precalc final
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
y=sinx
domain: (-∞, ∞)
Range: [-1, 1]
Period: 2π
x-int: πk
max: (π/2)+2πk
min: (3π/2)+2πk
Derivative: y1=cosx
![<p>domain: (-<span>∞, ∞)</span><br><span>Range: [-1, 1]</span></p><p><span>Period: 2</span>π</p><p>x-int: πk</p><p>max: (π/2)+2πk</p><p>min: (3π/2)+2πk</p><p>Derivative: y<sup>1</sup>=cosx</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/43c563e0-8e18-48a6-95ba-96ab003be5ce.png)
y=cosx
domain: (-∞, ∞)
Range: [-1, 1]
Period: 2π
x-int: (π/2)+πk
max: 2πk
min: π+2πk
Derivative: y1=-sinx
![<p>domain: (-∞, ∞)<br>Range: [-1, 1]</p><p>Period: 2π</p><p>x-int: (π/2)+πk</p><p>max: 2πk</p><p>min: π+2πk</p><p>Derivative: y<sup>1</sup>=-sinx</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d540dbde-0e7b-415c-a761-c22f7cc5b09c.png)
y=tanx
domain: R except (π/2)+2πk
Range: (-∞, ∞)
x-int: x=πk
derivative: sec2x
asymptotes: x = π/2 + πk
y=sin-1x
inputs of y-coordinates on the unit circle, outputs of angles between [-π/2, π/2]
domain: [-1, 1]
range: [-π/2, π/2]
![<p>inputs of y-coordinates on the unit circle, outputs of angles between [-π/2, π/2]</p><p>domain: [-1, 1]</p><p>range: [-π/2, π/2]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ff391caa-9aeb-457e-a106-627a41e8207b.png)
y=cos-1x
inputs of x-coordinates on the unit circle, outputs of angles between [0, π]
domain: [-1, 1]
range: [0, π]
![<p>inputs of x-coordinates on the unit circle, outputs of angles between [0, π]</p><p>domain: [-1, 1]</p><p>range: [0, π]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/44d74fab-35c9-4fe1-af45-e71c9df4687a.png)
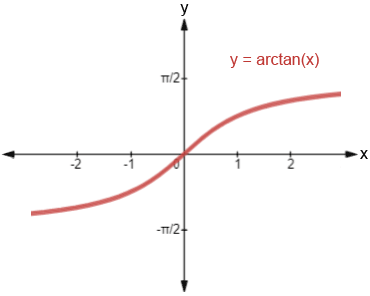
y=tan-1x
inputs of slopes on the unit circle, outputs of angles between (-π/2, π/2)
domain: (-∞, ∞)
range: (-π/2, π/2)
y=cscx
cscθ=1/sinθ
sinθ=1/cscθ
domain: R except x=π/k
range: (-∞, -1] U [1, ∞)
period: 2π
![<p>cscθ=1/sinθ</p><p>sinθ=1/cscθ</p><p>domain: R except x=π/k</p><p>range: (-∞, -1] U [1, ∞)</p><p>period: 2π</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1d0a4b6d-4365-44a0-a836-a2ae7d762c0c.jpg)
y=secx
secθ=1/cosθ
cosθ=1/secθ
domain: R except x=π/2+πk
range: (-∞, -1] U [1, ∞)
period: 2π
![<p>secθ=1/cosθ</p><p>cosθ=1/secθ</p><p>domain: R except x=π/2+πk</p><p>range: (-∞, -1] U [1, ∞)</p><p>period: 2π</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c9be13d2-2799-4829-bf0e-68a87bd87b69.png)
y=cotx
cotθ=1/tanθ=cosθ/sinθ
tanθ=1/cotθ=sinθ/cosθ
domain: R except x=πk
range: (-∞, ∞)
period: π
asymptotes: πk
Sinusoids
y=Asin(b(x-c))+D
y=Acos(b(x-c))+D
amplitude: |A| — vertical stretch/displacement, distance from midline to max or min
vertical displacement: D — vertical shift (average of max or min)
period: 2π/b — horizontal stretch, compression
phase shift: c — horizontal shift
y=ex
y=lnx
odd function
symmetric around origin
f(-x)=-f(x)
even function
symmetric over y-axis
f(x)=f(-x)
eccentricity
PF/Pd=1 (parabola)
0<PF/Pd<1 (ellipse)
PF/Pd>1 (hyperbola)
e=c/a
continuity calc definition
f(c) exists
lim(x→c) of f(x) exists
lim(x→c) of f(x) = f(c)
remainder theorem
if a polynomial function, f, is divided by (x - a), then the remainder is f(a).
factor theorem
if (x - a) divides a polynomial function, f, evenly, then f(a) = 0.
possible zeros are +- factors of the leading coefficent over the constant
slope of a tangent line
f'(c)=lim(x→c) = f(x)-f(c)/x-c
rational function asymptote
y=0 when the degree of q > the degree of p
y=a/b when the degree of q = the degree of p
(where a = leading coefficient of p and b = leading coefficient of q)
slant asymptote when the degree of q < the degree of p
rational function slant asymptote
divide function
logbc
logac/logab
logbxy
logbx+logby
logb(x/y)
logbx-logby
logbxy
y(logbx)
SAS Area
A=1/2*a*b*sinC
Law of sines
a/sinA=b/sinB=c/sinC
Law of cosines
a2=b2+c2-2bc*cosA
Pythagorean IDs
sin2θ+cos2θ=1
csc2θ-cot2θ=1
sec2θ-tan2θ=1
Even/Odd IDs
sin(-x)=-sin(x)
cos(-x)=cosx
tan(-x)=-tan(x)
Co-Function IDs
sin(90-θ)=cosθ, cos(90-θ)=sinθ
sec(90-θ)=cscθ, csc(90-θ)=secθ
cot(90-θ)=tanθ, tan(90-θ)=cotθ
sin(A+B)
sinAcosB+sinBcosA
cos(A+B)
cosAcosB-sinAsinB
tan(A+B)
(tanA+tanB)/1-tanAtanB
sin(2x)
2sinxcosx
cos(2x)
cos2x-sin2x
1-2sin2x
2cos2x-1
acisα*bcisβ
abcis(α+β)
(rcisθ)n
rncis(n*θ)
derivative of xn (power rule)
n*xn-1
derivative of ex
ex
derivative of ebx
b*ebx
derivative of bx
lnb*bx
derivative of ln(x)
1/x
derivative of logbx
1/x*ln(b)
derivative of sinx
cosx
derivative of cosx
-sinx
limit definition of a derivative at a point
lim(h→0) (f(x+h)-f(x))/h
combinations
n!/(n-k)!k!
added k b/c order doesnt matter, get rid of repeats
permutations
n!/(n-k!)
tan2x
2tanx/(1-tanx)