Chapter 4: Histology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/145
Last updated 2:44 AM on 11/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
1
New cards
Histology
the study of tissues
2
New cards
collagen fiber
3
New cards
elastic fiber
4
New cards
Definition of tissues
the collections of specialized cells and the extracellular substance surrounding them
5
New cards
the purpose of a biopsy
for diagnostic purposes (Ex: to diagnose Celiac)
6
New cards
What is an autopsy?
examination of organs to determine cause of death or to study the changes caused by disease
7
New cards
Which of the following is not used to classify epithelial tissues?
A. Matrix
B. Structure
C. Function
D. Location
A. Matrix
B. Structure
C. Function
D. Location
D. Location
8
New cards
epithelium characteristics
A. made almost entirely of tightly packed cells (not much matrix)
B. Covers body surfaces and forms glands (skin, digestive tract, respiratory tract, heart and blood vessels, many body cavities)
C. Most have a free and a basal surface (lateral surface is in between cells)
D. Basement membrane
E. Avascular
F. Capable of regeneration mitosis
B. Covers body surfaces and forms glands (skin, digestive tract, respiratory tract, heart and blood vessels, many body cavities)
C. Most have a free and a basal surface (lateral surface is in between cells)
D. Basement membrane
E. Avascular
F. Capable of regeneration mitosis
9
New cards
T or F: Epithelium cannot undergo mitosis because it is avascular.
False
10
New cards
What is the basement membrane of an epithelial cell?
an extracellular material formed by secretions from epithelial and connective tissue cells
11
New cards
What does the basement membrane do?
1. helps attach epithelial cells to the underlying connective tissues
2. guides cell migration for tissue repair
3. filters (in the nephrons of the kidney)
2. guides cell migration for tissue repair
3. filters (in the nephrons of the kidney)
12
New cards
Do all epithelium cells have a basement membrane?
No
13
New cards
the function of epithelial tissues
(Before you go, Don't Forget Some Apples Peel)
Barrier, Diffusion, Filtration, Secretion, Absorption, Protection
Barrier, Diffusion, Filtration, Secretion, Absorption, Protection
14
New cards
the free surface of an epithelial cell can be/have: (and what do they do?)
1. Smooth to reduce friction (blood vessels)
2. Microvilli/brush border to increase surface area for absorption or secretion
3. Cilia to move materials across the cell surface
2. Microvilli/brush border to increase surface area for absorption or secretion
3. Cilia to move materials across the cell surface
15
New cards
simple squamous epithelium locations
lining of blood vessels & heart, lymphatic vessels (endothelium), and alveoli of lungs
16
New cards
function of simple squamous epithelium
diffusion (oxygen in lungs), filtration (kidneys), some secretion, some protection
17
New cards
simple cuboidal epithelium locations
microvilli in kidney tubules & terminal bronchioles in lungs
18
New cards
functions of simple cuboidal epithelium
secretion & absorption
19
New cards
simple columnar epithelium locations
microvilli in GI tract & cilia in lungs
20
New cards
functions of simple columnar epithelium
secretion and absorption in intestine & particles out of bronchioles in the cilia in the lungs
21
New cards
stratified squamous epithelium locations
non-keratinized: mouth, throat, esophagus
keratinized: skin
keratinized: skin
22
New cards
non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
living cells in the deepest and outermost layers that are covered with a layer of fluid on the outer layer (they are moist)
23
New cards
keratinzed stratified squamous epithelium
living cells in the deepest layers, and dead cells containing the protein keratin in the outer layers (they are dry, durable, and moisture-resistant)
24
New cards
functions of stratified squamous epithelium
protection from abrasion, chemicals, water loss, and infection
25
New cards
stratified cuboidal epithelium locations
sweat gland ducts
26
New cards
functions of stratified cuboidal epithelium
secretion, absorption, & protection against infection
27
New cards
stratified columnar epithelium locations
mammary gland duct, larynx, portion of male urethra
28
New cards
function of stratified columnar epithelium
secretion and protection
29
New cards
pseudostratified columnar epithelium characteristics
almost always ciliated, have goblet cells, & are mucous
30
New cards
pseudostratified columnar epithelium locations
nasal sinuses, bronchi of lungs, trachea
31
New cards
functions of pseudostratified columnar epithelium
secrete and move mucus
32
New cards
transitional epithelium locations
lining of urinary bladder and ureters
33
New cards
functions of transitional epithelium
stretch with volume changes of organ & protects against caustic effects of urine
34
New cards
transitional epithelium shape
cube when not stretched, squamous when stretched
35
New cards
cell connectors
desmosomes (& Hemidesmosomes), tight junctions, adhesion belts, gap junctions
36
New cards
function of a desmosome
bind cells together
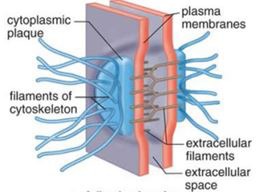
37
New cards
function of a hemidesmosome
bind cells to basement membrane
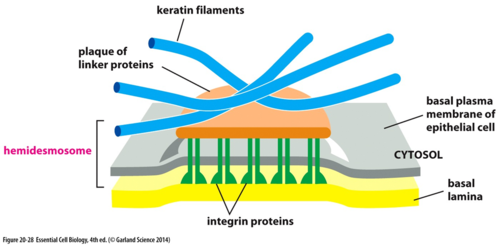
38
New cards
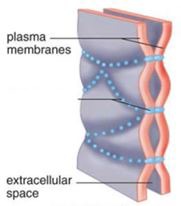
function of a tight junction
holds cells together & forms a permeability layer
39
New cards
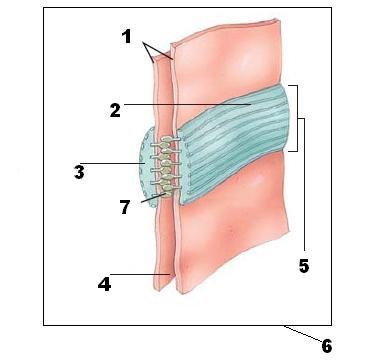
function of an adhesion belt
help the tight junctions anchor the epithelial cells to each other
40
New cards
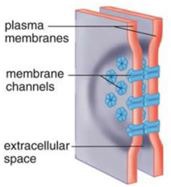
function of a gap junction
intercellular communication
41
New cards
endocrine glands
secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream (no ducts), which means its secretions are separated from the epithelium of origin
42
New cards
exocrine glands
has ducts, which means its secretions maintain open contact with the epithelium from which it developed
43
New cards
goblet cells
unicellular glands that secrete mucus
44
New cards
How are multicellular exocrine glands classified?
the structure of their ducts or by their method of secretion
45
New cards
T or F: most glands are multicellular
true
46
New cards
simple structure glands
ducts with a few branches
47
New cards
compound structure glands
ducts with many branches
48
New cards
tubular structure glands
secretory regions shaped like tubes
49
New cards
acinar (alveolar) structure glands
sac-like structures
50
New cards
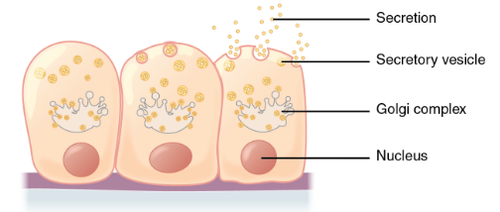
merocrine secretion
no loss of cellular material (like sweat)
51
New cards
apocrine secretion
part of cell pinches off (like mammary glands)
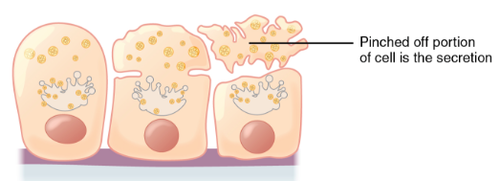
52
New cards
holocrine secretion
whole cell is part of secretion (like sebaceous gland)
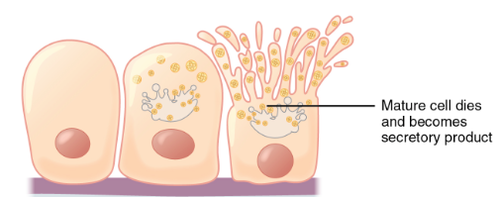
53
New cards
T or F: connective tissue is found in every organ.
true
54
New cards
functions of connective tissue, and examples of connective tissues that do those things
1. enclose/encapsulate organs (ex: muscles, arteries, veins)
2. connect tissues (ex: tendons and ligaments)
3. support and movement (ex: bones provide rigid support)
4. storage (ex: fat stores high energy molecules, bone stores minerals like Ca and P)
5. cushion/insulation (ex: fat)
6. transport (ex: blood)
7. protection (ex: immune system cells, bones)
2. connect tissues (ex: tendons and ligaments)
3. support and movement (ex: bones provide rigid support)
4. storage (ex: fat stores high energy molecules, bone stores minerals like Ca and P)
5. cushion/insulation (ex: fat)
6. transport (ex: blood)
7. protection (ex: immune system cells, bones)
55
New cards
what connective tissue function does the word stem "blast" identify?
create matrix
56
New cards
what connective tissue function does the word stem "cyte" identify?
maintain matrix
57
New cards
what connective tissue function does the word stem "clast" identify?
break down matrix (for remodeling)
58
New cards
types of connective tissue cells
1. adipose/fat cells (adipocytes)
2. mast cells - contain heparin, histamine, and proteolytic enzymes & are released in response to injury/infection
3. white blood cells - respond to injury/infection as well
4. macrophages - phagocytize to provide protection (can be fixed or wandering
5. undifferentiated mesenchyme (stem cells)
2. mast cells - contain heparin, histamine, and proteolytic enzymes & are released in response to injury/infection
3. white blood cells - respond to injury/infection as well
4. macrophages - phagocytize to provide protection (can be fixed or wandering
5. undifferentiated mesenchyme (stem cells)
59
New cards
What are the 3 parts of the extracellular matrix of connective tissue?
protein fibers, ground substance, & fluid
60
New cards
3 different types of protein fibers of the matrix of connective tissue
collagen, reticular, & elastic
61
New cards
collagen protein fiber characteristics
most common protein in the body (approx. 6% of body weight) & very strong and flexible but very inelastic
62
New cards
reticular protein fiber characteristics
these are fine collagen fibers that form a branching network and fills spaces between tissues and organs & it is not as strong as most collagen fibers
63
New cards
elastic protein fiber characteristics
returns to original shape
64
New cards
ground substance of connective tissue extracellular matrix
the shapeless background in a microscope
65
New cards
3 types of ground substance in the matrix of connective tissue
hyaluronic acid, proteoglycans, & adhesive molecules
66
New cards
hyaluronic acid
a polysaccharide that is the lubricant for joint cavities
67
New cards
proteoglycans
protein + polysaccharide that traps large amounts of water and provides cartilage with its resilient nature
68
New cards
adhesive molecules
hold proteoglycans together
69
New cards
What is the component that is not part of the extracellular matrix of Connective Tissues?
A. Fluid
B. Protein fibers
C. Holocrine tissue
D. Ground substance
A. Fluid
B. Protein fibers
C. Holocrine tissue
D. Ground substance
C. Holocrine tissue
70
New cards
loose (areolar) connective tissue
the loose packing material of most organs and tissues that attaches skin to underlying tissues
71
New cards
dense regular connective tissue
has abundant collagen fibers and resists stretching
72
New cards
tendons
muscle to bone
73
New cards
ligaments
bone to bone
74
New cards
dense irregular collagenous connective tissue
has collagen fibers that are randomly oriented and is tough
75
New cards
what connective tissue makes up most of the dermis of the skin, as well as scars?
dense irregular collagenous connective tissue
76
New cards
What tissue makes up the epidermis?
stratified squamous epithelium
77
New cards
What tissue makes up the dermis?
dense irregular collagenous CT
78
New cards
What tissue makes up the hypodermis (subcutaneous)?
loose (areolar) CT
79
New cards
adipose tissue
made of adipocytes, and can be yellow/white or brown
80
New cards
yellow/white adipose tissue
Most abundant type and is white at birth then yellows with age
81
New cards
brown adipose tissue
in axillae and neck and is more abundant in babies
82
New cards
reticular tissue
provides a super structure for lymphatic and hemopoietic tissues like lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow, & the spaces in between cells contain white blood cells and dendritic cells
83
New cards
cartilage characteristics
firmest structure in the body except bone, avascular, no blood/nerve supply, and heals very slowly
84
New cards
perichondrium
dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds nearly all cartilage and secretes cartilage cells
85
New cards
When do cartilage cells become chondrocytes?
when surrounded by the matrix and are located in spaces called lacunae
86
New cards
the 3 types of cartilage
hyaline, fibrocartilage, elastic
87
New cards
hyaline cartilage structure
collagen fibers and proteoglycans in the matrix
88
New cards
hyaline cartilage locations
where strong support and some flexibility is needed (rib cage, trachea, bronchi), on articulation surfaces, embryo skeletons, & bone growth zones
89
New cards
fibrocartilage structure
thick collagen fibers in matrix that are slightly compressible and tough
90
New cards
fibrocartilage locations
areas of pressure on joints (knees, interverbal disks)
91
New cards
elastic cartilage structure
elastic and collagen fibers and proteoglycans in the matrix that are rigid but elastic
92
New cards
elastic cartilage location
external ears
93
New cards
bone
hard connective tissue made of osteocytes (living cells) + mineralized matrix
94
New cards
bone matrix
provides strength/rigidity and is made up of organic collagen fibers and inorganic hydroxyapetite (Ca++ and PO4)
95
New cards
Where are bone osteocytes located?
in lacunae
96
New cards
types of bone
cancellous/spongy bone & compact bone
97
New cards
cancellous/spongy bone
trabeculae of bone with spaces that is found inside the bone, skull, vertebrae, sternum, and ends of long bones
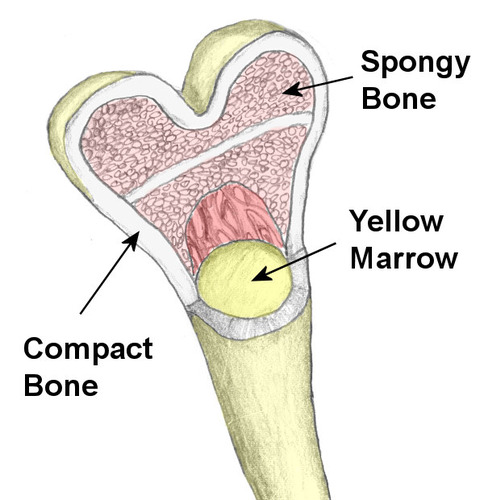
98
New cards
compact bone
concentric layers around a central canal and is around the periphery of the bone
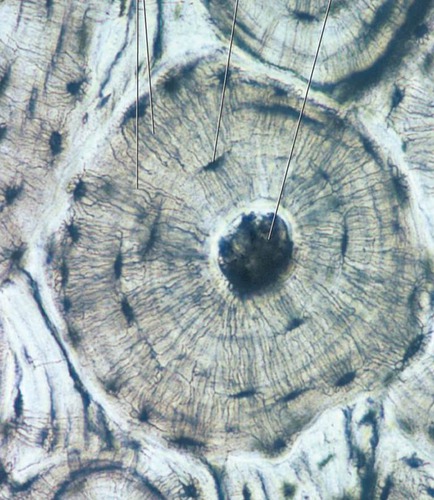
99
New cards
blood matrix
liquid/fluid plasma (lacks fibers) that allows materials like food, oxygen, and waste products to move quickly through the body
100
New cards
formed elements in blood
red cells, white cells, & platelets