Unit 2 -AP Gov
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
How do Representatives and Senators represent their constituents? Does Congress reflect the racial and gender makeup of the US at large?
2 senators per state (100)
435 house (proportionate to state pop)
less minority groups
How do Congressional elections work?
senate and house elected by state citizens
What are the roles of leaders, parties, and committees in Congress?
leaders: to facilitate, influence, organize and delegate to the congress
parties: political parties, usually vote with bills that have the ideals of their party
committees: to specialize in certain issues to discuss potential laws (bills) ex: agriculture, budget, armed forces, transportation
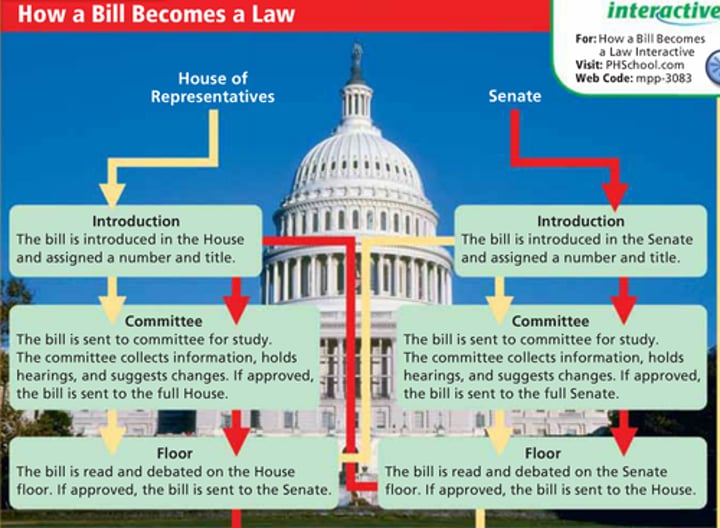
Know the lawmaking process in Congress
bills can be drafted by anyone, can only be proposed by congress members
What are the factors that influence how members of Congress make decisions?
getting reelected (pork)
voting with same party members
influence by whips and other congress members
What is the House ways and means committee and what is it responsible for?
chief tax writing committee of the congress
members on this committee are not allowed to serve on any other committee
responsible for making recommendations to the house on all bills for raising revenue. concerns on taxes, customs duties, and international trade agreements
Explain the role and importance of the House Rules Committee
in charge of determining under what rule other bills will come to the floor
not actually responsible for a certain area of policy
reviews, adopts and schedules consideration of floor resolutions
How often does the president veto a bill?
average president veto rate is 1.9%, so not very often
How does congress override a veto?
2/3 vote in both houses
What does a "closed rule" mean on a House bill?
a procedural maneuver that prohibits any amendments to bills up for a vote on the House floor, unless they are recommended by the committee reporting the bill
How Congress "check" the power of the courts?
impeach judges
confirm nominations of judges
How does Congress "check" the power of the Executive branch?
budget
approve nominations
can use majority rule to override vetos
Who decides and controls the committee chairs in Congress?
appointed by president of the senate or speaker of the house or president pro tempore, or a committee, or a vote is necessary
How are the House and Senate different?
house
-2 yr term
-435 members (proportinate to state pop.)
-power to initiate revenue bills, impeach officials
senate
-6 yr term
100 members (2 per state)
-ratify treaties, confirm presidential nominations, try impeached officials
How does Congress impeach the president?
first vote in house, if pass..
senate holds a trial overseen by chief justice of supreme court (senate is jury)
if 2/3 of senate find guilty, he is removed and vp takes over
How can the president influence legislation?
threat of a veto
can propose alternations to avoid veto
Who makes up the president's cabinet?
vice president
15 heads of executive departments
U.S. Department of Agriculture
U.S. Department of Commerce
U.S. Department of Defense
U.S. Department of Education
U.S. Department of Energy
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
U.S. Department of Homeland Security
U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development
U.S. Department of Justice
U.S. Department of Labor
U.S. Department of State
U.S. Department of the Interior
U.S. Department of the Treasury
U.S. Department of Transportation
U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs
Know the many roles of the president
(1) chief of state, (2) chief executive, (3) chief administrator, (4) chief diplomat, (5) commander in chief, (6) chief legislator, (7) party chief, and (8) chief citizen
List and explain the expressed and implied powers of the president and describe the differences between the two
expressed powers of the president
-execute law
-appoint department heads
-veto legislation
-deliver state of the union
-make policy recommendations
-convene and adjourn congress
-appoint ambassadors
-receive ambassadors
-serve as commander in chief
implied powers of the president
-organize federal bureaucracy
-issue executive orders
-exercise executive privilege
-enter into treaties with foreign nations
-serve as head of state
How can a president be removed?
impeachment and conviction by the senate for treason bribery, or other high crimes and misdemeanors (impeachment)
How has office of the President expanded since ratification of the Constitution?
changed from about three cabinet members to 15 cabinet members
hundreds of people work in the white house itself
What are the roles of the Vice President? Cabinet? Executive Office? White House Staff?
vp: presiding officer over the senate, ceremonial duties
cabinet: advise the president on any subject he may require relating to the duties of each members respective office
executive office: (EOP) provide the president with the support they need to to govern effectivly
white house staff: personal assistants to the President
How does the president use the bully pulpit?
to influence the public
ex: Teddy Roosevelt used popularity and access to the media to ask the American people to change things - not wait around for gov to fix things, but to fix things themselves
ex: FDR fireside chats = faith and unity in the government
How does the President win congressional support?
developing good relations with Congress, good tactics, good powers of persuasion and bargaining
What are the factors the affect the president's ability to get public support?
Size of the mandate at the last election
Previous Washington experience
Oratorical skills
Competent senior White House staff
Good at handling crises
Good relations with congress and effectiveness in congress
Provide some examples of executive actions/agreements
ex: executive agreement:
North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
entered into with congressional authority, negotiated by president then submitted to Congress for approval
US and Mexico created large free trade for imports and exports between the country for goods and services
ex: executive action
trump can make an executive order to build a wall, but it is up to congress to appropriate funds for it to actually happen
What "checks" does the president have on the judiciary?
nominate judges
What "checks" does the president have on Congress?
may veto bills, may adjourn Congress in certain situations
What was the intent of the War Powers Resolution? (What events led to its creation?) How effective is it in limiting the president?
intended to check the president's power to commit the US to an armed conflict without the consent of the senate
It provides that the U.S. President can send U.S. Armed Forces into action abroad only by declaration of war by Congress
has been violated
Diagram the Executive Branch (White House Staff, Executive Office, Independent Agencies, Executive Departments) and describe the function/examples of each
-president
-white house staff: provide for needs within the white house
executive departments: the cabinet, includes defense, education, homeland security
executive office: supports the work of the President, ex: office of management budget
independent agencies: ex: EPA, FCC
Who are and what makes up the Bureaucracy?
cabinet department
independent regulatory commission
government corporations
independent executive agencies
How do federal bureaucrats get their jobs?
they are appointed based on the merit principle (used to be based on patronage but pendleton civil service act banned that)
president and congress have a say in hiring head officials of agencies
NOT elected by the people
What are the four types of agencies into which the federal bureaucracy is organized?
cabinet department
-15, each headed by a secretary
independent regulatory commission
-gov agency with responsibility for making and enforcing rules to protect public interest in some sector of economy and for judging disputes over rules
government corporations
-gov organizations that provides a service that could be delivered by the private sector and typically charges for its service (postal service)
independent executive agencies
-gov agencies not accounted for by cabinet departments. admin appointed by president and serve at president's pleasure (NASA)
What are the factors that influence the effectiveness of bureaucratic implementation of public policy?
factors that can cause failure..
-program design
-lack of clarity
-administrative routine
-administration's dispositions
-lack of resources
-lack of authority
-fragmentation
so opposite of ^^ = effective implementation of public policy
How do bureaucracies regulate and assess deregulation?
lifting of gov restrictions on businesses, industry or professional activities
problems of regulation
-raising prices
-failing to work well
-hurting US competitive positions abroad
How is the bureaucracy controlled? (checks on the bureaucracy)
president
-appoint people to head agency
-issue orders (executive order)
-alter budget
-reorganize agency
congress
-influencing appointment of agency heads
-alter agency's budget
-hold hearings
-rewrite legislation or make it more detailed
What is the role of Iron Triangles?
also known as sub governments, mutually dependent and advantageous relationship between bureaucratic agencies, interest groups and congressional committees or subcommittees. dominate some areas of domestic policy making
Why does Congress delegate "rulemaking authority" to the Bureaucracy?
Congress passes the bills to make them laws, bureaucracies actually implement the laws into the public
bicameral
divided into two parts, or houses
bill
a proposed law presented to a legislative body for consideration, drafted in legal languages, house or reps or senate has to formally submit for consideration (anyone can draft one)
casework
Activities of members of Congress that help constituents as individuals; cutting through bureaucratic red tape to get people what they think they have a right to get
caucus
A group of members of Congress sharing some interest or characteristic. Most are composed of members from both parties and from both houses.
cloture
A procedure for terminating debate, especially filibusters, in the Senate.
committee chairs
The most important influencers of the congressional agenda. They play dominant roles in scheduling hearings, hiring staff, appointing subcommittees, and managing committee bills when they are brought before the full house.
conference committees
formed when the senate and the house pass different versions of the same bill, members from both iron out differences and bring back to pass as a single bill
constituent
a person whom a member of Congress has been elected to represent
delegate model of representation
a model of representation in which representatives feel compelled to act on the specific stated wishes of their constituents
divided government
one party controls the White House and another party controls one or both houses of Congress
earmark
Funds that an appropriations bill designates for a particular purpose within a state or congressional district
executive agency
An administrative agency within the executive branch of government. At the federal level, executive agencies are those within the cabinet departments.
filibuster
A procedural practice in the Senate whereby a senator refuses to relinquish the floor and thereby delays proceedings and prevents a vote on a controversial issue.
franking privelage
benefit allowing members of congress to mail letters and other materials for free
gerrymandering
Process of redrawing legislative boundaries for the purpose of benefiting the party in power.
house rules committee
reviews all bills coming from a House committee before they go to the full House and schedules before full house
house ways and means committee
The House of Representatives committee that, along with the Senate Finance Committee, writes the tax codes, subject to the approval of Congress as a whole.
impeachment
The political equivalent of an indictment in criminal law, prescribed by the Constitution. The House of Representatives may impeach the president by a majority vote for "Treason, Bribery, or other high Crimes and Misdemeanors."
incumbent
individuals who already hold office, in congressional elections, incumbents usually win
legislative oversight
Congress's monitoring of the bureaucracy and its administration of policy, performed mainly through hearings.
legislative veto
A vote in Congress to override a presidential decision. if challenged, Supreme Court could find it in violation of separation of powers
logrolling
An agreement by two or more lawmakers to support each other's bills
majority leader
partisan ally of speaker of house, majority party's manager in senate, responsible in each house for scheduling bills, influencing committee assignments, and rounding up votes on behalf of party's legislative positions
minority leader
The principal leader of the minority party in the House of Representatives or in the Senate.
pocket veto
A veto taking place when Congress adjourns within 10 days of submitting a bill to the president, who simply lets it die by neither signing nor vetoing it.
pork
federally funded projects designed to bring to the constituency jobs and public money for which the members of Congress can claim credit
rider
A provision attached to a bill - to which it may or may not be related - in order to secure its passage or defeat.
seniority system
in effect until 1970s, member serving the longest and whose party controlled the chamber became chair
speaker of the house
chosen by majority party, has formal and informal powers, second in line (after vp) to succeed presidency
standing committees
handle bills in different policy areas
subcommittee
Division of existing committee that is formed to address specific issues
trustee model of representation
a model of representation in which representatives feel at liberty to act in the way they believe is best for their constituents
bully pulpit
the president's use of his prestige and visibility to guide or enthuse the American public
cabinet
Advisory council for the president consisting of the heads of the executive departments, the vice president, and a few other officials selected by the president. (14 secretaries, attorney general and others)
executive agreement
A formal agreement between the U.S. president and the leaders of other nations that does not require Senate approval.
executive privilege
The power to keep executive communications confidential, especially if they relate to national security.
expressed / enumerated presidential powers
powers to the president directly stated in the constitution
informal / inherent / implied presidential powers
inherent powers:powers that are needed to get the job done, go without saying (ex: anything that defends borders)
implied powers: those implied by express powers but not stated "the express power to appoint implies the power to dismiss"
line-item veto
Presidential power to strike, or remove, specific items from a spending bill without vetoing the entire package; declared unconstitutional by the Supreme Court.
twenty-fifth amendment
A 1967 amendment to the Constitution that establishes procedures for filling presidential and vice presidential vacancies and makes provisions for presidential disability.
twenty-second amendment
Passed in 1951, the amendment that limits presidents to two terms of office.
veto
a constitutional right to reject a decision or proposal made by a law-making body by the president
war powers resolution
law passed in 1973 the requires presidents to consult with congress whenever possible prior to using military force and to withdraw forces after 60 days unless congress declares war or authorizes an extension
watergate
The events and scandal surrounding a break-in at the Democratic National Committee headquarters in 1972 and the subsequent cover-up of White House involvement, leading to the eventual resignation of President Nixon under the threat of impeachment.
white house staff
Personnel who run the White House and advise the President. Includes the Chief of Staff and Press Secretary
administrative discretion
The authority of administrative actors to select among various responses to a given problem. Discretion is greatest when routines, or standard operating procedures, do not fit a case.
bureaucracy
According to Max Weber, a hierarchical authority structure that uses task specialization, operates on the merit principle, and behaves with impersonality.
civil service
A system of hiring and promotion based on the merit principle and the desire to create a nonpartisan government service.
command and control policy
The typical system of regulation whereby government tells business how to reach certain goals, checks that these commands are followed, and punishes offenders.
deregulation
The lifting of government restrictions on business, industry, and professional activities.
executive orders
Regulations originating with the executive branch. Executive orders are one method presidents can use to control the bureaucracy.
gov corporations
gov organization that provides a service that could be delivered by a private sector and typically charges for its service (ex: Postal Service)
hatch act
A federal law prohibiting government employees from active participation in partisan politics while on duty
incentive system
market like strategies are used to manage public policy
independence executive agency
government agencies not accounted for by cabinet departments. admin appoint by presidents and at president's pleasure (ex: NASA)
independent regulatory commission
A government agency with responsibility for making and enforcing rules to protect the public interest in some sector of the economy and for judging disputes over these rules.
independent regulatory commission / agency
A government agency with responsibility for making and enforcing rules to protect the public interest in some sector of the economy and for judging disputes over these rules.
iron triangles (subgovernments)
A network of groups within the American political system that exercise a great deal of control over specific policy areas. They are composed of interest group leaders interested in a particular policy, the government agency in charge of administering that policy, and the members of congressional committees and subcommittees handling that policy.
issue networks
The loose and informal relationships that exist among a large number of actors who work in broad policy areas
merit system
entrance and promotion are awarded on the basis of demonstrated abilities rather than "who you know"
office of personnel mangament
office in charge of hiring for most agencies of federal government, using rules in the process
patronage
One of the key inducements used by party machines. A patronage job, promotion, or contract is one that is given for political reasons rather than for merit or competence alone.