chem test that I'm cooked for (pls pray for me)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Group
a column on the periodic table
Period
a row on the period table
What is carbon’s group
14 or 4A
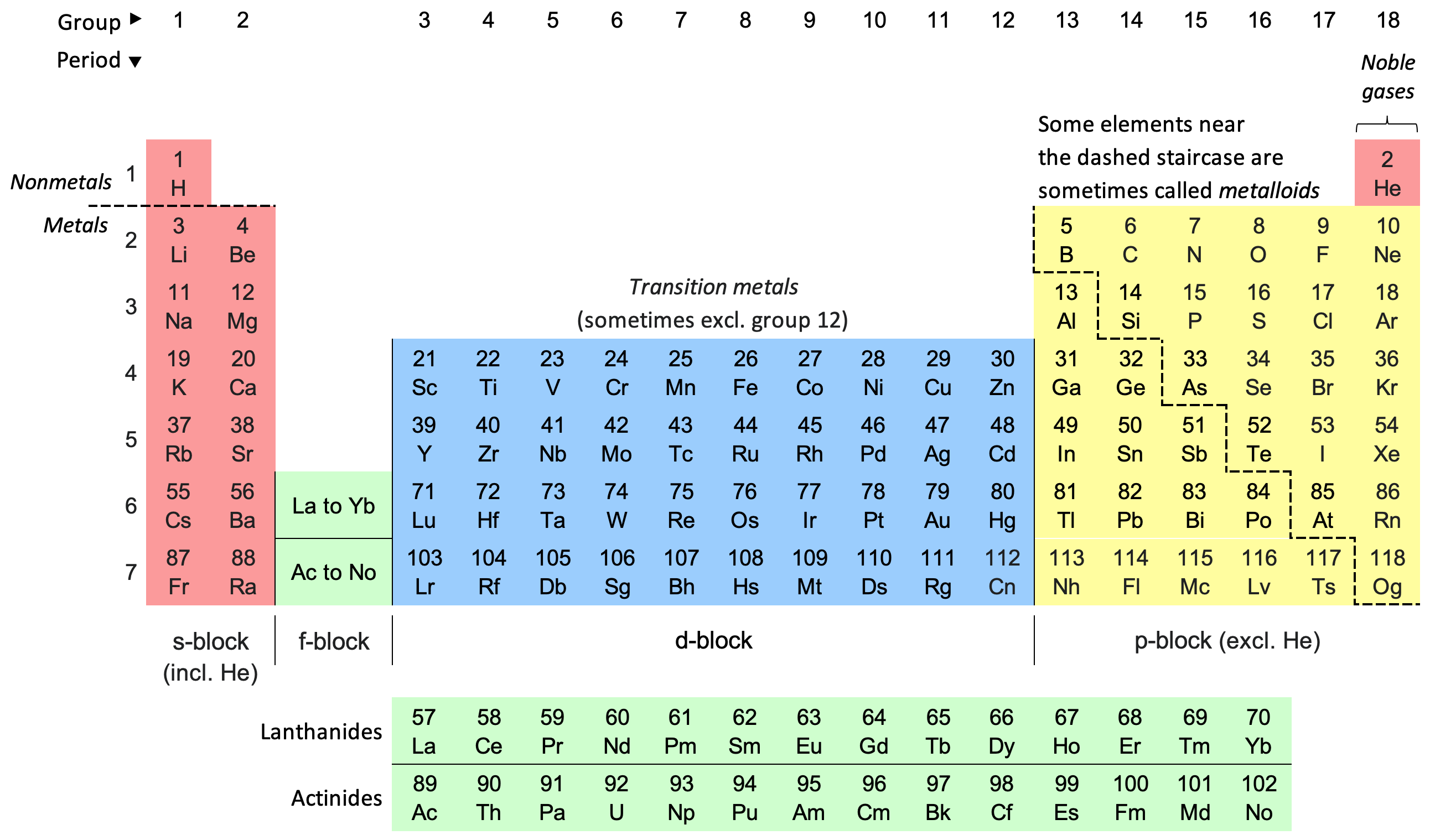
What is carbon’s period
2
Group 1, with the exception of hydrogen, are all…
alkali metals
Group 2 are all
alkaline earth metals
Group 17 are all
halogens
Group 18 is all
noble gases
Everything to the left of the staircase, with the exception of hydrogen, is a….
metal
Everything to the right of the staircase is a…
nonmetal
The “f” block consists of
inner transition metals
The “d” blockconsists of
transition metals
The metalloids are
bordering the staircase (B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, Po, At)
Mendeleev organized his periodic table by
increasing atomic mass
Mosely organized his periodic table by
increasing atomic number
Qualities of alkali metals
VERY reactive
Qualities of alkaline earth metals
highly reactive
Qualities of halogens
VERY reactive
Qualities of noble gases
not reactive
How does effective nuclear charge change across a period and down a group
increases in a period, decreases down a group
How does shielding change across a period and down a group
Does not change across a period, increases down a group
How does atomic radius change across a period and down a group?
Decreases across a period, increases down a group
How does electronegativity change across a period and down a group
Increases across a period, decreases down a group
How do the sizes of cations differ from the atoms they form from?
They are smaller than their parent because they have less electrons, so they are more drawn towards the nucleus.
How do the sizes of anions differ from the atoms they form from?
They are larger than their parent because they have more electrons, so they have a stronger repulsion which moves them further from the nucleus.