Week 1 - Cloud Computing 2025 Introduction
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a model that allows convenient, on-demand access to a shared pool of computing resources (like processors, storage, and networks) that can be quickly used and released with little effort.
💡 Think of it like renting computer power from a giant company instead of buying your own.
What does "on-demand self-service" mean?
It means you can set up and use computing resources (like virtual machines) whenever you need them, without talking to anyone.
💡 Just like buying something online — you choose, click, and get it instantly.
What is meant by "broad network access"?
Cloud services can be accessed over the internet from many different types of devices (like laptops, phones, etc.).
💡 It's like using Google Drive — you can open it on any device that’s connected to the internet.
What is "resource pooling"?
Cloud providers share and manage computing resources among many users using a multi-tenant model.
💡 Imagine a hotel where many guests share the same building and services — that’s how cloud resources are shared.
What is "rapid elasticity"?
It means computing resources can be quickly increased or decreased depending on demand.
💡 If your app suddenly gets a lot of users, the cloud will automatically give it more power.
What is "measured service"?
You only pay for what you use, just like a utility (like electricity or water).
💡 If you only use cloud storage for a few hours, you only get charged for those hours.
What motivates cloud computing?
If one computer is not enough, we buy a better server-class computer, if not still, we buy and connect many servers together (Cluster), if still not enough, we buy many clusters to get a Data Center (many clusters needs lots of power which generates heat and need massive cooling). if still not enough, data centers are distributed globally.
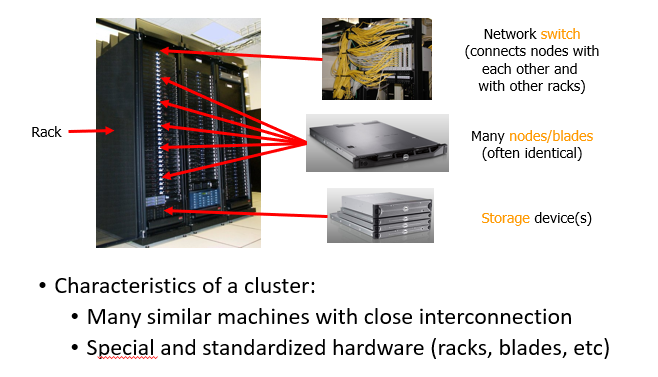
What are the main components of a cluster?
Nodes/blades (individual computers)
Network switch (connects all nodes)
Storage devices
Rack (physical structure holding everything)
What’s inside a data center?
Thousands of racks, hugh-capacity networking infrastructure, redundant and scalable power supplies, large-scale cooling infrastructure.
Why do we need to distribute the data centers globally?
Three main reasons:
Reduced Latency: It's the benefit of having cloud services close to users, so data loads faster.
Disaster Recovery: If one data center fails, others take over and keep the services running.
Regional Markets: Cloud providers can tailor services to meet the specific needs of different regions (languages, laws, user behavior).
What are the benefits of data centers for cloud computing?
4 main benefits:
Economies of scale: It’s cheaper to run one large data center than many small ones.
Statistical resource multiplexing: It means cloud providers use hardware more efficiently by sharing it among many users.
Scalability: You can instantly increase or decrease resources like servers based on your needs.
No up-front commitment: You don’t need to buy expensive equipment. You pay only for what you use.
What is utility computing?
A cloud computing model where you pay only for the services you use, like paying for electricity.
What is the Web in a cloud computing context?
The Web is the system we use to share information online. Most web services run on cloud platforms.
What is the Internet in a could computing context?
The Internet is the global network that connects devices and allows services like the Web and cloud computing to work.
The evolution of Cloud Computing has been compared to the evolution of electricity supply as a utility. Describe 3 specific problems that cloud computing solves as compared to businesses running their own data centers (Exam Revision)
Operational expenses – no need to invest in infrastructure. Businesses can apply for a subscription and pay as they use the resources.
Scalability – resources can be added on-demand. For example, virtual machines being provided as instances in AWS’s
Resource utilization – efficient sharing of resources across users. Cloud computing provides multi-tenant environments by allocation resources efficiently for different users according to their needs.
An established financial company is about to launch their new banking application. Give 3 reasons why the company should use their own data center rather than cloud computing (Exam Revision).
Data Security – more control over sensitive data.
Data Sovereignty – ensure compliance with local laws.
Optimized Performance – full control over infrastructure for high performance.