Module 2 - Physics
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
What is matter?
Matter is a substance that an object is made up of, as long as its mass and dimensions can be measured.
what are the 3 main states of matter?
Solids, Liquids, Gases
how many elements are currently discovered?
118
What are the 3 main characteristics of an atom?
cannot be broken down further
can be made of 1 atom, or molecule
only consists of one type of atom
what are the horizontal rows on the periodic table called?
Periods
What are the vertical rows on the periodic table called?
Groups - have similar properties
What is an atoms nucleus made up of? and what are there charges?
Protons and neutrons, protons carry a + charge, while neutrons are neutral in charge.
How much do protons and neutrons weigh?
1.67 × 10²7
what surrounds the nucleus? and what’s its charge?
electrons, they carry a negative charge.
how much does an electron weigh?
9.11 × 10³1
what are shells? and what are the varying shells capacities?
shells carry electrons orbiting the nucleus, the first carries 2, the next 8, next 18, next 32 and so on. the formula is 2n².
what’s the outermost shell called? explain how it effects the elements properties?
Valence shell, which contain valence electrons. if the shell is full its said to be stable, if not full the elements is likely to be more reactive, or a good conductor. full valence shells means that the element is an insulator. a half full valence shell means its likely to be a semiconductor, where its state dependant on if the substance conducts well .
what is an isotope?
an isotope is a variation of an element, that has a different number of neutrons than the original element.
What is the atomic number, and were is it usually represented?
atomic number indicated the amount of protons, it is usually on the top of the element on the periodic table. it can be on the bottom when written in isotope notation.
what is the atomic mass, and where is it usually represented.
atomic mass is the number of protons and neutrons combined, usually shown on the bottom of the element on the periodic table.
What is a molecule?
where 2 or more atoms are combined chemically.
what are the 2 types of chemical bonds?
covalent - between 2 non-metals, where atoms are shared.
Ionic - between a metal and non-metal, where atoms are transferred, usually from the metal to non-metal leading to a positive charged metal and negatively charged non-metal.
What is a compound?
a pure substance where 2 or more elements are chemically combined, and cannot be physically separated.
What is a mixture?
2 or more elements that are combined, but not chemically so can be physically separated.
What are the types of mixtures?
solution - sea water
colloids
suspension - sand in water
What is density?
Density is the amount of mass within 1 unit volume
It is measured in kg/m3, or g/cm3
Describe a solid.
regular and rigid formation of particles with strong forces between them
they are usually dense
don’t react much to heat or compression
have there own surface
describe a liquid.
somewhat weak bonds and particles can freely move to a degree, they fill there container and react to heat, but much less to pressure.
Describe a gas.
Gasses have very weak bonds, and move very freely within there container, they react wildly to heat and compression.
what is evaporation?
process of liquid to gas below its boiling point, endothermic reaction.
what is boiling?
process from liquid to gas above its boiling point consistently, endothermic .
what is condensation?
process of gas to liquid, exothermic reaction.
what is freezing?
process of liquid to solid, in an exothermic reaction.
what is melting?
Process of solid to liquid. and is an endothermic reaction.
what is sublimation?
process of solid to gas. is an endothermic reaction.
what is deposition?
process of gas to solid, is an exothermic reaction.
What is an ion?
an ion is formed when an atom gains or loses an electron and its charge is charged. an anion is a negatively charged atom, and a cation is a positively charged atom.
What is newtons first law?
That an object will remain still, or at a constant speed unless forces act against it.
What is a vector quantity?
Has both magnitude and direction.
e.g. velocity, momentum, acceleration
What is a scalar quantity?
has magnitude only.
E.g. length, temperature, mass, distance
what is a moment? and what is its formula and units?
Moment is the turning effect of force, acting on a pivot point
Moment = force x distance
measured in Nm
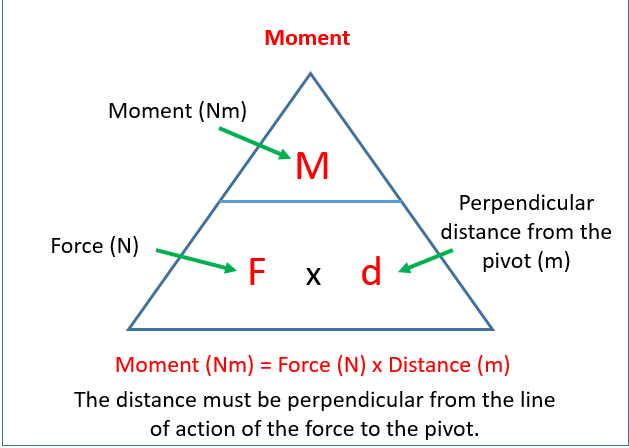
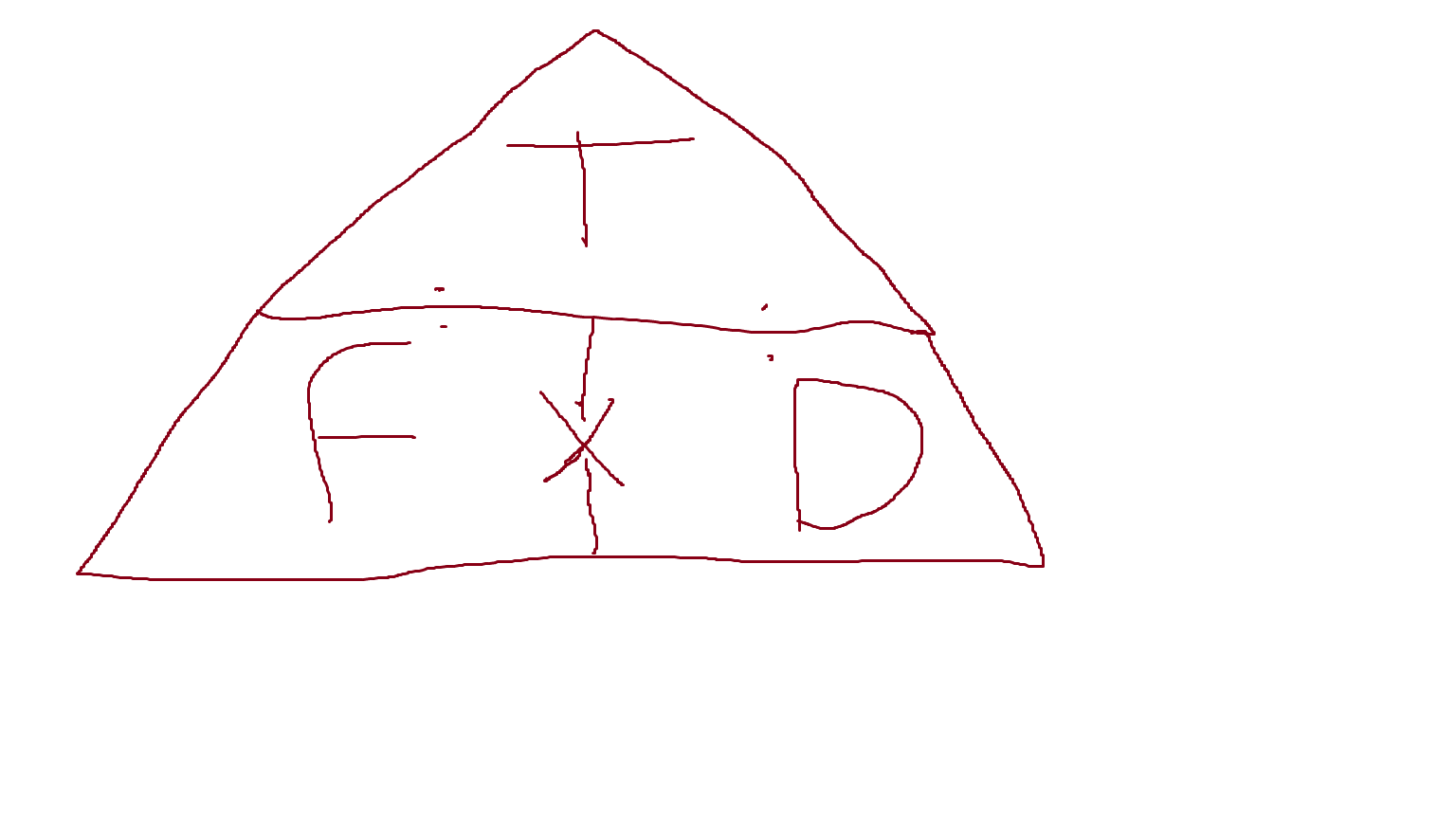
What is a couple? and what’s its formula and units?
torque created, by 2 opposite direction forces
torque = force x distance between moments
measured in Nm
what is the resultant?
two forces of the same quantity acting with or against eachother
what is CG?
centre of gravity, the point at which all the weight of an object is said to act, can be subject to change in aviation.
calculated by calculating all the individual moments, adding them and dividing that total by the total weight of the aircraft.
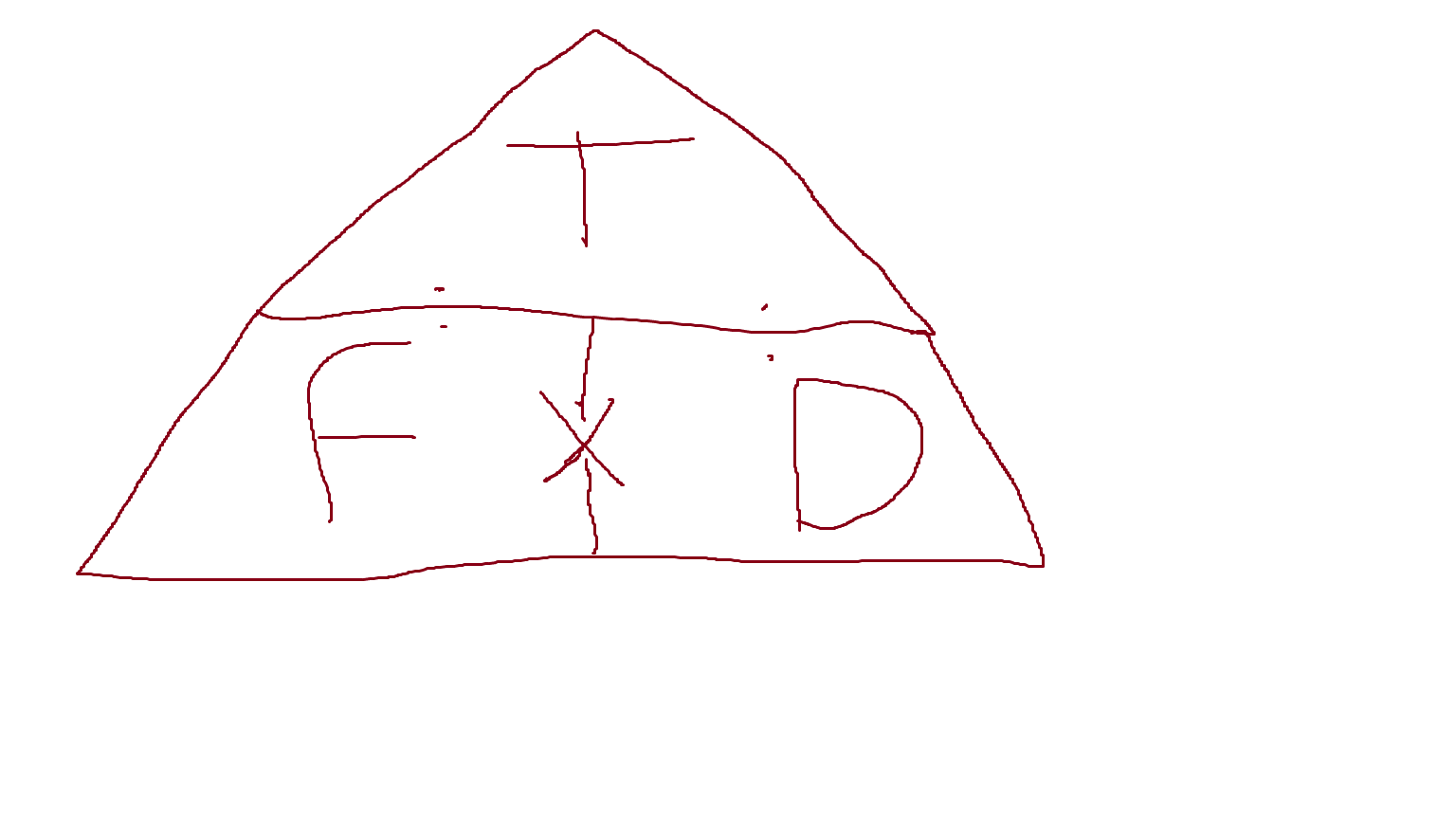
What is stress?
Stress is the force per unit area that causes material deformation
it is measured is Nm or Pa
and its Calculated by stress = force/area
What is tension/tensile stress?
Forces pulling material apart
What is compressive stress?
Forces pushing material together
What is shearing stress?
Layers sliding over eachother
What is bending stress?
One side stretches, while the other compresses
What is tensile stress?
Twisting motion/forces.
What is strain?
Strain is how much a material turns back to its original form after stress. strain is what stress results in.
it is displayed as a ratio, and is calculated by change/original shape.
What is elasticity?
the ability for a material to return to its original shape after forces are removed
What is plasticity?
plasticity is material that is permanently deformed.
what is Hooke’s law?
states that the extension is directly proportional to the force applied
Calculated by Force = Spring constant k x extension e
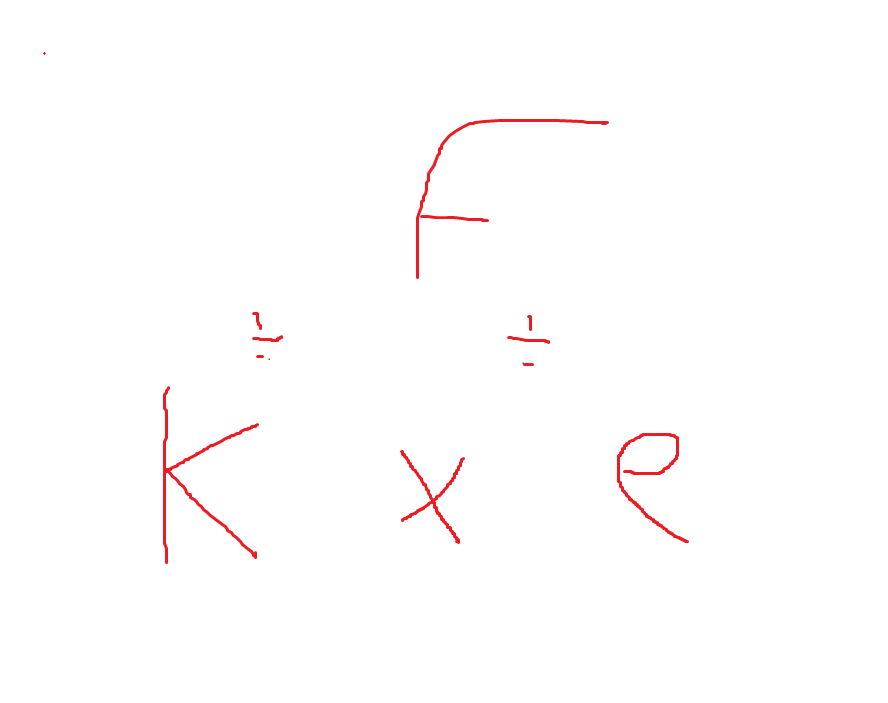
what is young’s modulus?
measure of how stiff/elastic a material is within the elastic region.
Stress / Strain
What is hardness ?
Hardness is the resistance to surface penetration, indentation and wear. Not necessarily to fracture.
What is strength ?
Strength is the ability for a material to withstand applied force without fracture, plastic deformation etc.
What is toughness ?
Toughness is the ability for a material to not break under sudden impacts, or after being deformed.
What is brittleness ?
Brittleness is when a material breaks without changing shape, it is worse during the cold
What is elasticity ?
Elasticity is the ability for a material to return to its original shape after force is removed.
What is plasticity ?
The tendency of a material to stay deformed even after force is removed.
What is Malleability ?
The ability of a material to not break or fracture, under compressive forces which may deform the material
What is Ductility?
Ductility is the ability of a material to resist tensile forces and not break
What is a vapour ?
A gas that can be liquified by pressure, below its boiling point
What is a volatile liquid ?
A liquid that can evaporate in its container, while at a normal temperature, below its boiling point.
What is flammability/inflammability?
how easily a liquid or gas catches fire, volatile liquids often give off flammable gases
What is the flash point ?
The temperature at which gases are produced that can ignite with a flame, e.g. petroleum at - 23
What is toxicity ?
How poisonous a material is? Can be ingested or contact the body in many ways and caused many effects.
What is an inert gas/liquid ?
doesn’t react chemically
What is pressure ?
Pressure is the amount of force per unit area, it is represented by Nm, Pa, or psi 1Nm is 1Pa. P = f/a
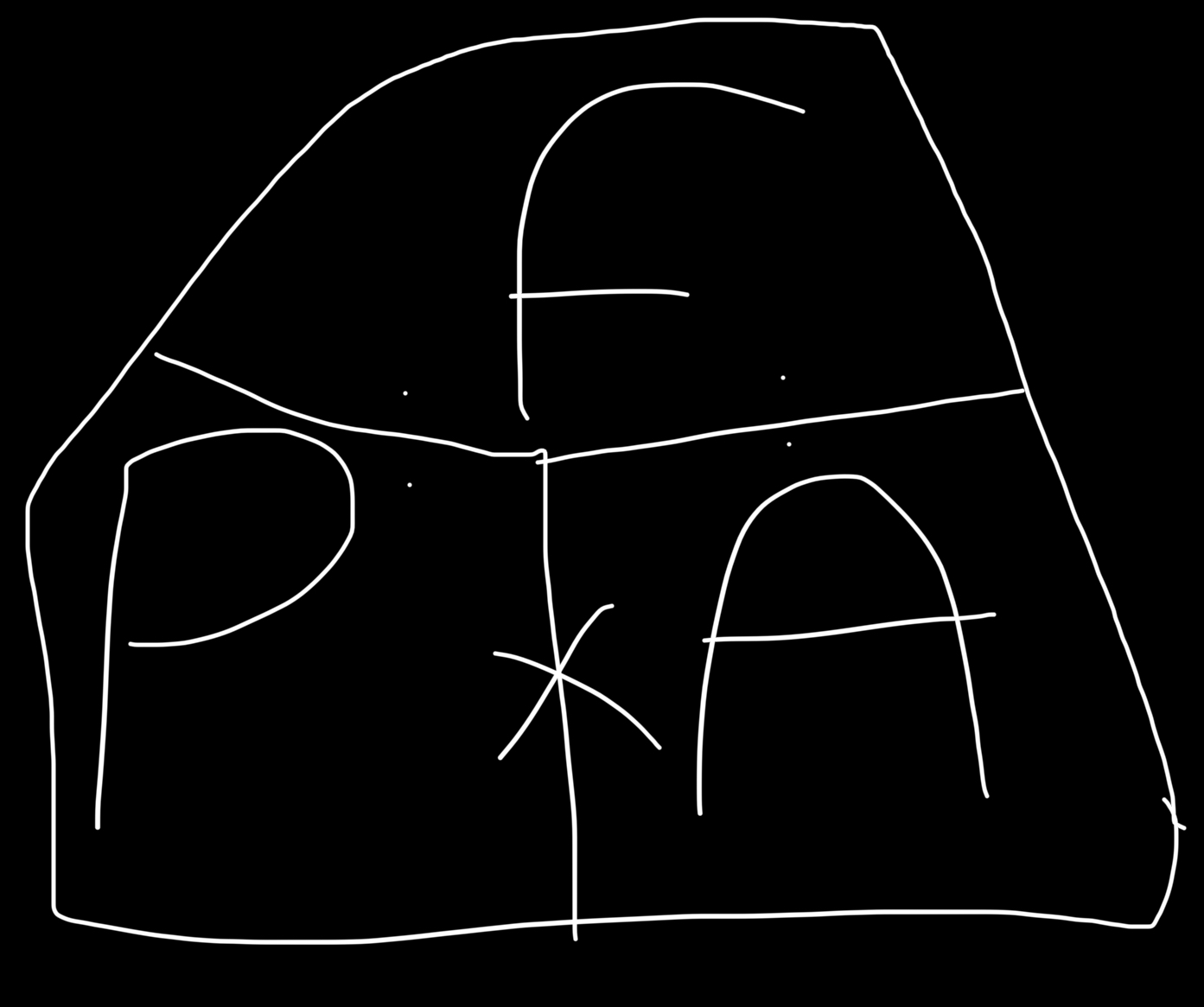

What is atmospheric pressure?
The pressure of the atmosphere pressing down, it decreases with altitude as air becomes less dense, standard at sea level is around 14 psi, 1000hpa.
What is gauge pressure vs absolute pressure ?
Gauge pressure is the pressure above atmospheric pressure e.g. tire gauge shows 30psi, 30 above the atmospheric.
Absolute pressure is pressure at absolute 0 in a vacuum. = gauge + atmospheric
What is the different types of buoyancy ?
Object weight < buoyant force = positive so will float
Object weight > buoyant force = negative so will sink
If they are equal the object will be suspended
What is density in context of floating ?
the density of an object will determine if it sinks or floats based on the ratio of object density to fluid density, based on the fluids density. If the object is more dense it will sink, if it’s less dense then it will float. It is calculated by D = M/A and it represented by kg\m³
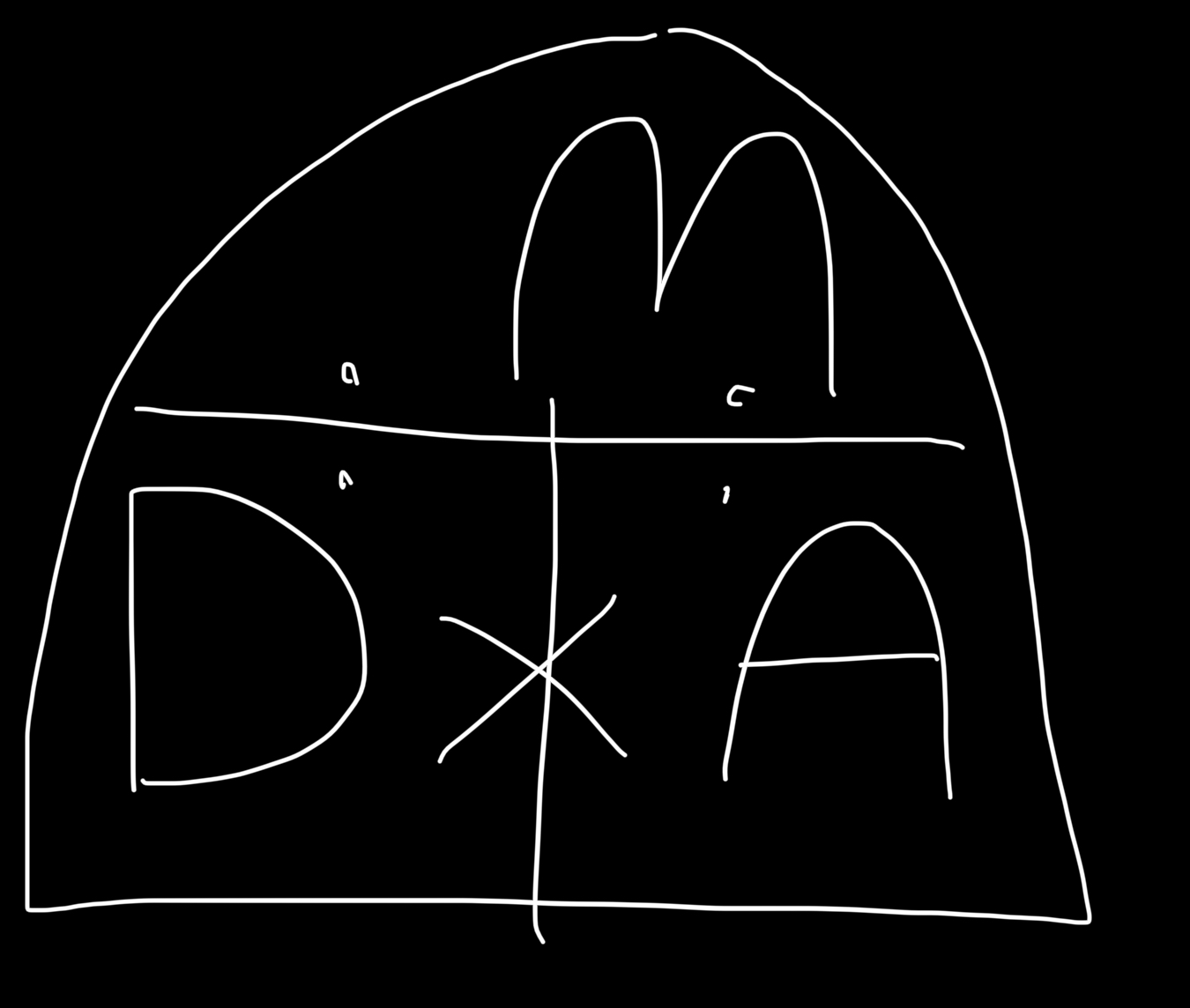
What is displacement ?
Displacement is a vector quantity that is concerned with the amount of distance traveled from a start to an end point, and in which direction.
What is speed?
Speed is a scalar quantity, that is concerned with amount of distance covered over time, ie how fast something travels.
Speed = distance/ time
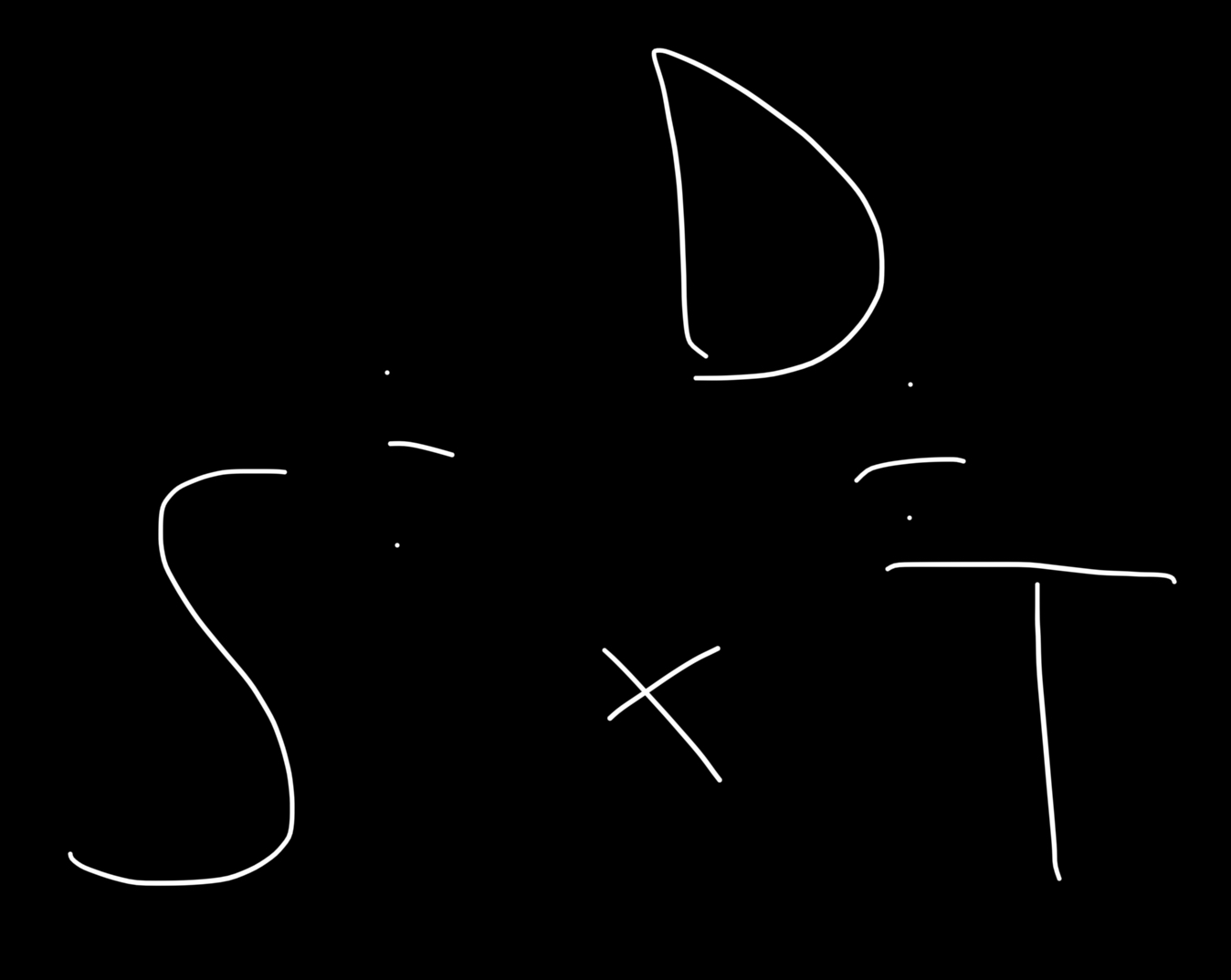
What is velocity ?
Velocity is speed with direction, the change in displacement over time, it’s a vector quantity
Velocity = change in displacement / time
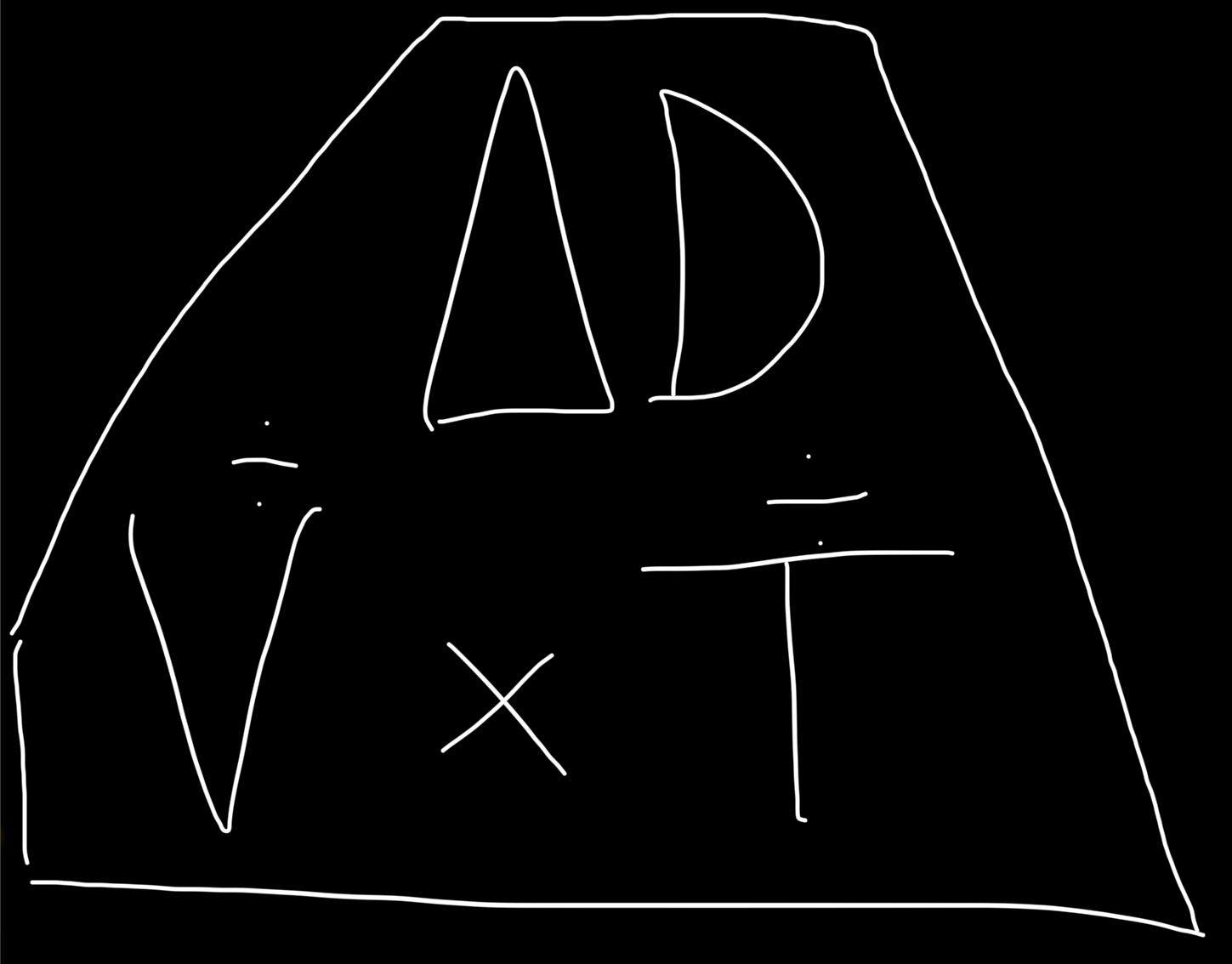
What is acceleration ?
Acceleration is the change in velocity over time
Acceleration = change in velocity / time
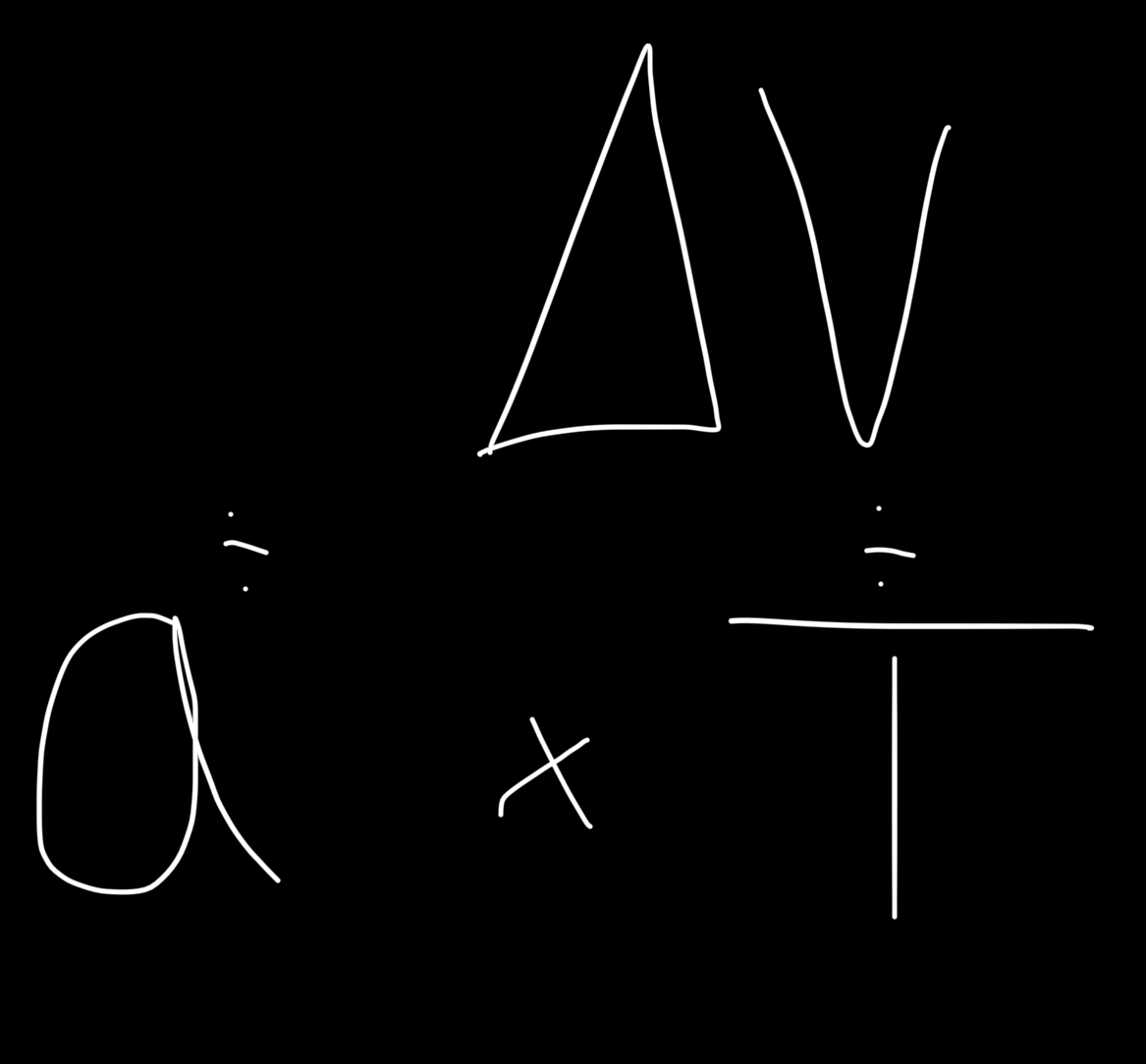
What is uniform motion ?
Uniform motion is consistent distances being covered, as speed isn’t changing and no acceleration is present
What is non-Uniform motion ?
Non uniform motion is where acceleration is present, and velocity is changing as a result.
What is centripetal force ?
Centripetal force is the force keeping an object moving an a circular motion toward a central point
What is rotational movement ?
When an object moves around a central point, the velocity is constantly changing because the direction is.
What us centripetal acceleration ?
The acceleration caused by the constant direction changes (not the speed changes)
What is centrifugal force?
The apparent forces felt by an object, it isn’t a real force, created by the object feeling like moving away from the centre point.
Define all the pendulum motion terms: amplitude, oscillation, length, period, cycle, frequency.
Amplitude: distance from resting point to highest point
Oscillation: one full motion there and back
Length: the pivot to bob length
Period: how long it takes to complete one oscillation
Cycle:a whole back and forth motion
Frequency: how many cycles per second
What is Damping?
Damping is the gradual loss of energy over time, reducing the movement. Can be due to forces such as air resistance or friction.
What is vibrations ?
Back and forth movements from a fixed point, can be random and regular, and useful or unuseful
what is free vibration ?
When an object is disturbed and left to vibrate on its own, will eventually dampen
What is forced vibration ?
Vibrations caused by purposeful external force, the vibrations will be at the frequency of the force and energy is constantly supplied to maintain it
What is resonance ?
Resonance is when a forced vibration matches an objects natural frequency, therefore reaches its max amplitude. Can cause damage.
What is fundamental frequency and harmonies ?
Fundamental frequency is the lowest natural frequency of an object, harmonies are just multiples of these.
What is velocity ratio ?
Velocity ratio is how much the input effort moves the load. VR = distance moved by effort / distance moved by load
What is mechanical advantage and efficiency.
How much the input is multiplied MA = output/input
Efficiency is how well the input is converted to output and is calculated by MA/ VR X 100
What is Newton’s first law ?
What is newtons 2nd law ?
First law is that an object will remain still or at contestant speed unless forces act on it
2nd law is force is equal to mass x acceleration f = m x a
Define mass.
Mass is the amount of matter in an object and it measured in kg
Define weight.
Weight is the amount of gravitational force acting on an object, it’s shown in N and is calculated by w = m x g
What is work?
work happens when force causes movement, without movement no work is done. It’s displayed in Joules J and is calculated by w = F x d
What is power?
Power is the rate at which work is done, shown in watts w ans calculated by p = w/t
What is energy? Name some different types.
Energy is the capacity to do work, there are many different types such as heat, chemical, kinetic and potential.
What is momentum ?
Momentum is the quantity of motion that an object has depending on mass and velocity, it is calculated by p = m x v
What are the 2 main types of momentum ?
Elastic - this is a collision where the objects bounce off one another, the energy and kinetic energy will be conserved.
Inelastic - the objects may collide then stick together so kinetic energy in lost, momentum will be conserved.
What is impulse?
Impulse is equal to the momentum of an object, enough to stop this object e.g. catching a ball, Turing the momentum to zero
What is a gyroscope ? And there purpose in aircraft?
It is an instrument containing a spinning disk called a rotor, axis and a gimbal. The spinning disk maintains the gyroscopes heading and direction. It provides stable information to the gyroscopic instruments in aircraft
What is friction ? And the 3 types ?
Friction is the force that arises when there is resistance to motion
static friction - break away, has to be overcome to move
Sliding friction - friction when moving
Rolling friction - friction between a rolling object and the surface
What is specific gravity (SG)
The specific gravity of an object is the density of an object compared to a reference substance, liquids and solids are compared to water at 4 degrees, gasses are compared to air at 20 degrees.