OB Lecture Exam 3
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ch. 5 (violence against women), ch. 13 (a&p of pregnancy), ch. 14 (nursing care of the family during pregnancy), ch. 15 (maternal nutrition)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
ch. 13 (uterus during pregnancy) - alters size, shape, and position; Hegar sign indicates softening of the lower uterine segment by 6 weeks
uterine growth
ch. 13 (uterus during pregnancy) - increased blood flow and contractility lead to Braxton Hicks contractions; fetal-related changes include ballottement and maternal perception of __________
quickening (first movements perceived by the pregnant woman)
ch. 13 (cervix during pregnancy) - the cervix remains firm and closed; __________ develops from increased vascularization; mucus plug (operculum) forms
Goodell sign (softening of the cervix during early pregnancy)
ch. 13 - ovarian ovulation ceases; __________ produces hormones that support amenorrhea in early pregnancy (ovaries during pregnancy)
corpus luteum
ch. 13 (vagina during pregnancy) - __________ appears; hormonal changes increase leukorrhea and lower vaginal pH
Chadwick sign (blue discoloration of vaginal and pelvic mucosa)
ch. 13 - __________ pelvic blood flow and uterine pressure cause vulvar edema and varicosities (vulva during pregnancy)
increased
ch. 13 - __________ from plasma volume increase leads to physiologic anemia; Hgb <11 g/dL (1st/3rd trimester) or <10.5 g/dL (2nd trimester) is diagnostic (blood during pregnancy)
hemodilution
ch. 14 - is calculated from the first day of the last menstrual period using Nägele’s Rule—subtract 3 months, add 7 days, and adjust the year; can also be confirmed by early ultrasound, with pregnancy lasting ~280 days or 40 weeks
estimated date of birth (EDB)
ch. 14 - was is the EDB when the patient says the first day of her last menstrual period was december 21, 2024?
september 28, 2025
ch. 14 - __________ is the number of times a woman has been pregnant, regardless of outcome; __________ counts pregnancies reaching 20 weeks, not the number of fetuses
gravity (G); parity (P)
ch. 14 - what is the gravida & parity of a woman who had 3 pregnancies and normal deliveries, but the third was a twin birth?
G3; P3
ch. 14 - what does GTPAL stand for?
G - gravida
T - term
P - preterm
A - abortion
L - living
ch. 14 - J. D. is 8 weeks pregnant and is at her first prenatal visit. she has two children aged 9 delivered at 38 weeks and 4 delivered at 36 weeks. what is the GTPAL?
G - 3
T - 1
P - 1
A - 0
L - 2
ch. 14 - who provides prenatal care (PNC)?
obstetricians, certified nurse midwives, and family physicians
ch. 14 - where is PNC provided?
clinics, hospitals, and private practices
ch. 14 - what is the goal of PNC?
to promote a healthy pregnancy, monitor fetal/maternal well-being, and prevent complications
ch. 14 - how early should PNC begin?
as early as possible—ideally in the first trimester (by 12 weeks)
ch. 14 - what are barriers to attending PNC?
lack of insurance, transportation, and childcare
ch. 14 - what care is offered during PNC visits?
physical exams, labs, and screenings
ch. 14 - 1st (weeks 1-13), 2nd (14-26), 3rd (27-40)
pregnancy has 3 trimesters
ch. 14 - every 4 weeks until 28 weeks, every 2 weeks until 36 weeks, then weekly until birth
prenatal visits
ch. 14 - includes interview, full health and OB history, physical exam, lab tests, and education on pregnancy care, nutrition, hygiene, and breastfeeding prep
initial PNC visit
ch. 14 - include interview, vital signs, weight, urinalysis, physical exam, fundal height, fetal assessment, and ongoing teaching
PNC follow-up visits
ch. 14 - position supine with right hip wedge, inspect, palpate, and measure fundal height from pubic bone to fundus (from 2nd trimester)
abdominal assessment
ch. 14 - check gestational age, fetal heart tones (~12 weeks via Doppler), movements, quickening (16–20 weeks), and confirm with ultrasound if needed
fetal assessment
ch. 14 - poses increased risk in pregnancy; assess privately using direct questions, build trust, and follow ABCDES (alone, belief, confidentiality, documentation, education, safety) interventions
intimate partner violence (IPV)
ch. 14 - by 13 weeks, the uterus rises into the abdomen; at __________, it’s midway between pubis and umbilicus
16 weeks
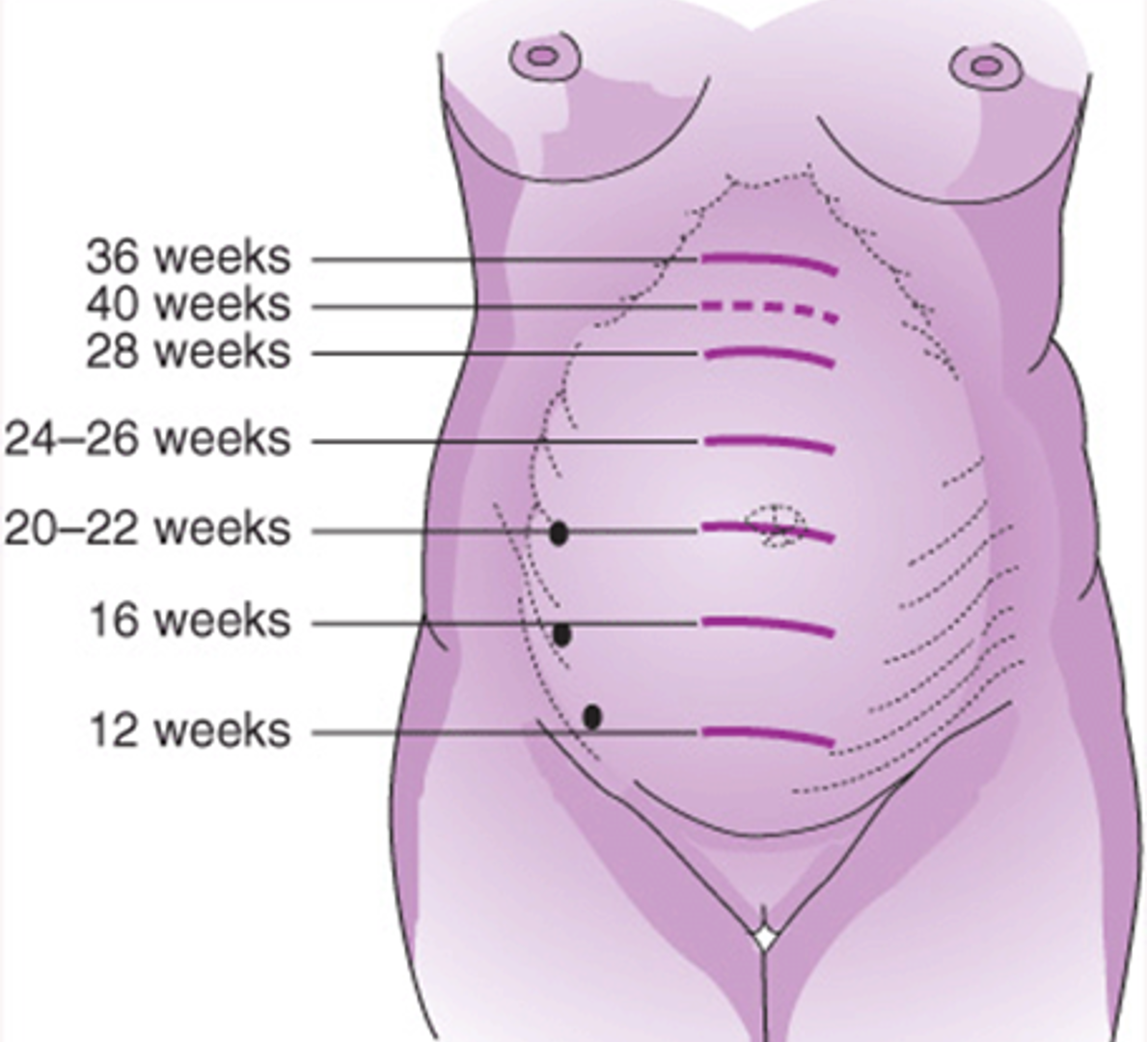
ch. 14 - at __________, the fundus reaches the umbilicus
20-22 weeks
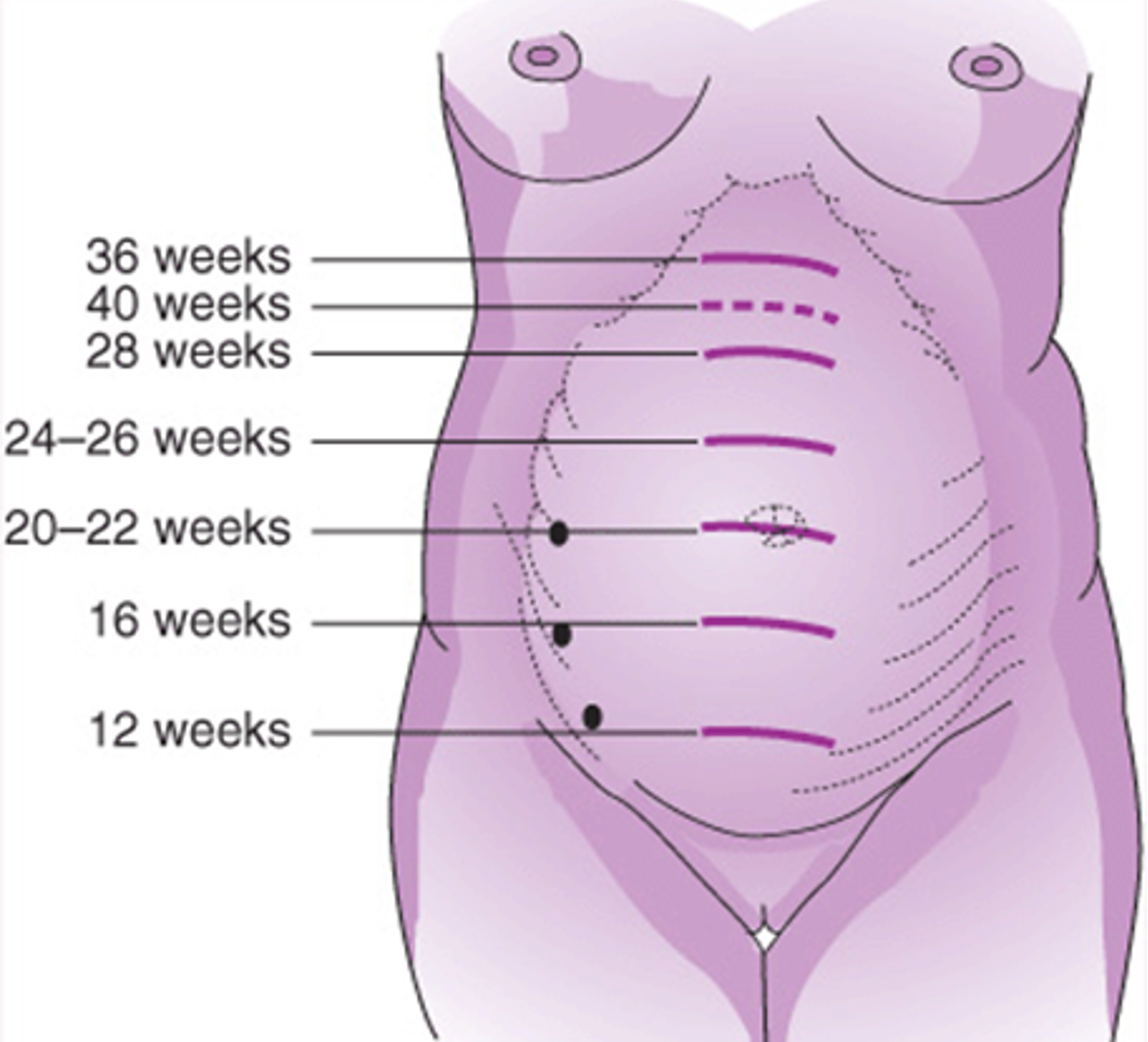
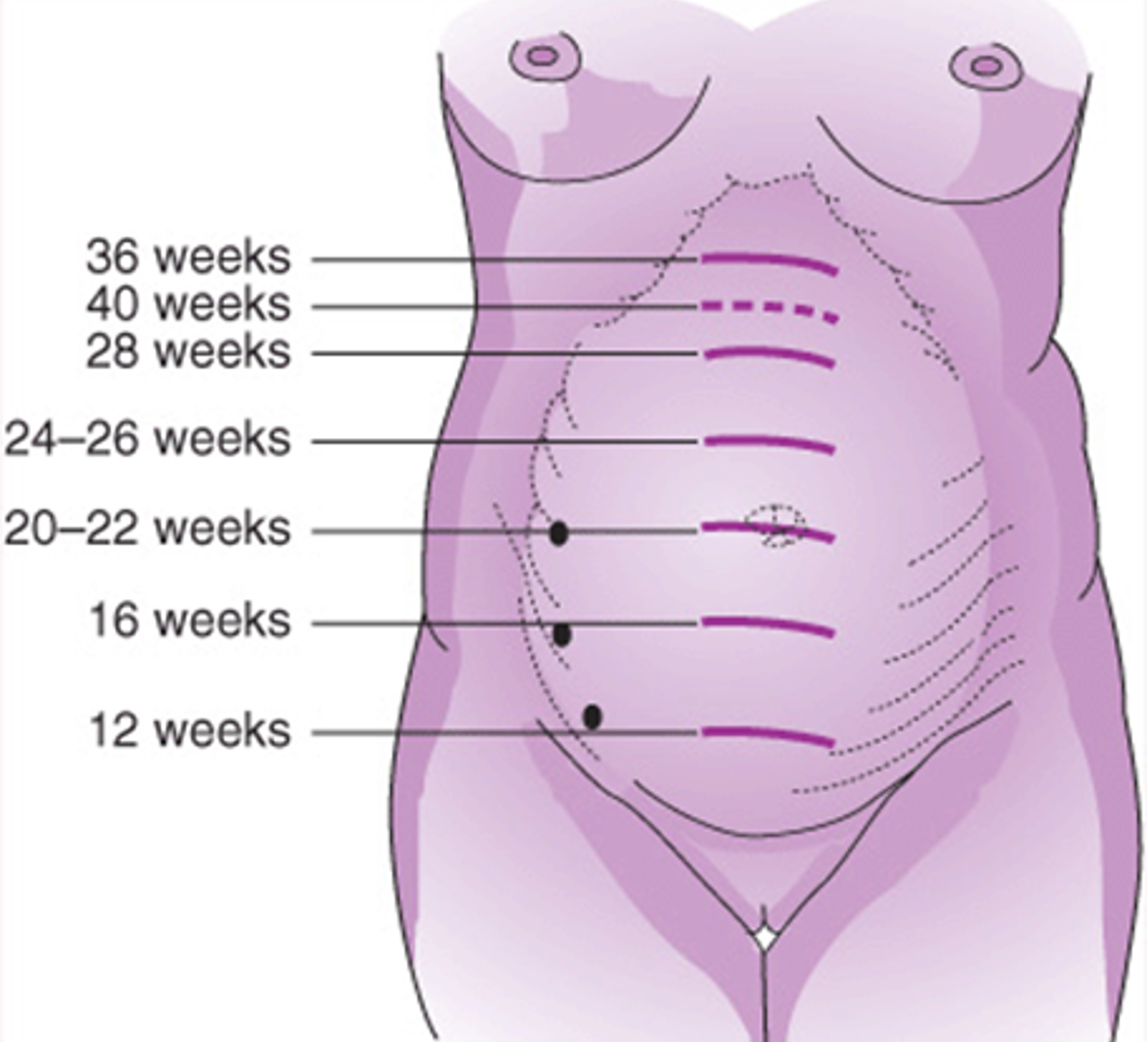
ch. 14 - between 28–32 weeks, fundal height matches gestational age ±2 weeks; by __________, it’s midway to xiphoid
26-28 weeks
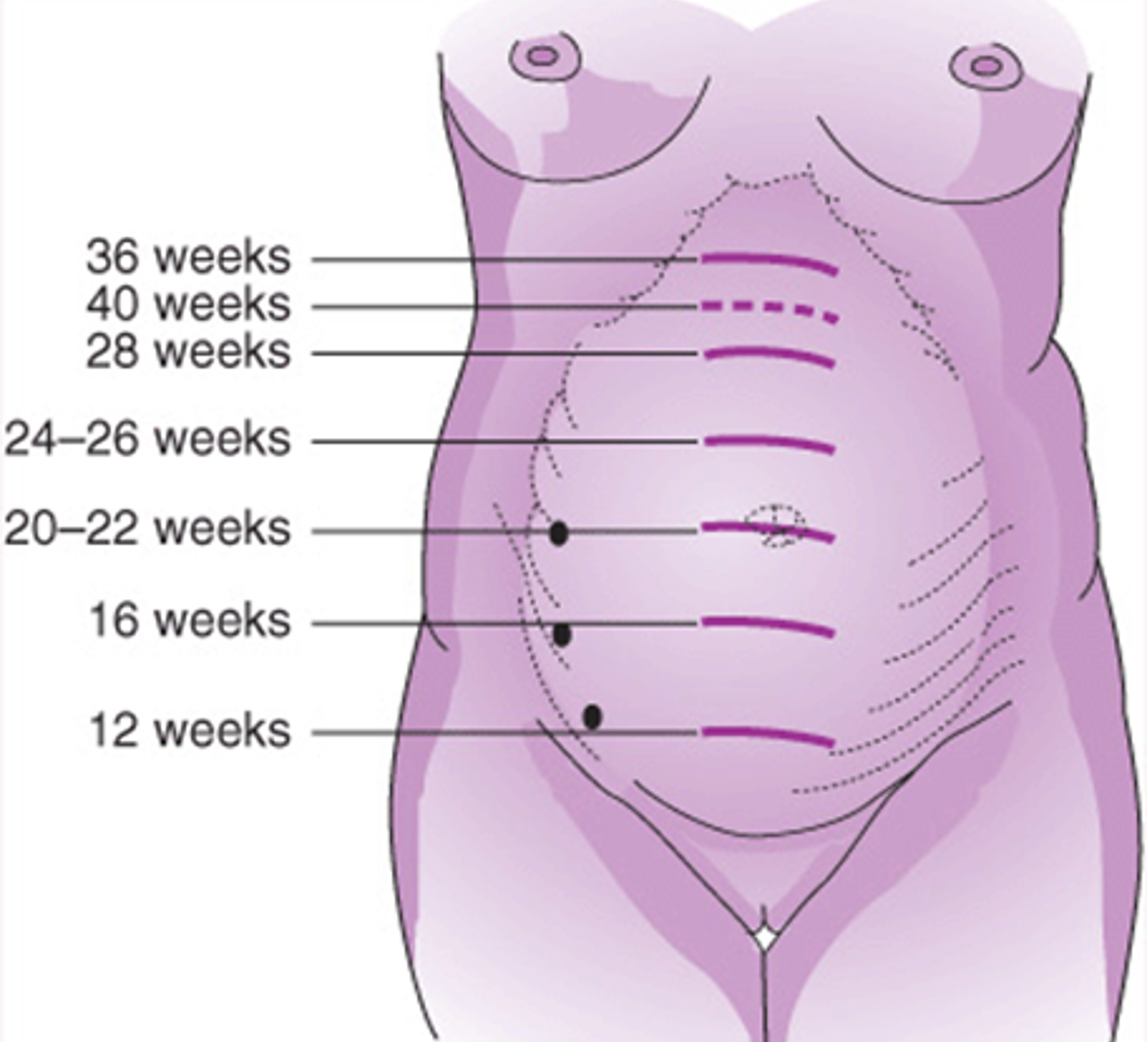
ch. 14 - at 36 weeks, it reaches the xiphoid; at __________, fundal height may drop due to lightening
38-40 weeks
ch. 14 - include CBC, blood type and Rh with antibody screen, urinalysis with culture, rubella titer, STI panel (syphilis, HIV, hep B), gonorrhea and chlamydia testing, and optional ultrasound/genetic screening
labs at PNC initial visit
ch. 14 - repeat CBC, syphilis, HIV, and hep B labs; screen for gestational diabetes, chromosomal abnormalities, and NTDs
28 week visit labs
ch. 14 - test for group B streptococcus and administer recommended immunizations including Rhogam (if Rh negative), Tdap, hep B, and influenza
35-37 week visit labs & immunizations
ch. 14 - key topics such as nutrition, prenatal vitamins, personal hygiene, infection prevention, safe physical activity, and preparation for breastfeeding
self-management during pregnancy
ch. 14 - high-mercury fish (shark, swordfish, king mackerel), raw/smoked seafood, unpasteurized dairy (soft cheeses), uncooked eggs/sprouts, unheated deli meats/hotdogs, and all alcohol
foods to avoid during pregnancy
table 14.3 - what are five most common discomforts in the first trimester of pregnancy?
N/V (morning sickness), fatigue, breast tenderness, urinary frequency, and mood swings/emotional lability
table 14.3 - what are five common discomforts in the second trimester of pregnancy?
heartburn, constipation, backache, round ligament pain, and supine hypotension
table 14.3 - what are five common discomforts in the third trimester of pregnancy?
SOB, urinary frequency, Braxton Hicks contractions, leg cramps, and ankle edema
table 14.4 - what are five signs of potential complications in the first trimester of pregnancy?
severe vomiting, fever/chills, burning with urination, abdominal cramping, and vaginal bleeding
table 14.4 - what are five signs of potential complications in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy?
sudden fluid discharge from the vagina before 37 weeks, decreased fetal movement, severe backache, visual disturbances, and swelling of the face and fingers
ch. 15 - __________ should be taken before conception to help prevent NTDs; found in leafy greens, legumes, citrus fruits, and fortified grains
folate (400 mcg daily)
ch. 15 - what are the nutrient and weight gain needs during pregnancy?
prepregnancy BMI guides healthy weight gain. gaining too little or too much can increase risks for mother and baby.
ch. 15 - 2–4 lbs in the 1st trimester, then ~1 lb/week for normal weight; 0.6 lb/week if overweight; 0.5 lb/week if obese
weight gain patterns during pregnancy
table 15.2 - what tissues contribute to maternal weight gain at 40 weeks gestation?
fetus, placenta, amniotic fluid, increased blood volume, and maternal fat stores
ch. 15 - pregnant women need protein for __________, fats and carbs for __________, plus vitamins (A, D, E, K, folate, B6, B12, C) and minerals (iron, calcium, magnesium, zinc, choline) to support fetal development and maternal health.
growth; energy
table 15.3 - calcium needs during pregnancy and lactation are 1000–1300 mg daily. what are non-dairy sources of calcium?
sardines (with bones), calcium-set tofu, and dark leafy greens (except spinach or Swiss chard)
ch. 15 - vegetarian diets vary in form, with all emphasizing plant-based foods; lacto-vegetarians include dairy, lacto-ovo-vegetarians include eggs and dairy, while vegans consume only plant products and may risk deficiencies __________, __________, and __________ during pregnancy.
iron; vitamin B12; calcium
ch. 15 - gluten-free diets, often chosen for perceived health benefits, are only medically necessary for those with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity and may lead to deficiencies in __________, __________, and __________ if not balanced with gluten-free whole grains.
folate; thiamine; iron
CDC article in ch. 15 pptx - __________, a harmful germ found in some foods, can cause pregnancy loss or serious newborn illness even if the mother shows mild symptoms; pregnant women should avoid high-risk items like unheated deli meats, raw sprouts, and unpasteurized dairy, and instead choose safer options like reheated meats, pasteurized cheeses, and cooked sprouts to protect their baby
listeria
quiz 2 prep - as the clinic nurse, what instructions would you give to a group of pregnant women in preventing constipation? select all that apply.
a) perform regular exercises such as walking
b) take stool softeners as needed
c) increase green leafy veggies
d) consume 8-10 glasses of water daily
e) have 20 mL olive oil once a week
a. perform regular exercises such as walking
c. increase green leafy veggies
d. consume 8-10 glasses of water daily
rationale: pregnant women should prevent constipation by exercising regularly, eating high-fiber foods like leafy greens, and drinking plenty of water. stool softeners are not routinely recommended without a provider’s order. olive oil is not a standard or evidence-based remedy for constipation in pregnancy.
quiz 2 prep - a pregnant client visits the clinic for her first prenatal visit. H\her obstetric history includes 2 live births at term, 1 stillborn at term, and 1 miscarriage at 6 weeks. what is her GTPAL?
a) G4T3P1A1L2
b) G5T3P0A1L2
c) G5T3P1A1L3
d) G4T3P0A1L2
b) G5T3P0A1L2
rationale:
G (gravida) = 5 → 2 live + 1 stillborn + 1 miscarriage + 1 current
T (term) = 3 → all 3 babies were full-term
P (preterm) = 0 → no babies born between 20–36 weeks
A (abortion) = 1 → 1 miscarriage before 20 weeks
L (living) = 2 → only the 2 live births are living
quiz 2 prep - hormone produced by the ovary that relaxes smooth muscles during pregnancy
progesterone