Organic Chem
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is organic chem
carbon based chem
why is carbon so important in chem
has 4 binding sites allowing for huge variety of different molecules
what is a functional group
a group of atoms responsible for the characteristic reactions of a particular compound.
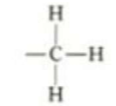
which functional group is this, what type of molecules is it in, what are it’s properties?
Methyl. fats, amino acids. non-polar
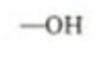
which functional group is this, what type of molecules is it in, what are it’s properties?
Alcohol/hydroyl. alcohol, carbohydrates, amino acids. polar
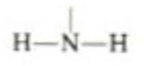
which functional group is this, what type of molecules is it in, what are it’s properties?
Amino. amino acid. basic
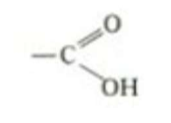
which functional group is this, what type of molecules is it in, what are it’s properties?
Carboxylic acid. Amino acid. acidic
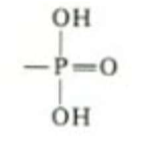
which functional group is this, what type of molecules is it in, what are it’s properties?
Phosphate. nucleotides (DNA/RNA) phospholipid. polar - energetic bond
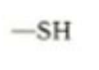
which functional group is this, what type of molecules is it in, what are it’s properties?
Sulfhydral. amino acid (cysteine). links chains of amino acids together
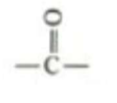
which functional group is this, what type of molecules is it in, what are it’s properties?
Keto. sugars, amino acids. polar
what is an Anabolic reaction
reaction that creates larger molecules from smaller molecules
what is a condensation reaction
an anabolic reaction that forms H2O
what is a peptide bond
covalent chemical bond that links two amino acid together
what is a Catabolic reaction
a reaction that makes smaller molecules from larger molecules
what is a hydrolysis reaction
a catabolic reaction that breaks H2O
what is a monomer
an individual or smaller molecule
what is a polymer
a large molecule made from smaller molecules
what are the 4 main classes of biomolecules
carbohydrates, lipid, protien
what is a carbohydrate
a biomolecule, primarily used for energy and structure, consists of C:H:O generally in a 1:2:1 ratio
what are monosaccarides
simple sugar, a type of carbohydrate, easily dissolved in H2O
What is a polysaccharide
polymer of monosaccarides
what is starch
a polysaccharide, excess glucose in a plant for energy use, lots of branches, we have the digestive enzyme to break it down
what is cellulose
a polysaccharide, glucose polymer for structure in plants, straight chain, we don’t have the digestive enzyme to break it down, fiber is a cellulose
what is glycogen
a polysaccharide, excess glucose in animals, stored in the liver and muscles, very branched
what are lipids
a biomolecule, stores huge amounts of energy, doesn’t dissolve in H2O, fatty acids. Acid to make polar and methyl to make non-polar
what does it mean by saturated
It’s saturated by hydrogen, so no double bonds between carbons (solid)
what does it mean by unsaturated
not saturated by hydrogens, double bonds between carbons (liquid)
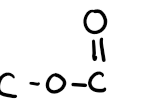
what is this bond
ester bond, unique with lipids
3 fatty acids + glycerol →
triglyceride (polymer of lipid) + H2O
what is phospholipid
2 fatty acids + phosphate. is the main component of cell membrane. head and tails create bilayer
what are steroids
classified as lipiids, 4 rings of carbons, based in cholesterol, (progesterone, estrogen, testosterone)
what manufactures lipids
the smooth endoplasmic reticulum
what are protiens
a type of biomolecule. has an amino group, an acid group and a variable
what is a monomer of protien
amino acid
What does DNA do
provides code for which amino acids to use in a protien
what is a dipeptide vs polypeptide
2 amino acids long vs 3 amino acids long