Chemical Reactions and Equations Overview
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
145 Terms
Chemical Reaction
a chemical change that forms a new substance
Catalyst
a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction but is not used up in the reaction. (Written above the arrow.)
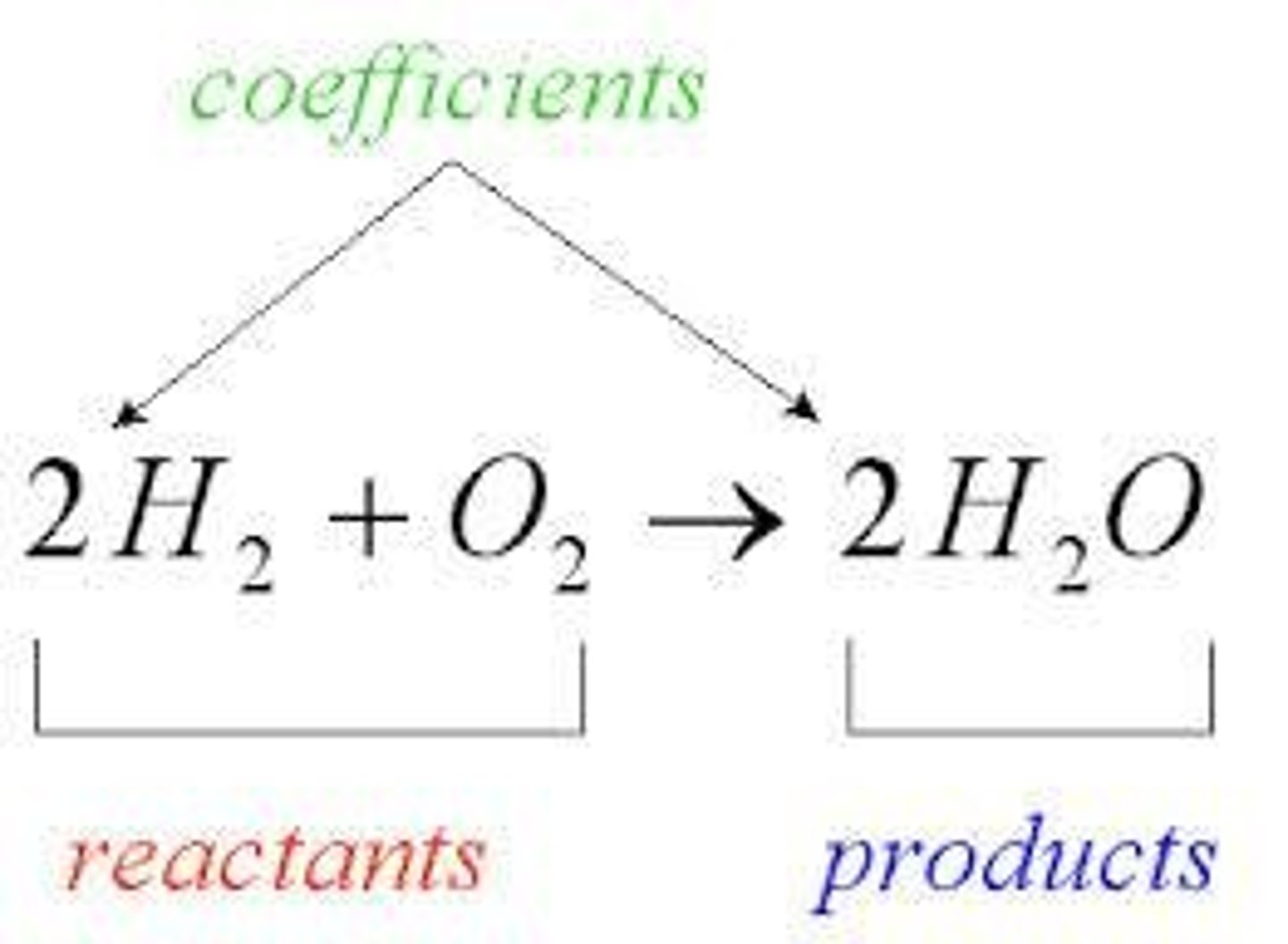
Reactants
the substances that 'react' (found on the left of the equation)
Products
the substances that are 'produced' (found on the right of the equation)
Arrow
separates the reactants from the products ('yields', 'forms', 'makes', etc.)
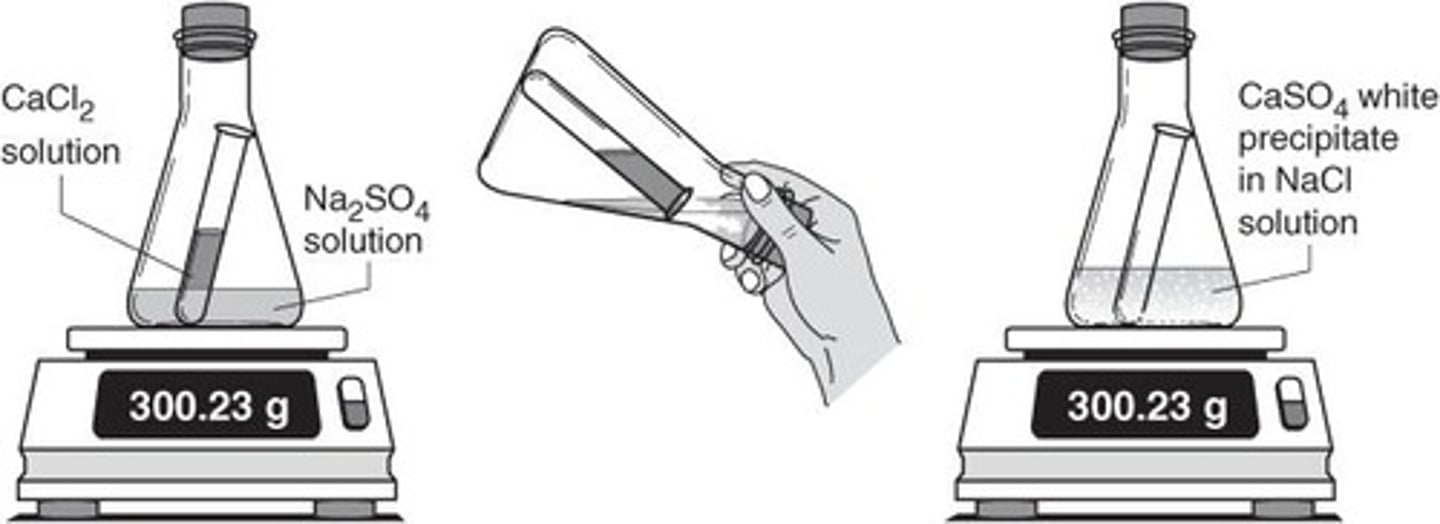
Law of Conservation of Mass
Matter cannot be created or destroyed in any chemical reaction. This means that the mass of the reactants MUST EQUAL the mass of the products.
Balanced Equation
There must be an EQUAL number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation.
Steps to Balancing Equations
1. Draw a line under the arrow to separate the reactants and the products. 2. List all the elements that are on the left side of the equation. 3. Take inventory. 4. Decide if the equation is balanced. 5. Balance the equation using COEFFICIENTS. 6. Coefficients can only go IN FRONT OF any reactant or product. 7. FINAL CHECK: check your equation one more time to make sure everything is balanced.
Coefficients
Numbers placed in front of reactants or products to balance a chemical equation.
Polyatomic Ions
If the polyatomic ion appears on both sides of the equation, you may write it down as a unit.
Chemical Formula
A representation of a substance using symbols for its constituent elements.
Example of a Chemical Equation
2H2O2 (aq) Pt → 2H2O (l) + O2 (g)
Example of Balancing Coefficients
For the equation CuO2 → CuO + O2, the coefficients are 2, 1, 1.
Example of Balancing Coefficients
For the equation Mg(OH)2 (aq) + SO2 (g) → MgSO3 (s) + H2O (l), the coefficients are 3, 3, 3, 2.
Example of Balancing Coefficients
For the equation Ca(C2H3O2)2 + K3PO4 → Ca3(PO4)2 + KC2H3O2, the coefficients are 3, 3, 1, 2.
Example of a Chemical Equation Supporting Conservation of Mass
2H2O (l) → H2 (g) + O2 (g)
Example of a Chemical Equation Supporting Conservation of Mass
Zn (s) + HCl (aq) → ZnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Example of a Chemical Equation Supporting Conservation of Mass
Al4C3 (s) + H2O (l) → CH4 (g) + Al(OH)3 (s)
Example of a Chemical Equation Supporting Conservation of Mass
CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2H2O (g)
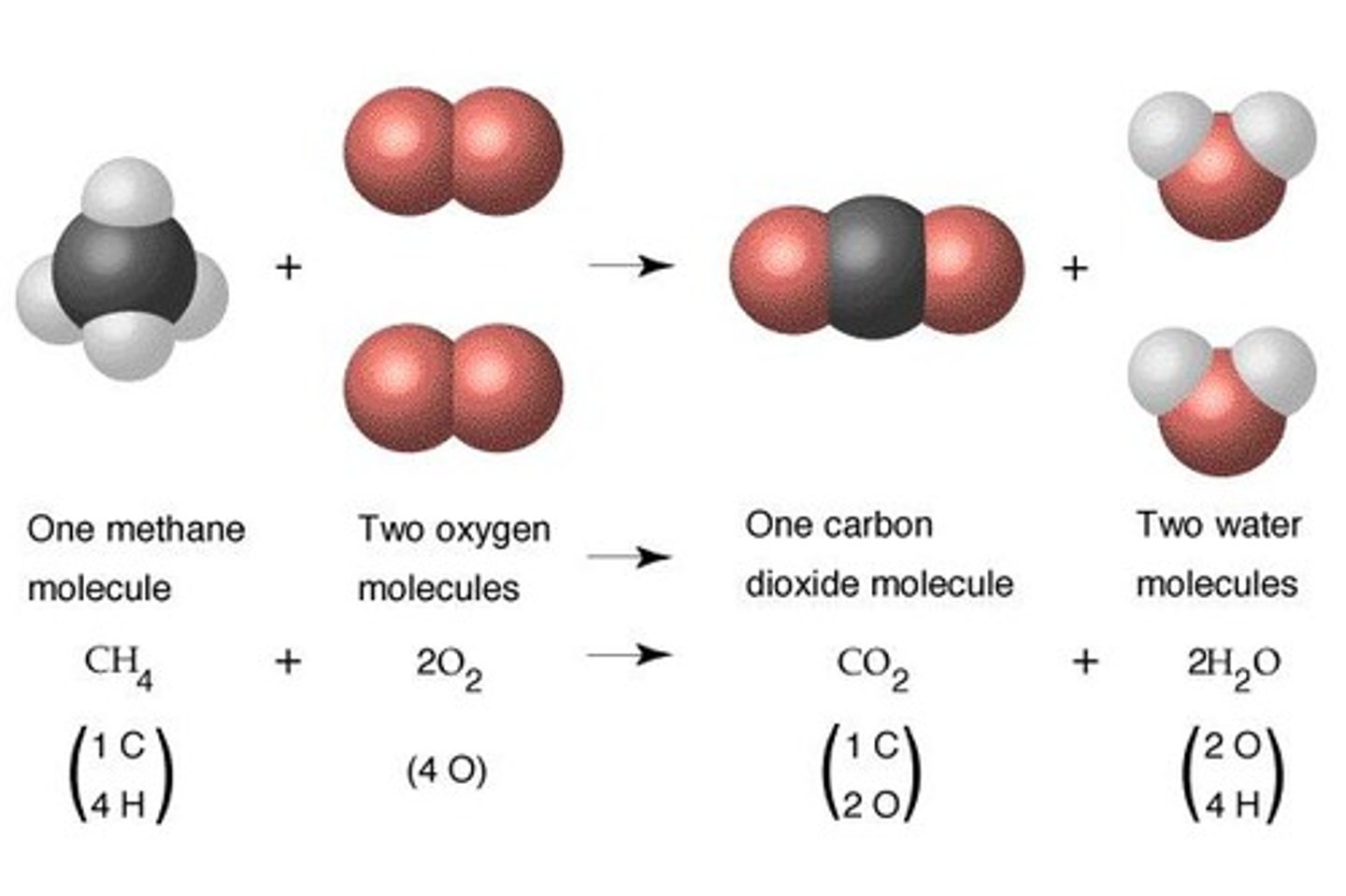
Skeletal Equation
A chemical equation that does not indicate the relative amounts of reactants and products involved.
Synthesis Reactions
2 or more substances combine to form 1 substance.
Single Replacement Reactions
One element replaces another element that is part of a compound.
Decomposition Reactions
A compound breaks apart into two or more simpler substances.
Combustion Reactions
A type of reaction where a substance combines with oxygen, releasing energy in the form of light or heat.
Diatomic Elements
Elements that exist as molecules composed of two atoms, such as H2, O2, N2, etc.
Chemical Equation
A representation of a chemical reaction using symbols and formulas.
Balanced Equation
An equation where the number of atoms for each element is the same on both sides of the equation.
Reactants
Substances that undergo a chemical change in a reaction.
Products
Substances formed as a result of a chemical reaction.
Coefficients
Numbers placed in front of compounds in a chemical equation to indicate the number of molecules or moles.
Aluminum Oxide
A compound formed when aluminum reacts with oxygen.
Hydrochloric Acid
A strong acid formed from the reaction of hydrogen chloride gas with water.
Iron(II) Sulfide
A compound formed when iron reacts with sulfur.
Diphosphorus Pentoxide
A compound formed when phosphorus reacts with oxygen.
Potassium Bromide
A compound formed when potassium reacts with liquid bromine.
Ammonium Phosphate
A compound that reacts with calcium chloride to produce calcium phosphate and ammonium chloride.
Hydrogen Gas
A diatomic gas that is produced when acids react with metals.
Chemical Reaction
A process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another.
Aluminum Chloride
A compound formed when aluminum reacts with chlorine gas.
Silver Sulfide
A compound formed when silver reacts with sulfur.
Calcium Phosphate
A compound produced from the reaction of ammonium phosphate with calcium chloride.
Bromine
A chemical element that reacts with sodium nitride to produce sodium bromide and nitrogen gas.
Chemical Reactions Song
A song by Mr. Parr that helps in learning about chemical reactions.
Double Replacement Reactions
Involves an exchange of positive ions between two reacting compounds.
Combustion Reactions
An element or a compound reacts with oxygen (O2) often producing energy as heat and light.
Hydrocarbons
These reactions often involve hydrocarbons.
Products of Hydrocarbon Combustion
When hydrocarbons react with O2, the products are ALWAYS: CO2 and H2O.
Skeletal Equation Reminders
When writing out equations, remember to check if elements are diatomic.
Diatomic Elements
If 'yes' - they need a subscript '2'. If 'no' - they don't get a subscript.
Compounds Naming
Are there any prefixes in the name? If 'yes' - then use the prefixes. If 'no' - then criss-cross the charges.
Types of Chemical Equations
Label the following as synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement, or combustion.
Synthesis Reaction Example
2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl
Decomposition Reaction
Most decomposition reactions require energy in the form of heat, light, or electricity.
Predicting Products
Write out the symbols/formulas for the reactants and products. Balance the equation.
Balanced Equation Example
__2__Na + __1__Cl2 → __2__NaCl
Single Replacement Reactions
Whether or not a metal will replace another metal depends on its reactivity to other metals.
Chemical Reaction Types
Identify the type of reaction: synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement, or combustion.
Aluminum and Bromine Reaction
Aluminum + Bromine → AlBr3
Calcium and Oxygen Reaction
Calcium + Oxygen → CaO
Iron and Nitrogen Reaction
Iron (II) + Nitrogen → Fe3N2
Magnesium and Iodine Reaction
Magnesium + Iodine → MgI2
Lead and Fluorine Reaction
Lead (IV) + Fluorine → PbF4
Carbon Monoxide
A compound formed from carbon and oxygen.
Zinc Phosphide
A compound formed from zinc and phosphorus.
Copper (I) Selenide
A compound formed from copper and selenium.
Silver Nitride
A compound formed from silver and nitrogen.
Single Replacement Reaction
A reaction where a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal in a compound.
Activity Series of Metals
A list that ranks metals by their reactivity, used to predict if a reaction will occur.
Decomposition Reaction
A reaction where a single compound breaks down into two or more products.
Double Replacement Reaction
A reaction where two compounds exchange components to form two new compounds.
Precipitate
A solid that forms and separates from a liquid mixture during a chemical reaction.
Solubility Rules
Guidelines used to predict whether a compound will dissolve in water.
Halogen Group
A group of elements in the periodic table known for their reactivity, including fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine.
Reactivity
The tendency of a substance to undergo a chemical reaction.
Molecular Compound
A compound formed from two or more nonmetals that share electrons.
Gas Production
A sign of a chemical reaction where gas bubbles are formed and escape from the solution.
Replacement of Nonmetals
A reaction where a more reactive nonmetal displaces a less reactive nonmetal in a compound.
Fluorine Activity
Fluorine is more active than iodine in chemical reactions.
Balancing Equations
The process of ensuring that the number of atoms for each element is the same on both sides of a chemical equation.
Potassium + Calcium Chloride Reaction
__2__K + __1__CaCl2 → __2__KCl + __1__Ca
Gold + Potassium Nitrate Reaction
To be determined.
Zinc + Silver Nitrate Reaction
To be determined.
Aluminum + Sulfuric Acid Reaction
To be determined.
Magnesium + Nitric Acid Reaction
To be determined.
Gold + Hydrochloric Acid Reaction
To be determined.
Mercury + Zinc Nitrate Reaction
To be determined.
Chlorine + Potassium Bromide Reaction
To be determined.
Bromine + Barium Fluoride Reaction
To be determined.
Fluorine + Tin (IV) Iodide Reaction
To be determined.
Hydrochloric Acid + Calcium Hydroxide Reaction
To be determined.
Silver Sulfate + Aluminum Chloride Reaction
To be determined.
Lead II Nitrate + Magnesium Iodide Reaction
To be determined.
Lead II nitrate + magnesium iodide
Chemical reaction equation.
Sodium hydroxide + iron III nitrate
Chemical reaction equation.
Sulfuric acid + barium chloride
Chemical reaction equation.
Aluminum sulfate + ammonium nitrate
Chemical reaction equation.
Silver nitrate + hydrogen sulfide
Chemical reaction equation.
Calcium chloride + lead II nitrate
Chemical reaction equation.
Calcium nitrate + sodium carbonate
Chemical reaction equation.
Lead II acetate + lithium chloride
Chemical reaction equation.