DECA Marketing cluster exam
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Exclusive Distribution
Situation where suppliers and distributors enter into an exclusive agreement that only allows the named distributor to sell a specific product.
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) Systems
The electronic interchange of business information using a standardized format; a process which allows one company to send information to another company electronically rather than with paper.
Trading Partners
Business entities conducting business electronically.
Streamline
Make (an organization or system) more efficient and effective by employing faster or simpler working methods.
Slotting Allowances / Slotting Fee
A fee charged to produce companies or manufacturers by supermarket distributors (retailers) in order to have their product placed on their shelves. Known as Pay-to-Stay.
Consumer Choice
The range of competing products and services from which a consumer can choose.
Tariff
A tax or duty to be paid on a particular class of imports or exports. OR. Fix the price of (something) according to a tariff.
Horizontal Conflict
Refers to a disagreement among two or more channel members at the same level. For example, suppose a toy manufacturer has deals with two wholesalers, each contracted to sell products to retailers in different regions. If one wholesaler decides to branch its operations into the other wholesaler's region, a conflict will result.
Vertical Conflict
A disagreement between two channel members on consecutive levels. For example, if the toy manufacturer discovers its products are arriving at retail stores later than scheduled, a conflict might develop between the manufacturer and the wholesaler responsible for shipping to retailers.
Chargeback
A demand by a credit-card provider for a retailer to make good the loss on a fraudulent or disputed transaction.
Scrambled Merchandising
When a shop sells goods that are usually sold by another type of shop, in order to increase profits or attract new customers.
Direct Selling
The marketing and selling of products directly to consumers away from a fixed retail location. Peddling is the oldest form of direct selling. Modern direct selling includes sales made through the party plan, one-on-one demonstrations, and other personal contact arrangements as well as internet sales.
4 P's of Marketing
Product
Price
Place
Promotion
Executive Summary
Sometimes known as a management summary, is a short document or section of a document, produced for business purposes, that summarizes a longer report or proposal or a group of related reports in such a way that readers can rapidly become acquainted with a large body of material without having to read it all.
Project Status Meeting
A meeting to see how the project is progressing.
Brand Promise
Benefits and experiences that marketing campaigns try to associate with a product in its current and prospective consumers' minds.
First-Line Managers
Term describing the management level of a company employee directly above non-managerial workers. First line managers generally supervise production on line tasks in the manufacturing business, and typically consist of positions such as foreman, section head and shift boss. First line managers are an important source of information about worker satisfaction for higher management to take into account in their organizational planning process.
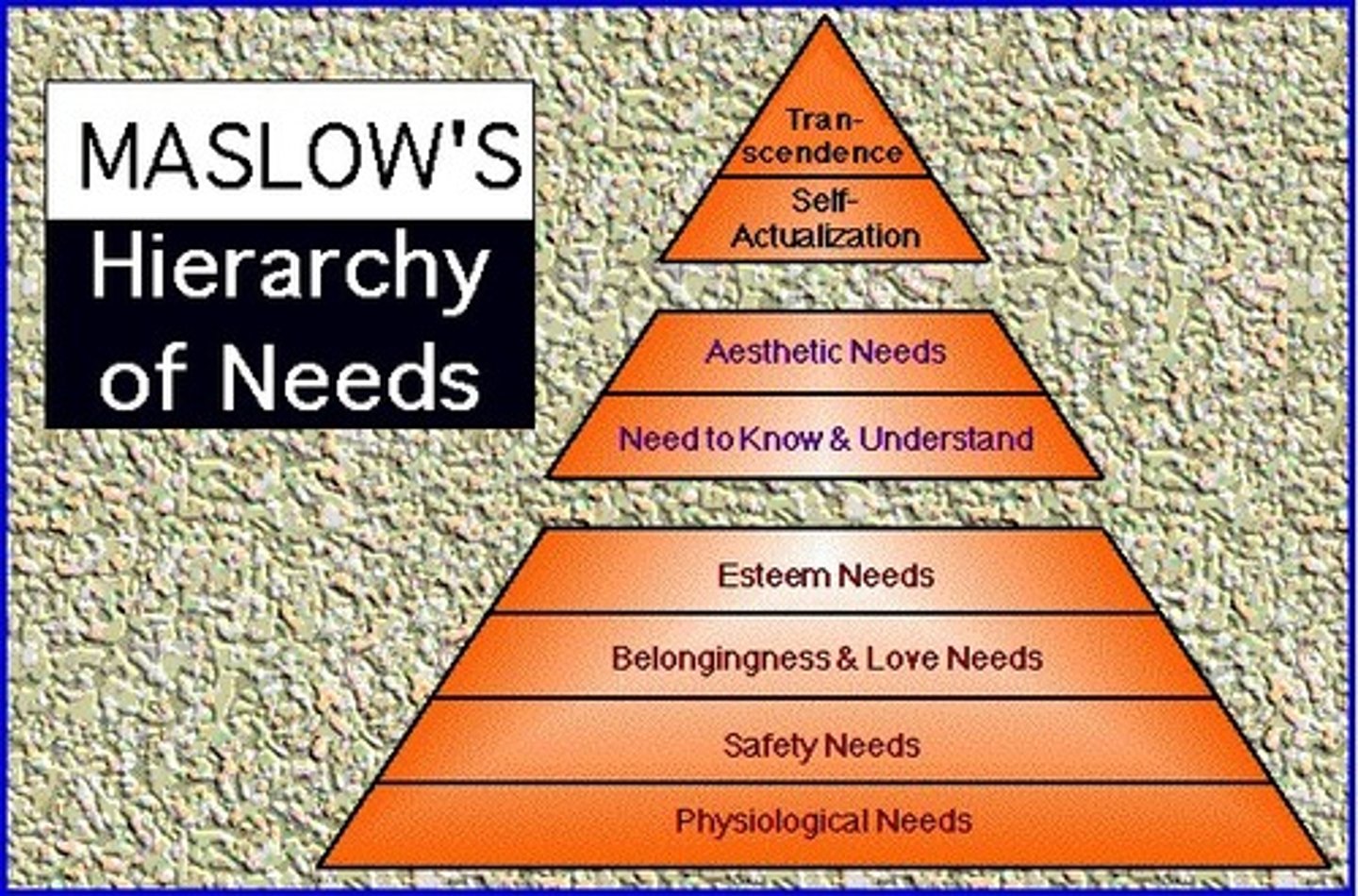
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
A description of the needs that motivate human behavior. In 1943, Abraham Maslow proposed five different kinds of human needs, beginning with the most basic: survival. Physiological needs, such as food and shelter, are followed by needs related to safety. Next, there are needs of love and belonging. Fourth, humans have needs of esteem, such as the need for being respected. The final need in the hierarchy is the need for self-actualization (fulfilling one's potential). The hierarchy suggests that basic needs must be met prior to less basic needs; for example, a starving person will seek food before self-actualization.
Marketing
The action or business of promoting and selling products or services, including market research and advertising.
Product Literature
A primary subset of business publishing specifically geared toward the selection, purchase and use of a business' products. Typically this includes product promotionally literature, product datasheets, product operating manuals and product purchase terms and conditions.
Entertainment Guidelines
Sets minimums for receiving business amenities.
Promotional Plan
An outline of the marketing tools, strategies and resources that a company intends to use to promote a product or service. A promotional plan is usually considered a vital planning tool by most business managers that helps contribute toward the successful launch of a new product or service or its expansion into a new market.
Internal Audience
Public relations term that refers to individuals or groups within (or closely associated with) an organization.
Public-Relations Activities
Advertising
Corporate Philanthropy
Corporate Sponsorship
Development
Lobbying
Promotion
Publicity
Public Relations Research
Special Event Management
Lobbying
The act of attempting to influence the decisions of others.
Corporate Philanthropy
The act of a corporation or business promoting the welfare of others, generally via charitable donations of funds or time.
Rebate
A partial refund to someone who has paid too much money for tax, rent, or a utility. A pay back.
Direct Marketing
A channel-agnostic form of advertising which allows businesses and nonprofit organizations to communicate straight to the customer, with advertising techniques that can include cell phone text messaging, email, interactive consumer websites, online display ads, database marketing, fliers, catalog etc.
Telemarketing
Marketing over the phone
Banner Ad
A form of advertising on the World Wide Web delivered by an ad server. This form of online advertising entails embedding an advertisement into a web page. It is intended to attract traffic to a website by linking to the website of the advertiser.
Interstitial
A page that is inserted in the normal flow of editorial content structure on a Web site for the purpose of advertising or promotion. It can be more or less intrusive and the reaction of viewers usually depends on how welcome or entertaining the message is.
Media-Rich Advertising
Involves animations that float across the computer screen and move back to their original space,
Puffery
Exaggerated or false praise.
Regulatory Agency
A public authority or government agency responsible for exercising autonomous authority over some area of human activity in a regulatory or supervisory capacity.
Scope
Sum of all individual jobs.
Depth
The influence of an employee in his work environment such as decision making and accountability. Higher level positions have more job depth as it involves decision making and greater discretion on how a job is done.
Cash Conversion Cycle
It measures how fast a company can convert cash on hand into even more cash on hand.
Liquid Asset
An asset that can be converted into cash quickly and with minimal impact to the price received.
Profit Margin
The amount by which revenue from sales exceeds costs in a business.
Dividend
A sum of money paid regularly (typically quarterly) by a company to its shareholders out of its profits (or reserves).
Sugging
The act of selling or attempting to sell a product under the guise of conducting market research.
Price Discrimination
The action of selling the same product at different prices to different buyers, in order to maximize sales and profits.
Scanner Fraud
When a store changes the sticker price of an object to be on sale, but doesn't change the price within the computer, so the consumer will pay the higher price at the point of sale.
Price Gouging
A seller prices goods or commodities at a level much higher than is considered reasonable or fair. This rapid increase in prices occurs after a demand or supply shock: examples include price increases after hurricanes or other natural disasters.
Invoice
A commercial document that itemizes a transaction between a buyer and a seller. Will usually include the quantity of purchase, price of goods and/or services, date, parties involved, unique invoice number, and tax information.
SWOT Analysis
A study undertaken by an organization to identify its internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as its external opportunities and threats.
Demographic
A particular sector of a population.
Geographics
A particular sector of the world/ geography.
Psychographics
Study of personality, values, opinions, attitudes, interests, and lifestyles. Because this area of research focuses on interests, attitudes, and opinions.
Six Thinking Hats
A creative-thinking technique that involves categorizing and focusing on different aspects of a problem, issue, or situation. Each "hat" represents one aspect or way (i.e., facts, positives, negatives, emotions, new ideas, organization) of looking at the situation. Brainstorming involves identifying as many different ideas as possible during a set time frame. Mind mapping is a form of brainstorming that organizes ideas and information graphically using shapes, pictures, and words. Unconscious problem solving involves relaxation and distraction from the product, situation, or issue.
Tort
A wrongful act or an infringement of a right (other than under contract) leading to civil legal liability.
Competition (of business)
The effort of two or more parties acting independently to secure the business of a third party by offering the most favorable terms.
Bilateral Contract
A reciprocal arrangement between two parties where each promises to perform an act in exchange for the other party's act. Each party is an (a person who is bound to another) to its own promise, and an obligee (a person to whom another is obligated or bound) on the other party's promise.
Executed Agreement
All parties have agreed to the terms and conditions of the proposed contract by signing and initialing any changes to the written document.
Sole Proprietorship
A business that legally has no separate existence from its owner. Income and losses are taxed on the individual's personal income tax return.
Sole Proprietor
An unincorporated business with one owner who pays personal income tax on profits from the business. With little government regulation, they are the simplest business to set up or take apart, making them popular among individual self contractors or business owners.
Bar Code
A machine-readable code in the form of numbers and a pattern of parallel lines of varying widths, printed on and identifying a product.
Price Look-Up Codes (PLU)
Identification numbers affixed to products in large retailers and supermarkets to make check-out and inventory control easier, faster, and more accurate. The code may be a four-digit number, currently in the 3000-4999 range, identifying the type of bulk produce, including the variety, or a five-digit number.
Tying Agreement
An agreement by a party to sell one product but only on the condition that the buyer also purchases a different (or tied) product, or at least agrees he will not purchase the product from any other supplier.
Automation
The use of largely automatic equipment in a system of manufacturing or other production process.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The monetary value of all the finished goods and services produced within a country's borders in a specific time period, though GDP is usually calculated on an annual basis.
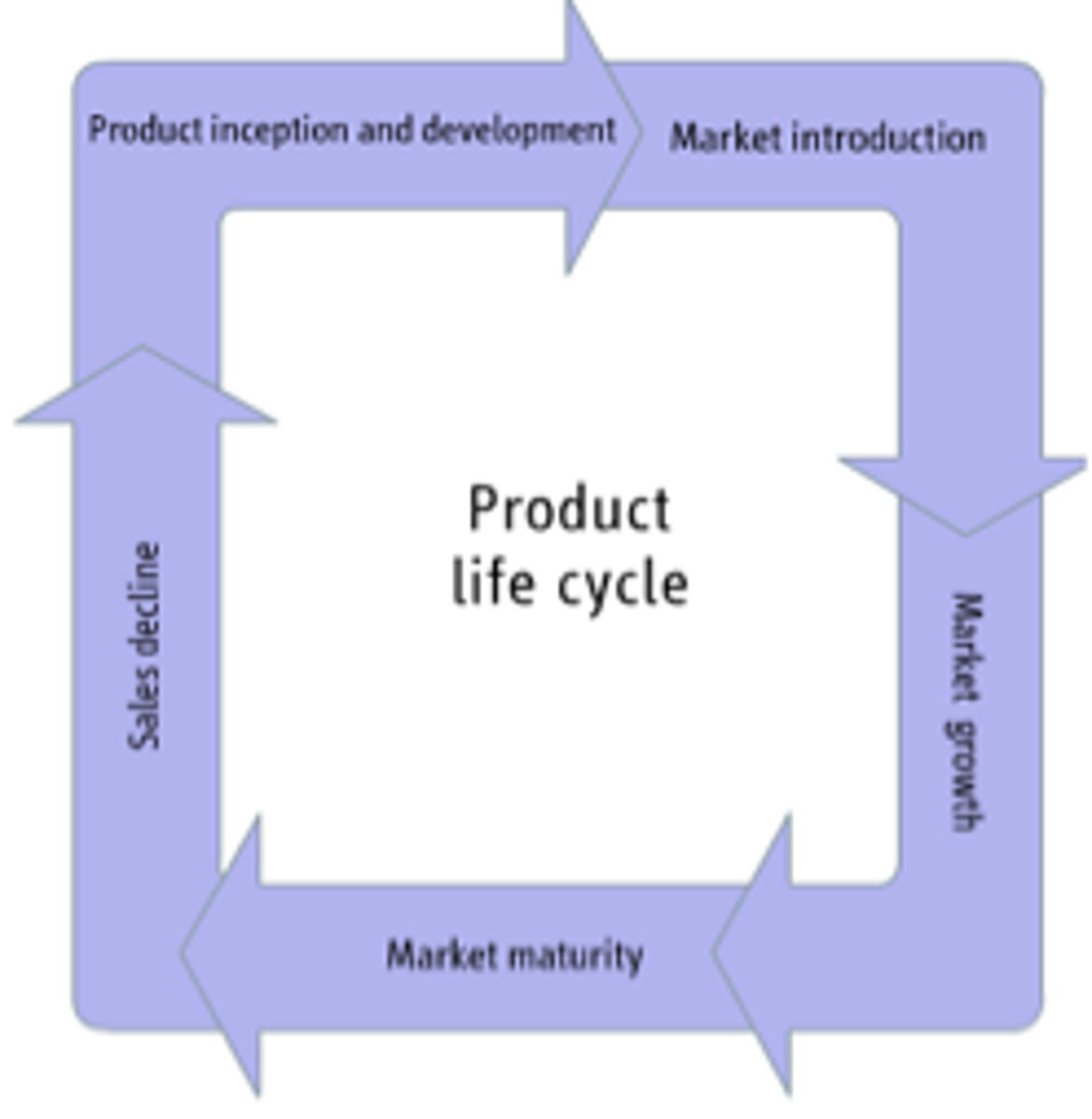
Product Life-Cycle
The cycle through which every product goes through from introduction to withdrawal or eventual demise.
Product Life-Cycle Stages
http://productlifecyclestages.com/
Introduction:
Launching a new product. The size of the market for the product is small, which means sales are low, although they will be increasing.
Growth:
Strong growth in sales and profits which allows more money to invest in promotion.
Maturity:
The product is established and the aim for the manufacturer is now to maintain the market share they have built up. This is probably the most competitive time for most products and businesses need to invest wisely in any marketing they undertake.
Decline:
the market for a product will start to shrink, and this is what's known as the decline stage. This shrinkage could be due to the market becoming saturated (i.e. all the customers who will buy the product have already purchased it), or because the consumers are switching to a different type of product
Certificate of Deposit (CDs)
A certificate issued by a bank to a person depositing money for a specified length of time.
Capital Investment
Funds invested in a firm or enterprise for the purposes of furthering its business objectives. May also refer to a firm's acquisition of capital assets or fixed assets such as manufacturing plants and machinery that is expected to be productive over many years.
Turnover
The amount of money taken by a business in a particular period. OR The rate at which employees leave a workforce and are replaced.
Inventory Clerks
Keeps track of stock that moves in and out of a specified location, commonly referred to as a stockroom.
Fixed Costs
Business costs, such as rent, that are constant whatever the quantity of goods or services produced.
A/B Testing
This is the process of comparing two variations of a single variable to determine which performs best in order to help improve marketing efforts
Blogging
Weblog or Weblog. Core component of inbound marketing as it can accomplish several initiatives simultaneously, such as website traffic growth, thought leadership, and lead generation. It does not, however, do your taxes.
Call-to-Action
A text link, button, image, or some type of web link that encourages a website visitor to visit a landing page and become of lead. Some examples of CTAs are "Subscribe Now" or "Download the Whitepaper Today."
Qualified Lead
A contact that opted in to receive communication from your company, became educated about your product or service, and is interested in learning more.
Niche Marketing
Market plan to serve a specific demographical, geographical, psychographics slice of the market place.