Ch. 9 & Ch. 13 - Nucleic Acids & Nucleic Acid Biotech Techniques
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
pyrimidines
compounds that contain a 6-membered ring
C, U, T
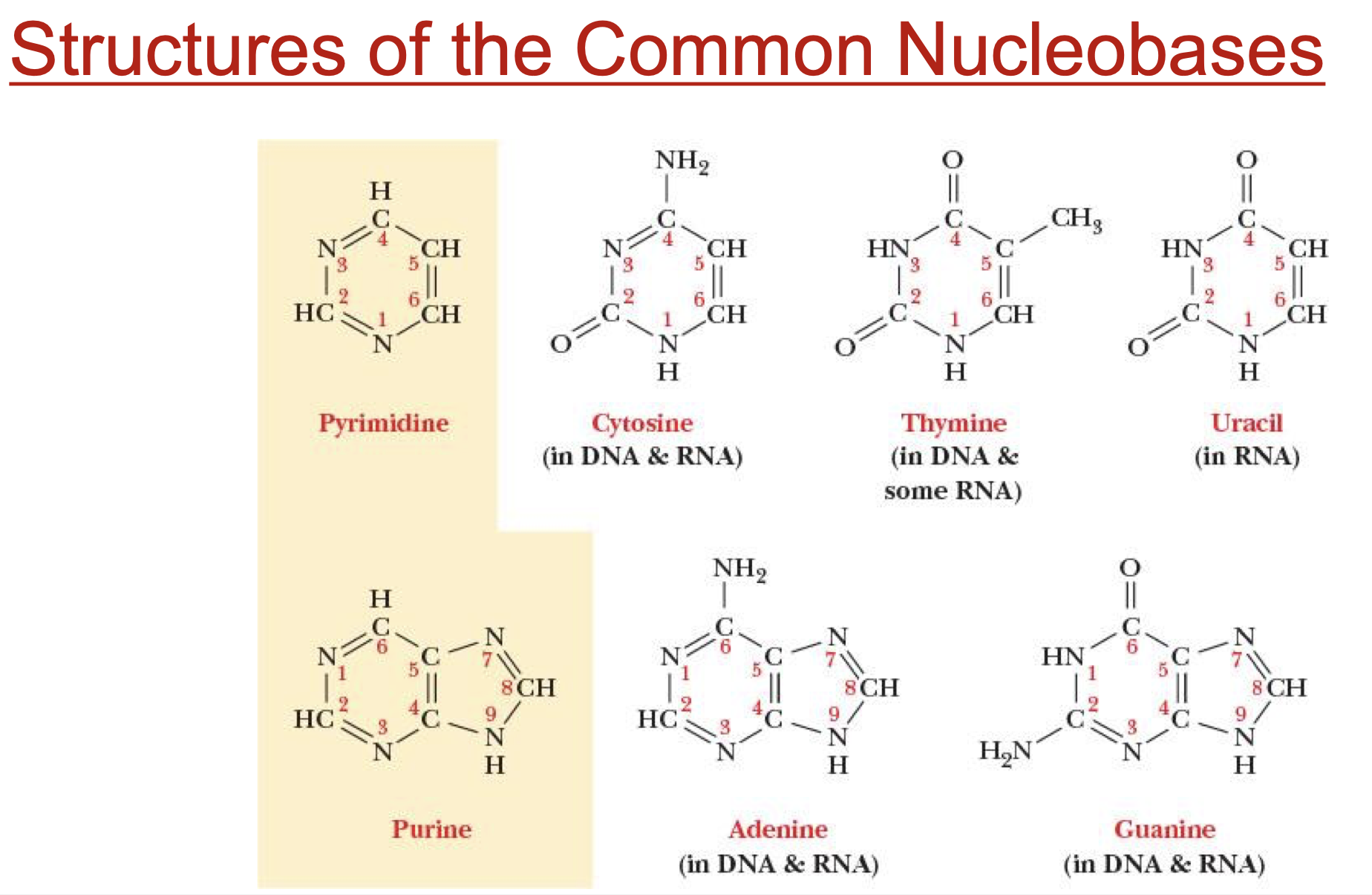
purines
compounds that contain a 6-membered ring connected to 5-membered ring
A, G
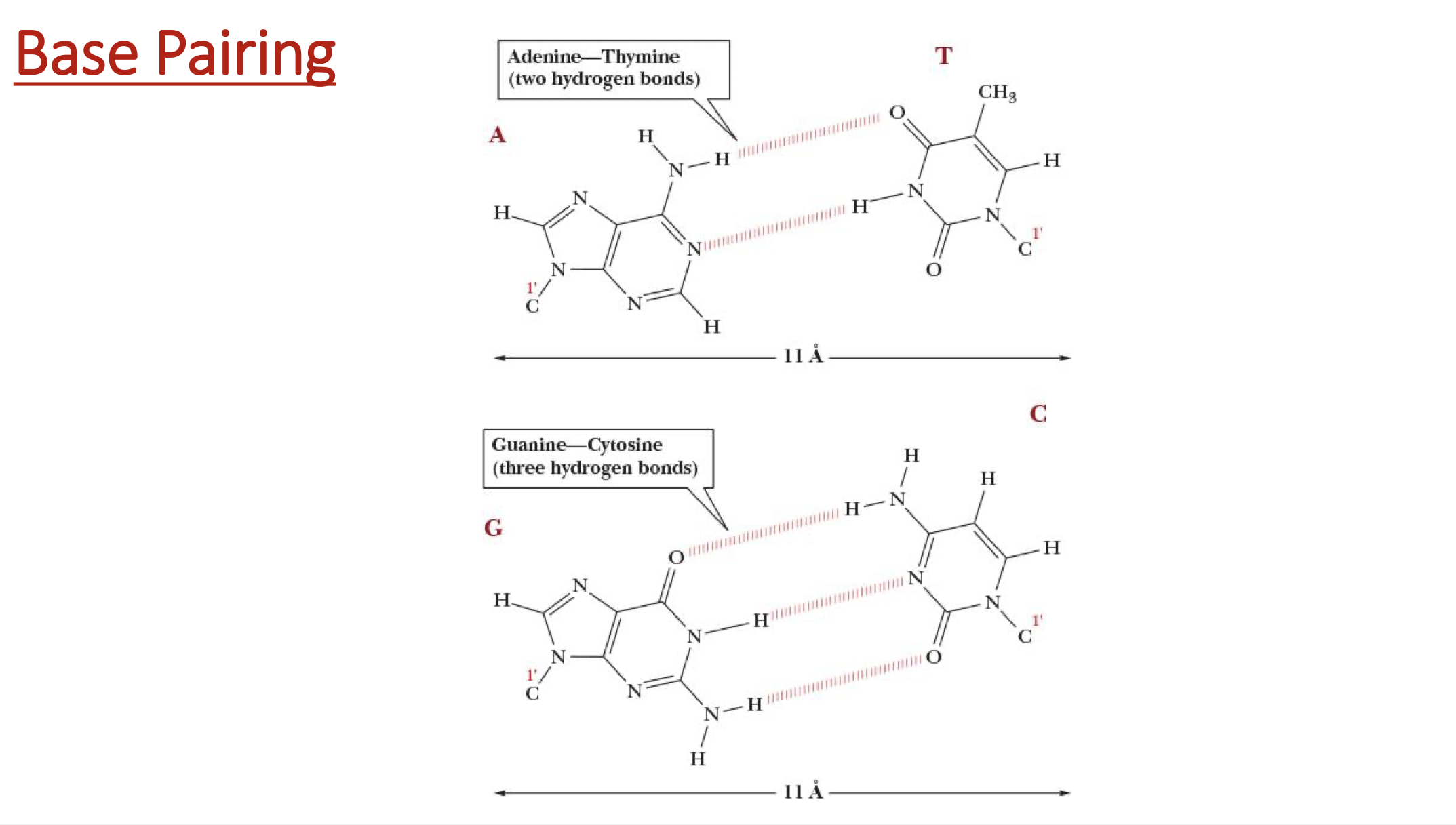
when does DNA denature and renature?
Is C + G stronger than A + T?
yes, 3 H-bonds vs. 2
circular DNA
double-stranded DNA where 5’
negative supercoils
circular DNA w/ fewer than normal # of turns of the helix
positive supercoils
circular DNA w/ more than normal # of turns of the helix
topoisomerases
enzymes that relax supercoiling in closed circular DNA
2 types:
Class I – cut the phosphodiester backbone of 1 strand, pass the other end through, & reseal
Class II -
DNA gyrase
Chromatin
complex of DNA & protein found in eukaryotic nuclei
Histones
basic proteins complexed to eukaryotic DNA
5 main types:
H1, H2A, H2B, H3, H4
rich in basic a.a residues: K & R
nucleosome (individual beads of the chromatin)
globular structure in which DNA is wrapped around an aggregate of histone molecules
each core has 8 histones: H2A, H2B, H3, & H4 (2 of each)
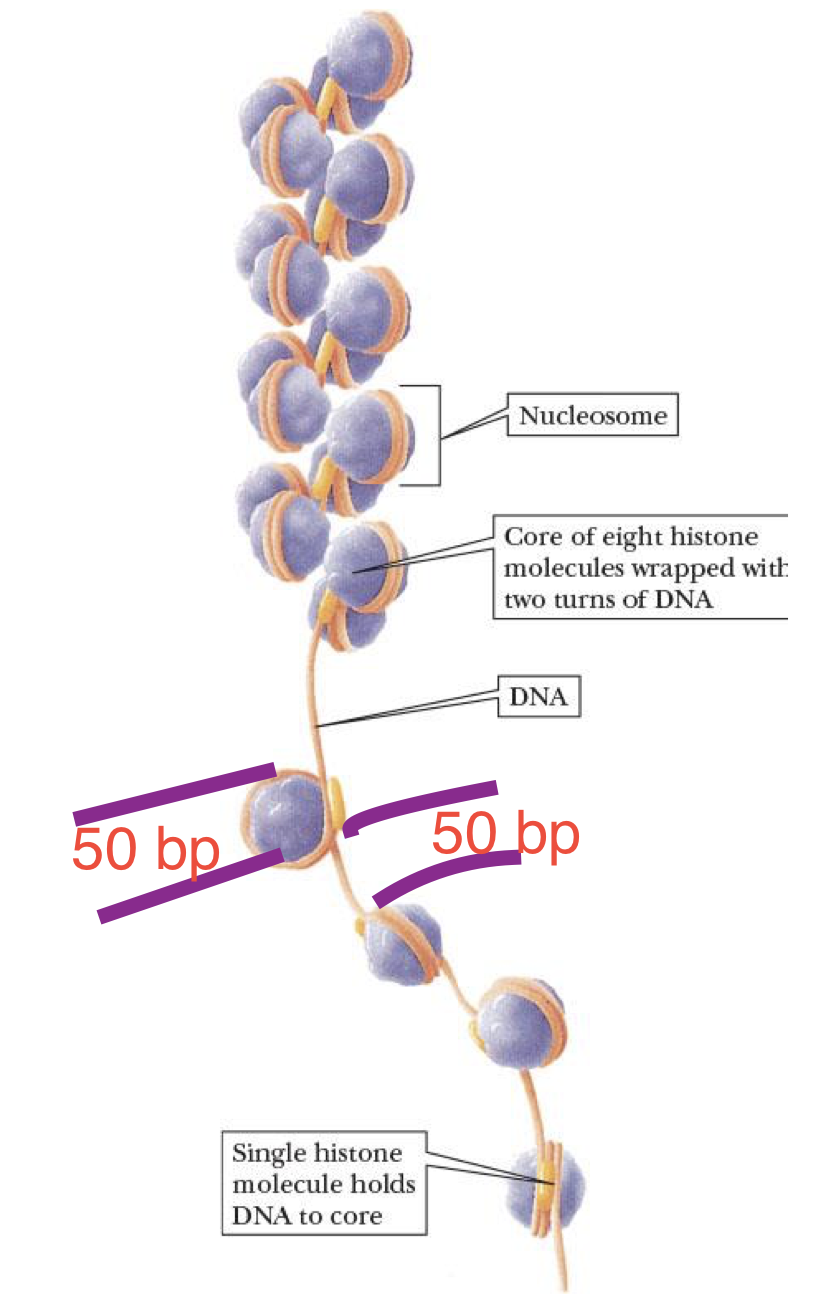
spacer regions
string portions of chromatin w/o nucleosome
hyperchromicity
melting
heat denaturation of DNA
TM
melting temperature
midpoint of melting curve
TM ⬆ when C–G % is higher
TM ⬆ when pH ⬇ & vice versa
TM ⬆ when DNA strand
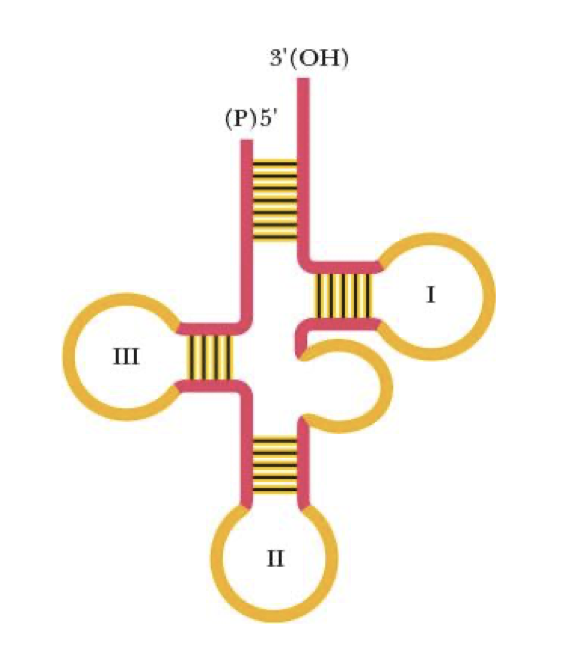
t(transfer)RNA
single stranded polynucleotide chain btw 73 & 94 nucleotides long
carries a.a at 3’ end
intrachain H-bonding
r(ribosomal)RNA
2 subunits (1 larger than the other)
m(messenger)RNA
initially larger precursor molecule–heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA)
carries coded genetic info from DNA → ribosomes
small amount in cells & short lived
copies info from top strand of DNA (5’–3’)
sn(small nuclear)RNA
100–200 nucleotides long
in nucleus of eukaryotic cells
snRNPs (type of snRNA)
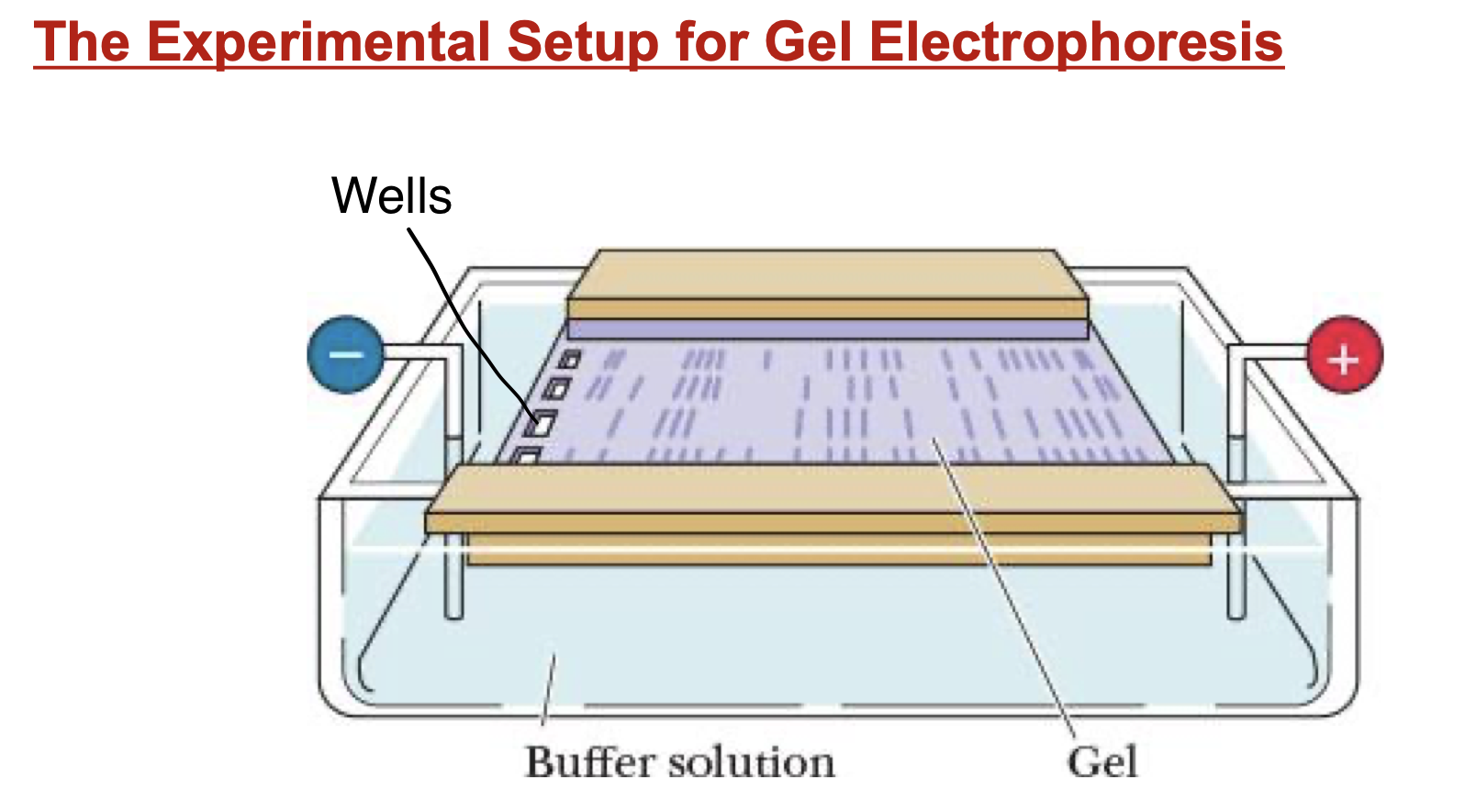
Gel Electrophoresis
separate molecules based on charge:size ratio
DNA already –
electric current applied
agarose
autoradiography
locating radioactively labelled substances by exposing them to photographic film
fluorescence
sensitive method for detection & ID of substances that absorb & re-emit light
ethidium bromide (EtBr)
slips btw DNA bases
strong carcinogen
SyBr Green & SyBr Gold newer options
nucleases
enzymes that hydrolyze nucleic acids
exonuclease
cleaves from ends of molecule
endonuclease
cleaves in middle of chain
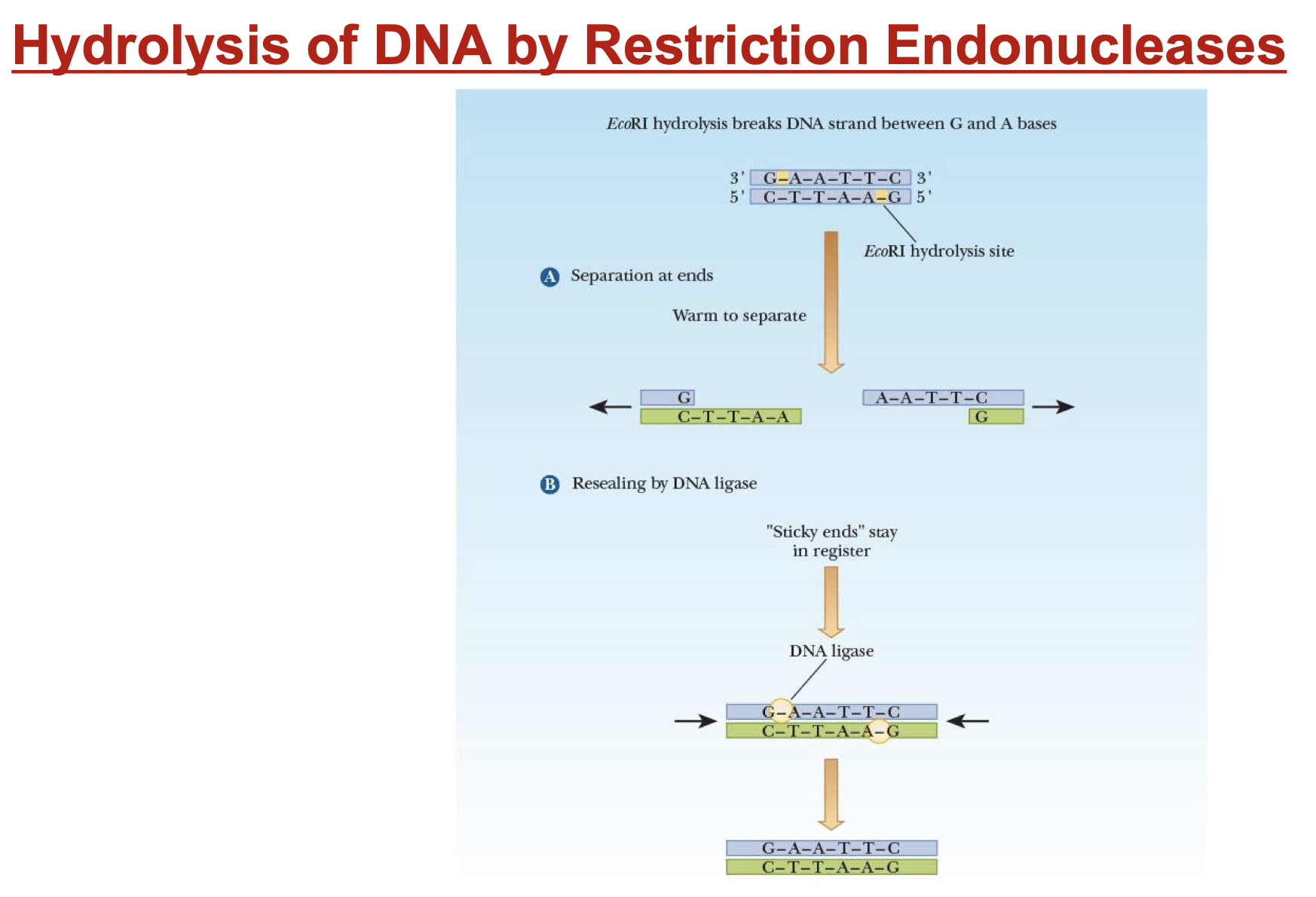
restriction endonucleases
enzymes that hydrolyze double-stranded DNA at specific spots on opp. strands
recognizes only specific palindromes
palindrome
msg that reads the same backward or forward
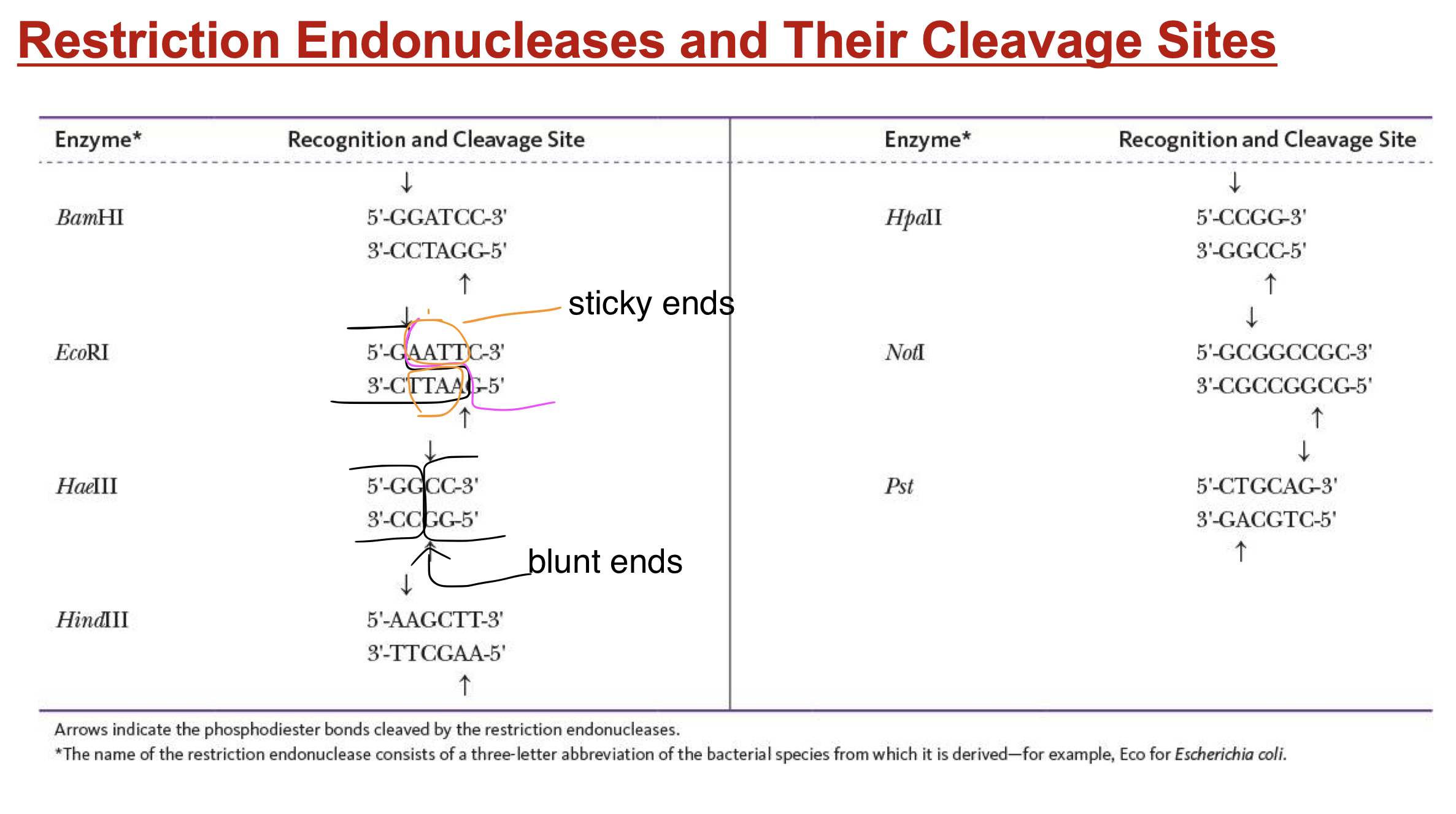
sticky ends
short, single-stranded stretches at ends of double-stranded DNA
can join by H-bond btw complementary bases
provides site where other DNA w/ sticky ends can be linked
DNA ligases
enzyme that join DNA strands tgt through phosphodiester bond formation
4 cutters, 6, cutters, 8 cutters
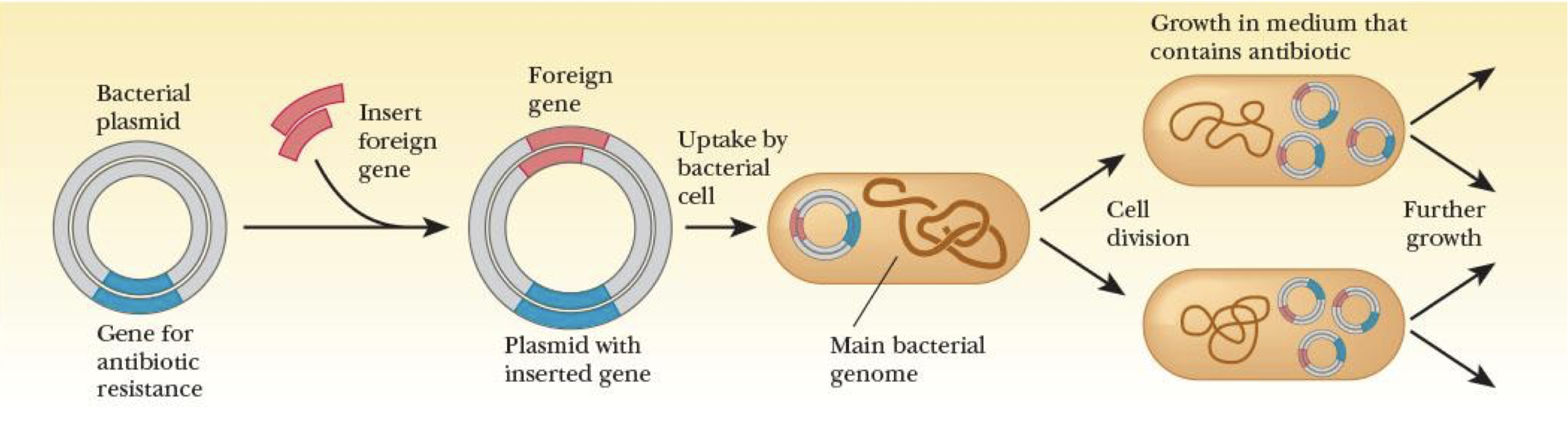
plasmids
DNA molecules that contain genes for antibiotic resistance & are used in cloning
selection process
allows bacteria that have been transformed to be identified & isolated
plasmid has selectable marker for ID
ampicillin (Ampr) & tetracycline (Tetr)
antibiotics
Ori
origin of replication—DNA sequence that tells bacteria to replicate
multiple cloning sites (MCS)
region of bacterial plasmid that has short stretch of DNA w/ many restriction sites
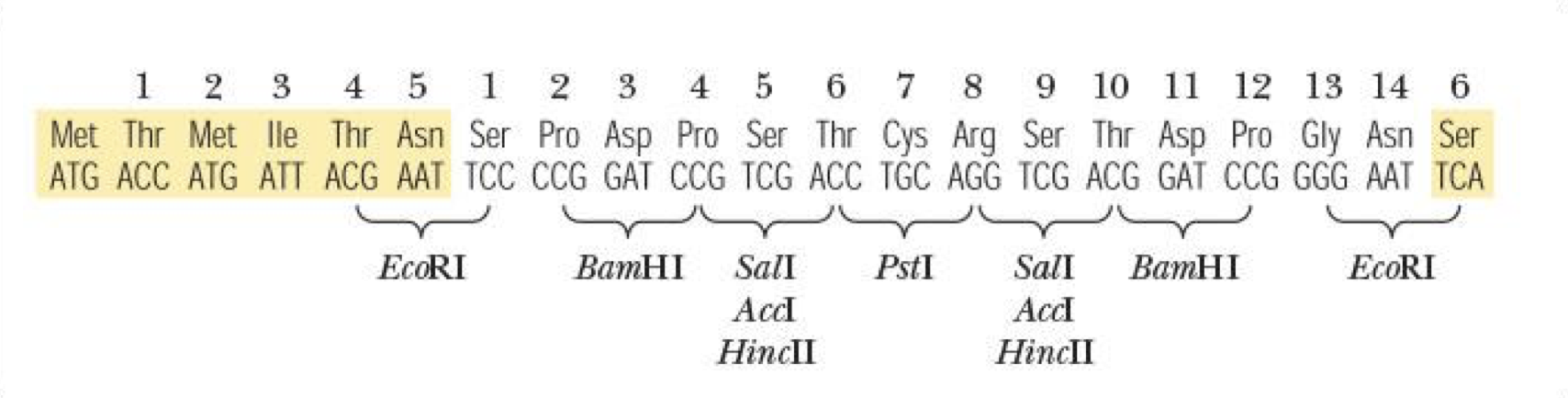
why having 2 restriction enzymes is beneficial (2 different sticky ends)
will not self-ligate bc not complementary
insert will only go in 1 direction (guarantees directionality)
gene therapy
cells of specific tissues altered to alleviate symptoms of a disease
production of recombinant human insulin
insert DNA encoding A chain & B chain into separate plasmid expression vectors
transform E. coli w/ vectors & clone separately
add induce to start protein synthesis
purify & mix A and B chains tgt
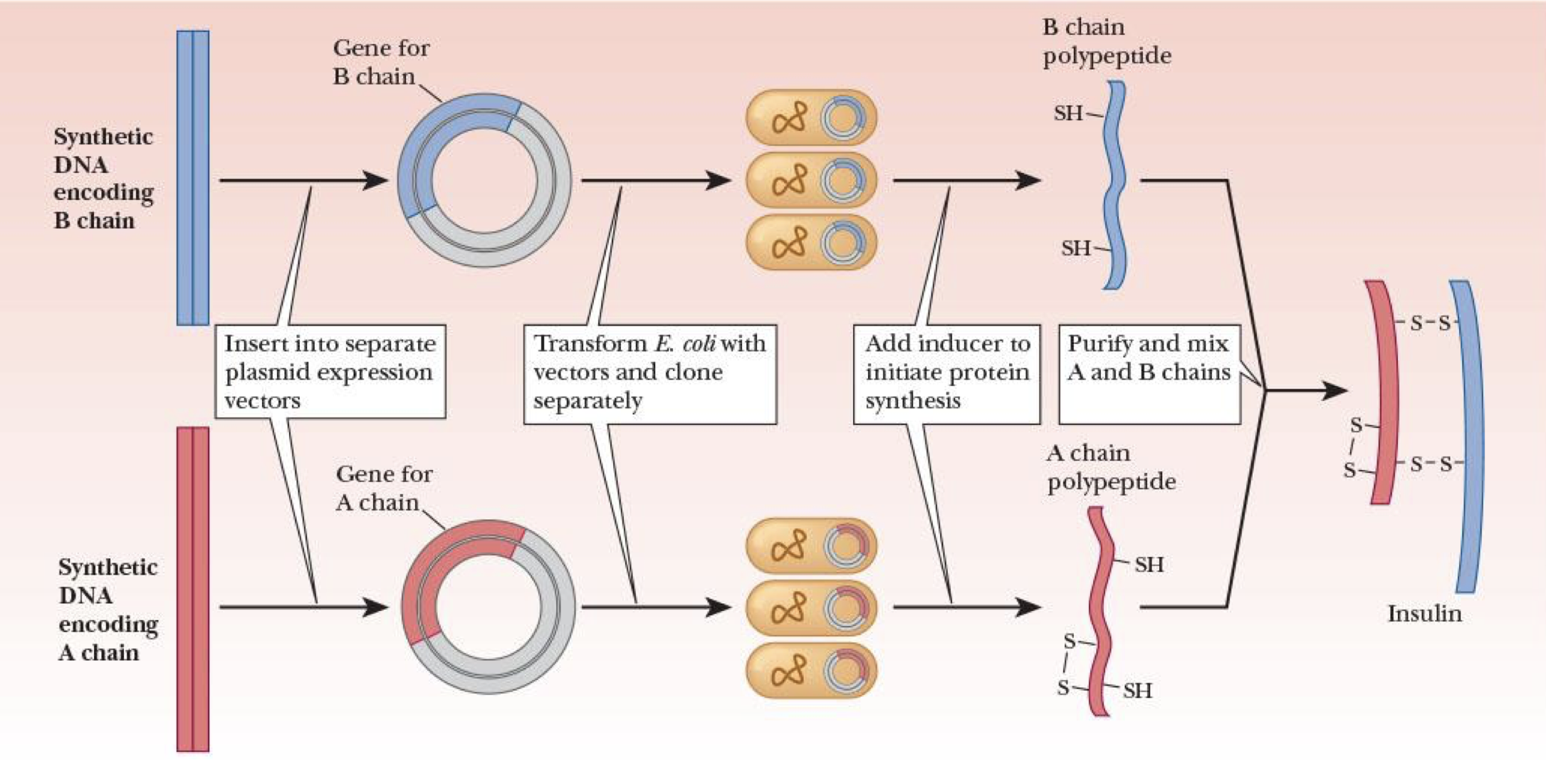
expression vectors/plasmid
plasmids that
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
like cloning but no reliance of any organism such as bacteria
PCR steps
template/targeted sequence (must know the
primers (complementary to each template) added
3’ ends inward toward desired
DNTPs added to build the DNA
Taq DNA polymerase added
comes from thermus aquaticus
heat to 95ºC (denature) & cool to 55–60ºC to anneal
how to figure out number of copies generated from PCR
2n; n = number of cycles