will require debridement and grafting and will form a hypertrophic scar and contracture?
deep partial thickness
which layer of skin has the following characteristics? - composed of collagen & elastin - vascular - shiny appearance - capillary beds and blood vessels
dermis
the papillary region of the dermis lies just below the epidermis and includes ____ that make connection to stratum basale (capillaries)
dermal papillae
which region of the dermis consists of dense irregular connective tissue and makes up 80% of the dermal thickness?
Reticular
the _______ region of the dermis gives increased structural support to the skin by anchoring the glands, hair follicles, nerves, and blood vessels in place
reticular
the _______ ______ muscle is located within the reticular dermis where anchors itself to the hair follicle and is involved in extending the hair straight up when cold or scared
arrector pili
the dermis assists in ________ _______ and thermoregulation
infection control
which layer of the skin provides sensation as it contains nerve receptors associated with light touch, deep touch, and pain?
Dermis
__________ are the main cells found in the dermis that produce collagen and elastin
Fibroblasts
_______ are inflammatory cells located in the dermis which function to release histamine
Mast
_________ are cells located in the dermis which function in phagocytosis of dead skin cells
Macrophages
hair _________ and ________ glands are two critical sources of re-epithelialization
follicles; sebaceous
which accessory organ / appendage functions to keep skin from drying out and destroys some pathogens on the skin?
sebaceous glands
_______ sweat glands are responsible for odor and are located in the armpit & groin and are also sexual attractants
Apocrine
_______ sweat glands are the simple sweat glands located on the palms, soles, forehead and upper lip
Eccrine
in a ______ _______ burn, injury can reach the hypodermis and may possibly burn through the subcutaneous layer
full thickness
in a full thickness burn injury, there is a loss of skin barrier function which indicates
no possibility of healing from the wound base as all of the dermal regenerative cells have been obliterated
which type of burn injury has the following characteristics?- leathery brown or black eschar - dry - no capillary refill / blanching - pigmentation is fixed - pink/white may be present - shrinks or contracts due to dead tissue - no sensation
full thickness
what is only type of excision that PTs are allowed to perform?
selective sharp debridement (just nonviable tissue)
the ________ is not technically apart of the skin and is composed of adipose/fat cells, vascular supply, and connective tissue
hypodermis
the ________ binds the skin to the underlying structures (muscles, bones) and supports the dermis and epidermis
hypodermis
the hypodermis is composed of
-loose CT
- vascular supply
- adipose cells
superficial thickness burns depth/characteristics
depth:epidermis
characteristics:pain, redness, mild swelling
superficial partial thickness burns depth/characteristics
depth: dermis (papillary region)
characteristics:pain, blisters, splotchy skin, severe swelling
deep partial thickness burns depth/characteristics
depth: dermis (reticular region)
characteristics:white, leathery, relatively painless
full thickness burns depth/characteristics
depth:hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue)
characteristics:charred, insensate, eschar formation
which type of burn injury? - painful- does not blister- does not scar
superficial
which type of burn injury? - do not require surgery, but may scar and be more painful - blisters / weeps
superficial partial
which type of burn injury? - require surgery and form more scars - less painful - blisters/weeps
deep partial
which type of burn injury?- dry - insensate to light touch and pin prick - small areas will heal with substantial scar or contracture - large areas require skin grafting - high risk of infection
full thickness
TBSA is used to estimate _____ and ______ requirements and predicts morbidity and mortality
fluid; calorie
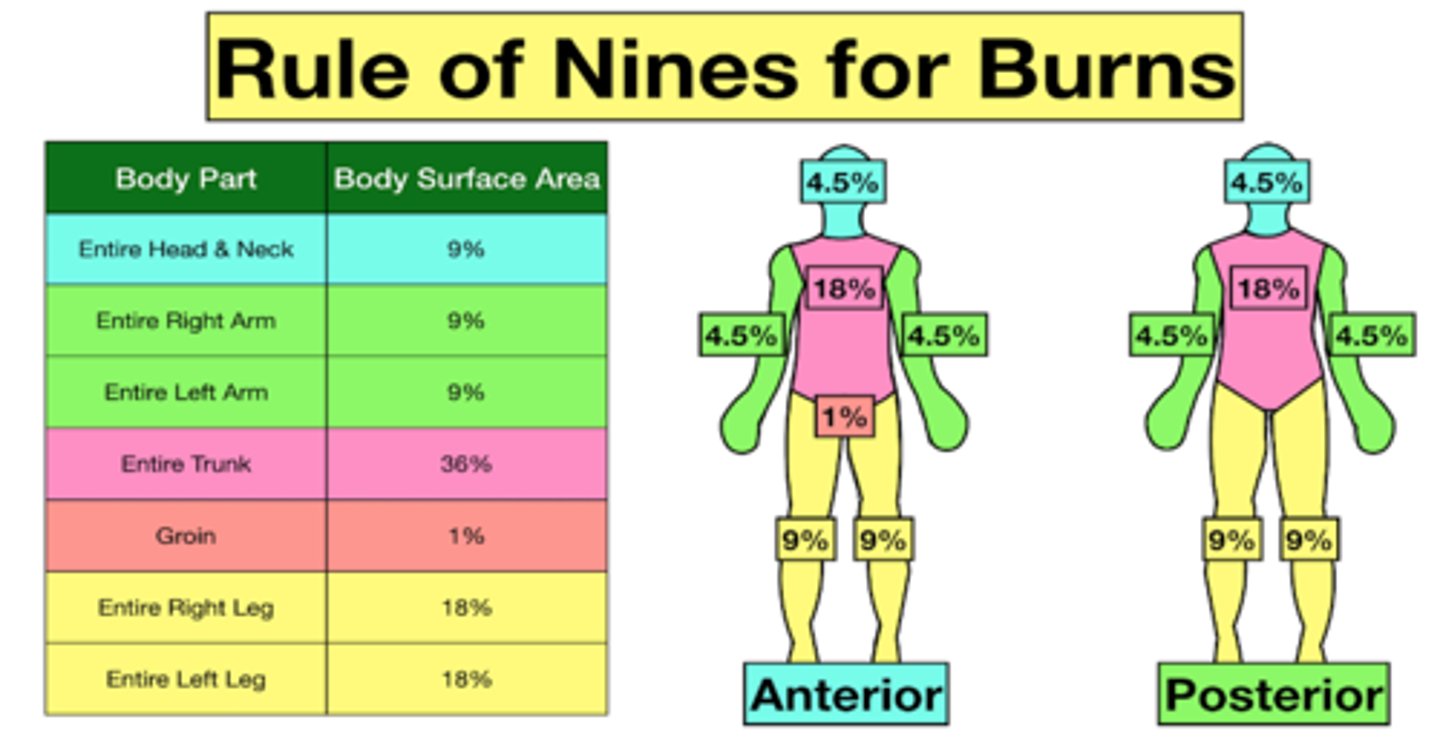
the "rule of nines" is used for rapid and easy assessment of burn injuries in adults with BMI < ___ but the "rule of sevens" is used if the individuals BMI is > _____
35
the ______-______ chart is a more accurate method and is useful in the pediatric population, but it is more time consuming
lund-browder
Rule of Nines for Burns diagram
-
a ________ burn is a result of the direct energy transfer to the tissue in relation to temperature and contact time
thermal
Types of thermal burns
- scald - flame - contact - frostbite
a _______ burn is a type of thermal burn that is a result of contact with hot liquids
scald
true or false: a scald burn is the most common burn etiology in the developed countries
true
Grease burns are scald burns. Why is this more worrying than water?
the substance stays on the skin longer
140 deg F can take 3-5 seconds to cause a
deep partial thickness burn
_______ is the second most common mechanism of burns and smoke inhalation is a major concern
Flame
Inhalation injury should be suspected if the physical examination reveals
- singed nasal hairs
- voice changes
- carbonaceous sputum (black colored)
- stridor (noisy breathing)
_______ burns are a result of skin contact with hot objects such as metals, plastic, glass or coal
Contact
in contact burns, the depth of the burn is in relation to ________ of contact and ______ of object
duration; temperature
Frostbite most commonly occurs at temperatures below ____ and is due to ____________
-28.4º F
- the slow freezing of tissues and subsequent intra- and extra-cellular crystal formation
frostbite results in injury that progresses from _______ to _______ extremities and other exposed structures such as the ears and nose
distal; proximal
frostbite: low temperatures = _________ of blood vessels
vasoconstriction
frostbite injuries are mostly ________ since the medium is the cold air which requires referral to a burn center
circumferential
________ is a good prognostic factor in frostbite injuries
Sensation
for a frostbite / cold burn injury, surgical intervention is delayed for ____-____ days to allow the injury to fully declare itself
10-14
true or false:fingers and toes can self amputate in a frostbite injury
true
treatment for frostbite
- rewarm the body rapidly - vasodilators (tPA)
_____ injury occurs secondary to acid or base making contact with the skin
Chemical
Which chemical burns are less severe - acid or base? Why?
ACID - coagulation necrosis protein eschar impairs further penetration
Why are Basic chemical burns worse?
liquefication necrosis of tissue -->deeper penetration
________ burns are dependent on type of energy source, total dose and time administered, location and size of exposed areas
Radiation
______ radiation burns = skin changes within first 6 weeks
Acute
______ radiation burns = skin changes for months to years
Chronic
Presentation & Treatment of Radiation burns
- tight, flaky, warm, dry
- treat: moisturize
true or false: electrical burns can be caused by both high and low voltages
true
individuals are usually kept for 24-48 hours post _______ injury to monitor the heart on telemetry due to the involvement of organ systems
electrical
electrical currents cause muscle ___
tetany
electrical burns travel from least to most resistance: ______ has high resistance and will heat up causing injury to adjacent muscle and lead to compartment syndrome which requires a fasciotomy
bone
Least to most resistance for electrical burns
- blood
- vessels
- nerves
- muscle
- skin
- tendon
- fat
- bone
road rash is a type of ______ _____ _______ burn injury
superficial partial thickness
TBSA determines ________ resuscitation & ________
fluid; nutrition
initial assessment includes the "ABCs" - what does this mean?
Airway breathing circulation