Chemistry Required Practicals: Methods
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Making a Standard Solution
Ensuring a stock solution of known volume and concentration
Measure _g of solute on a weighing boat
Wash the solute into a beaker
Add some water and use a stirring rod to completely dissolve solute
Pour the solution into a volumetric flask and do washings of the beaker, rod and funnel into the volumetric flask
Add distilled water until it reaches the graduation line
Put in the stopper and do multiple inversions
Titration
Determining unknown concentrations
Using a glass pipette, place 25cm3 of the solution to be analysed in a conical flask
Add a few drops of a suitable indicator
Fill a burette with the standard solution
Open the tap to add the solution until the indicator just shows a colour change. Note down the volume of solution used (to the nearest 0.05cm3)
Repeat until you reach concordant results. Take a mean of the concordant results
Back Titrations
Determining unknown masses
Used for acids / bases which are not very soluble in water or react slowly
Add a known volume and concentration of an acid / alkali in excess to the sample
Titrate the left over acid / alkali
Heating to Constant Mass
Determining rate of reaction
Heat reaction mixture
Measure mass multiple times over a range of time
Once the mass stops changing, the reaction has stopped
Finding the Mr of a Volatile Liquid
Vaporise a known mass of liquid in at a known temperature and pressure
The liquid is injected from a hypodermic syringe into a gas syringe
Measure the volume and then use the ideal gas equation
Calorimetry
For determining the enthalpy change (of combustion)
The heat released / absorbed by a chemcial reaction is measured
The heat released warms up a known mass of water
Water’s specific heat capacity is knwon
The reaction ins done in a polystyrene cup
q = (mass of water) x (4.18) x (change in temp) is used
then, enthalpy change = -(q / 1000) / mol of substance
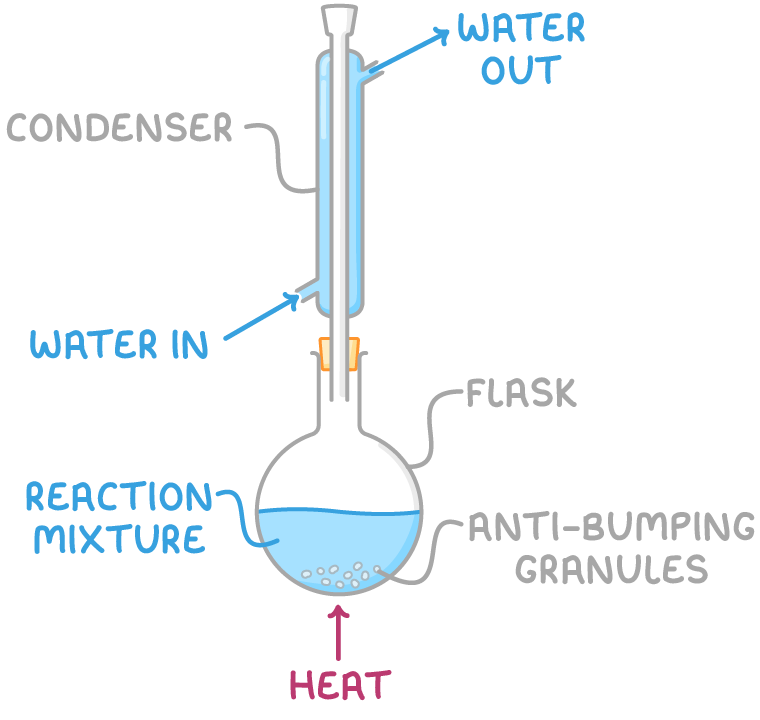
Reflux
For heating reactants at a constant temperature
Reactants are put in a Liebig Condenser
Antibumping granules are added
The water jacket is connected to a water source
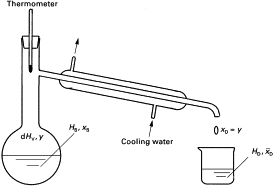
Simple Distillation
For separating a mixture of liquids
Place mixture in round-bottomed flask
Turn on water supply for water jacket
Heat to boiling point of desired product
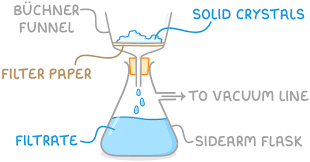
Filtration under Reduced Pressure
Separating solid from liquid
Attach water pump
Ensure vacuum is produced
Place filter paper in the Buchner funnel
Place solid (crystals) on the filter paper
Wait until liquid is removed
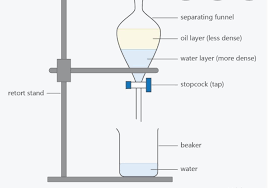
Purification
Removing impurities
Liquid collected from reaction is placed in separating funnel
Water is added to dissolve water-soluble impurities
Two layers will form
The less dense organic layer
The more dense aqueous layer
The organic layer is removed from the separating funnel
A drying agent is added to remove any remaining water
The organic layer is filtered from the drying agent
Recrystallisation
Removes insoluble impurities
Dissolve crystals in minimum volume of hot solvent
Product must be more soluble in got solvent compared to cold solvent
Filter hot solution using hot glassware and fluted filter paper
Solution is allowed to cool at room temperature
Product is filtered under reduced pressure with Buchner apparatus
Products is washed with small amount of cold solvent
Product is dried with filter paper
Using a Colourimeter
Measure the concentration of a substance as it is proportional to the absorbance
Standardise the colourimeter by measuring absorbance of distilled water in a cuvette
The value should be 0
Measure the absorbance of difference concentrations and record the value
A graph with a line of best fit can be used to determine an unknown concentration
Thin Layer Chromatography
Separate a mixture
Draw a pencil line as the origin
Add a concentrated dot of solution on the origin line
Place the silica plate in the solvent, ensuring the origin line lies above the solvent surface
Let the solvent move up the plate until it reaches near the top
Draw a line where the solvent front it
Leave plate to dry
Measure Rf values
Measuring EMF
In a beaker place a strip of metal and the metal ions
Eg copper and copper chloride
Do the same for a different metal in a second beaker
Soak a strip of filter paper in KNO3
Use the filter paper as a salt bridge
Connect crocodile clips to each metal strip and a voltmeter
Measure the potential difference