Chapter Summary 03 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:24 PM on 2/25/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
1
New cards
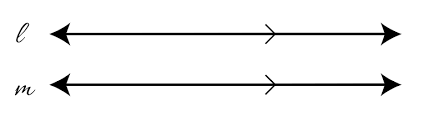
Parallel Lines
Two lines that do not intersect and are coplanar.
2
New cards
Skew Lines
Lines that do not intersect and are not coplanar.

3
New cards
Parallel Planes
Two planes that do not intersect.

4
New cards
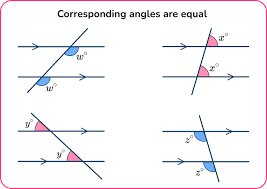
Corresponding Angles
Angles that have corresponding positions when two lines are cut by a transversal.
5
New cards
Alternate Interior Angles
Angles that lie between two lines and on opposite sides of a transversal.
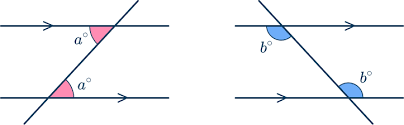
6
New cards
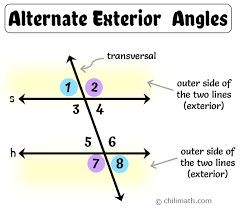
Alternate Exterior Angles
Angles that lie outside two lines and on opposite sides of a transversal.
7
New cards
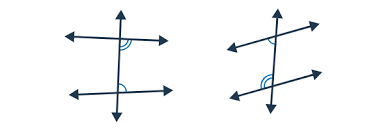
Consecutive Interior Angles
Angles that lie between two lines and on the same side of a transversal.
8
New cards
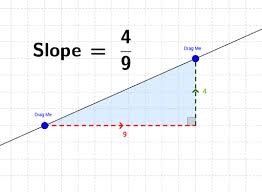
Slope
The ratio of the rise (change in y) to the run (change in x) of a line.
9
New cards
Slope-Intercept Form
A linear equation written in the form y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
10
New cards
Point-Slope Form
A linear equation written in the form y - y₁ = m(x - x₁), indicating the line passes through the point (x₁, y₁) with slope m.
11
New cards
Slopes of Parallel Lines
Two distinct non-vertical lines are parallel if and only if they have the same slope.
12
New cards
Slopes of Perpendicular Lines
Two non-vertical lines are perpendicular if and only if the product of their slopes is -1.
13
New cards
Distance from a Point to a Line
The length of the perpendicular segment from the point to the line; the shortest distance between the point and the line.