anesthetics - khan
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
which of the following are inhalation and IV anesthetics?
a. general anesthetics
b. local anesthetics
a.
what kind of inhalation anesthetic is nitrous oxide?
a. non-halogenated (gaseous)
b. halogenated (volatile)
a.
what kind of inhalation anesthetic is isoflurane, desflurane, and sevoflurane?
a. non-halogenated (gaseous)
b. halogenated (volatile)
b.
list the IV general anesthetics
propofol
dexmedetomidine
lorazepam
midazolam
ketamine
etomidate
what are the 5 desired effects of general anesthetics?
analgesia
amnesia
immobility
inhibition of autonomic reflexes
unconsciousness
list the 4 stages of general anesthesia
analgesia
excitement
surgical anesthesia
medullary depression
what stage of general anesthesia must be avoided?
a. stage I: analgesia
b. stage II: excitement
c. stage III: surgical anesthesia
d. stage IV: medullary depression
d.
the inhalation anesthestics are either ________ or ________ whose gaseous phase can be inhaled
gases or volatile liquids
how is the potency of inhalational anesthetics expressed?
in terms of the inspired concentration of the anesthetic required to produce anesthesia in half the subject
AKA the minimal alveolar concentration (MAC)
potency = _______
a. MAC/1
b. 2/MAC
c. MAC/3
d. 1/MAC
d.
based on this graphic, which agent is more potent?
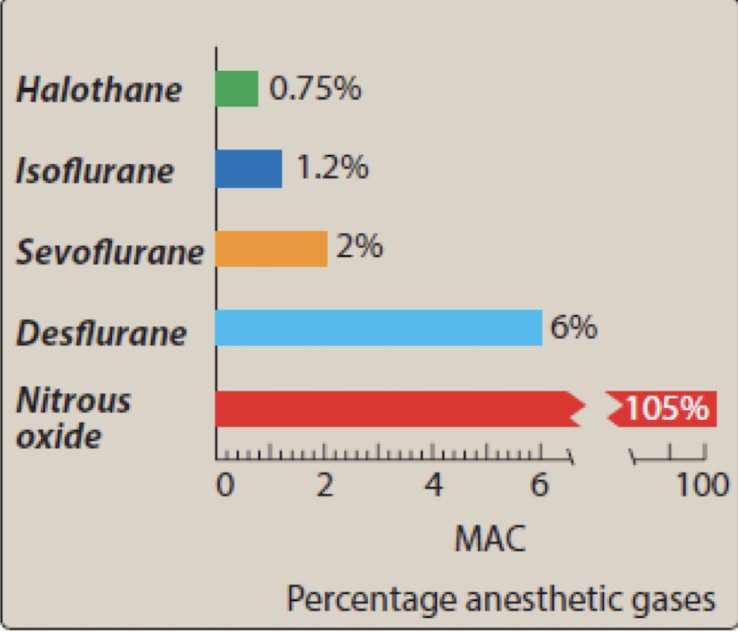
a. halothane
b. isoflurane
c. desflurane
d. nitrous oxide
a.
remember potency = 1/MAC
describe the MOA of inhalational anesthetics
potentiate inhibitory synaptic activity
enhance GABA and glycine receptors, incr. Cl- influx, activate K+ channels —> hyperpolarization
diminish excitatory synaptic activity
inhibit nACh and NMDA receptors, decr. Ca and Na influx
what is the least potent inhalational anesthetic and is also known as “laughing gas”?
nitrous oxide
what inhalational anesthetic has very rapid induction (very low gamma (blood/gas)) with greater solubility in the gas —> faster induction?
nitrous oxide
what halogenated anesthetic is a volatile liquid at room temperature with PUNGENT odor, and is typically used for maintenance? (SATA)
a. desflurane
b. sevoflurane
c. isoflurane
a. c.
what halogenated anesthetic is widely used for outpatient surgery because it has rapid onset AND recovery?
a. desflurane
b. sevoflurane
c. isoflurane
a.
what inhalational anesthetic is metabolized by CYP2E1 to release fluoride, potentially causing nephrotoxicity?
a. desflurane
b. sevoflurane
c. isoflurane
b.
what is the drug of choice for pediatric anesthetic induction?
a. desflurane
b. sevoflurane
c. isoflurane
d. nitrous oxice
b.
T/F isoflurane has a relatively fast onset and delivery
FALSE — relatively slow
what IV general anesthetic potentiates the GABAA receptor, is formulated as an emulsion (pain), and has potential for bacterial growth?
a. propofol (diprivan)
b. dexmedetomidine (precedex)
c. midazolam
d. lorazepam
a.
what are the effects of propofol (diprivan)? (SATA)
a. decr. BP
b. analgesia
c. respiratory depression
a. c.
list ADRs of propofol (diprivan)
hypotension
apnea
hypertriglyceridemia
green urine/hair/nail beds
propofol infusion syndrome (PRIS)
what IV general anesthetic is contraindicated with an allergy to egg or soy?
a. propofol (diprivan)
b. dexmedetomidine (precedex)
c. midazolam
d. lorazepam
a.
dexmedetomidine (Precedex) produces _________ and ________ by alpha2A activation
sedation and analgesia
list ADRs of dexmedetomidine (precedex)
hypotension
hypertension (higher doses)
bradycardia
what benzodiazepines are used as IV general anesthetics?
MOA?
midazolam and lorazepam
MOA: bind to allosteric site on GABA —> intensifying the inhibitory effects of endogenous GABA by increasing the frequency of chloride channel opening
what is the difference between the MOA of baributurates and benzodiazepines?
both incr. the duration of channel openings
barbiturates also can directly mimic GABA at higher doses
what is the risk associated with using benzodiazepines plus an opioid?
sedation
respiratory depression
coma
death
what is the boxed warning for midazolam?
respiratory depression/arrest
-use lower end of dosing in debilitated and geriatric population
-do NOT admin by rapid IV in neonates
ketamine is a ________
NMDA receptor antagonist
T/F the S isomer of ketamine is used because it’s more potent
FALSE — racemic mixture is used, but S isomer is more potent
what can reduce the incidence of emergence reactions (vivid dreams, hallucinations, delirium) with ketamine?
benzodiazepines
list ADRs of ketamine
emergence reactions
vivid dreams
hallucinations
delirium
incr. HR
incr. BP
incr. CO
what drug causes hypnosis but no analgesic effect and is ultra short-acting?
etomidate
list ADRs of etomidate
n/v
inhibits cortisol production
-monitor hypotension, hyperkalemia
T/F local anesthetics abolish pain sensation in a limited area of the body WITHOUT producing unconsciousness
TRUE
what would you use for topical burns and small cuts, as an injection during dental procdure, or epidural blocks during obstetric procedures/surgery?
a. inhalation anesthetics
b. IV general anesthetics
c. local anesthetics
c.
T/F local anesthetics are specific for pain fibers
FALSE - NOT specific; can block other fibers and APs
how do local anesthetics work?
do you need a low concentration or high concentration for it to work?
prevent impulse transmission by blocking individual sodium channel sin neuronal membranes
high concentration
most local anesthetic agents consist of a __________ connected to an _________ by an aliphatic chain via ________
lipophilic group connected to an ionizable group (tertiary amine) via ester/amide
explain how local anesthetics work as uncharged vs cations
cation: most active at receptor
uncharged: rapid penetration of membranes
list the ester local anesthetics
tetracaine
procaine
benzocaine
list the amide local anesthetics
lidocaine
mevipacaine
bupivacaine
levobupivacaine
ropivacaine
prilocaine
which has a shorter duration of action?
a. ester local anesthetics
b. amide local anesthetics
a.
idk if we need to know structures at all
which of these is procaine (hint: it’s an ester series)?
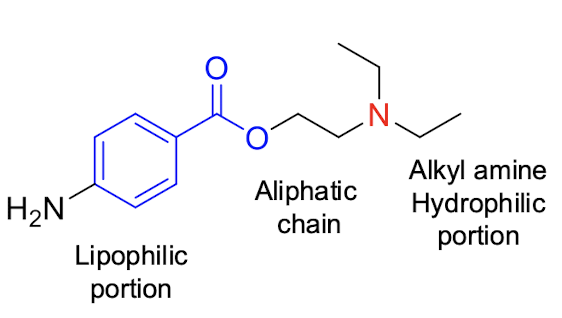
a.
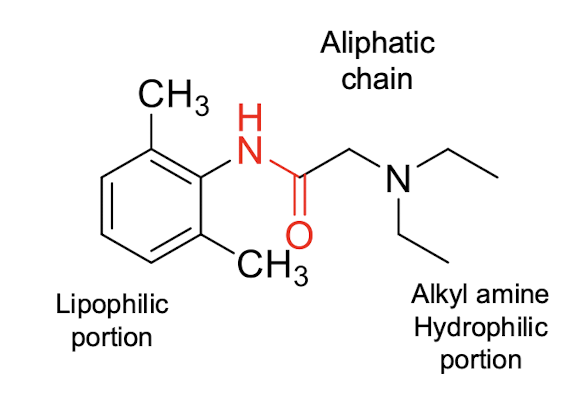
idk if we need to know structures at all
which of these is lidocaine (hint: it’s an amide series)?


b.
what group is essential for local anesthetic activity because it is important for binding to the receptors?
a. aromatic ring or dimethyl phenyl group
b. di-ortho substitution
c. aliphatic chain
d. tertiary alkyl amine
a.
_______ provides enhanced protection from amide hydrolysis in amide local anesthetics, resulting in longer duration of action?
a. aromatic ring or dimethyl phenyl group
b. di-ortho substitution
c. aliphatic chain
d. tertiary alkyl amine
b.
local anesthetics
_______ connects lipophilic portion and hydrophilic portion and is usually 1-3 carbons in length
a. aromatic ring or dimethyl phenyl group
b. di-ortho substitution
c. aliphatic chain
d. tertiary alkyl amine
c.
________ are more resistant to metabolic inactivation
________ are more susceptible to ester hydrolysis
amide local anesthetics are more resistant to metabolic inactivation
ester local anesthetics are more susceptible to ester hydrolysis
most local anesthetics have a _________ that helps in enhancing water solubility and interacts with receptor binding site when protonated
a. aromatic ring or dimethyl phenyl group
b. di-ortho substitution
c. aliphatic chain
d. tertiary alkyl amine
d.
local anesthetics show better absorption in _________ areas following multiple administrations
a. poorly perfused areas
b. highly perfused areas
b.
what is seen in the epinephrine-local anesthetic combinations?
increases the conc. and duration of action of LA at the site of injection
reduces systemic absorption of LA
reduces potentials for systemic toxicity
what are the downsides of using vasoconstrictors (epinephrine) with local anesthetics?
do NOT use in extremities —> limited circulation
can lead to hypoxia and damage
sequestration of LAs occurs in _______
fatty tissue
ester type LAs are hydrolyzed very rapidly in the blood by ________
a. butyryl cholinesterase
b. cytochrome P450
a.
amide type LAs are hydrolyzed by liver microsomal __________ so toxicity is more likely to occur in pts with liver disease
a. butyryl cholinesterase
b. cytochrome P450
b.
what is the MOA of local anesthetics?
block voltage-gated sodium channels
prevent depolarization and AP
what is the choice of local anesthetic for a specific procedure based on?
how can we prolong the duration of action for a short/intermediate acting agent?
based on duration of action
prolong by increasing dose or administering with a vasoconstrictor
what CV toxicities can be caused by local anesthetics?
severe hypotension
block cardiac Ca channels
prilocaine in high doses causes ________ as a result from _______
how do we fix it?
causes methemoglobinemia (cyanotic and chocolate-colored blood) as a result from formation of a metabolite (oxidizing agent)
IV admin of reducing agents converts it back to Hb
ester type drugs are metabolized to ________ derivatives which are responsible for _______
PABA —> allergic reactions
what drug exists in unionized form under most physiological conditions because it lacks a tertiary amine and has a short duration of action?
benzocaine
what local anesthetic has ADRs of drowsiness and seizure?
lidocaine
what drug has a higher lipid solubility and decreased hepatic degradation than lidocaine?
which enantiomer is responsible for cardiotoxicity?
bupivacaine
R enantiomer —> ventricular arrhythmia
which has a lower cardiotoxicity:
a. bupivacaine
b. levobupivacaine
b.