Day 5 - Oxygen Transport
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
How do heme proteins participate in protecting cells? (3)
- sequestering O2
- limiting the production of ROS
- detoxifying them

What are the 2 major heme proteins?
- myoglobin (Mb)
- hemoglobin (Hb)

What is the principal function of O2?
to serve as an electron acceptor in oxidative metabolism

What is the O2-binding moiety common to Hb and Mb?
heme
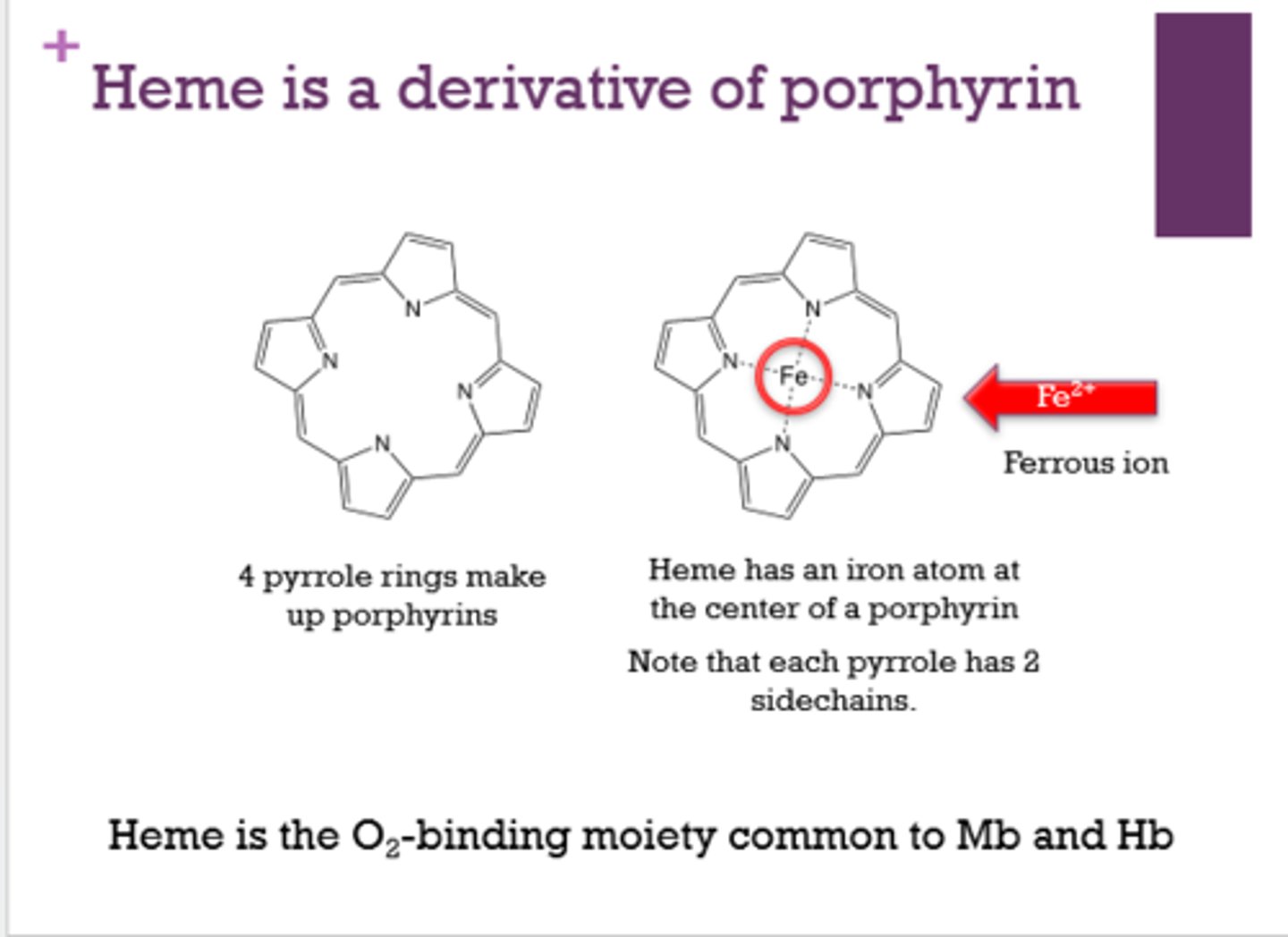
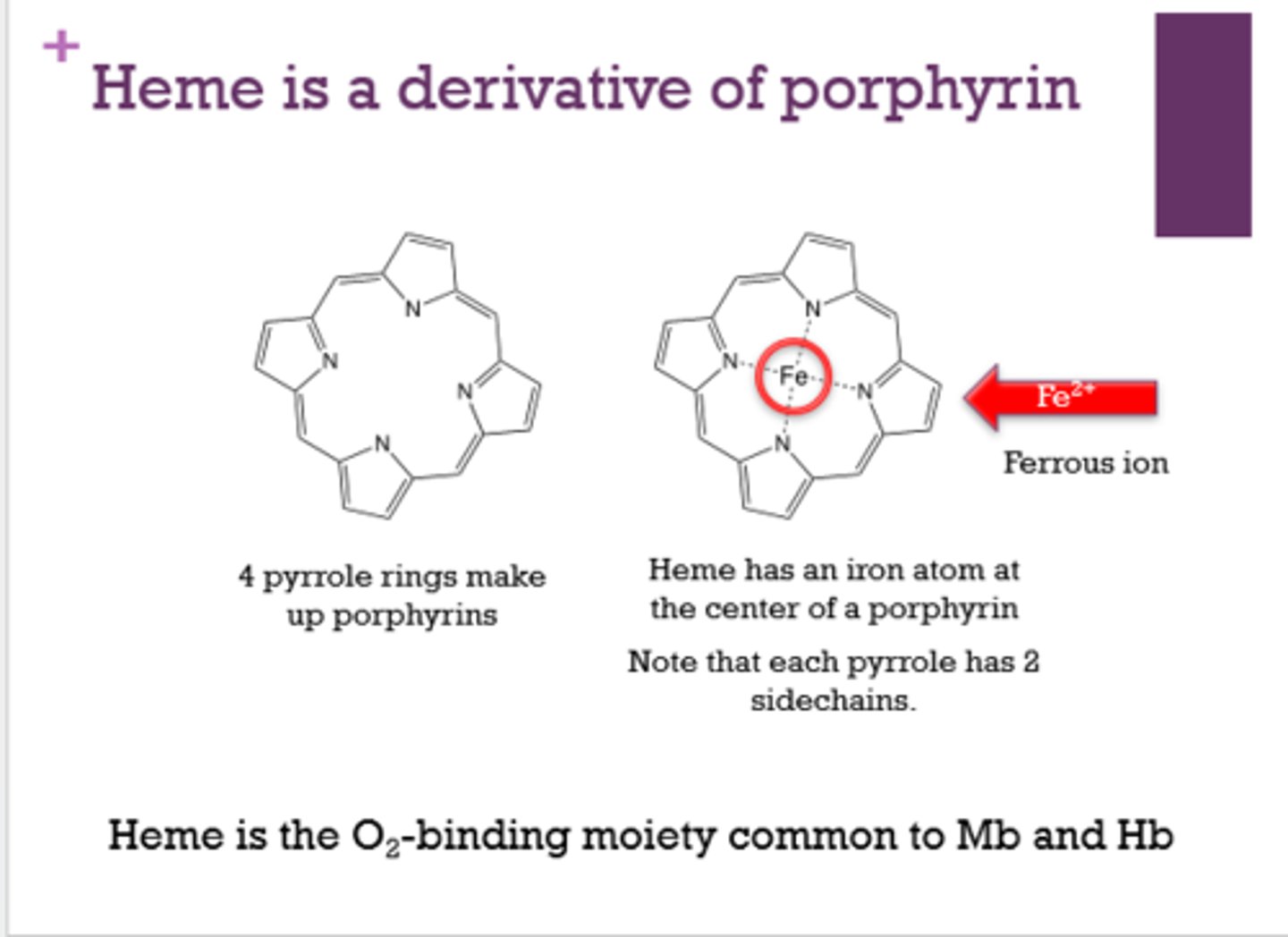
What makes up the outer portion of a heme molecule?
4 pyrrole rings
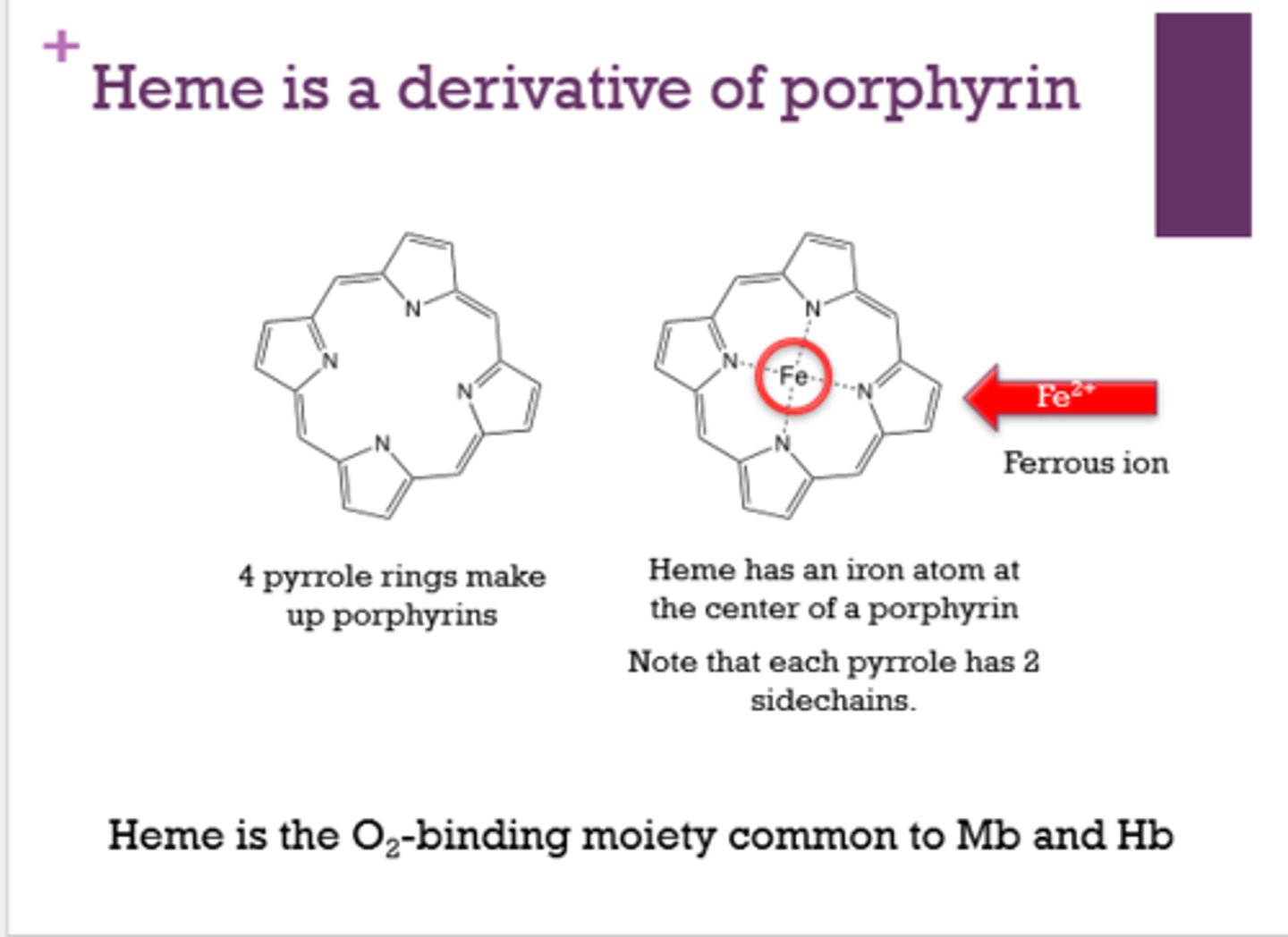
What is at the center of heme?
Fe2+. iron (ferrous ion)
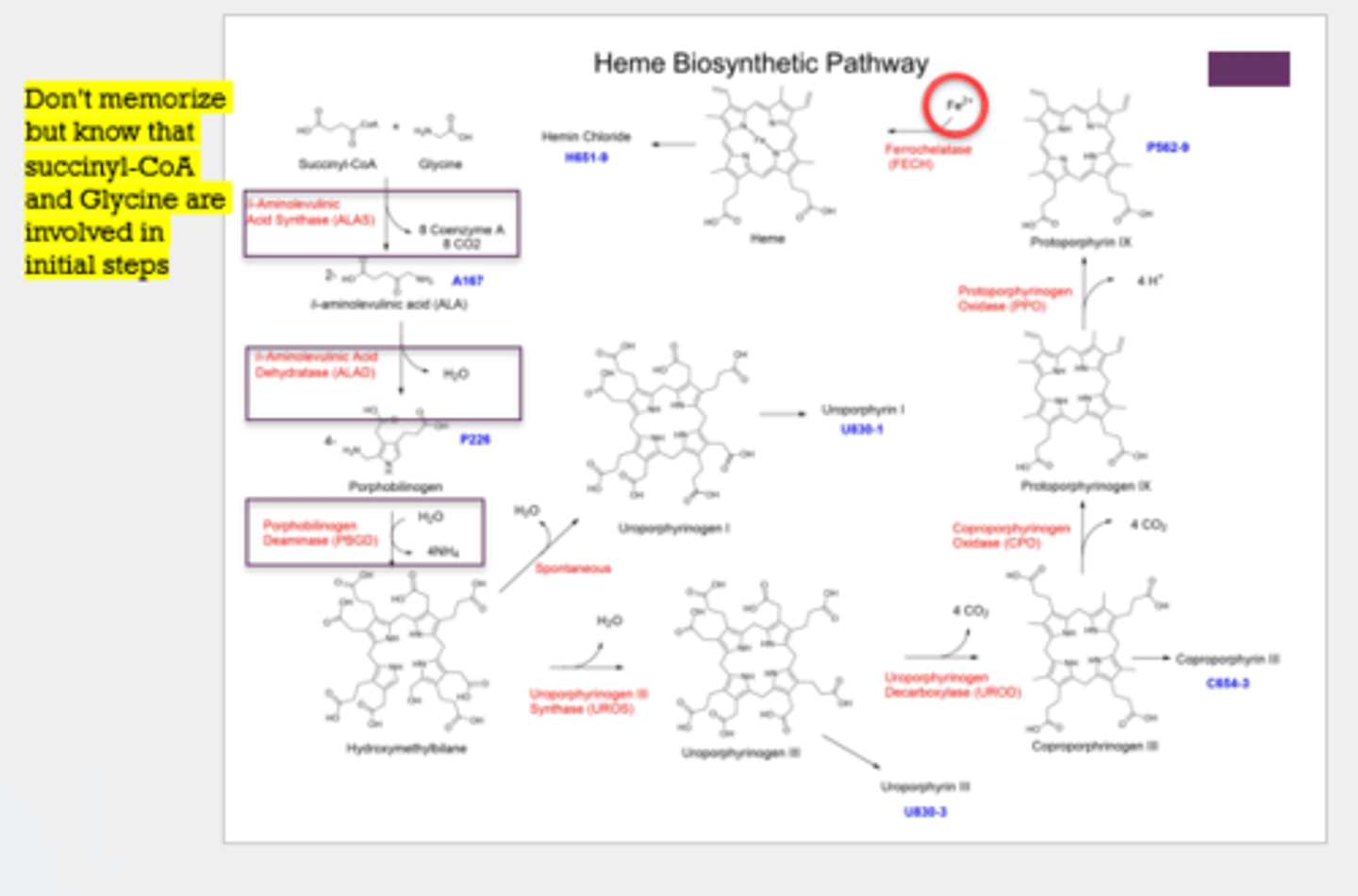
What 2 things are involved in the initial steps of heme synthesis?
succinyl-CoA and glycine
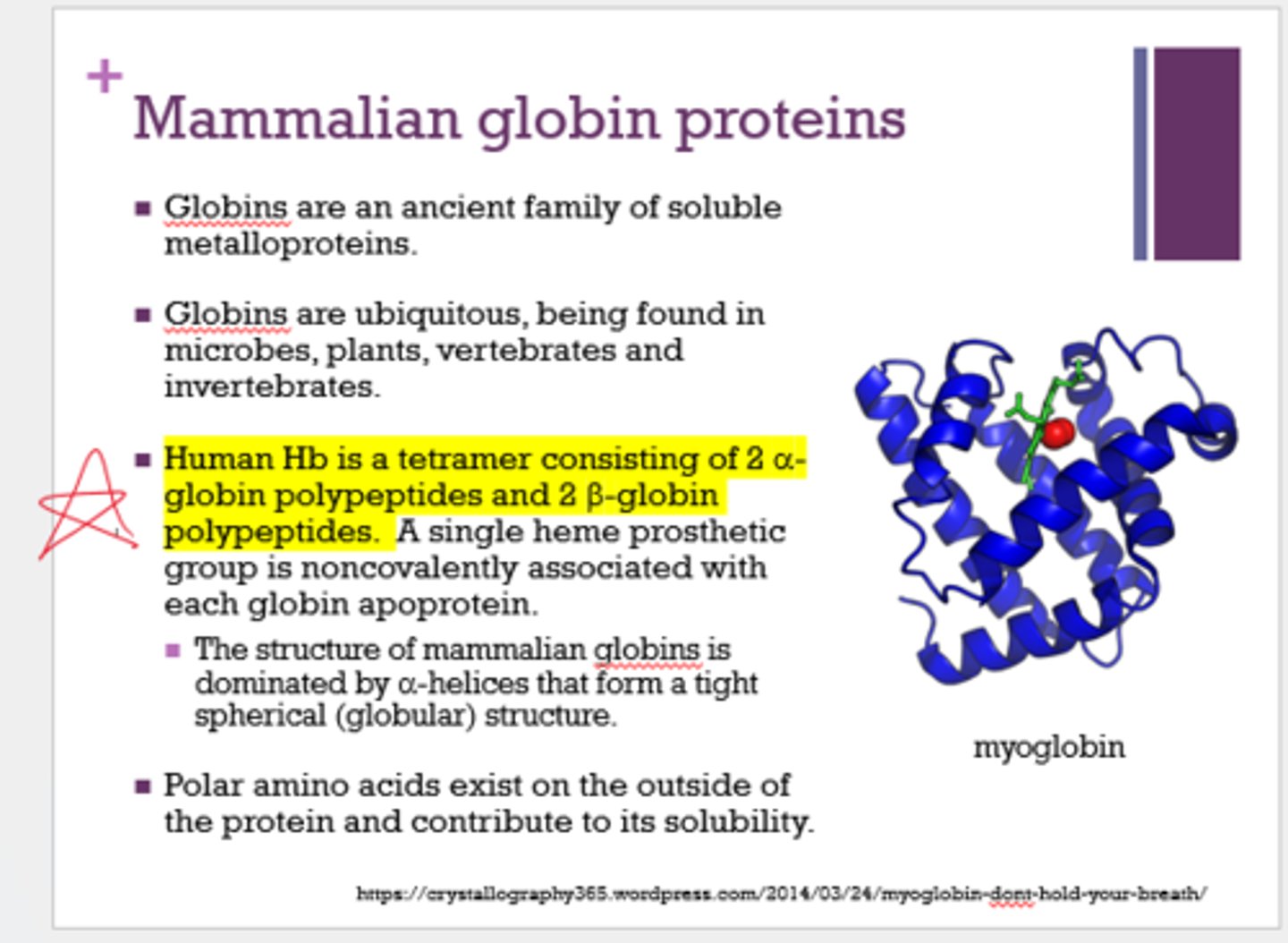
Human Hb is a tetramer consisting of ______ and ______.
- 2 alpha globin polypeptides
- 2 beta globin polypeptides
Where is myoglobin found? (3)
- cytosol of skeletal
- cardiac cells
- smooth muscle cells

True or False: Mb a tetramer protein.
False! it is a monomeric protein.

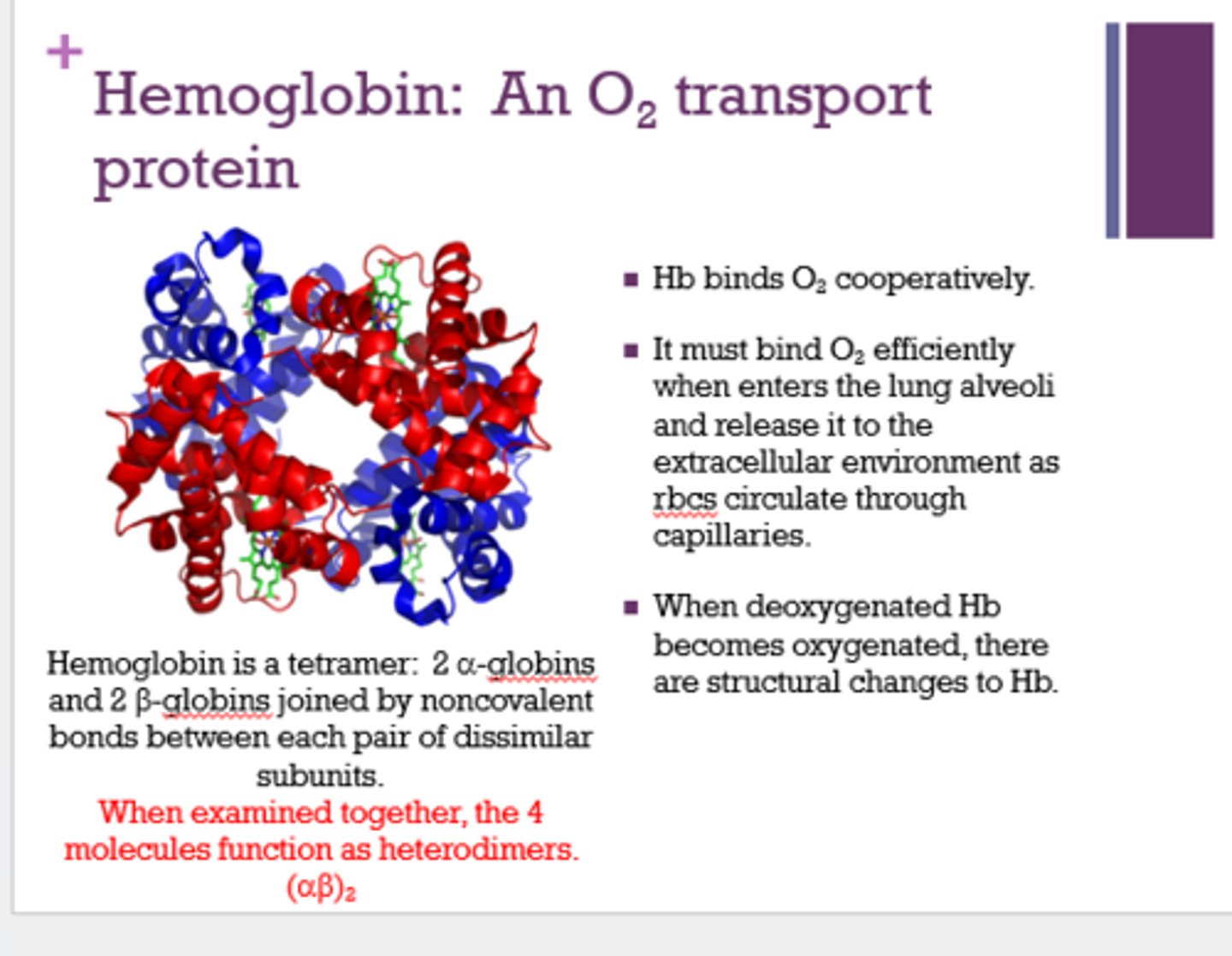
When the Hb subunits are examined together, the 4 molecules function as _________.
heterodimers
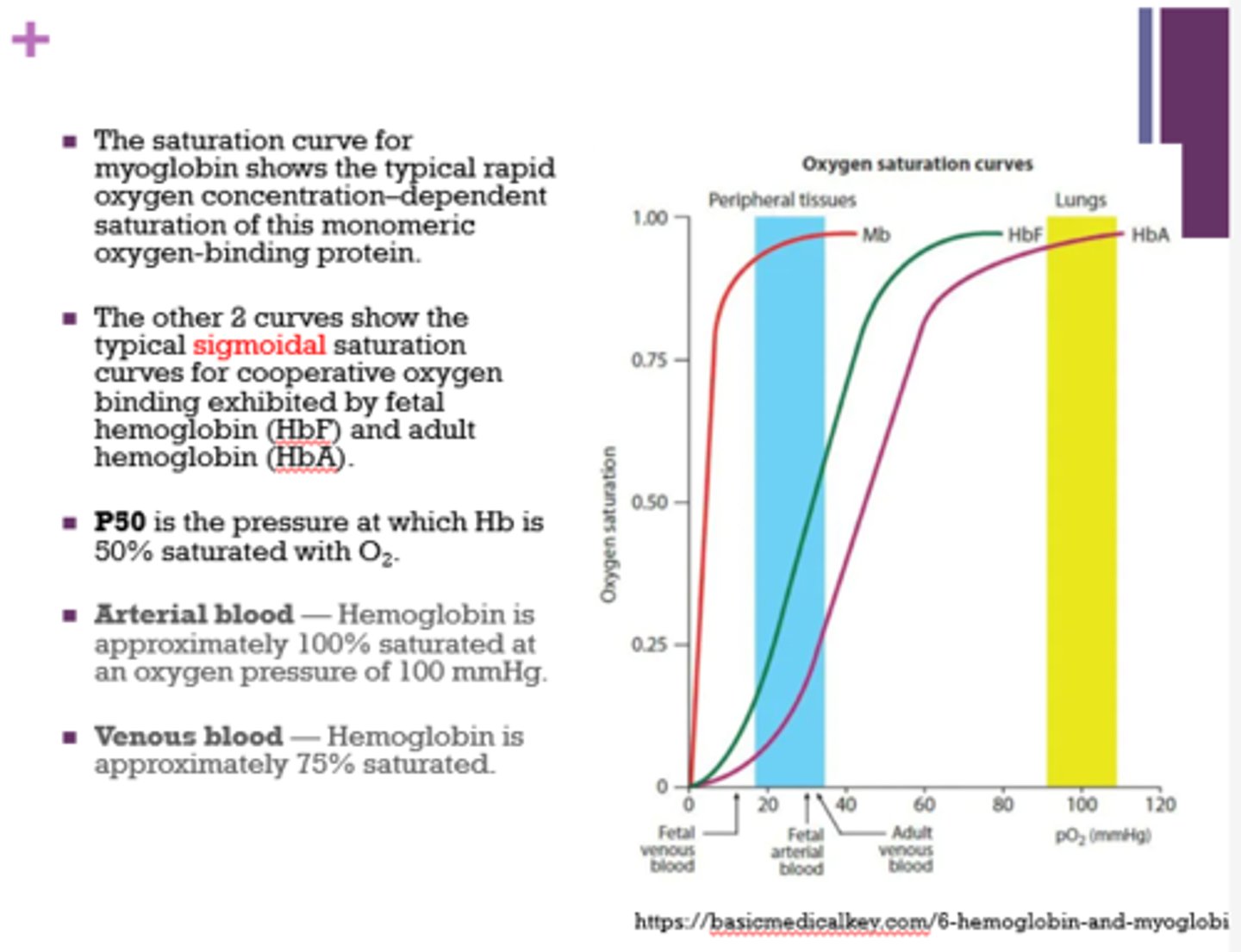
How do the oxygen saturation curves for myoglobin and hemoglobin differ?
- hemoglobin = sigmoidal
- myoglobin = typical rapid oxygen concentration-dependent saturation of a monomeric protein
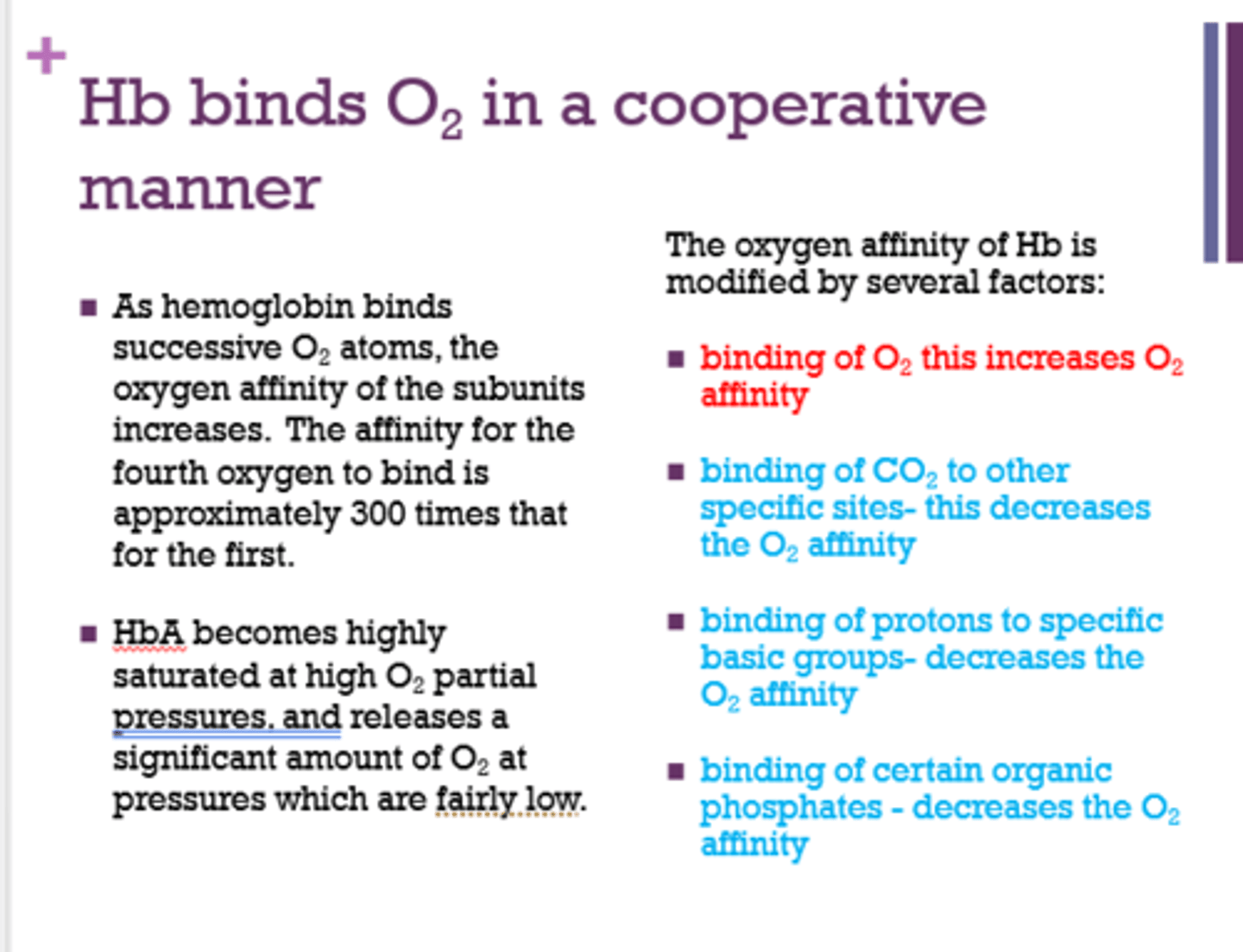
The oxygen of Hb is modified by several factors:
1. Binding of O2 to Hb [increases/decreases] O2 affinity.
2. Binding of CO2 to other specific sites [increases/decreases] O2 affinity.
3. Binding of protons to specific basic groups [increases/decreases] O2 affinity.
4. Binding of certain organic phosphates [increases/decreases] O2 affinity.
1. increases
2. decreases
3. decreases
4. decreases
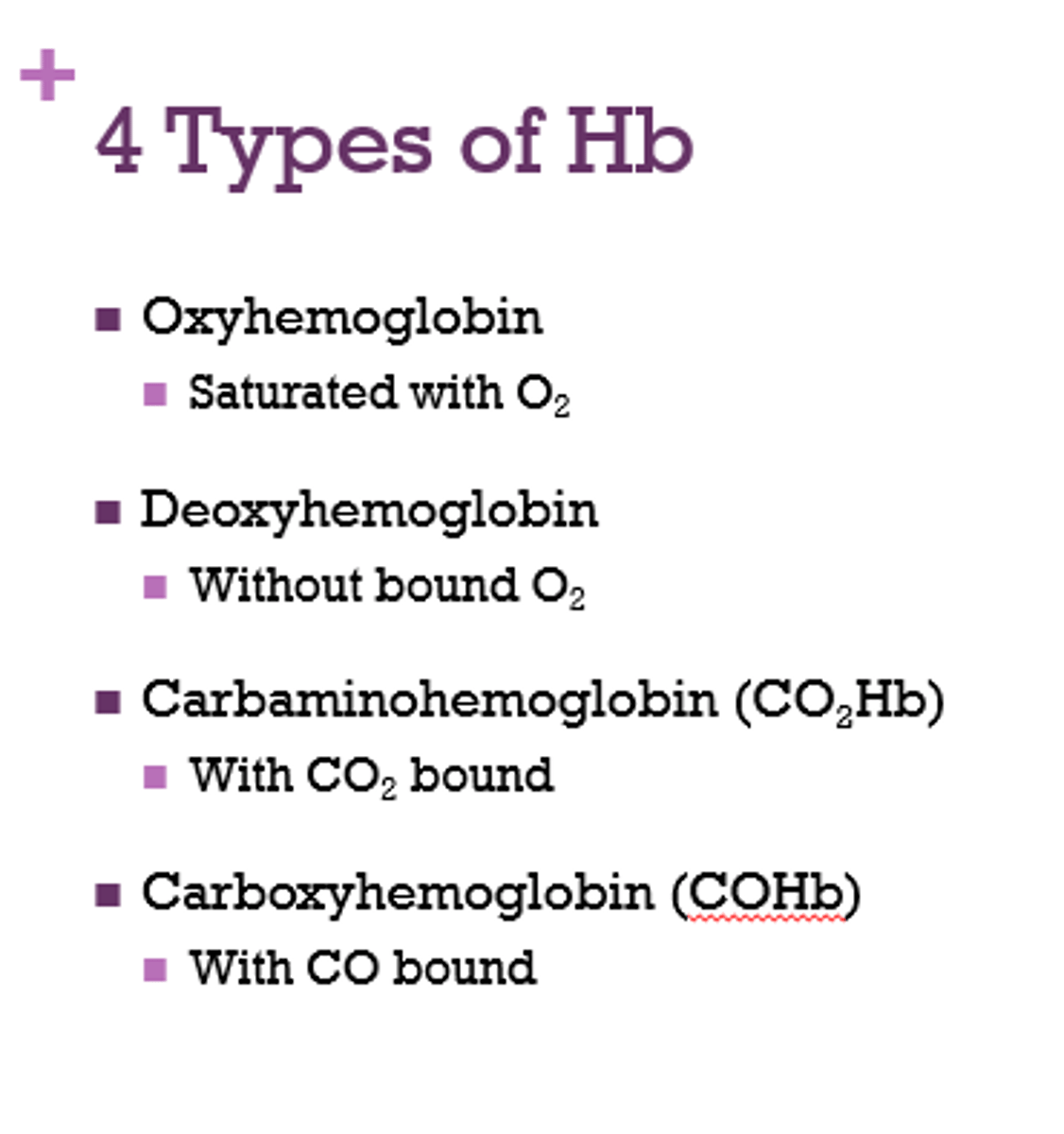
What are the 4 types of Hb?
- oxyhemoglobin
- deoxyhemoglobin
- carbaminohemoglobin
- carboxyhemoglobin
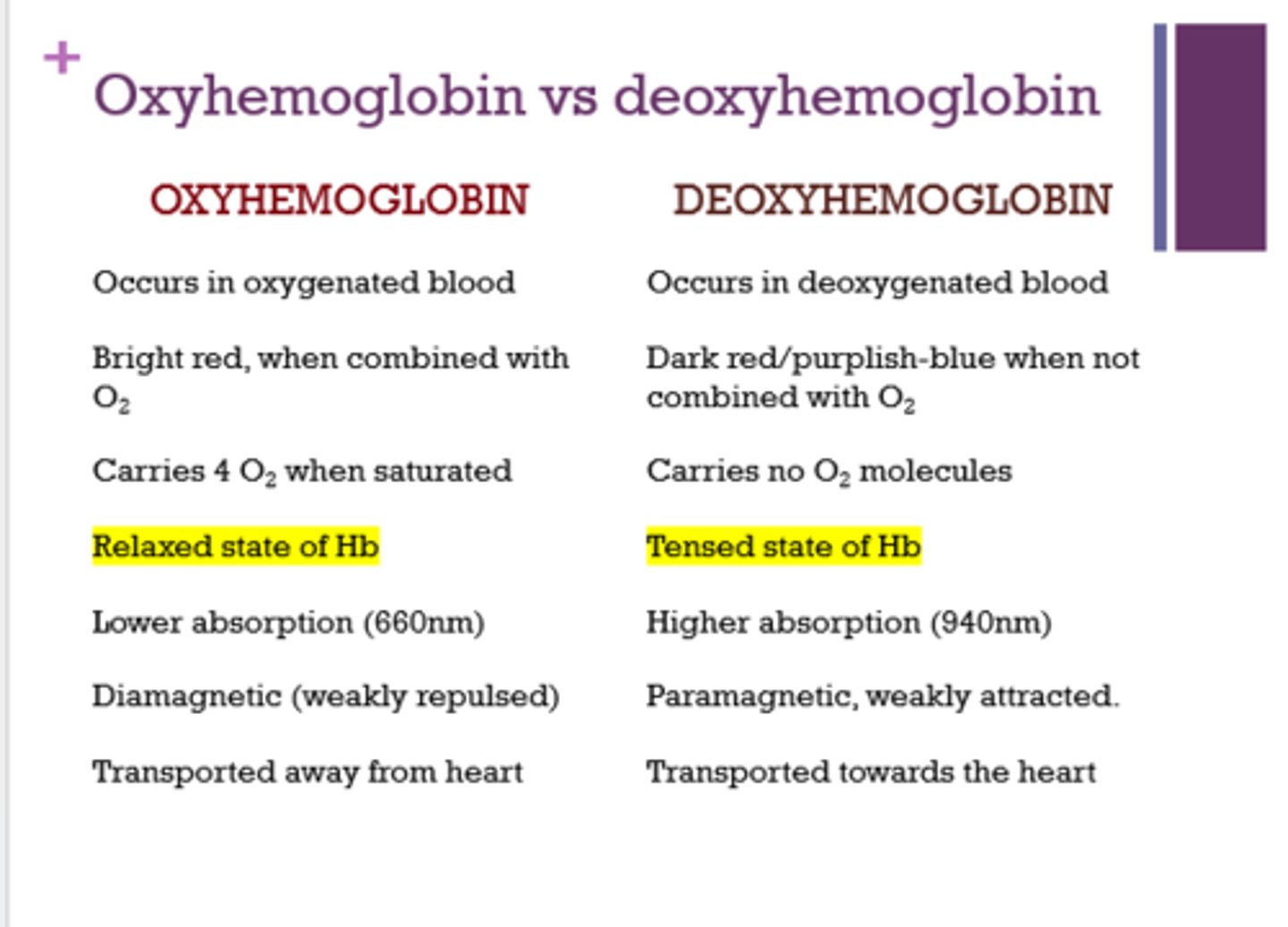
What are the relaxed and tense states for Hb?
- relaxed = oxyhemoglobin
- tense = deoxyhemoglobin
Are interactions between heterodimers stronger or weaker in the relaxed state?
stronger
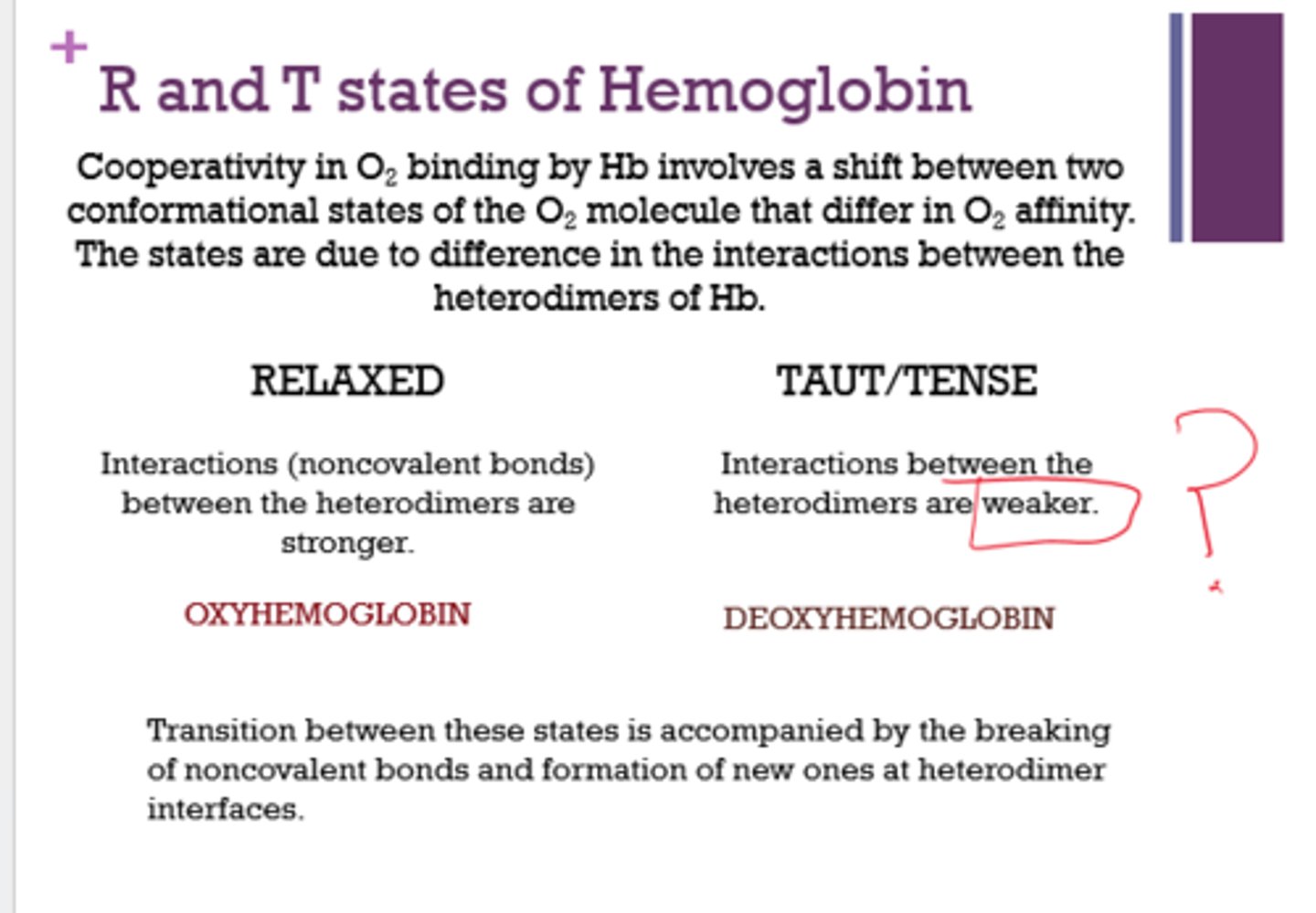
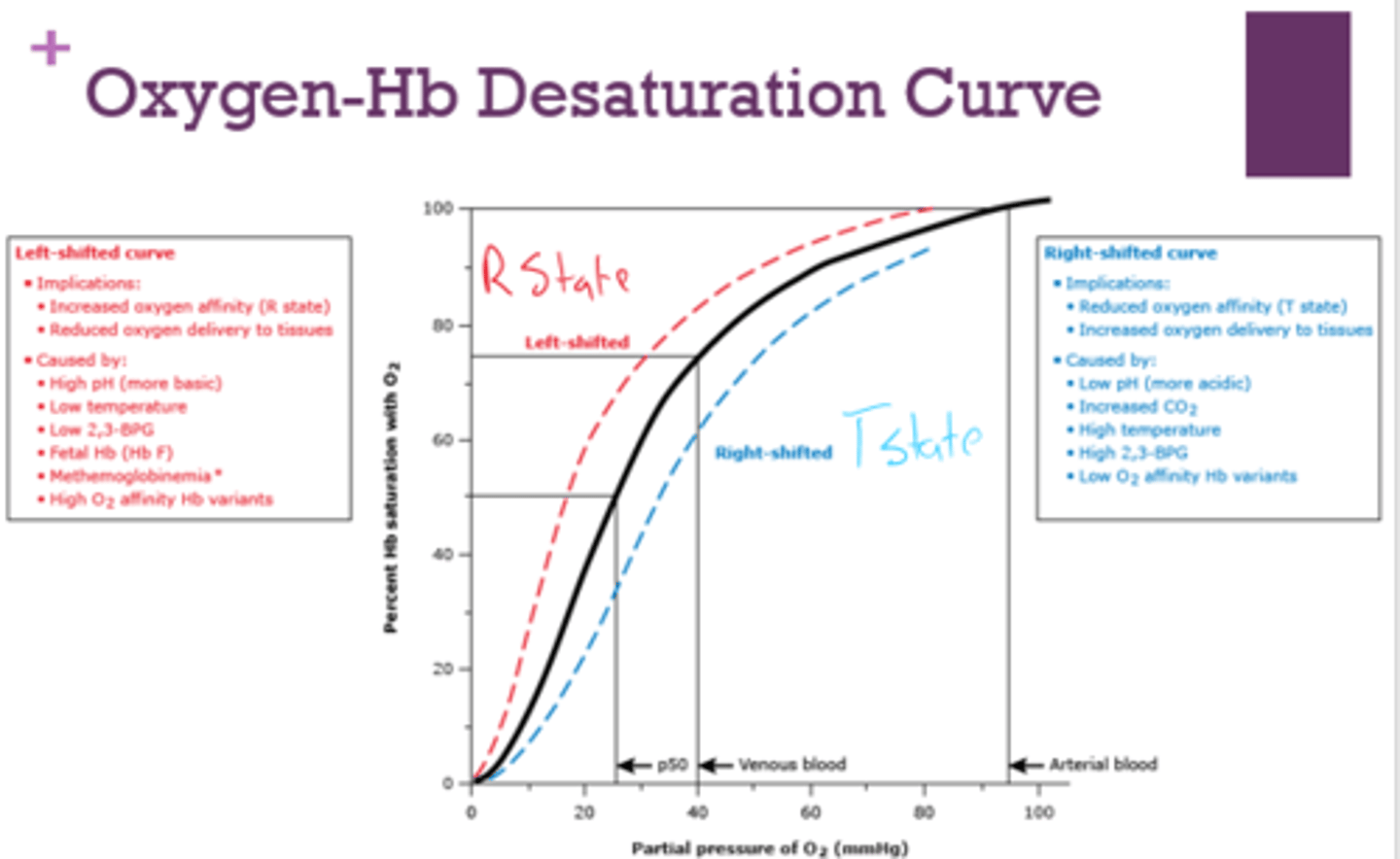
What has higher affinity for O2, R state or T state?
R state
What are the implications of a left-shifted oxygen-Hb desaturation curve?
- increased O2 affinity (r state)
- reduced oxygen delivery to tissues
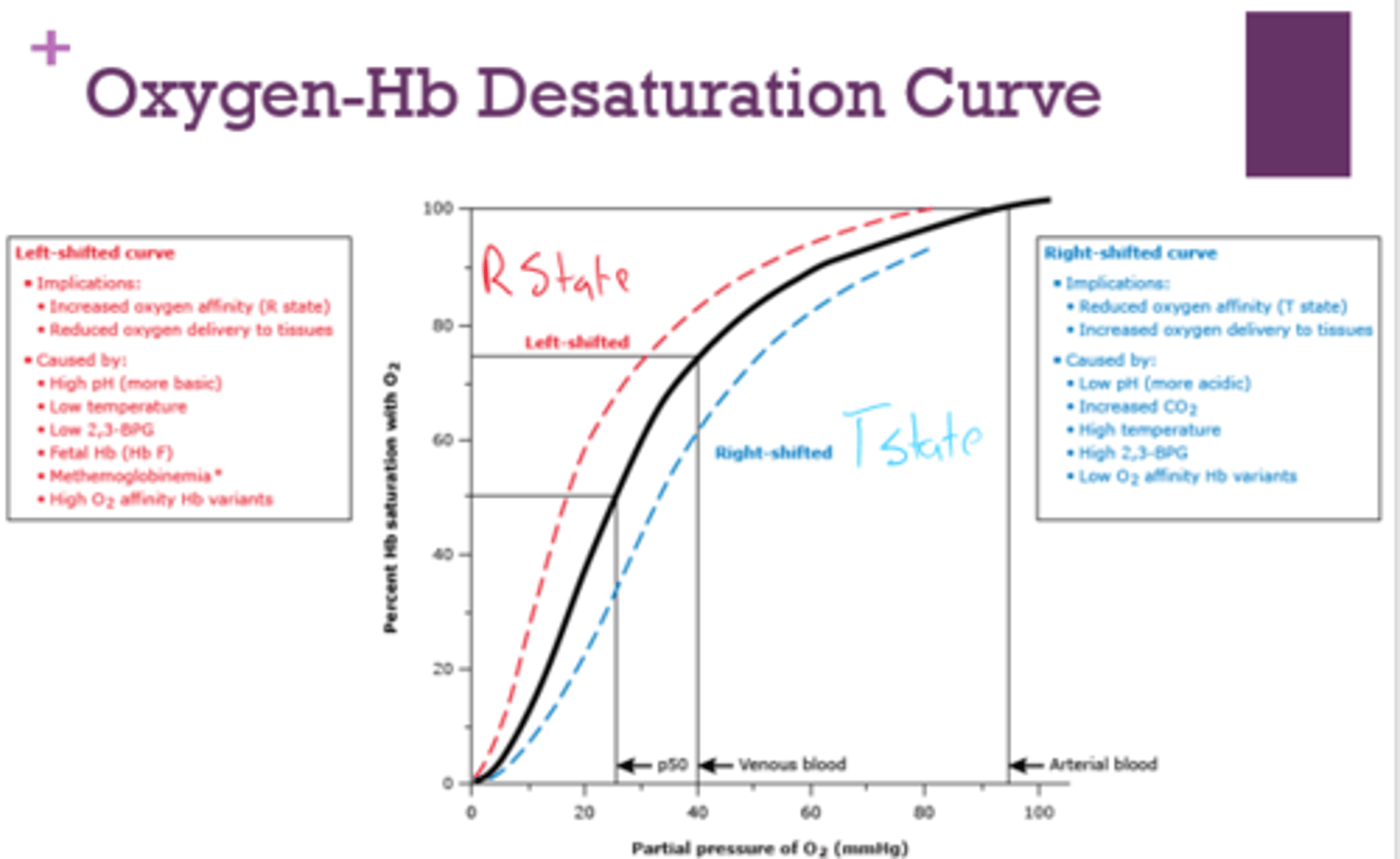
What is a left-shifted oxygen-Hb desaturation curve caused by?
- high pH
- low temp
- low 2,3-BPG
- fetal Hb
- methemoglobinemia
- high O2 affinity Hb variants
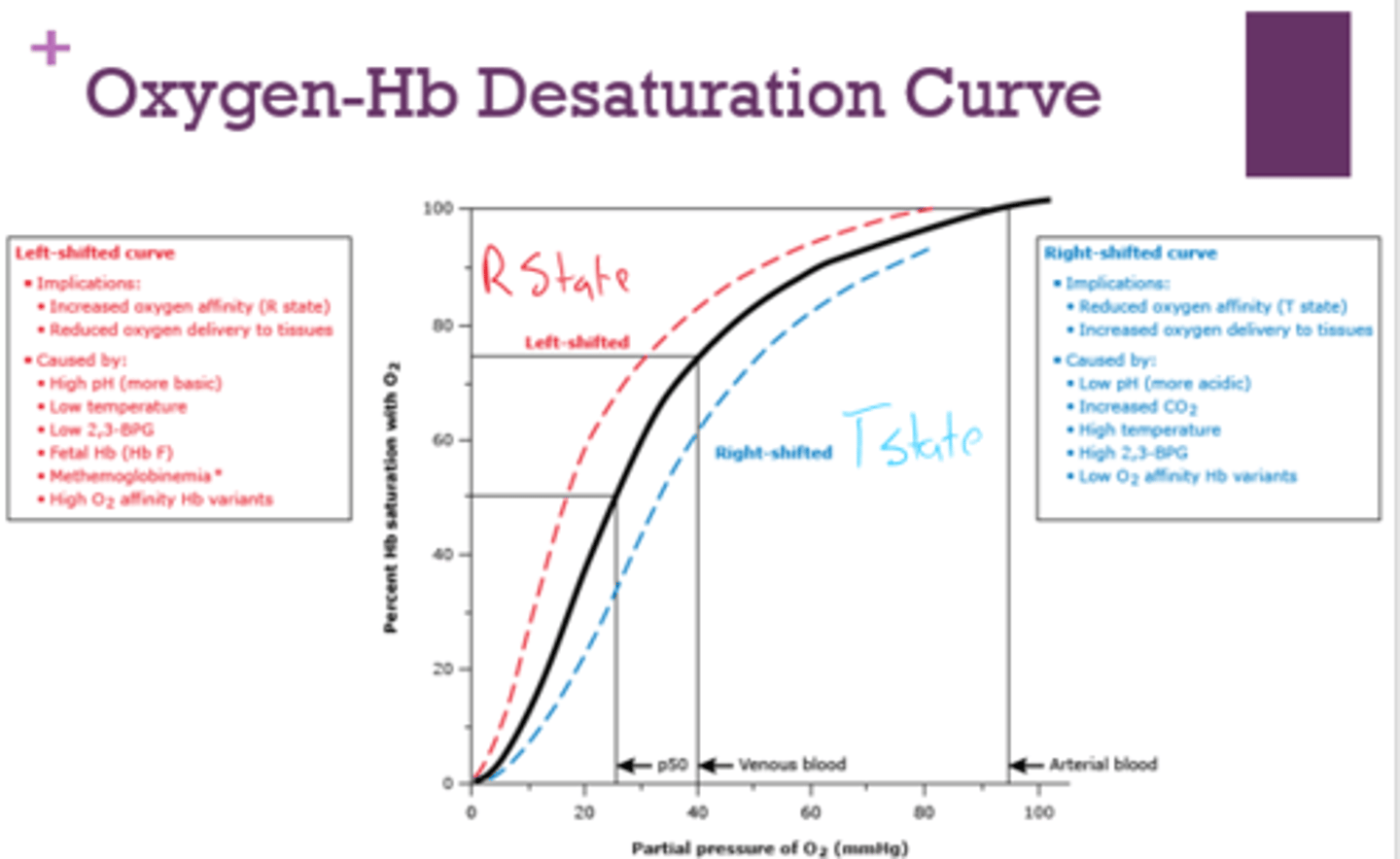
What are the implications of a right-shifted oxygen-Hb desaturation curve?
- reduced O2 affinity ( T state)
- increased oxygen delivery to tissues
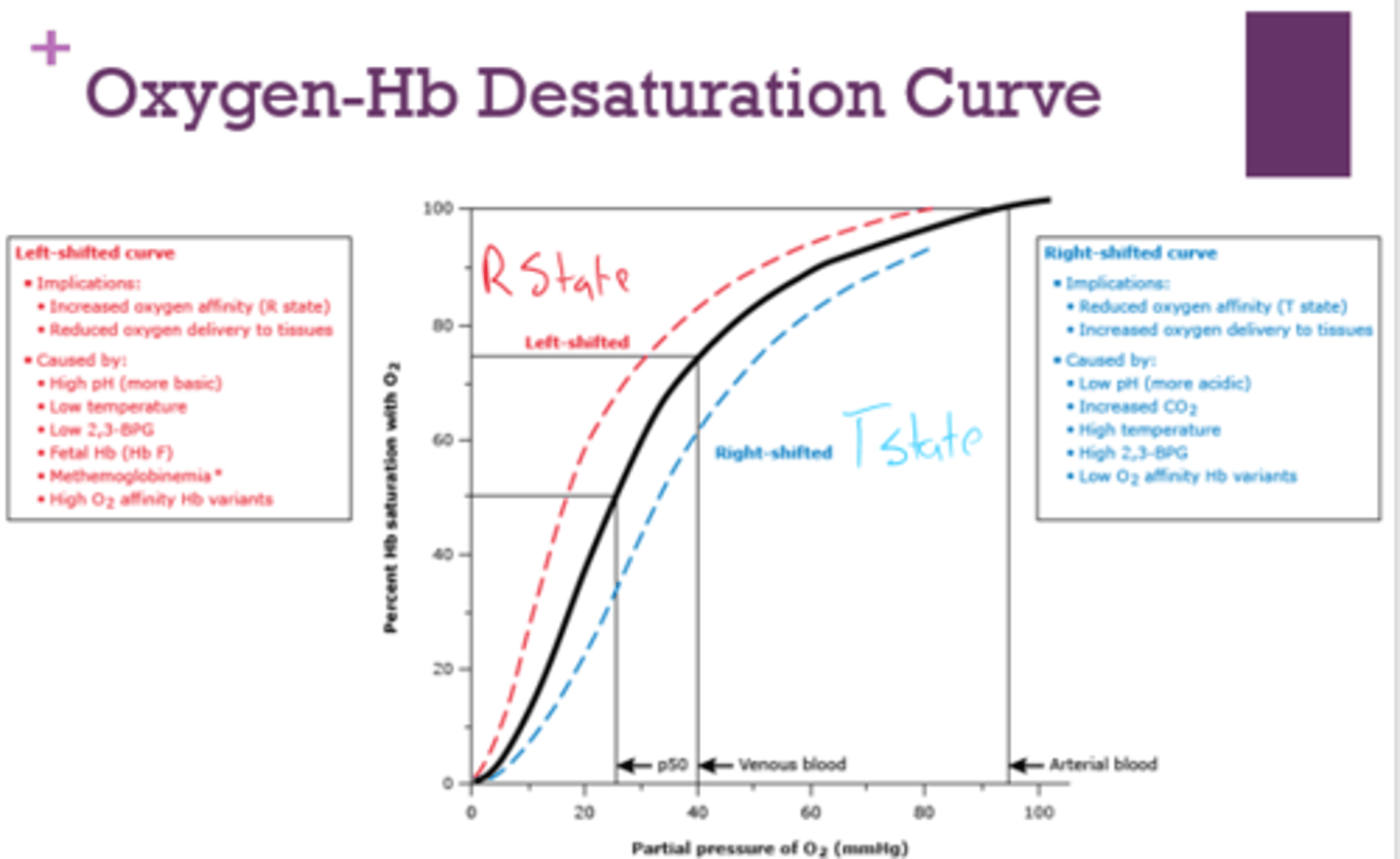
What is a right-shifted oxygen-Hb desaturation curve caused by?
- low pH
- increased CO2
- high temp
- high 2,3-BPG
- low O2 affinity Hb variants
What 2 things positively affect the O2 binding affinity of Hb?
- O2
- H+

What 2 things negatively affect the O2 binding affinity of Hb?
- CO2
- 2,3-BPG

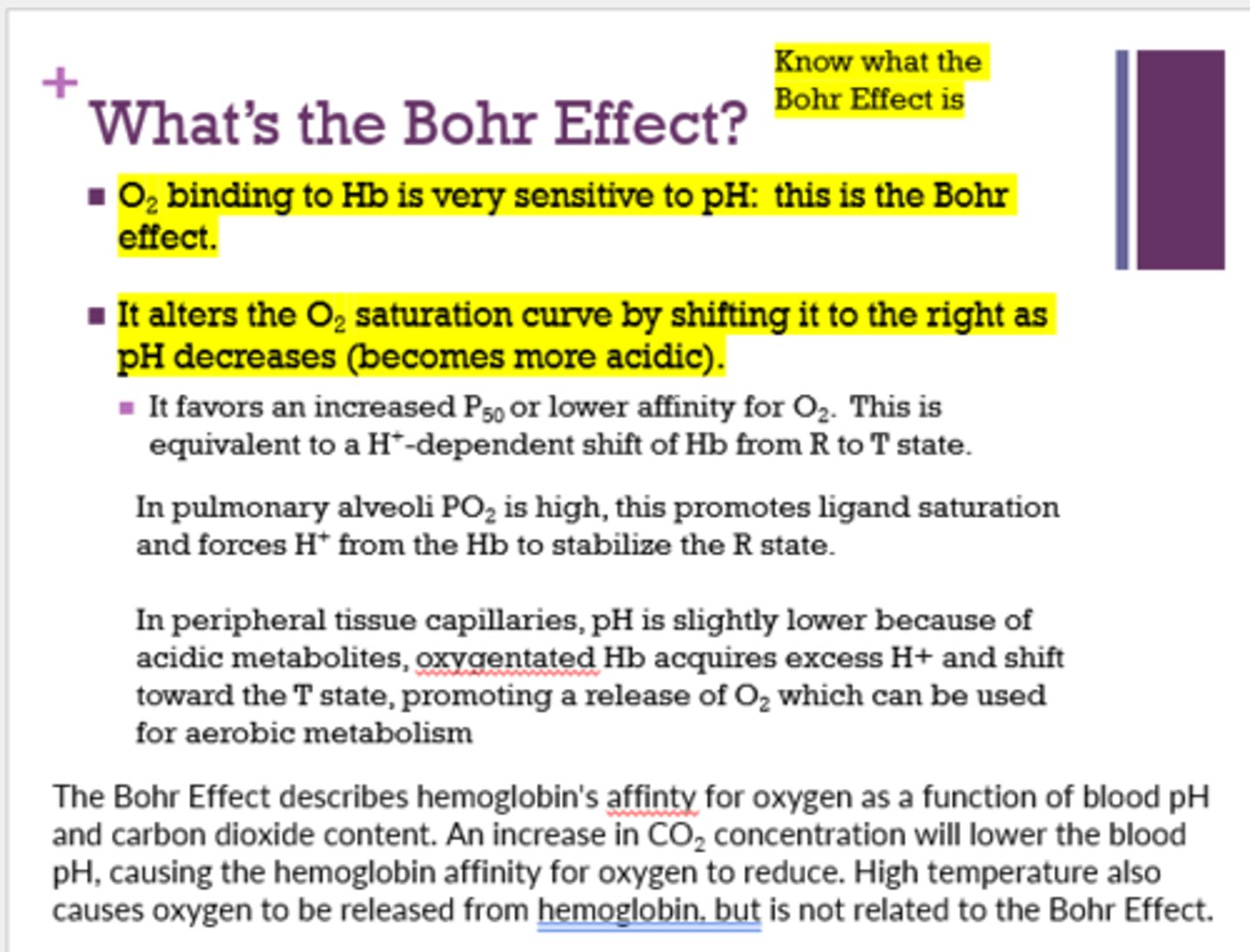
What is the Bohr Effect? (for sure on test)
O2 binding to Hb is very sensitive to pH
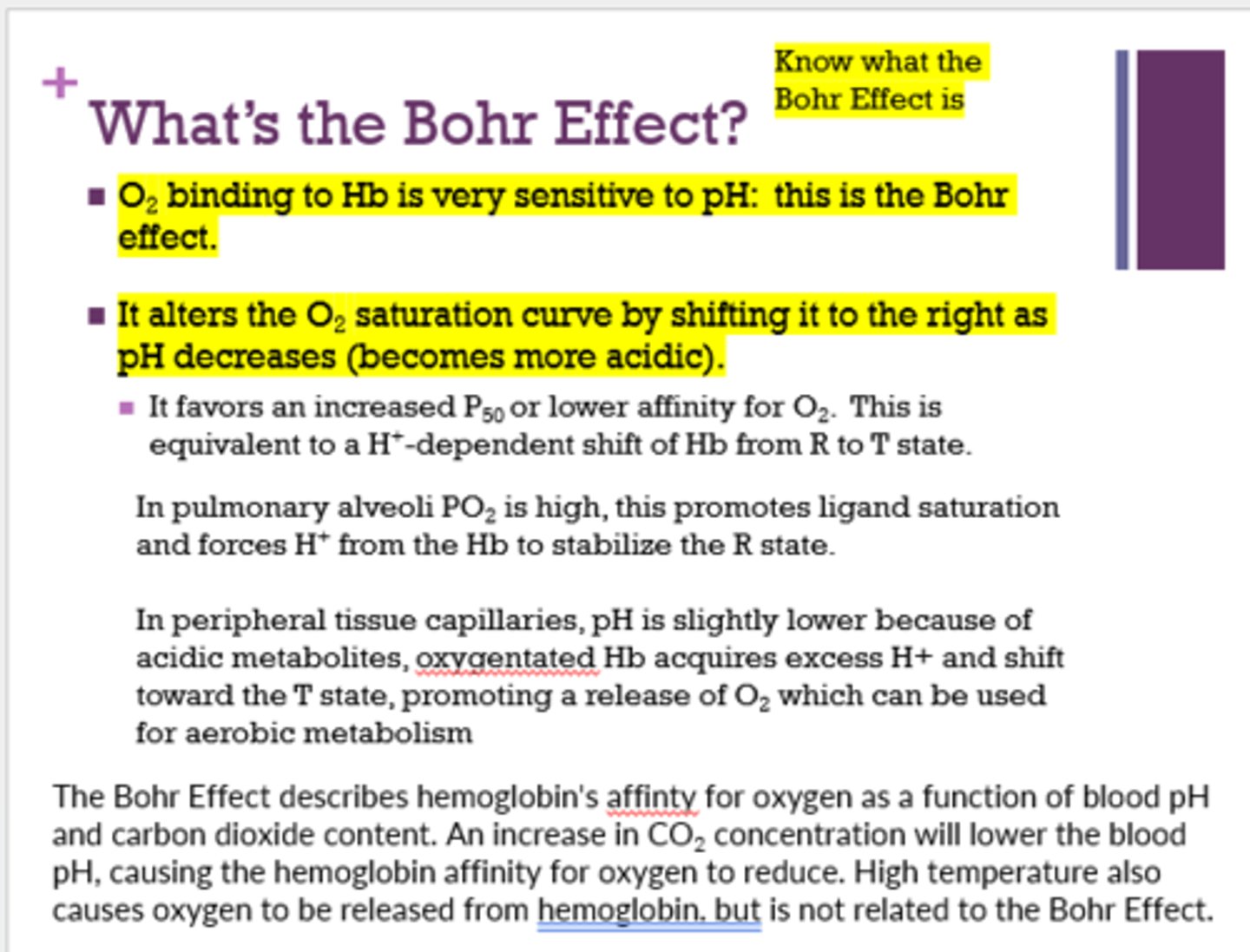
How does the O2 saturation curve shift with a decrease in pH (Bohr Effect)?
shifts right
How does CO2 affect Hb?
shifts the equilibrium to the T state and promotes release of O2
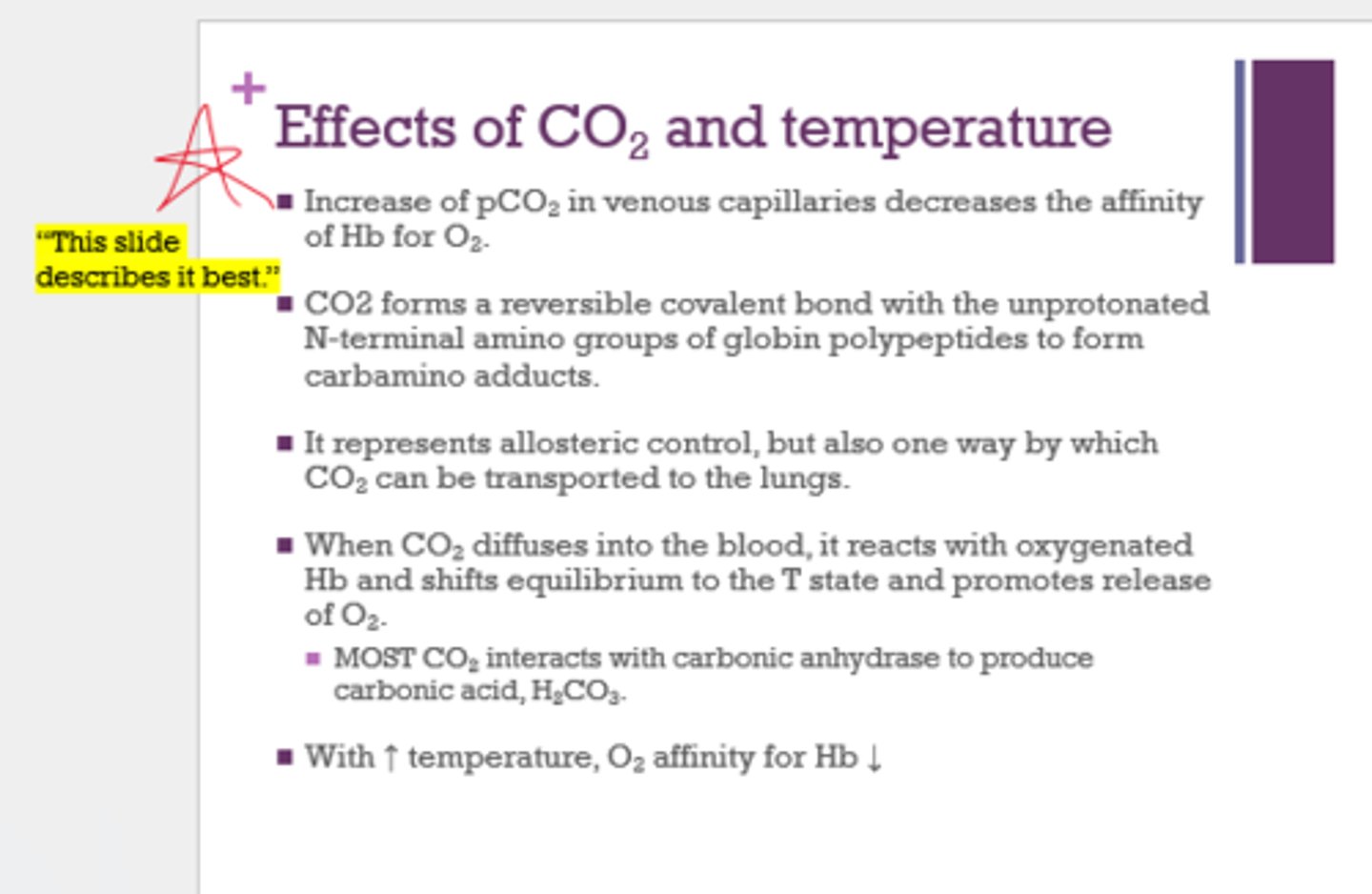
How does temp affect Hb?
with increased temp, O2 affinity for Hb decreases