Public Key Cryptography and Digital Signatures
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
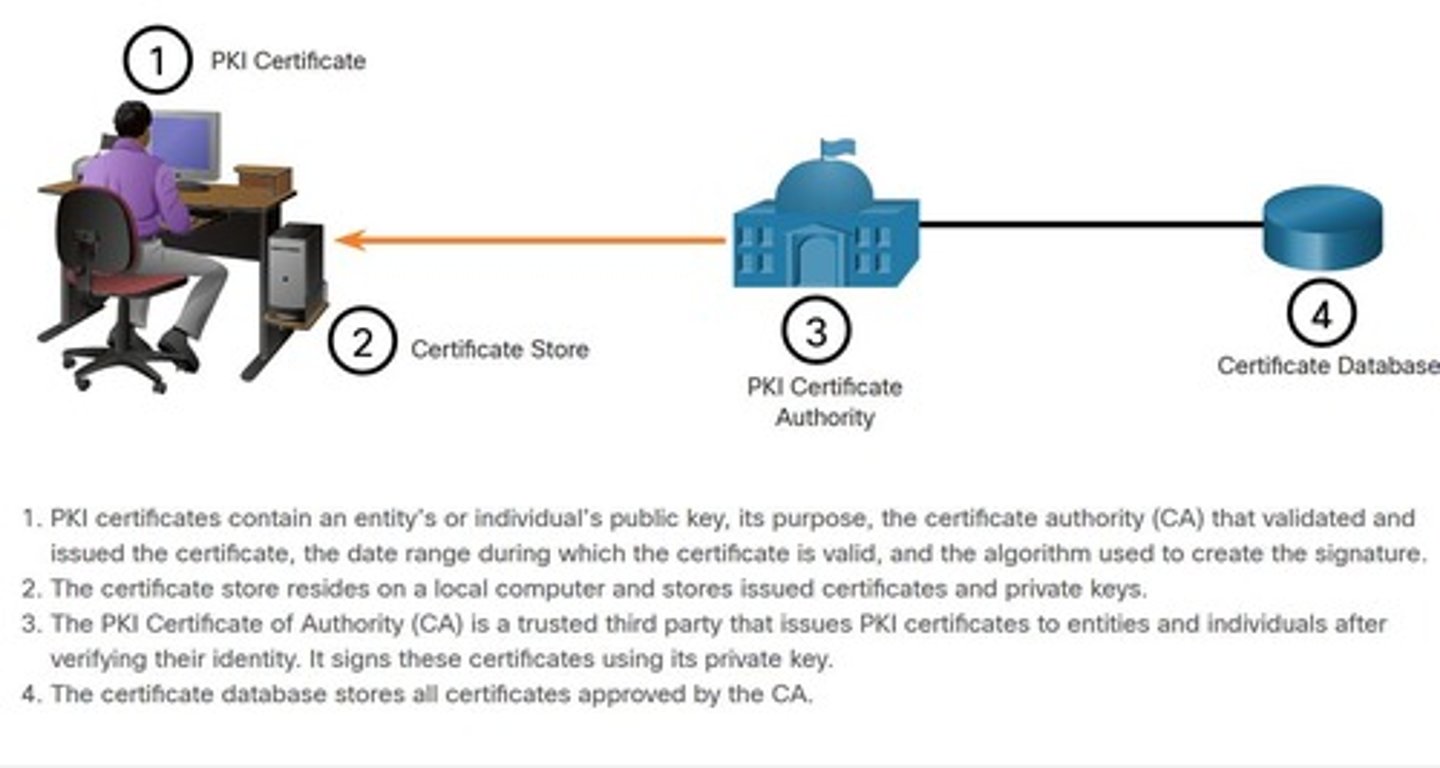
Public Key Infrastructure
System ensuring secure data exchange via keys; framework for managing digital certificates and encryption.
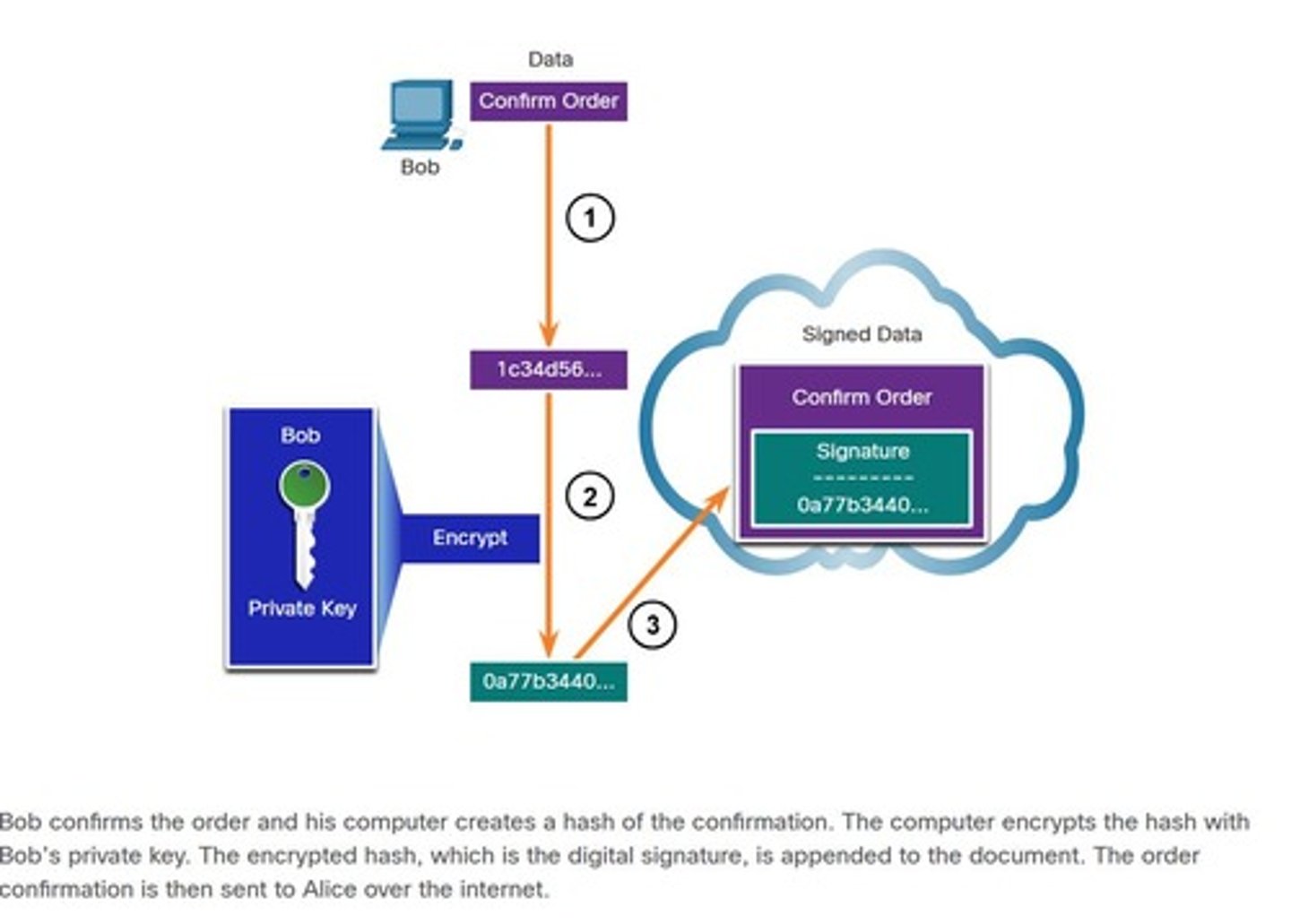
Digital Signature
Mathematical technique for authenticity and integrity; confirms authenticity of a message sender.
Authentic Signature
Proof that only the signer signed the document.
Unalterable Signature
Document cannot be changed post-signature.
Not Reusable Signature
Signature cannot transfer to another document.
Non-repudiated Document
Signed document equates to a physical signature; Prevents denial of signing a document.
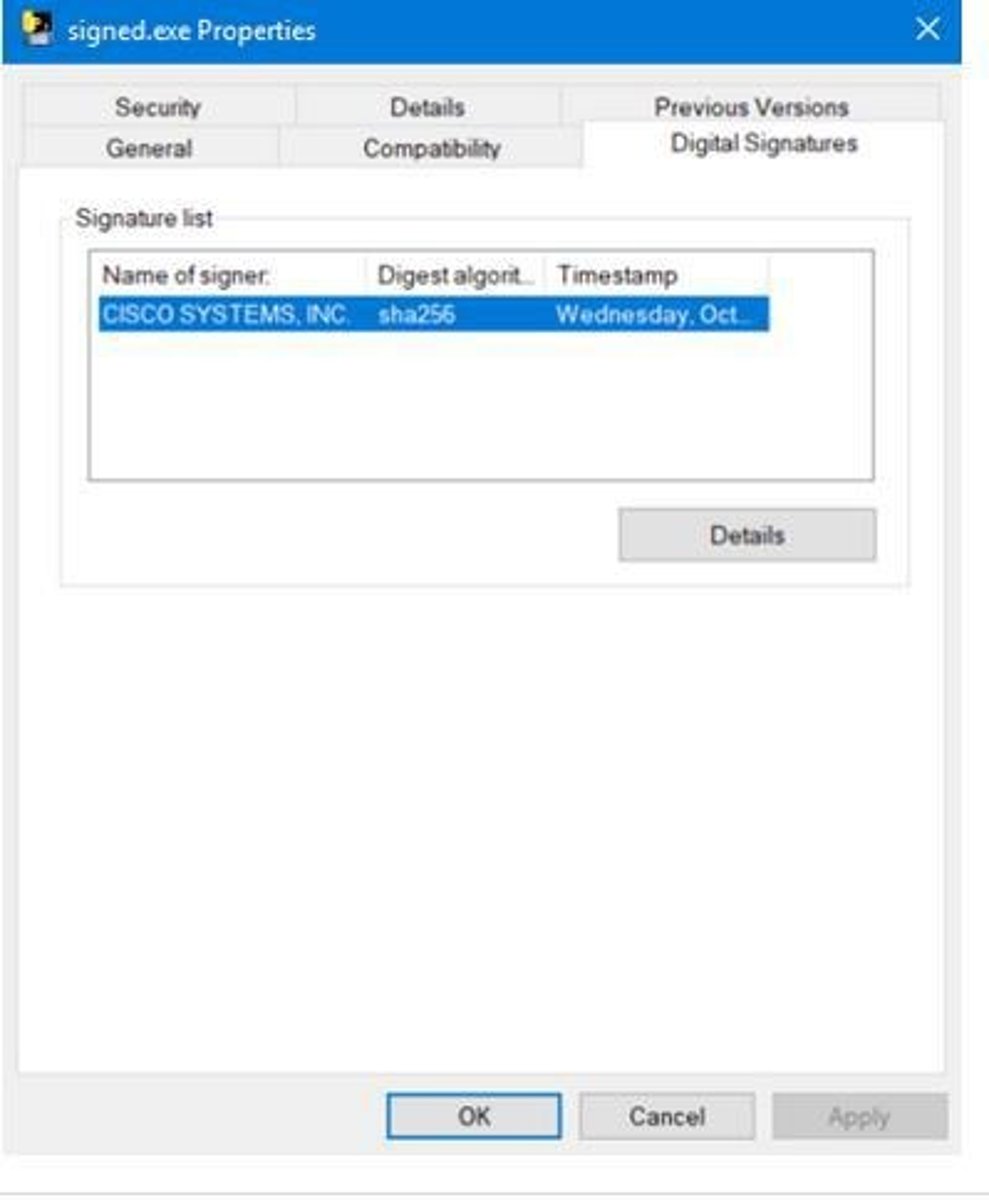
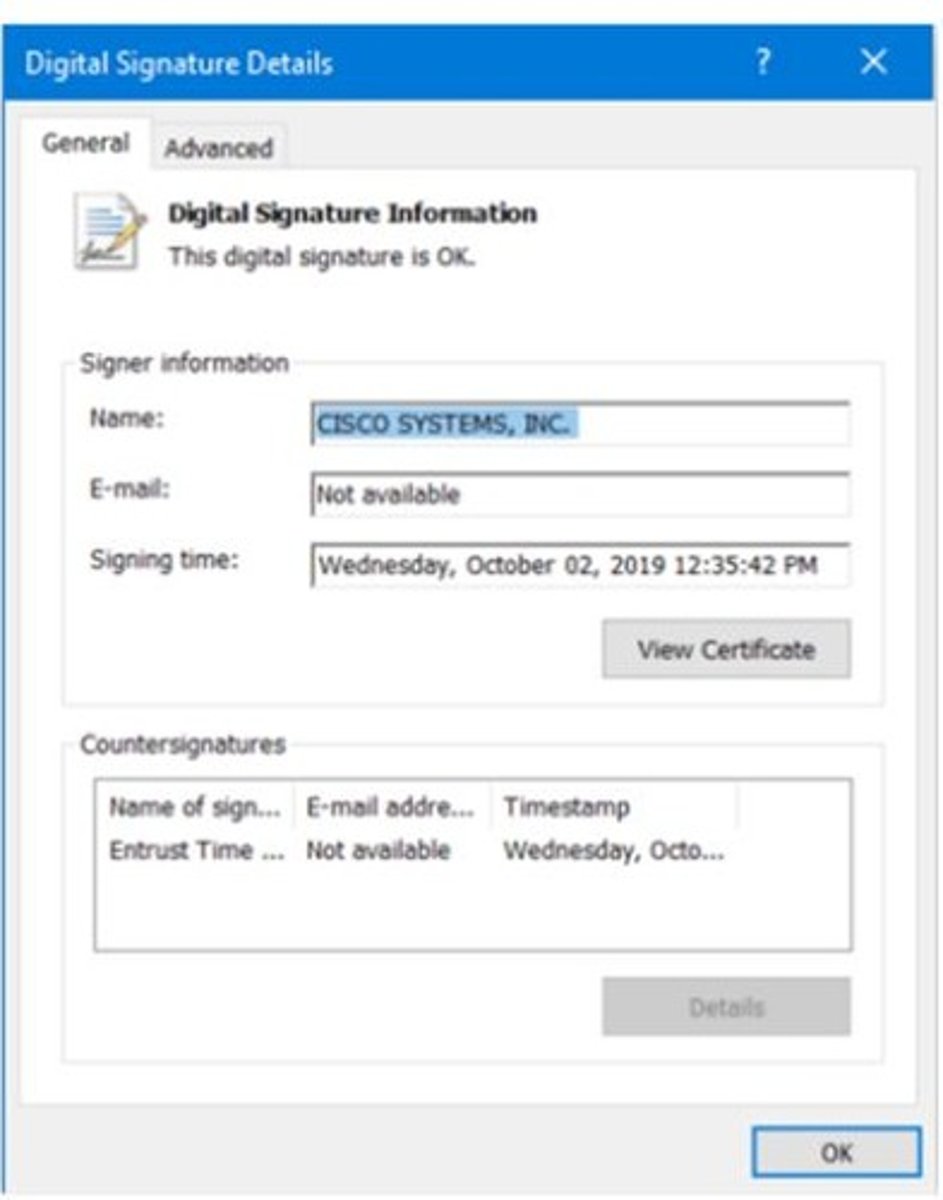
Code Signing
Verifying executable files with digital signatures; Process of digitally signing software to verify authenticity.
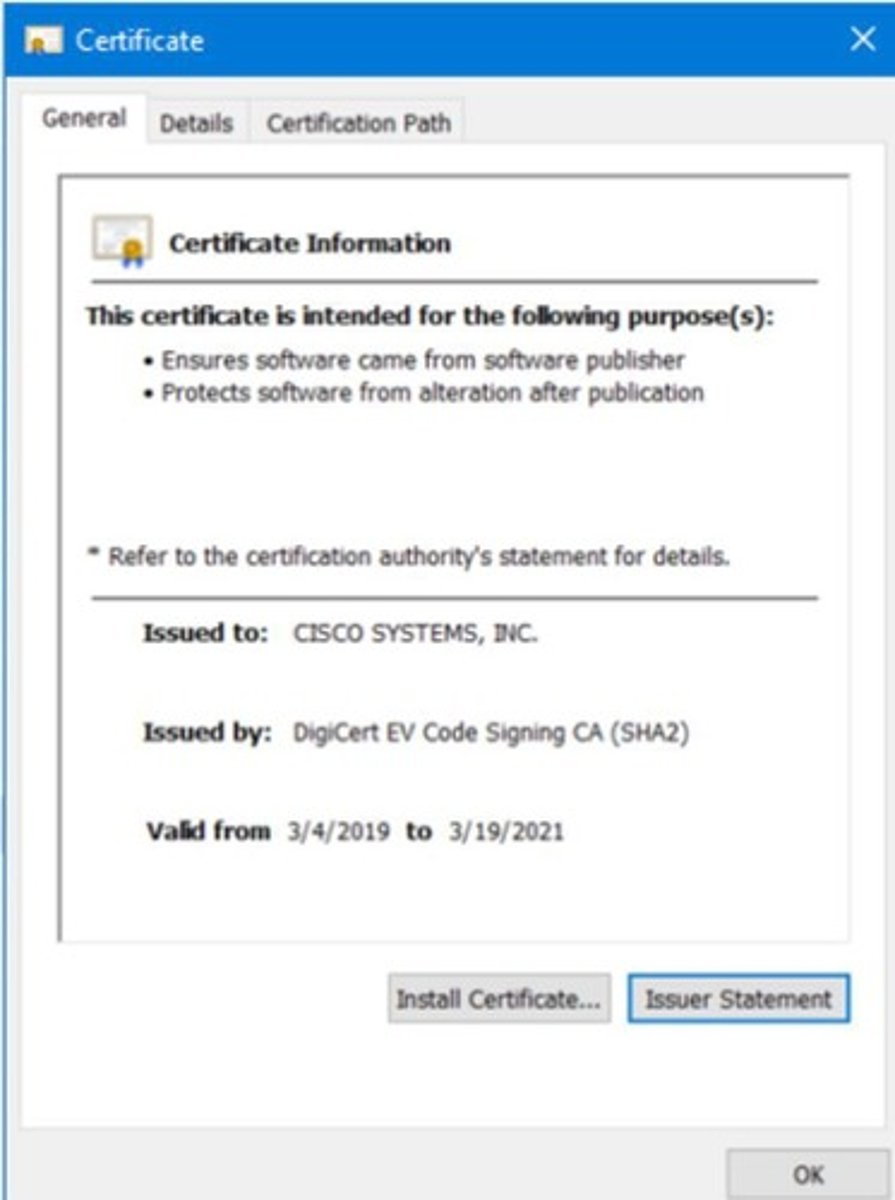
Digital Certificates
Electronic documents proving ownership of public keys.
Digital Signature Standard (DSS)
Standards for generating and verifying digital signatures.

Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA)
Original standard for public/private key pairs; Digital Signature Algorithm for secure digital signatures.
Rivest-Shamir-Adelman Algorithm (RSA)
Asymmetric algorithm for digital signatures; Rivest-Shamir-Adleman, a widely used public-key algorithm.
Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA)
Efficient digital signature algorithm with small sizes; Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm for efficient signatures.
Integrity
Assurance that data has not been altered.
Authenticity
Verification that data comes from a legitimate source.
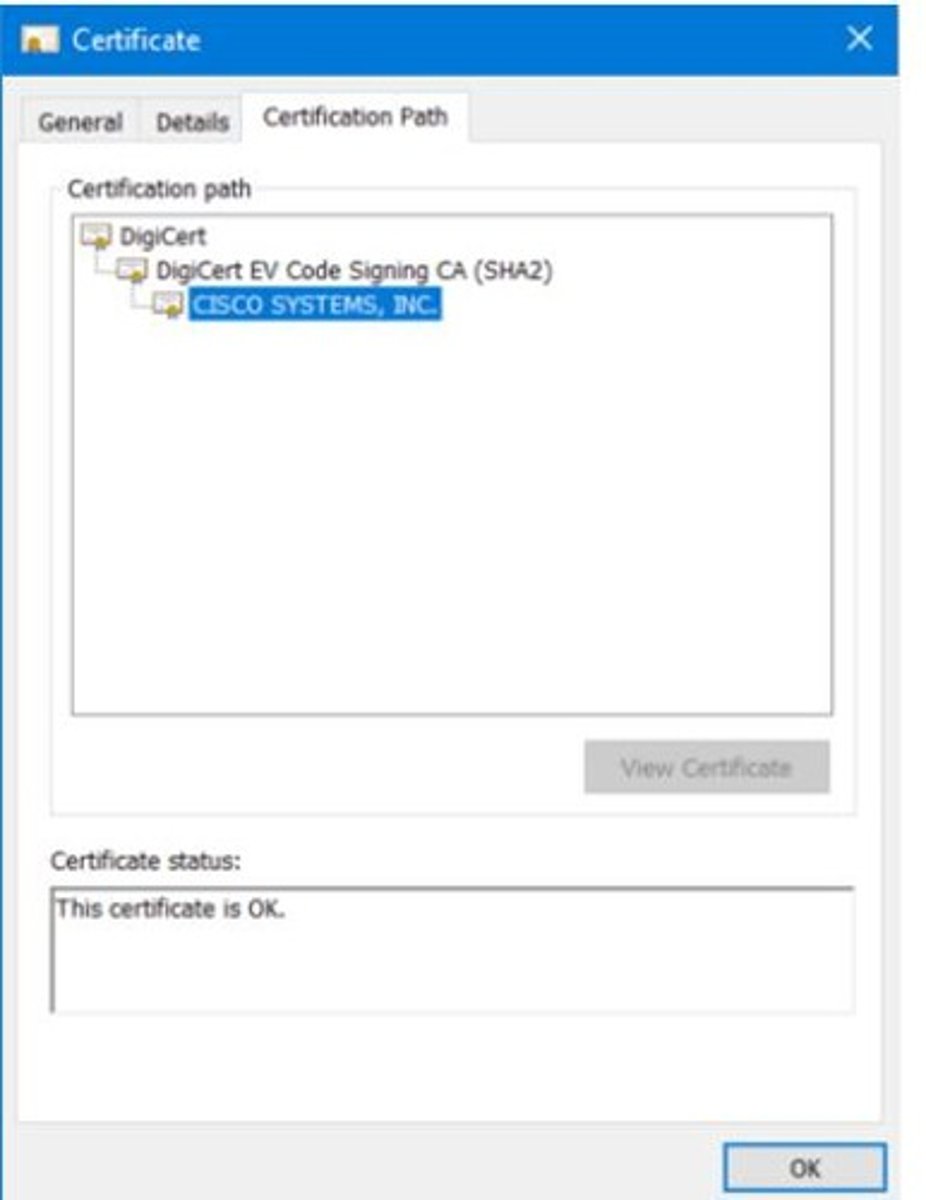
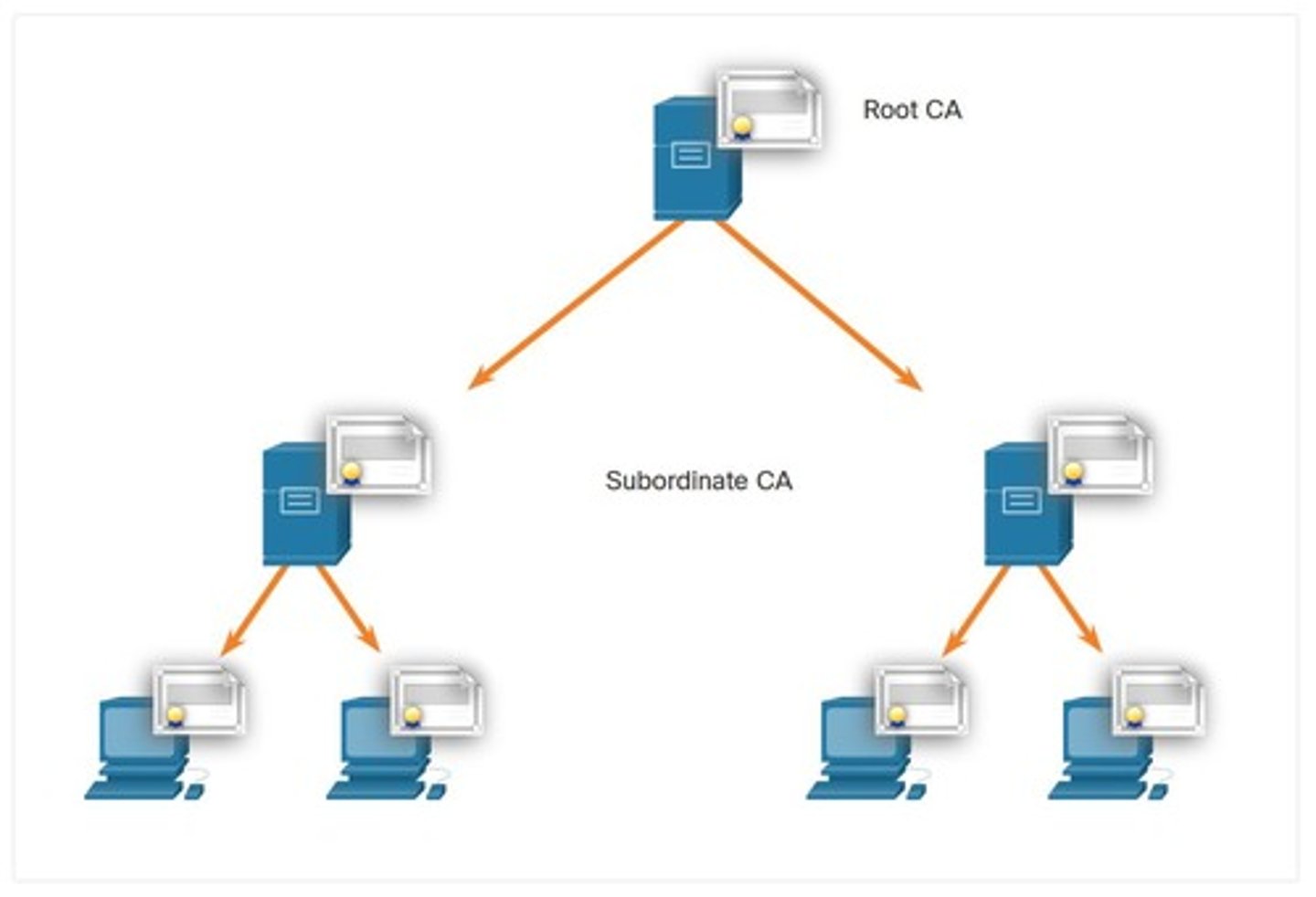
Certification Path
Chain of trust from signer to trusted authority.
DigiCert
Trusted certificate authority for digital signatures; Commercial CA providing SSL certificates.
How are digital signatures created
using various mathematical techniques
Public Key
Key used for encrypting data in PKI; Used to verify digital signatures and encrypt messages.
Private Key
Key used for decrypting data in PKI.
Digital Certificate
Authenticates and verifies user identity in communications.
Hash Value
Fixed-size output from hashing a document.
SSL Certificate
Confirms identity of a website domain.
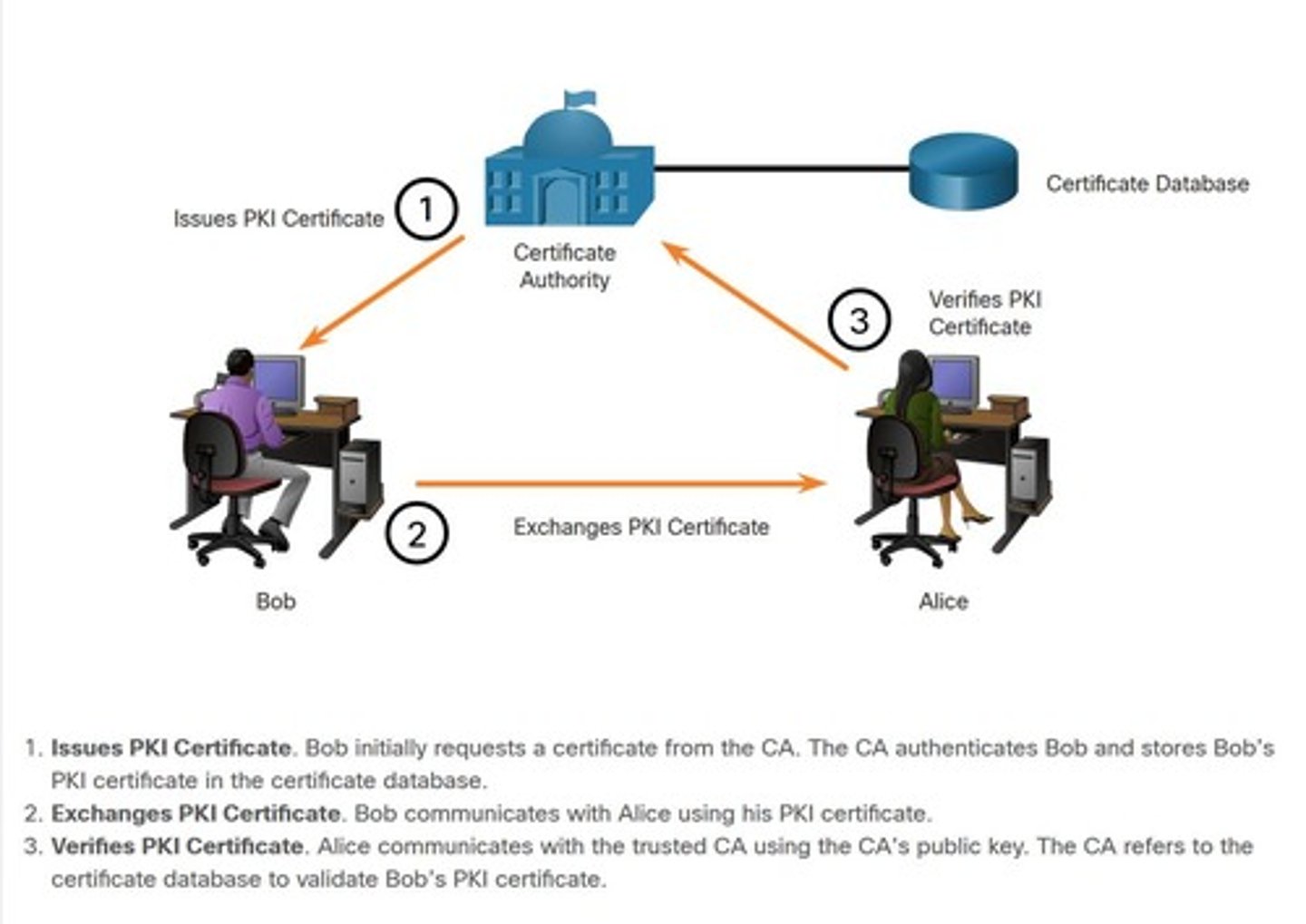
Certificate Authority (CA)
Trusted entity that issues digital certificates; Entity that issues digital certificates for identity verification.
Asymmetric Connection
Connection using a pair of public and private keys.
Credential Issuance
Process of issuing digital certificates by CAs.
Trusted Third Party
Entity that validates and issues digital credentials.
Certificate Validation
Process of confirming the authenticity of a certificate.
In-depth Investigation
CA's process to verify identity before issuing certificates.
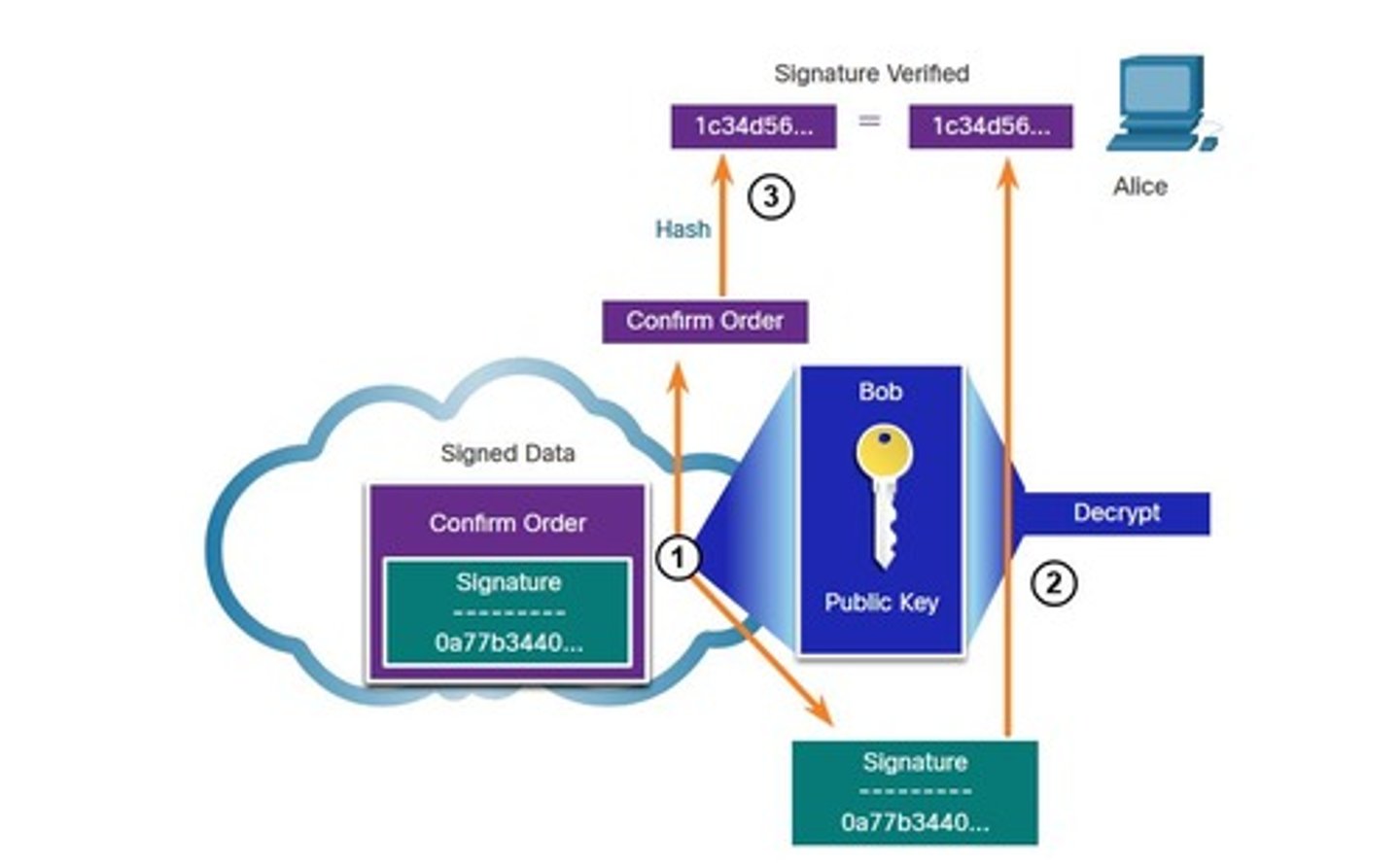
Hash Comparison
Checks if received document hash matches decrypted signature.
GlobalSign
CA providing digital certificates for various needs.
Sectigo
CA offering SSL and other digital certificates.
Public Key Management
Process of exchanging and managing public keys.
Class 0 Certificate
Testing certificate with no identity checks performed.
Class 1 Certificate
Email verification for individual users.
Class 2 Certificate
Identity proof required for organizations.
Class 3 Certificate
Used for server and software signing.
Class 4 Certificate
For online business transactions between companies.
Class 5 Certificate
Used for private organizations or government security.
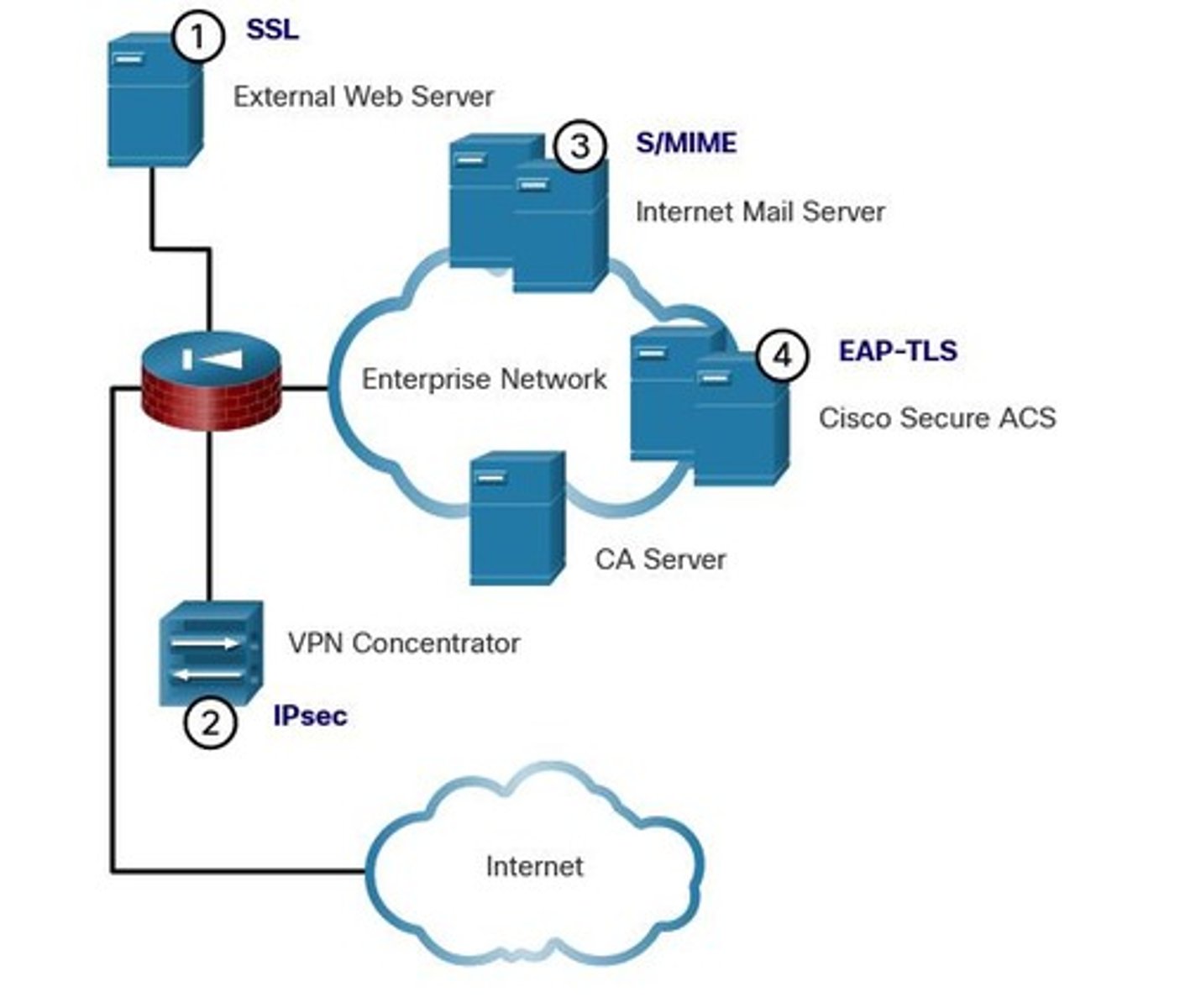
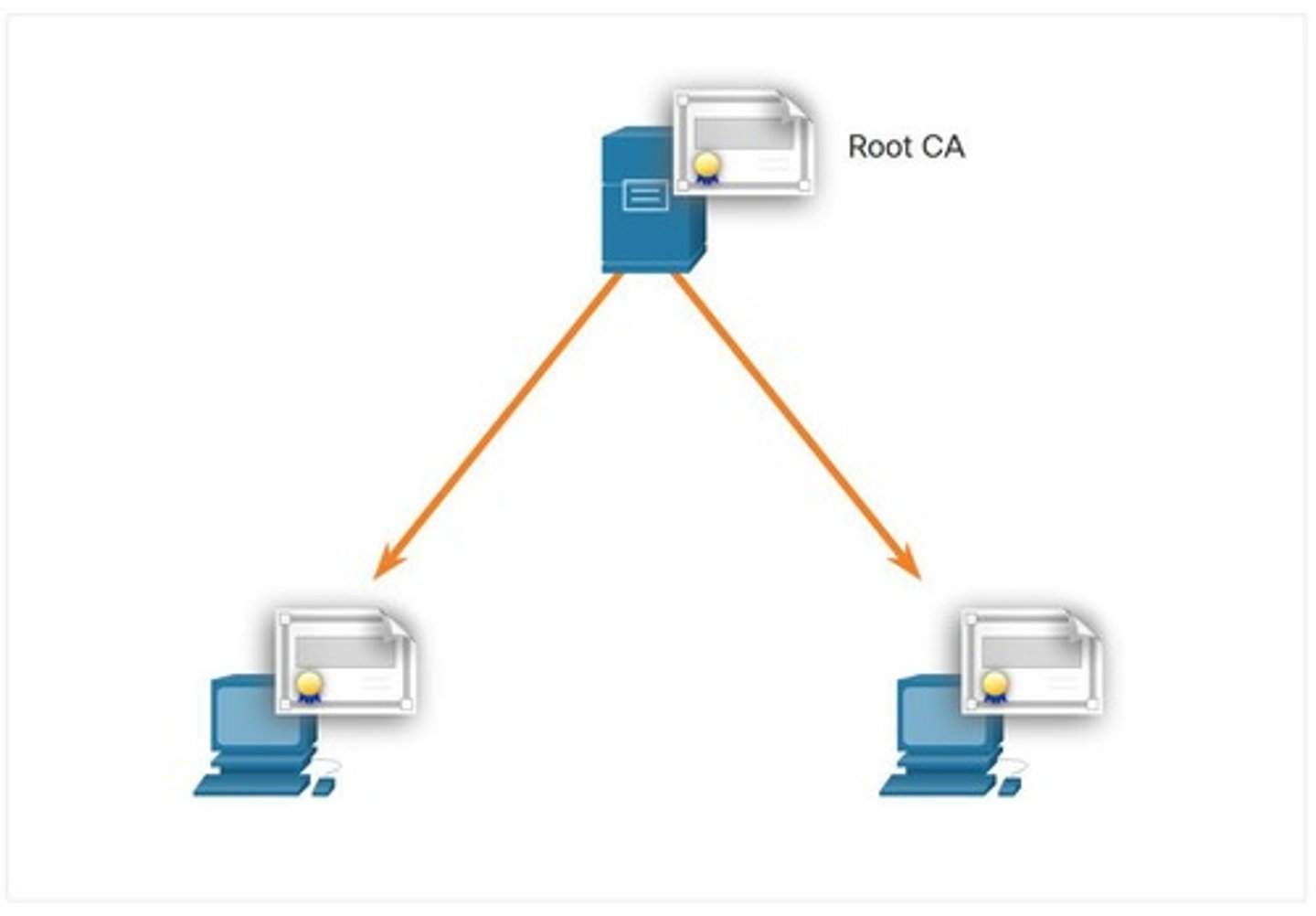
Single-root PKI Topology
Single CA issues all certificates within an organization.
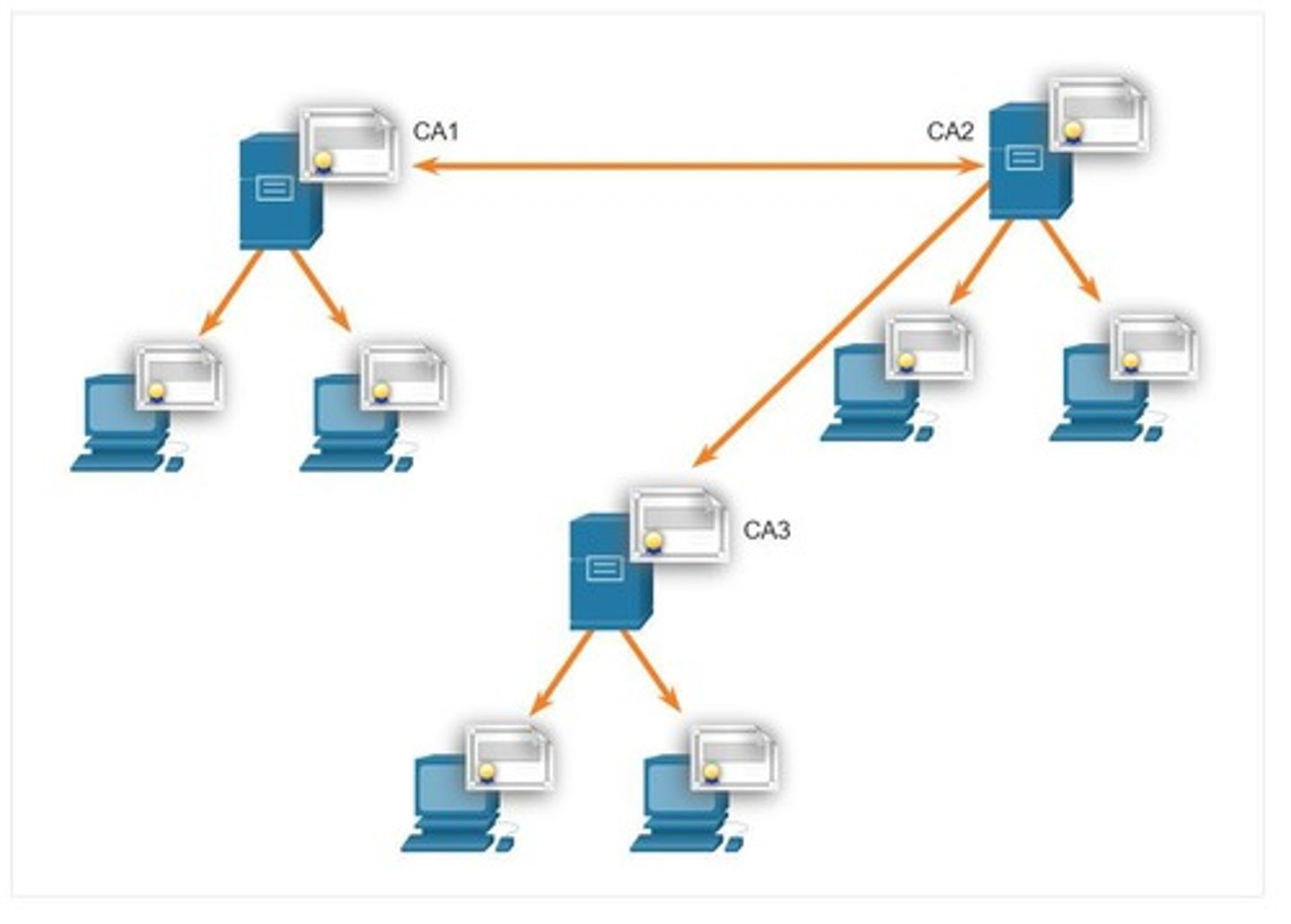
Cross-certified CA Topology
Multiple CAs linked for broader trust relationships.
Hierarchical CA Topology
Structured CA system with parent-child relationships.
Interoperability
Ability of different PKI systems to work together.
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
Protocol for accessing directory services over a network.
Self-signed Certificate
CA's public key used to verify issued certificates.
Certificate Enrollment Process
Process for a host system to register with PKI.
Certificate Revocation List (CRL)
List of certificates that have been revoked.
Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP)
Real-time protocol for checking certificate status.
Authentication
Process of verifying the identity of a user.
Certificate Exchange
Users share certificates containing their public keys.
SSL/TLS
Protocol for secure communication over a computer network.
IPsec VPNs
Secure network traffic using Internet Protocol Security.
HTTPS
Secure version of HTTP using SSL/TLS encryption.
802.1x authentication
Network access control protocol for port-based access.
S/MIME
Secure email protocol for encrypting and signing messages.
Encryption File System (EFS)
Windows feature for encrypting files on NTFS volumes.
Two-factor authentication
Security process requiring two forms of verification.
Smart cards
Physical cards used for secure authentication.
USB storage security
Protecting data on USB devices from unauthorized access.
Signature validation error
Failure to verify certificate authenticity due to issues.
Root certificate
Top-level certificate in a certificate authority hierarchy.
CRLs
Certificate Revocation Lists for invalidating certificates.
OCSP
Online Certificate Status Protocol for real-time certificate validation.