unit 1
1/80
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
community
(a bunch of) populations sharing habitat
competition
compete for the same resources
predation
one population consumes another
symbiosis
long term interactions between organisms
symbiosis (parasitism)
+\-
parasite benefits from living\consuming the host
symbiosis (mutualism)
+\+
both benefit from interaction
ex. protection
symbiosis (commensalism)
+\meh
one benefits and host isn’t affected
population
members of the same species living in the same area
ecosystem
abiotic environment + biotic community
types of aquatic ecosystems
marine
fresh water
types of biomes (land ecosystems)
tropical forest
boreal forest
savanna
tundra
desert
mountains
chaparral
polar ice
temperate forest
temperate grassland
biome
community of plants and animals living in a certain climate
tropical rainforest
near the equator
high rainfall
warm, wet climate
high biodiversity
temperate deciduous forest (seasonal)
cold, dry winters
hot, humid summers
shed leaves in winter
temperate rainforest
mild, frost-free winters
even rainfall
coniferous forest
AKA boreal forest or taiga forest
midway between equator and poles
short, warm, moist summers
long, cold, dry winters
Christmas trees
deserts
pretty much all latitudes
mostly 30 degrees north and south of equator
low rainfall
plants adapted to hold water
grasslands
any latitude
seasonal drought, fire, grazing
stop trees and shrubs from overgrowing
savannas
warmer grasslands
scattered trees
temperate grasslands
mild grasslands
few trees
also prairies and steppes
scrublands
AKA shrublands, chaparrals, woodlands
western coastal regions between 30 degrees and 40 degrees north and south of the equator
dominated by shrubs and short trees
tundra
arctic
most inhabitable
cold and dry
short growing season
low biodiversity
permafrost
variety of plants and animals
freshwater biome
little to no salt
ponds, lakes streams, rivers
drinking water
ponds
standing water
smaller than lakes and seasonal
lakes
standing water
larger than ponds and more permanent
four zones
littoral zone
top, near shore
lots of sun
wide variety of plants and animals
limnetic zone
AKA open water zone
photosynthesis
phytoplankton, zooplankton, freshwater fish
profundal zone
AKA deep water zone
too dark for photosynthesis
less dissolved oxygen
benthic zone
soil and soil organisms at bottom of lake
decomposers
streams and rivers
drain a landscape
three zones
source zone
transition zone
floodplain zone
source zone
where streams and rivers start
water at high elevations collect from precipitation and snowmelt
cold, fast moving, lots of dissolved oxygen
few plant species
transition zone
where headwaters merge
wider, slower moving, less dissolved oxygen
warmer, more nutrient rich
larger variety of plants and animals
floodplain zone
water spills onto land forming wetlands and temporary lakes
warm, nutrient rich, less dissolved oxygen
greatest variety of plants and animals
ways that atmospheric carbon dioxide is taken from the atmosphere
photosynthesis
sunlight is used to transform carbon dioxide into energy
ocean
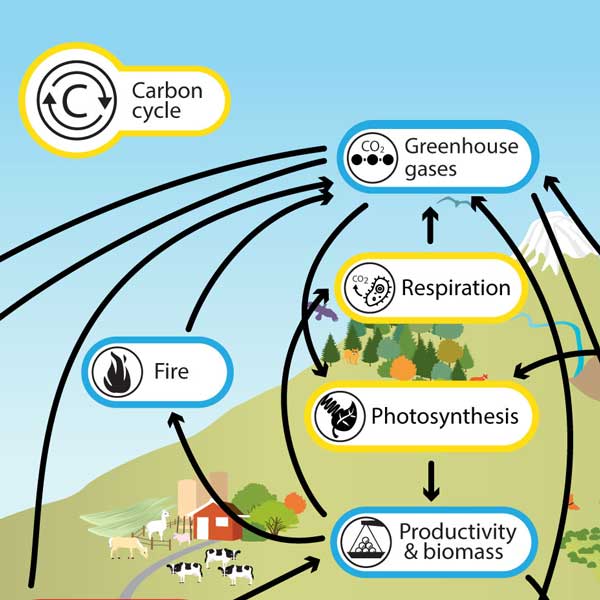
ways that carbon dioxide returns to the atmosphere
cellular respiration
decomposition
compressed organisms turning into fossil fuels
combustion
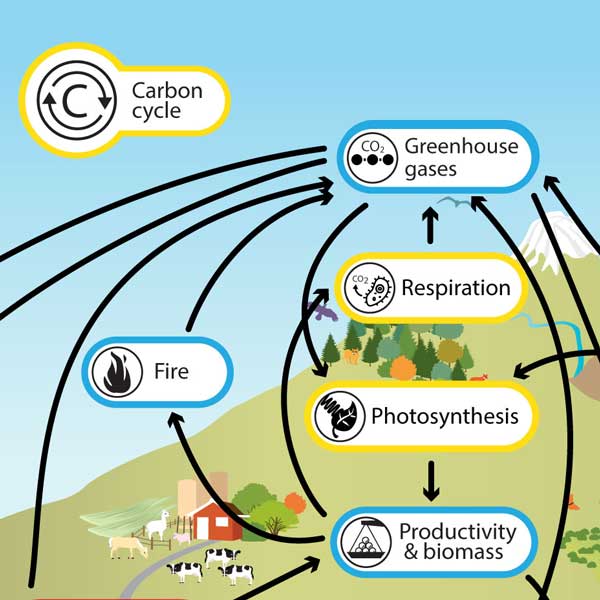
cellular respiration
organisms break down organic compounds to produce usable energy
release carbon dioxide in the process
C6H12O6 + O2 —> CO2 + H2O + cellular energy
carbon reservoir
where large amounts of carbon are stored
rocks, water, sediments
bodies of living organisms
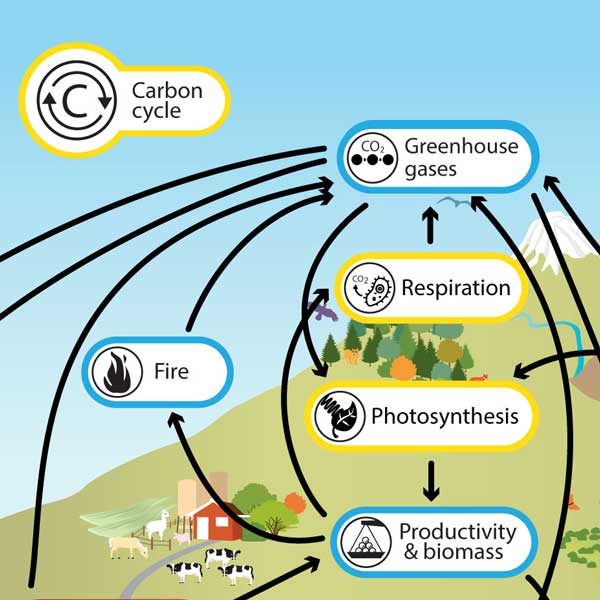
geological carbon cycle
carbon from rocks into oceans
weathering and rainwater
bicarbonate used in shells
sink and form sediment and rocks
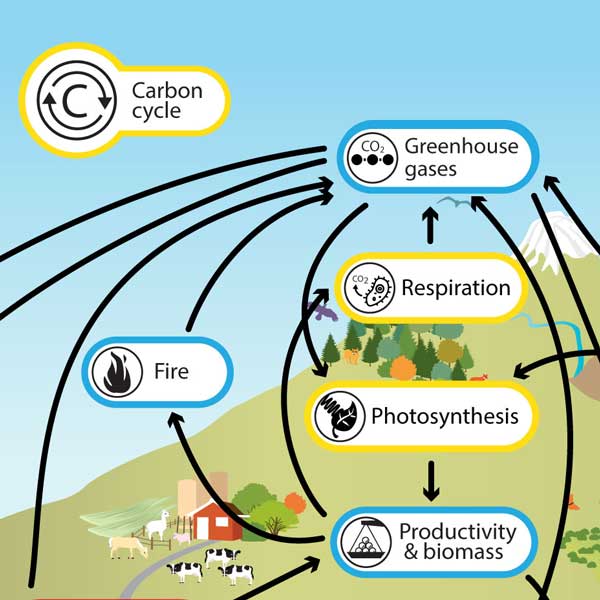
human impacts on carbon cycle
fossil fuels
deforestation
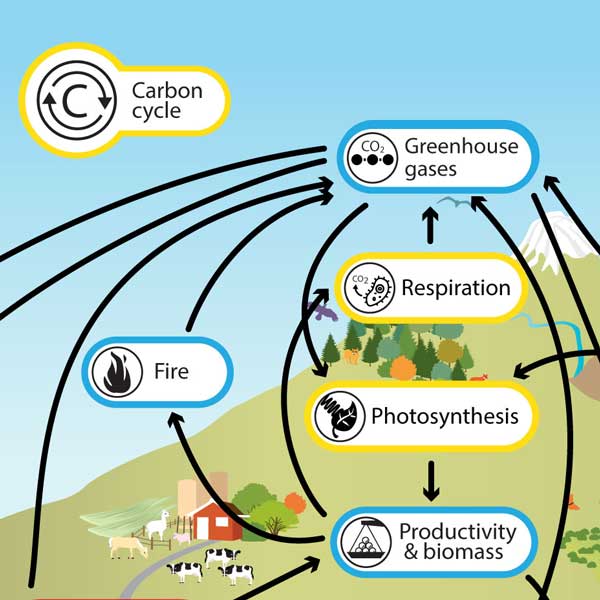
ways that nitrogen is removed from the atmosphere
nitrogen fixation
lightning
nitrogen-fixing bacteria
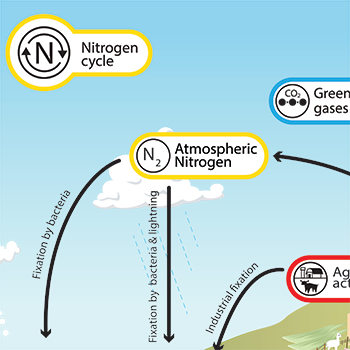
ways that nitrogen returns to the atmosphere
denitrification
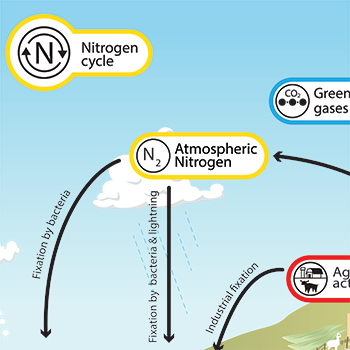
nitrogen reservoirs
atmosphere
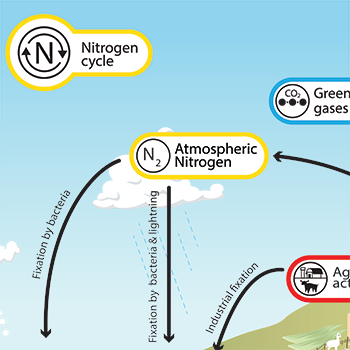
nitrogen-fixing bacteria
N2 —> NH3 (ammonia)
transforms into ammonia used by plants
ammonification
bacteria and fungi return ammonia and ammonium ions to environment from decomposing organisms
nitrification
bacteria convert ammonia and ammonium into nitrites, then nitrates
denitrification
bacteria convert nitrites and nitrates into nitrogen gas
phosphorus is what kind of nutrient in ecosystems?
limiting
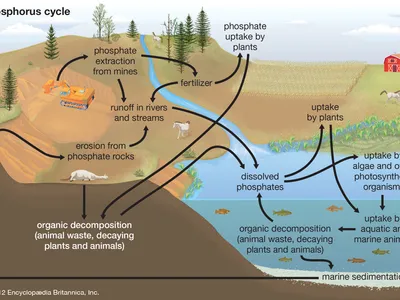
limiting nutrient
in shortest supply
limits growth
phosphorus reservoirs
rock and deep ocean sediments
not found in atmosphere
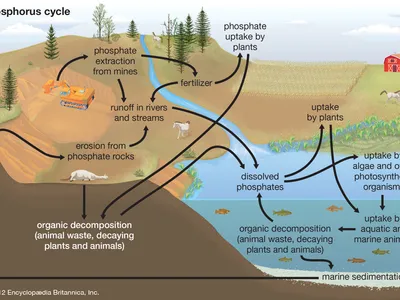
how phosphate is released
weathering
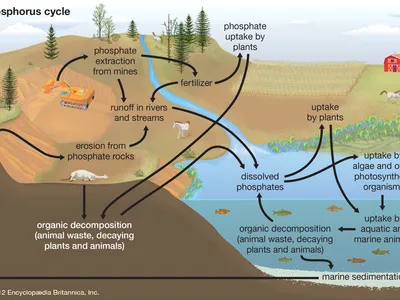
how phosphate ions are used
plants
move up the food chain
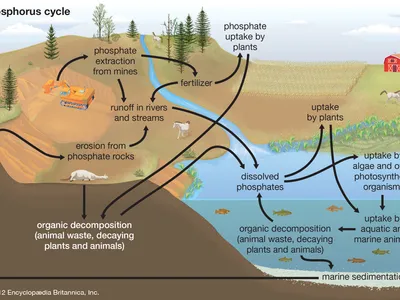
how phosphorus returns to rocks
decomposing organisms are compacted into layers of soil and rock
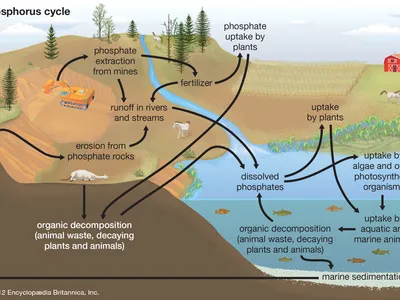
how humans influence the phosphorus cycle
animal waste and phosphate sediments to make fertilizer
enter aquatic systems as runoff
water “reservoir”
oceans
ice
groundwater
groundwater
between soil particles and in cracks
percolated, unevaporated water
freshwater reservoir
aquifers
groundwater reservoirs where we access freshwater
human impacts on water cycle
digging wells
collecting raiinwater
desalinisation
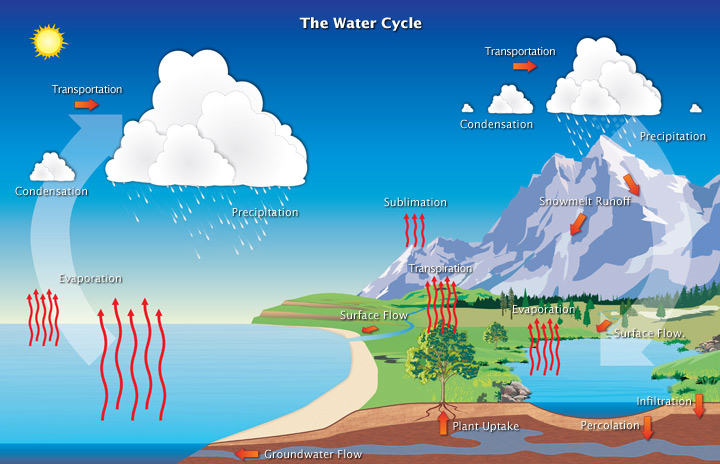
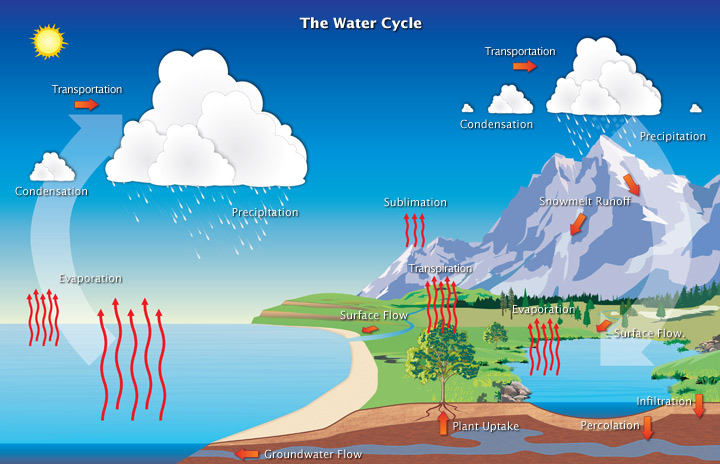
hydrologic cycle is driven by
the sun
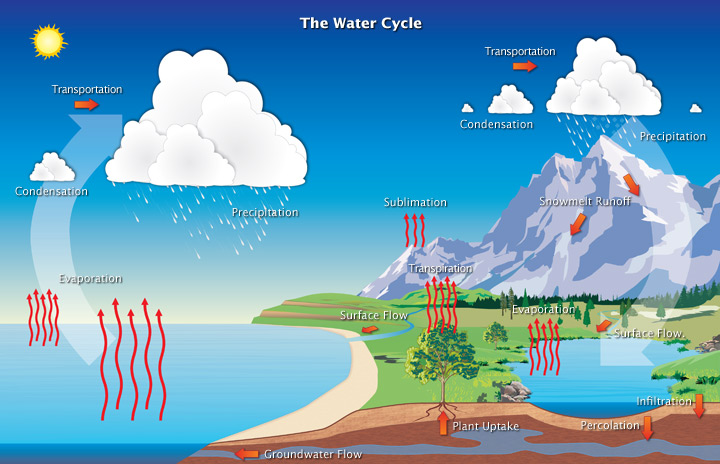
how water enters the atmosphere
evaporation
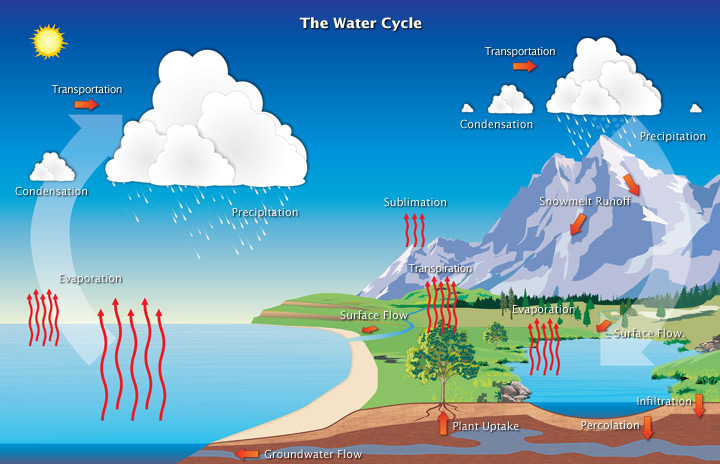
how water leaves the atmosphere
precipitation
rain and snow
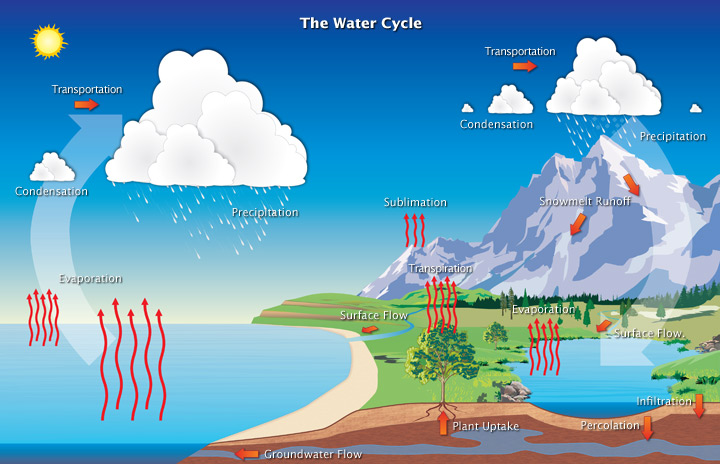
transpiration
water enters through roots
water evaporates through stomata (leaf pores)
used to move ions and minerals and cool
niche specialist
species that can survive in a narrow range of environmental conditions
photosynthesis
CO2 + H2O + light energy —> C6H12O6 (glucose) +O2
gross primary productivity
how much photosynthesis is occuring in a given area and time
net primary productivity
how much photosynthesis occurs over given area and time minus the respiration
gross primary productivity- respiration = net primary productivity
species richness
number of different species in an area
more species = higher species richness
species evenness
species abundance in an area
equal individuals in an area = higher species evenness
ecosystem resilience
ability of an ecosystem to adapt to change and return to equilibrium state after disturbance
specialist species
specific habitat, food, environmental conditions
sensitive to changes/threats
generalist species
variety of habitats, foods, environmental conditions
can adapt more to habitat changes