Ch. 6 Skeletal System: Bone Tissue and Functions
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Long Bone
Examples include humerus and femur.
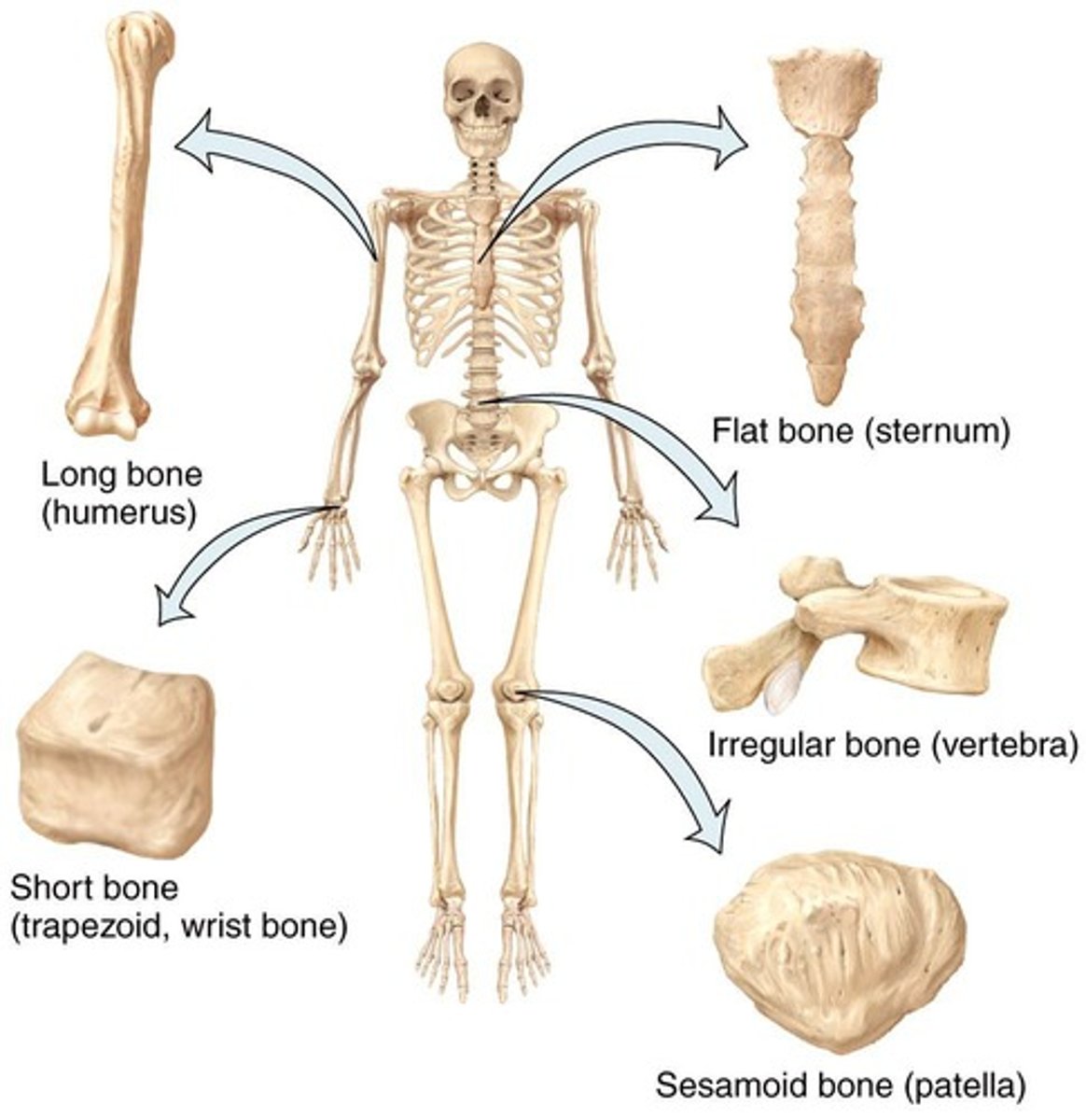
Flat Bone
Thin, flattened bone shape.
Short Bone
Cube-shaped bones, like carpals.
Sesamoid Bone
Bone embedded within a tendon.
Irregular Bone
Complex shapes, like vertebrae.
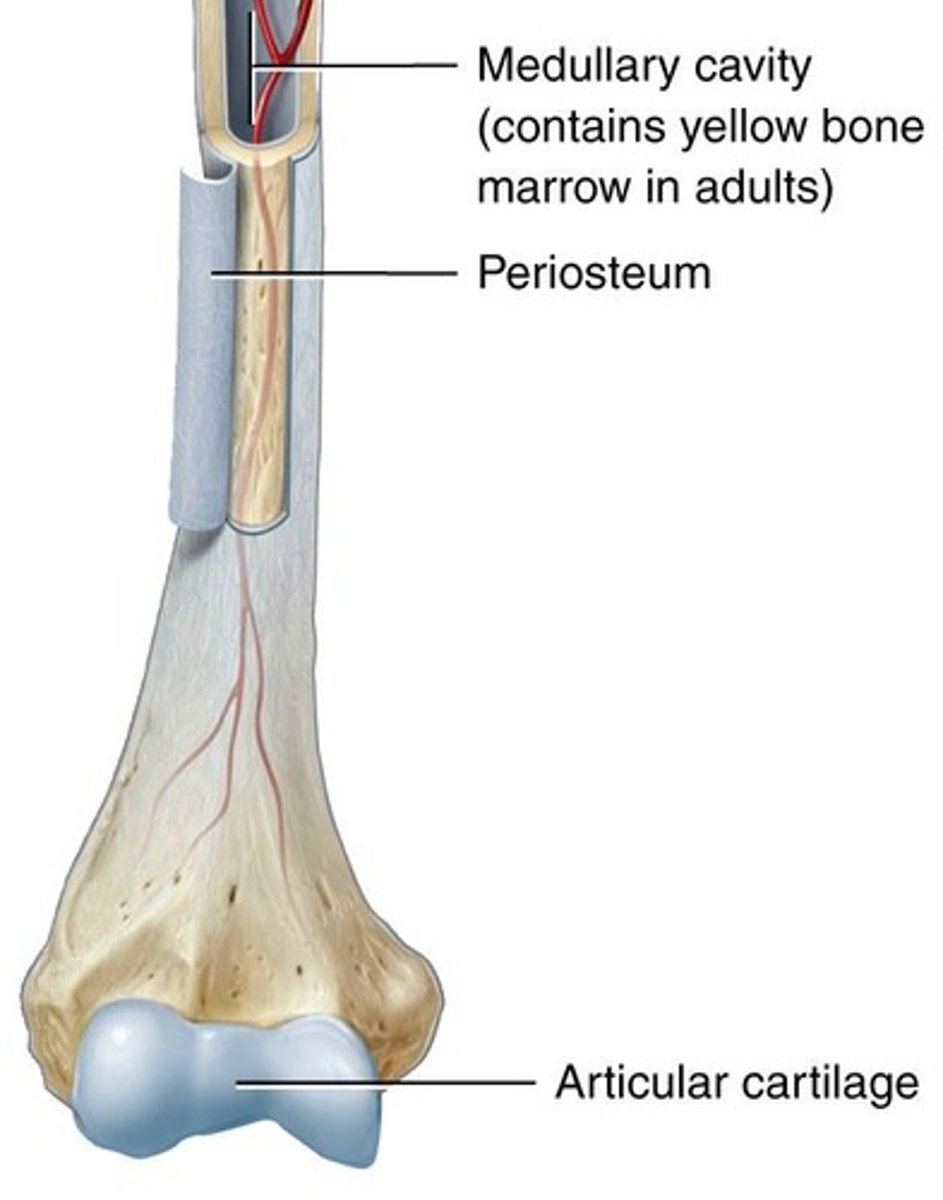
Articular Cartilage
Covers bone ends, reduces friction.
Spongy Bone
Lightweight bone with holes, contains marrow.
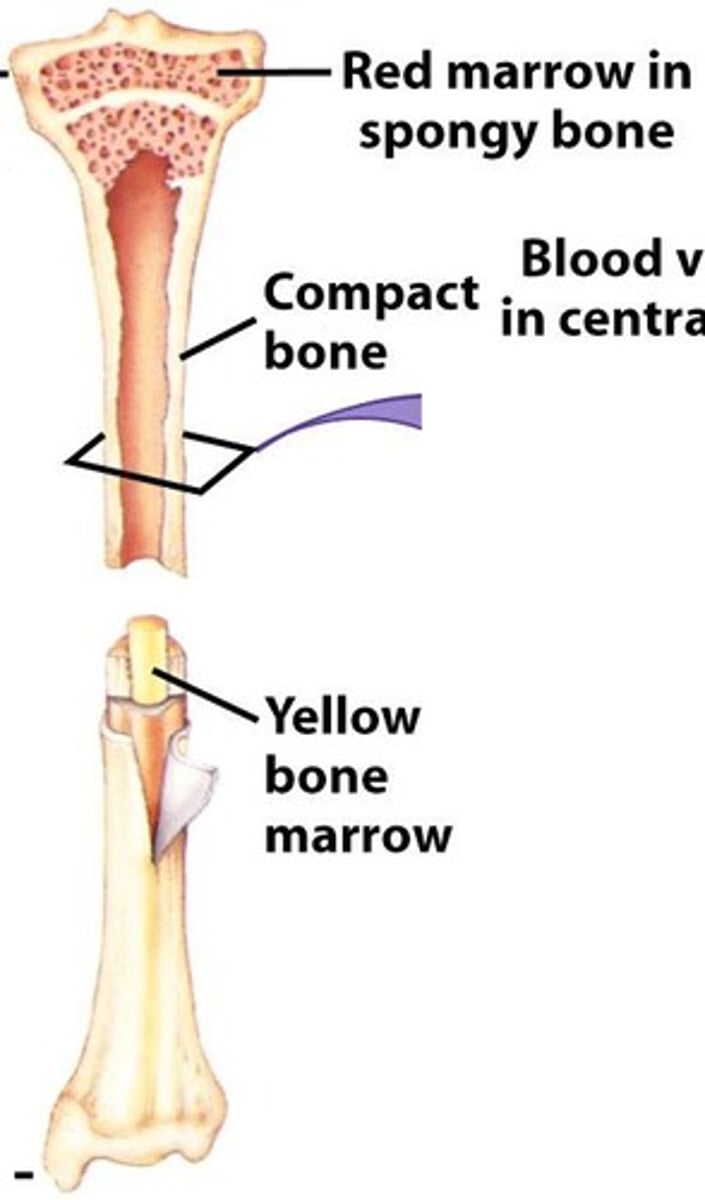
Compact Bone
Dense bone providing strength and support.
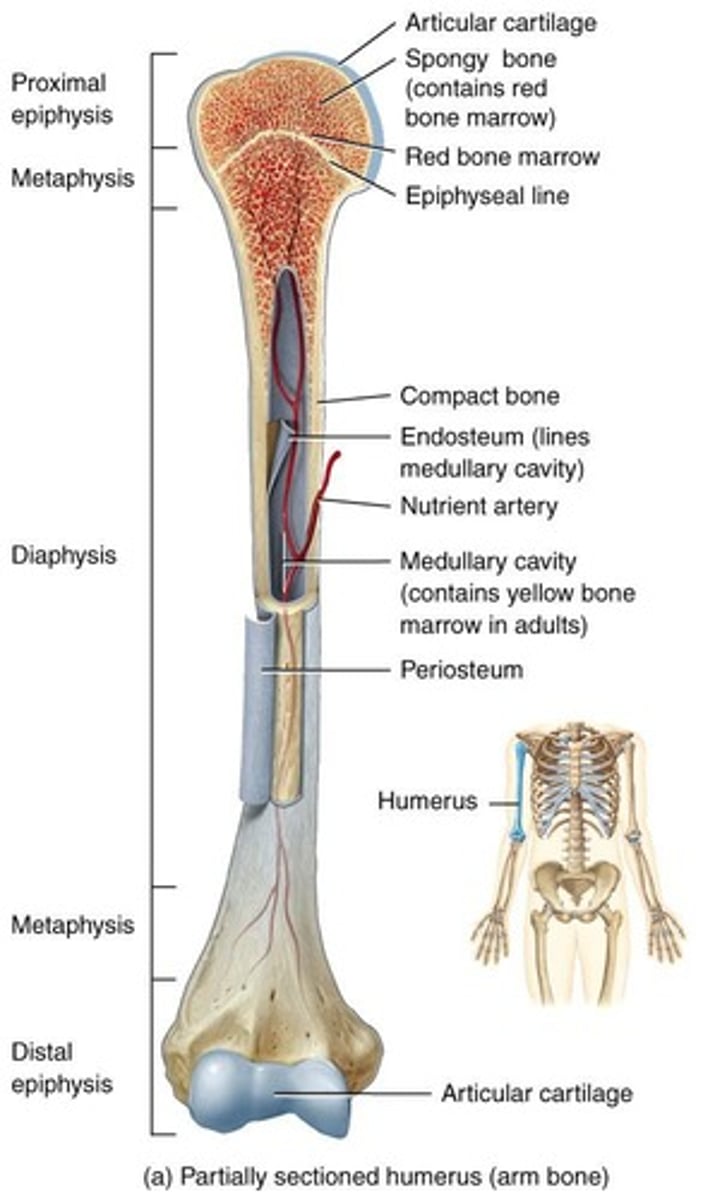
Diaphysis
Shaft of a long bone.
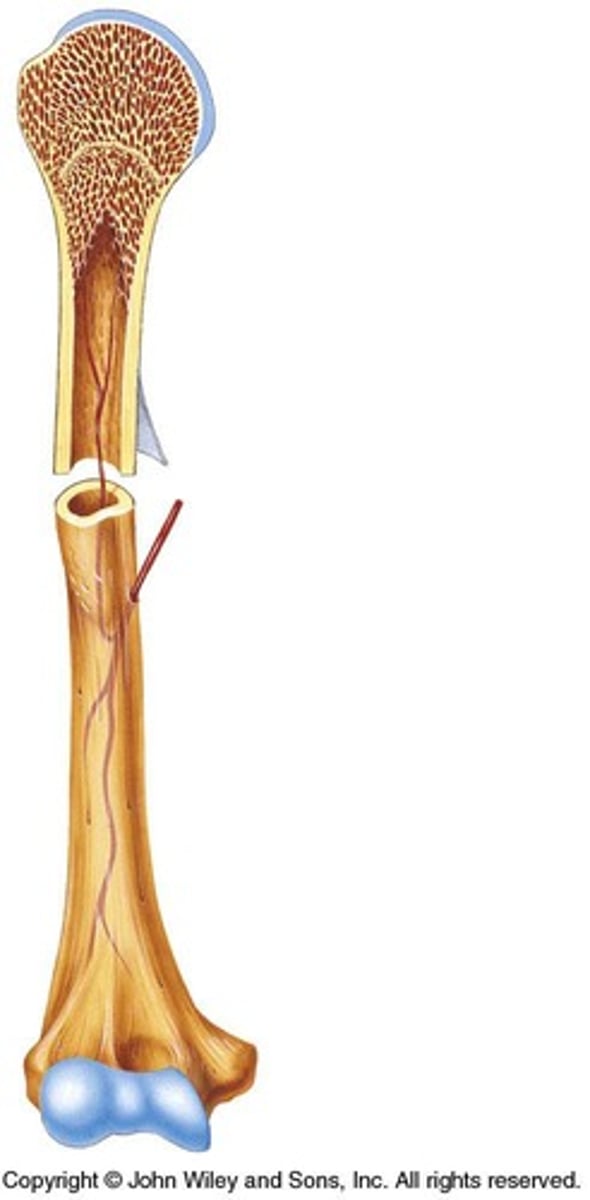
Epiphysis
Ends of long bones, contains spongy bone.
Metaphysis
Region between epiphysis and diaphysis.
Red Bone Marrow
Site of blood cell production.
Yellow Bone Marrow
Stores triglycerides, found in medullary cavity.
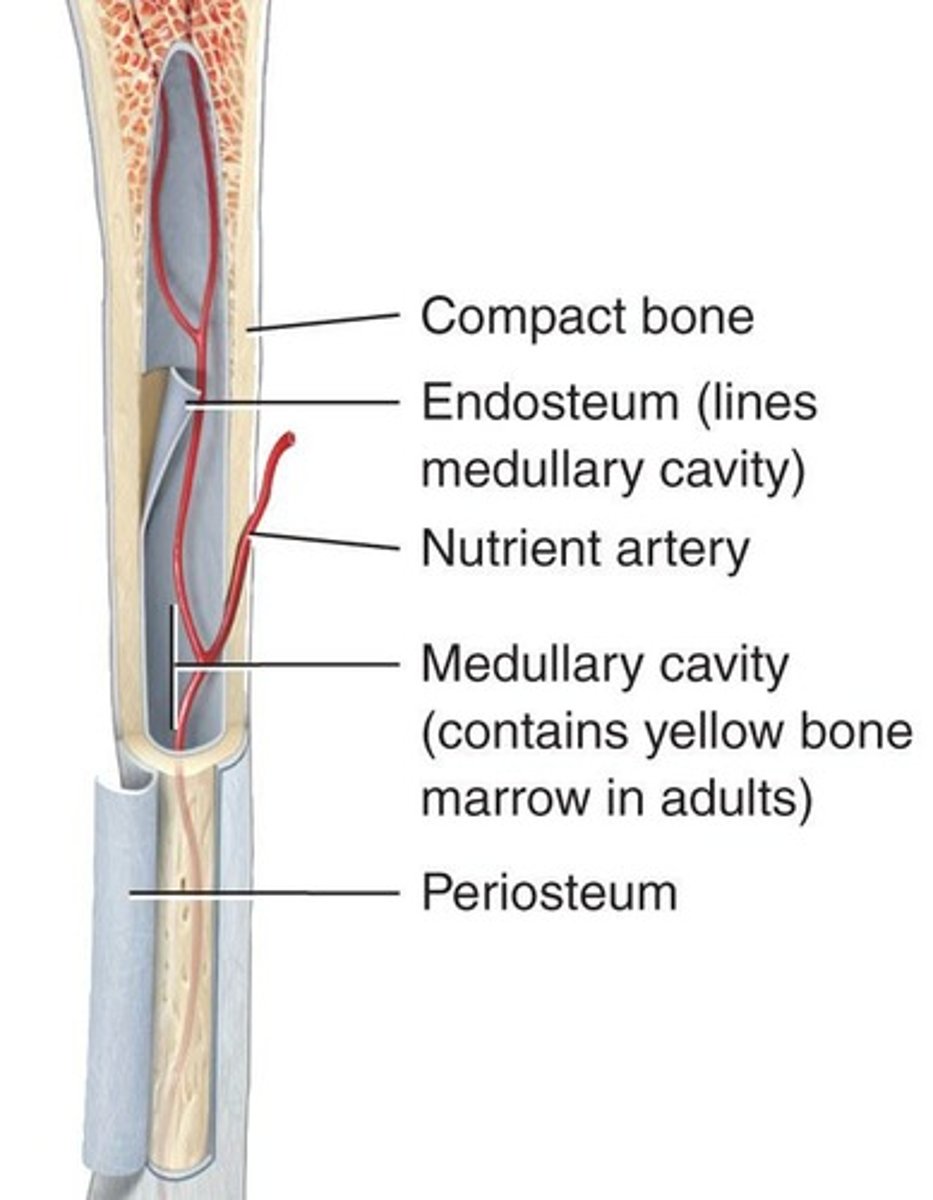
Endosteum
Lines the medullary cavity of bones.
Periosteum
Outer membrane covering bones.
Hematopoiesis
Blood cell production in red marrow.
Cranial Cavity
Houses the brain.
Thoracic Cavity
Contains lungs and heart.
Pelvic Cavity
Contains reproductive organs.
Vertebral Cavity
Houses the spinal cord.
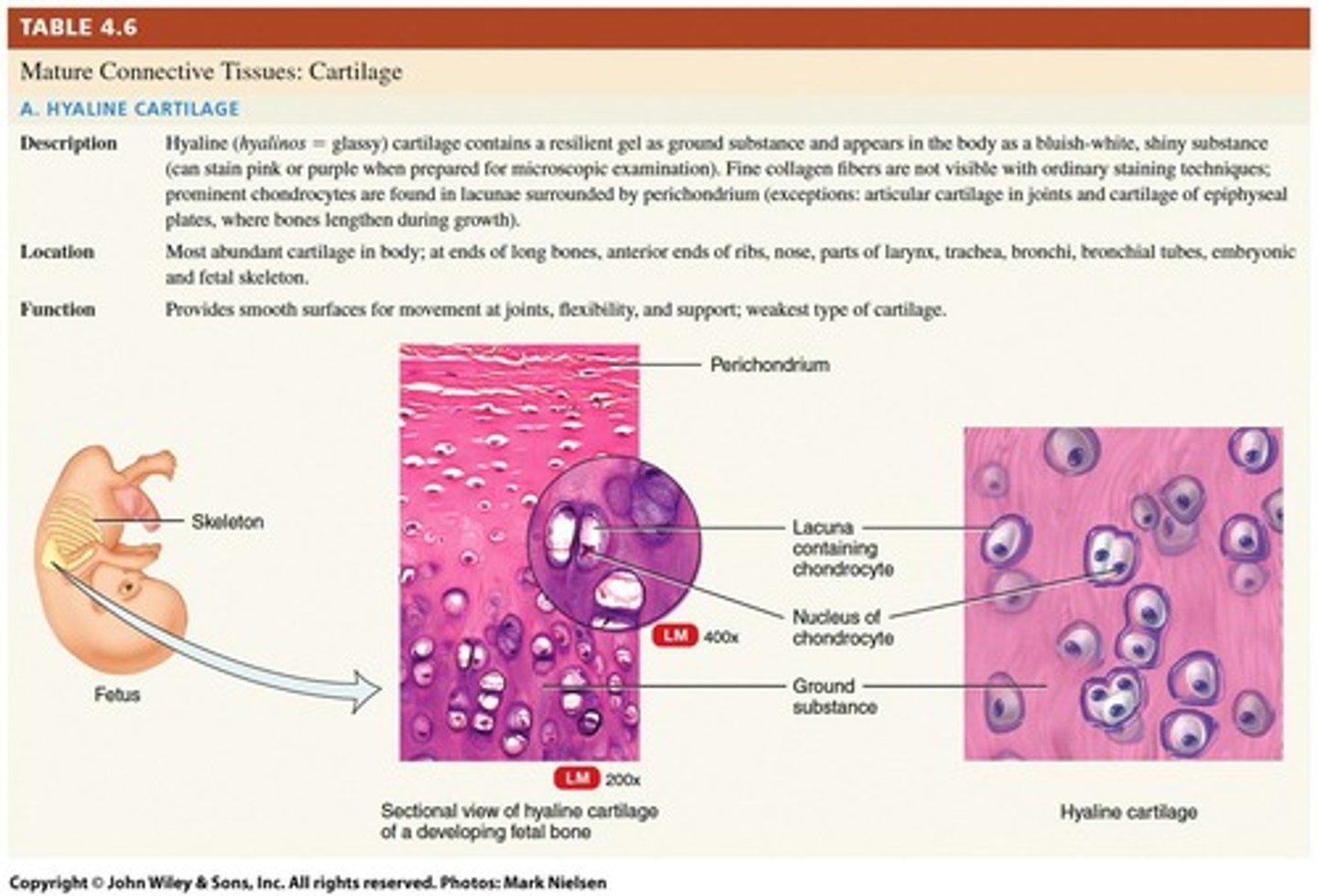
Hyaline Cartilage
Minimal fibers, ideal for joints.
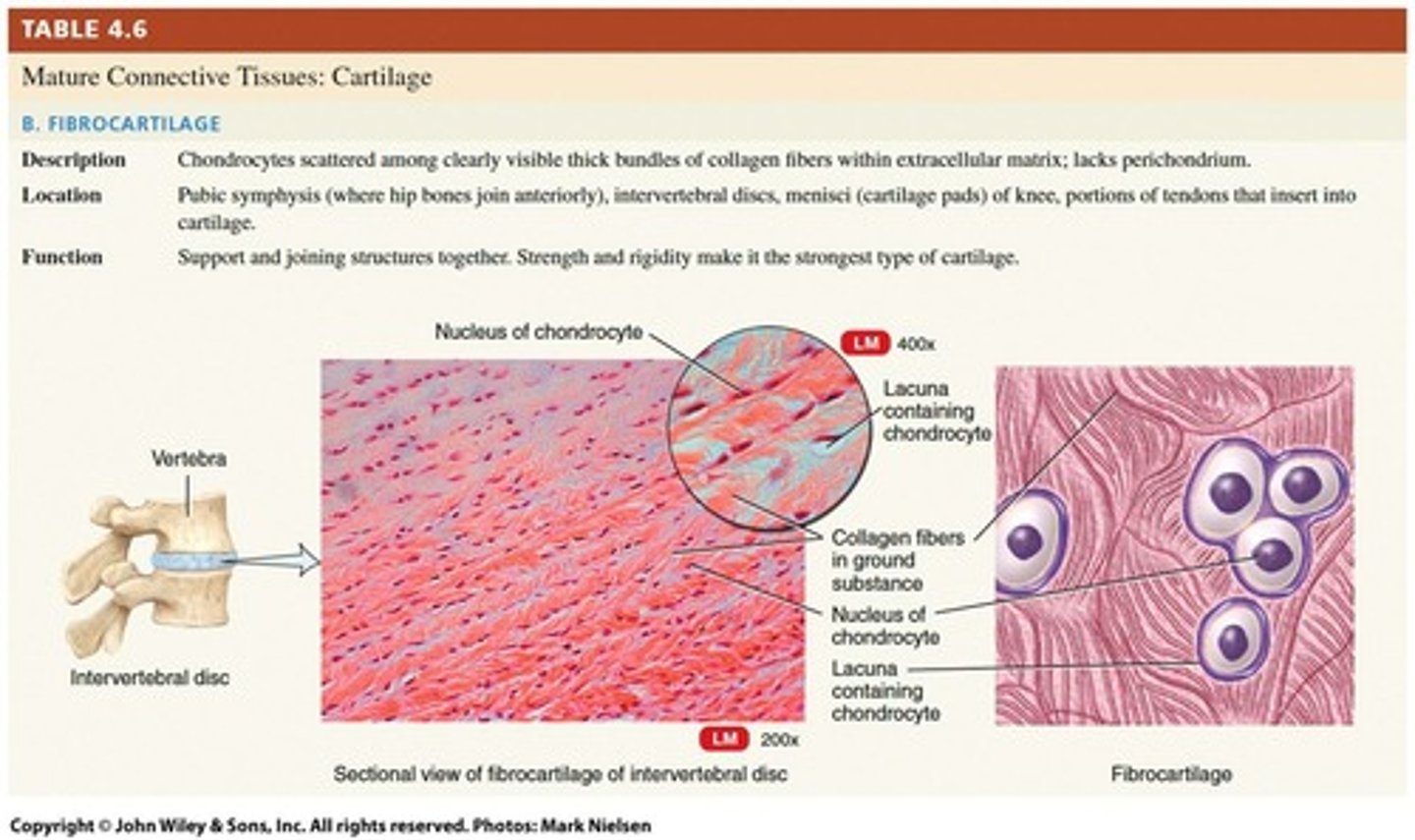
Fibrocartilage
Dense, strong cartilage for cushioning.
Elastic Cartilage
Contains elastin fibers for flexibility.
Articular Cartilage Function
Reduces friction at joint surfaces.
Vertebral Cartilage Function
Absorbs impact between vertebrae.
Bone Remodeling
Continuous process of bone formation and resorption.
Skeletal System Functions
Supports, protects, and stores minerals.
Bone Tissue Composition
Highly vascularized with mineralized matrix.
Epiphysial Plate
Growth region in long bones during adolescence.
Periosteum
Dense tissue covering bone, aids growth and repair.
Medullary Cavity
Hollow space in long bones containing yellow marrow.
Endosteum
Membrane lining medullary cavity, contains osteoblasts and osteoclasts.
Perichondrium
Connective tissue surrounding cartilage, supports growth.
Chondrocytes
Cells responsible for forming cartilage.
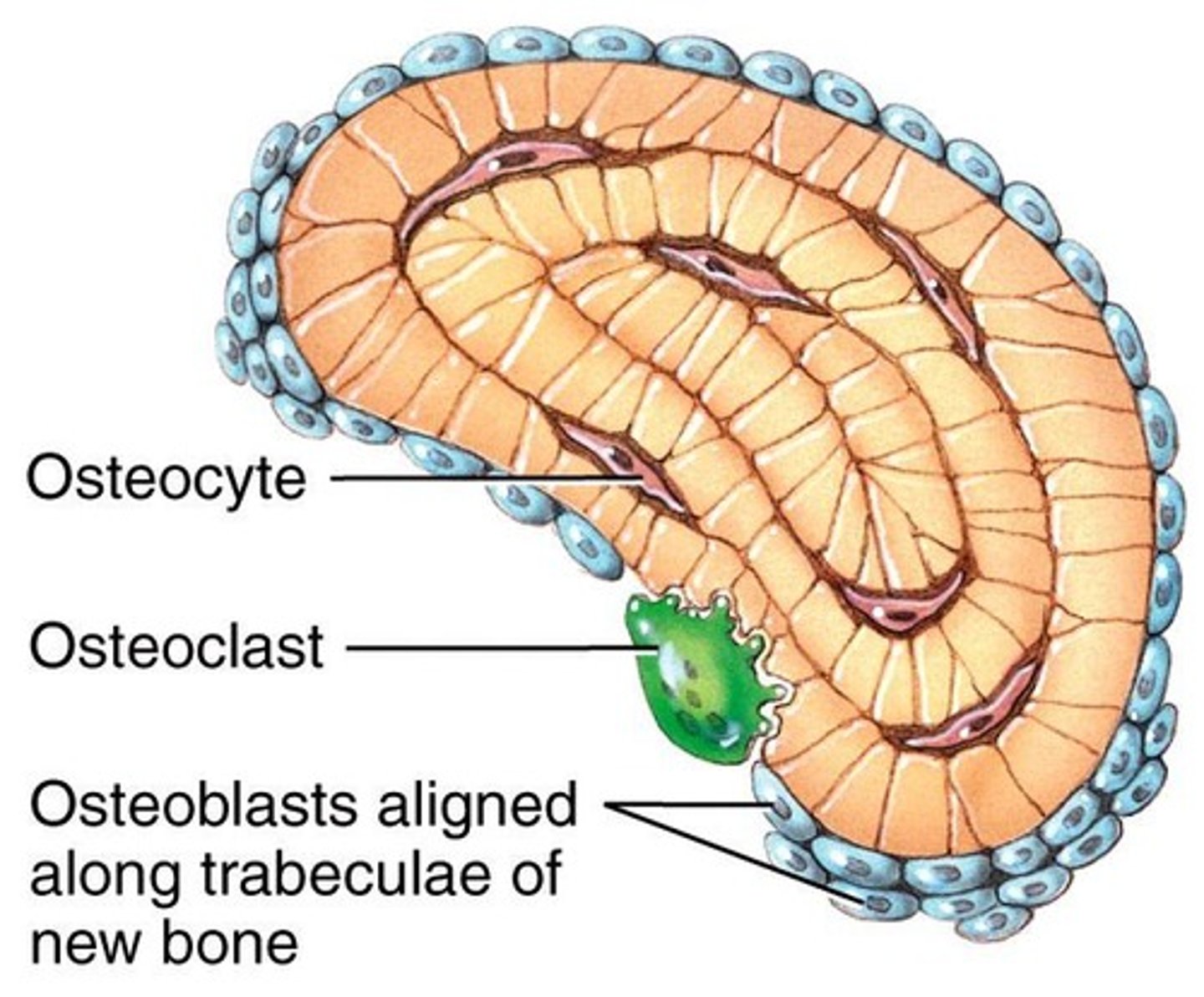
Osteoblast
Bone-forming cell derived from osteogenic cells.
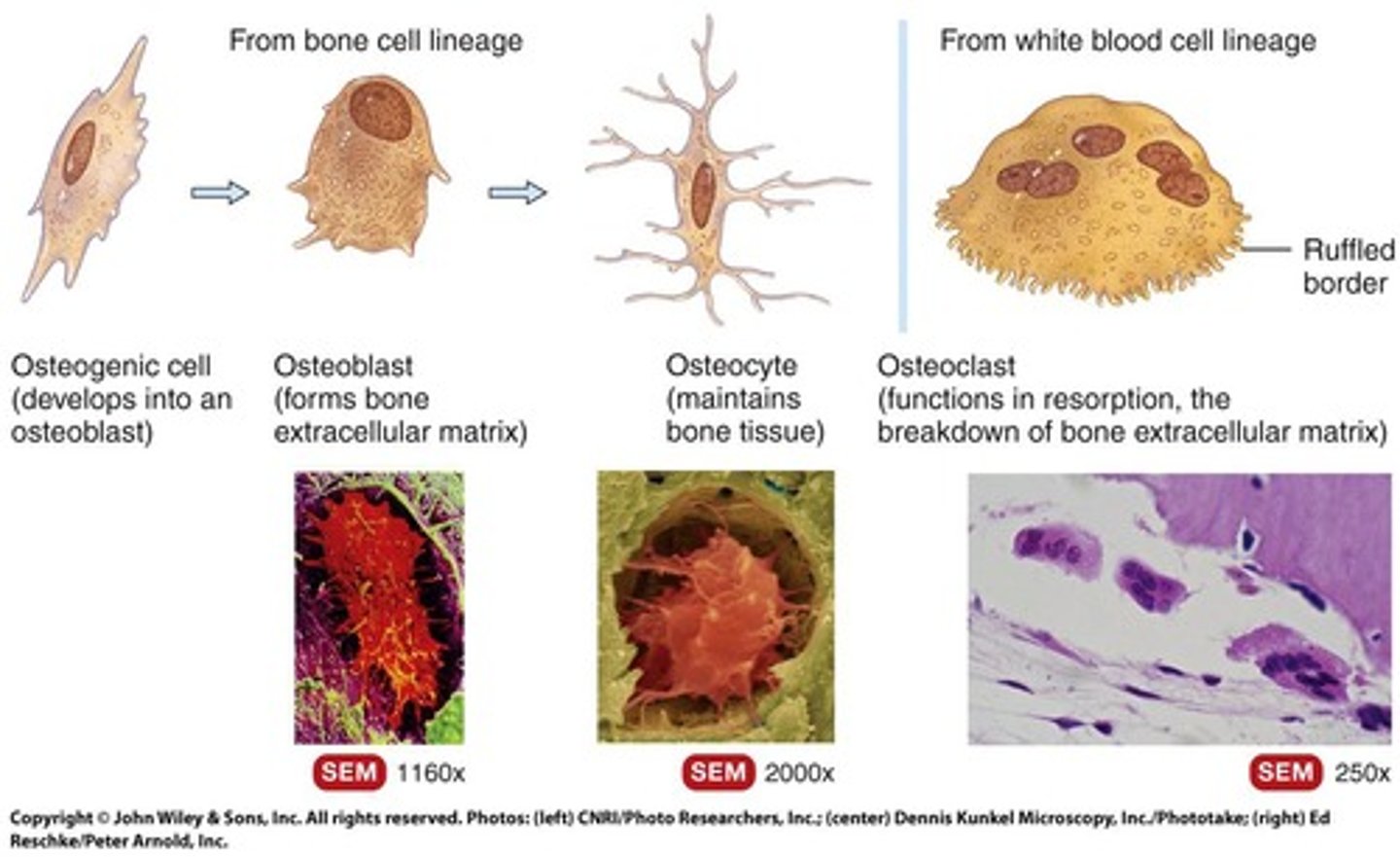
Osteocyte
Mature osteoblast that maintains bone tissue.
Osteogenic Cell
Stem cell that differentiates into bone cells.
Osteoclast
Cell that breaks down bone tissue, derived from WBCs.
Hematopoietic Stem Cells
Stem cells that produce blood cells.
Yellow Bone Marrow
Fat storage tissue in medullary cavity.
Red Bone Marrow
Site of blood cell production (hematopoiesis).
Collagen
Protein providing flexibility and tensile strength to bone.
Hydroxyapatite
Mineral salts providing hardness to bone structure.
Calcium Phosphate
Major inorganic component of bone mineral.
Epiphyseal Line
Remnant of growth plate in adult bones.
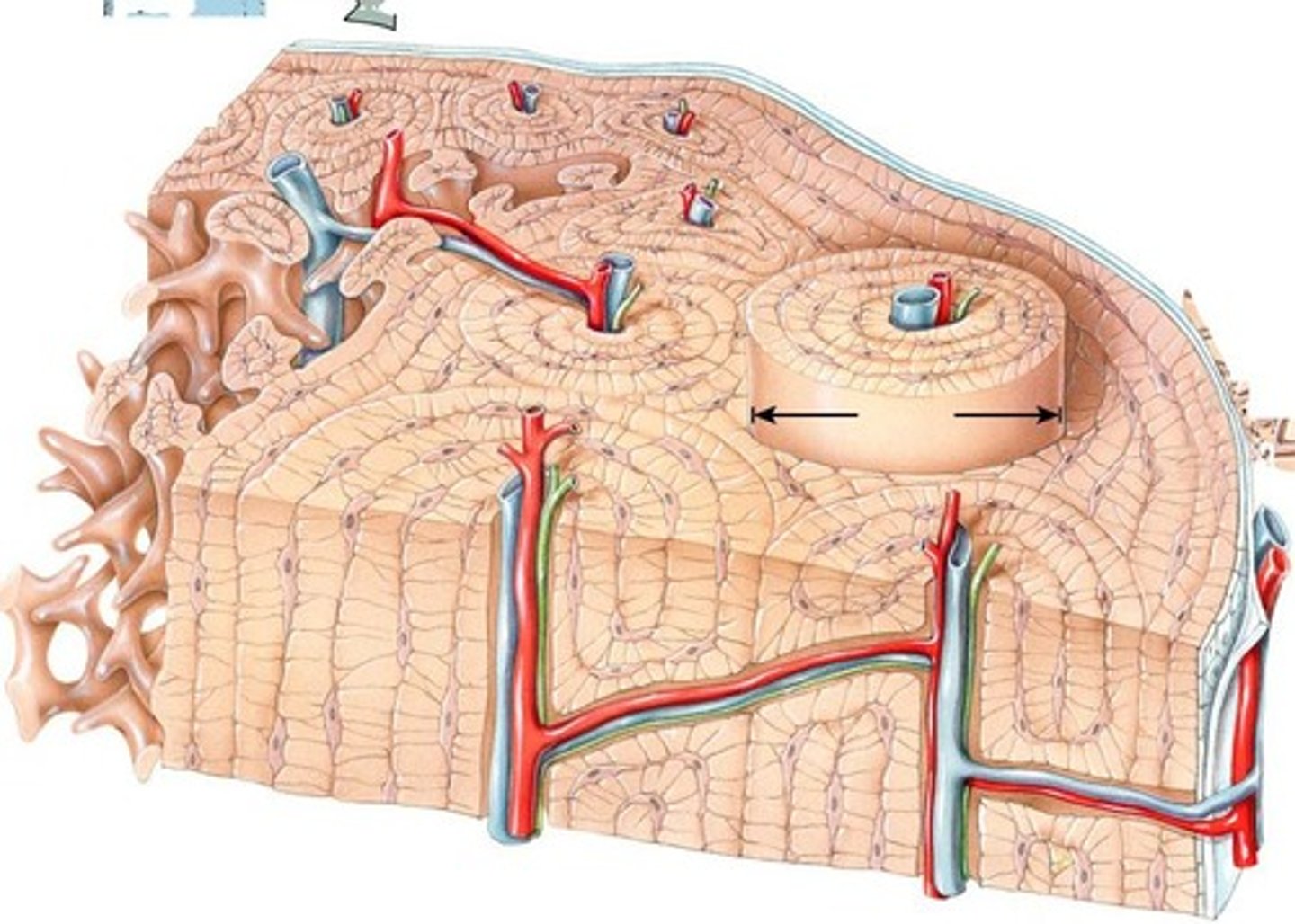
Osteon
Structural unit of compact bone, contains Haversian systems.
Lacunae
Small spaces housing osteocytes in bone matrix.
Canaliculi
Channels connecting lacunae, allowing nutrient exchange.
Circumferential Lamellae
Rings of bone matrix surrounding outer bone.
Concentric Lamellae
Rings of calcified matrix within osteons.
Interstitial Lamellae
Remnants of older osteons between current osteons.
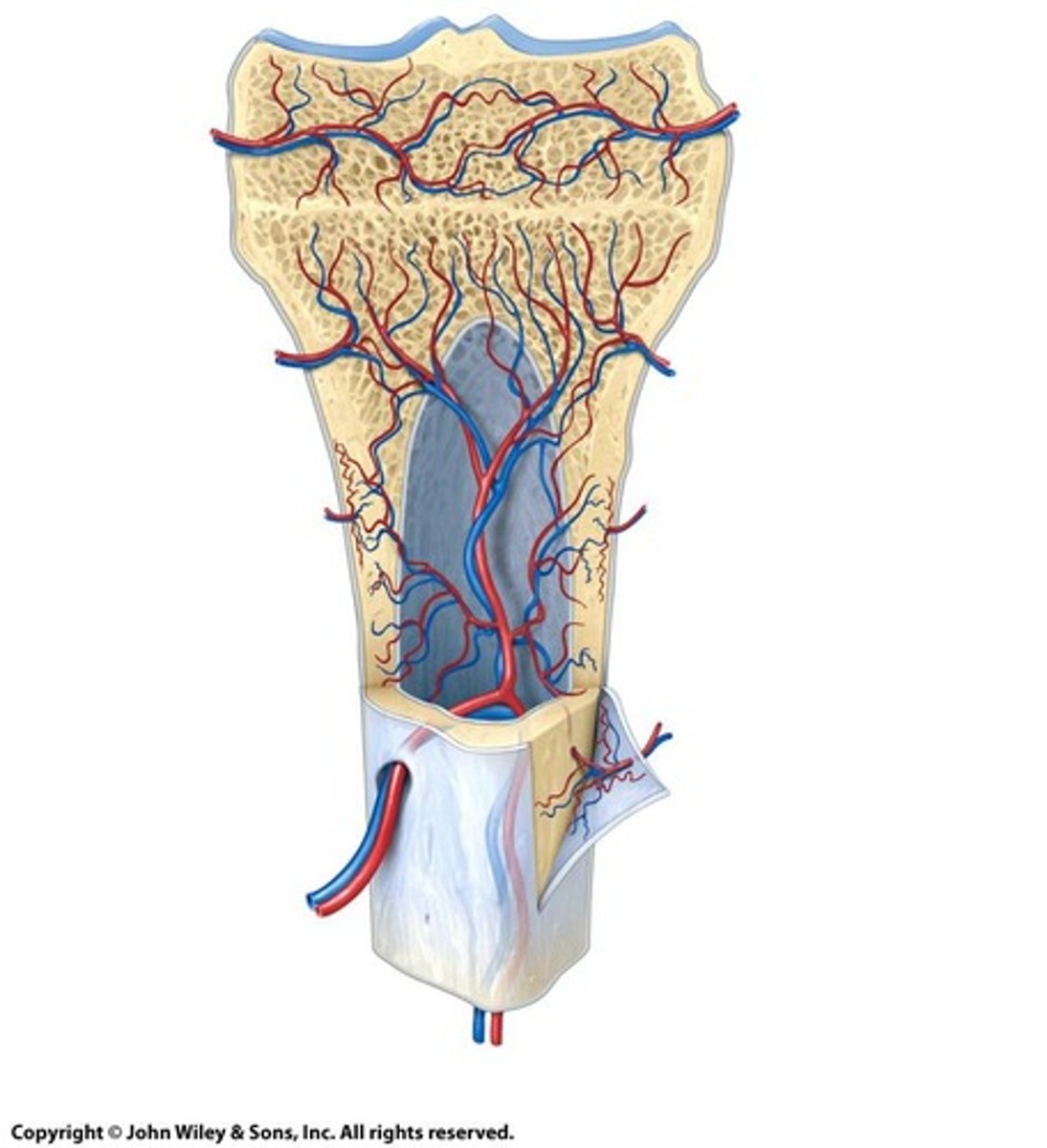
Vascularization
Blood supply through central canals in osteons.
Volkmann's Canals
Perforating canals connecting blood vessels to outer bone.
Bone Composition
Bone consists of 25% water, 25% proteins, 50% minerals.
Bone Remodeling
Process of bone resorption and formation.
Fracture Repair
Process involving periosteum and osteoblast activity.
Growth Plate Function
Site of active cell division for bone elongation.
Spongy Bone
Majority of epiphyses in long bones.
Compact Bone
Superficial bone along longitudinal length.
Ossification
Process of forming new bone.
Embryogenesis
Bone formation in an embryo.
Adolescent Growth
Growth of bones until adulthood.
Bone Remodeling
Continual process of bone renewal.
Fracture Repair
Restoration of bone after injury.
Intra-membranous Ossification
Produces spongy bone directly.
Endochondral Ossification
Cartilage replaced by bone.
Osteoblasts
Cells that secrete bone matrix.
Calcification
Recruitment of calcium and phosphates.
Periosteum
Membrane formed around bone surface.
Chondroblasts
Stem cells forming cartilage.
Chondrocytes
Cartilage cells that secrete fibers.
Primary Ossification Site
Location where spongy bone first forms.
Medullary Cavity
Hollow space within diaphysis.
Secondary Ossification Centers
Regions where bone replaces cartilage.
Articular Cartilage
Covers surface of epiphyses.
Epiphyseal Growth Plate
Responsible for longitudinal bone growth.
Lateral Bone Growth
Thickening of bones.
Longitudinal Bone Growth
Increase in bone length.
Human Growth Hormone
Stimulates bone and muscle growth.
Pituitary Gland
Secretes hormones regulating growth.
Hormonal Regulation
Control of bone growth by hormones.
Bone Growth Completion
Usually by ages 18-21.
Puberty Impact
Accelerates adolescent bone growth.
Gender Differences in Growth
Variations in growth patterns between sexes.
Collagen Fibers
Protein fibers providing structure to bones.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Develop into various cell types during growth.
Human Growth Hormone (hGH)
Stimulates growth of bone and muscle.
Side Effects of hGH
Can lead to fractures and muscle atrophy.
Growth Spurt
Rapid increase in height during puberty.
Estrogen
Promotes widening of female pelvis.
Testosterone
Contributes to male growth during puberty.
Epiphyseal Plates
Growth areas that close after puberty.
Osteoclasts
Cells that break down bone tissue.
Osteoblasts
Cells responsible for bone formation.
Acromegaly
Abnormal thickening of bones from excess tissue.
Osteoporosis
Condition of weakened bones due to calcium loss.
Rickets
Bone disease due to vitamin D deficiency.
Osteomalacia
Softening of bones due to mineral deficiency.
Calcium and Phosphorus
Essential minerals for bone growth and remodeling.
Vitamin A
Stimulates osteoblast activity for bone formation.