Chapter 25 Trauma
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 11:32 PM on 8/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
1
New cards
trauma emergencies
emergencies that are the result of physical forces applied to the body
2
New cards
medical emergencies
emergencies not caused by an outside force, illnesses or conditions
3
New cards
index of suspicion
awareness that unseen life-threatening injuries may exist when determining the moi
4
New cards
mechanism of injury
forces, or energy transmission, applied to the body that cause injury
5
New cards
multi system trauma
affects more than one body system

6
New cards
blunt trauma
cause injury without penetrating soft tissues or internal organs and cavities
7
New cards
penetrating trauma
pierce the surface of the body and damage internal tissues and organs, knives and bullets
8
New cards
frontal crashes
lower extremity fractures (knees into dashboard), rib fractures (rib cage into steering wheel), head trauma (head into windshield), internal organs hitting solid structures of the body, watch out for airbags that haven’t deployed
9
New cards
rear-end crashes
whiplash injuries
10
New cards
lateral crashes
lateral whiplash injuries, skull against doorpost or window
11
New cards
rollover crashes and rotational crashes
striking interior of vehicle, ejection or partial ejection (life-threatening injuries)
12
New cards
coup-contrecoup brain injury
compression (or bruising) to anterior portion of the brain and tension (stretching)of the posterior portion
13
New cards
important info
alert medical control and hospital staff to what you see (contusion on patient’s forehead and windshield is starred and pushed out), always take spinal precautions
14
New cards
falls
height, type of surface struck, part of the body that hit first, followed by path of energy displacement, older patients (osteoporosis)
15
New cards
cavitation
speed causes a bullet to generate pressure waves, which cause damage distant from the bullet’s path
16
New cards
problems in trauma patients (1)
\-
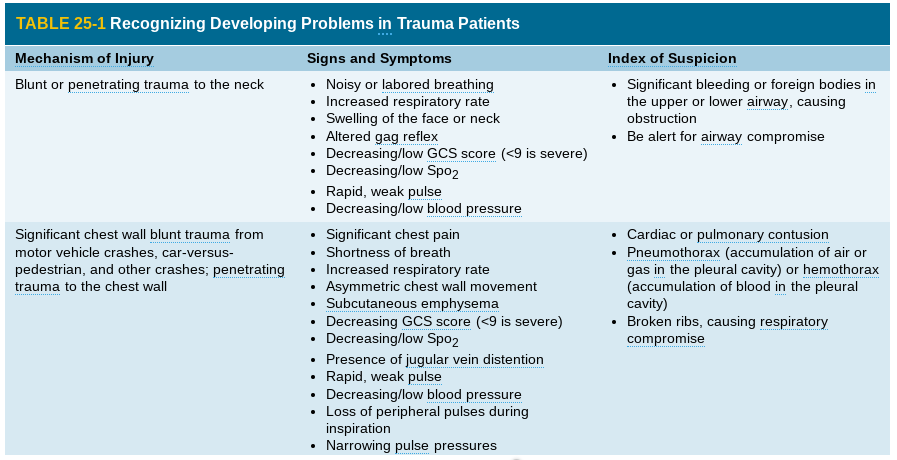
17
New cards
problems in trauma patients (2)
\-
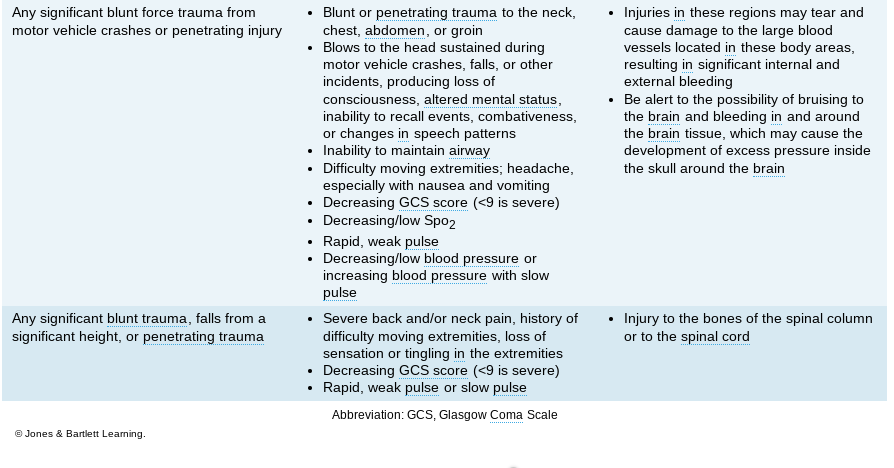
18
New cards
pulmonary blast injuries
pulmonary trauma resulting from short-range exposure to detonation of high-energy explosives
19
New cards
arterial air embolism
air bubbles in the arterial blood vessels
20
New cards
patient assessment
less than 10 minute on scene, DCAP-BTLS, (head) conduct frequent neurological examinations, (neck and throat) jugular vein distention and tracheal deviation, occlusive dressings, (chest) lung sounds and chest rise and fall, (abdomen) reassess abdominal region
21
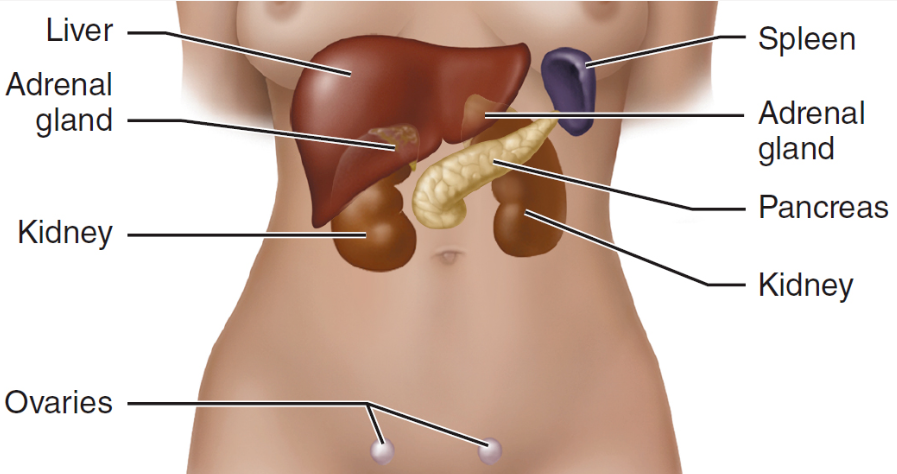
New cards
Glasgow Coma Scale (EVM)
eye, verbal, motor
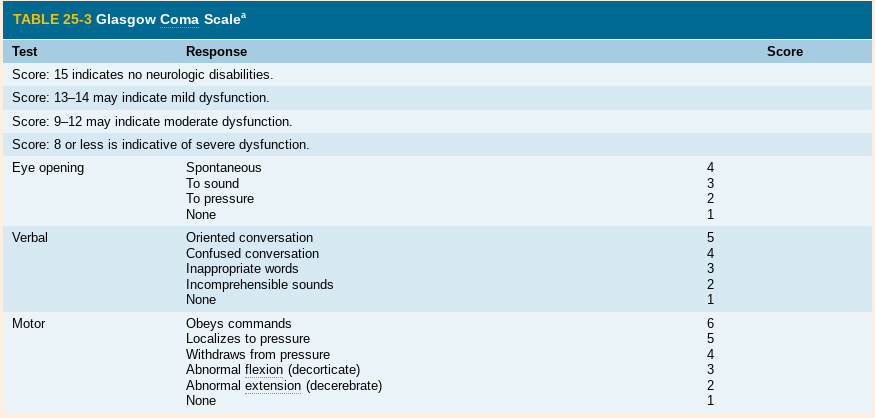
22
New cards
Revised Trauma Score
used for patients with head trauma
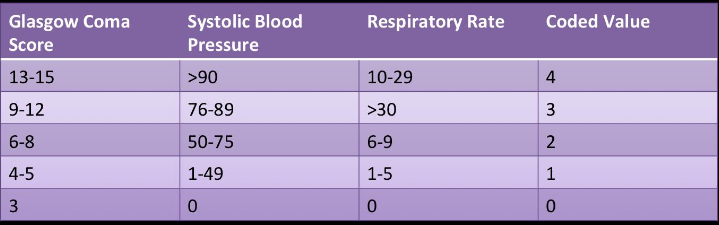
23
New cards
critical organs
heart-cardiovascular, brain-central nervous system, lungs-respiratory, kidneys-renal system
24
New cards
hemorrhage
bleeding, body can’t tolerate blood loss greater than 20% of total blood volume (2 pints or 1L)
25
New cards
hypovolemic shock
low blood volume, due to massive internal or external bleeding or extensive loss of body water, results in inadequate perfusion
26
New cards
capillary bleeding
dark red and oozes from a wound steadily but slowly
27
New cards
venous bleeding
darker than arterial bleeding and flows steadily
28
New cards
arterial bleeding
bright red and spurts in time with pulse
29
New cards
coagulation
formation of clots to plug openings in injured blood vessels and stop blood flow
30
New cards
contusion and ecchymosis
local swelling and bruising
31
New cards
internal bleeding
high energy MOI (falls, blast injuries, motor vehicle crashes, penetrating and blunt trauma), bleeding ulcers, bleeding from colon, ruptured ectopic pregnancy, aneurysms, common in head, extremities, and pelvic injuries
32
New cards
internal bleeding signs and symptoms
pain, swelling in the area of bleeding, abdominal distention, dyspnea, tachycardia, hemoptysis (coughing up blood),

33
New cards
care of external bleeding
direct pressure, pressure dressings or splints, tourniquets, junctional tourniquets, hemostatic dressing, wound packing
34
New cards
skills
(976) controlling external bleeding, packing a wound, commercial tourniquet, pelvic binder, bleeding from nose, ear, and mouth, stabilizing impaled objects, occlusive dressing, caring for burns, removing foreign object from under upper eyelid, stabilizing foreign object in eye, controlling bleeding from neck, applying cervical collar, securing a patient to a long board, caring for musculoskeletal injuries, splinting (hand, traction)
35
New cards
bleeding from nose or ears
indicate skull fracture, do not attempt to stop blood flow
36
New cards
epidermis
outer layer of skin that forms a watertight covering for the body
37
New cards
dermis
inner layer of the skin, contains follicles, sweat glands, nerve endings, and blood vessels
38
New cards
mucous membrane
linings of body cavities and passages that communicate directly or indirectly with the environment outside the body, mouth, nose, anus, vagina, moist compared to dry skin
39
New cards
closed injuries
damage occurs beneath the skin or mucous membrane, surface of skin remains intact
40
New cards
open injuries
break in surface of skin or mucous membrane
41
New cards
burn
soft-tissue damage as result of thermal heat, frictional heat, toxic chemicals, electricity, or nuclear radiation
42
New cards
hematoma
blood that has collected within damaged tissue beneath the skin or in a body cavity
43
New cards
abrasion
loss or damage of the superficial layer of the skin as a result of a body part rubbing or scrapping across a rough or hard surface, road rash, road burn, rug burn
44
New cards
laceration
jagged cut in the skin caused by a sharp object or blunt force that tears the tissue
45
New cards
incision
sharp, smooth cut in the skin
46
New cards
avulsion
soft tissue is torn completely loose or is hanging as a flap
47
New cards
amputation
part of the body is completely severed
48
New cards
signs of hypoperfusion
\-

49
New cards
care of closed soft-tissue injury (RICES)
Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation, Splinting
50
New cards
occlusive dressing
use in chest, upper abdomen, upper back, taped on three sides leaving one side open
51
New cards
evisceration
displacement of organs outside of the body

52
New cards
treatment for bites
place a dry, sterile dressing over bite wound, splint or bandage, provide transport to ED
53
New cards
burns
keep the patient warm and provide supplemental oxygen for burns, if the patient has altered level of consciousness suspect hypoperfusion, hypoxia, hypoglycemia, or head injury
54
New cards
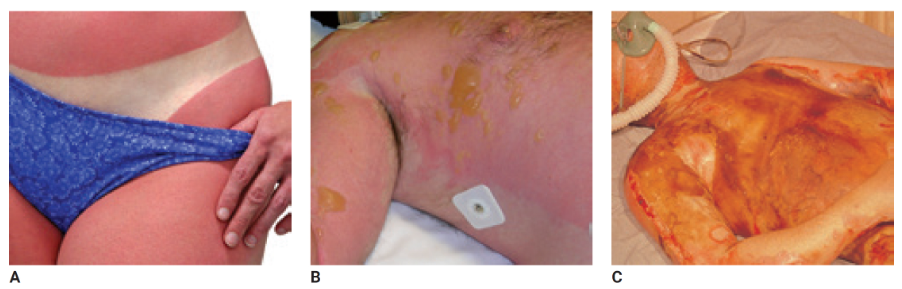
superficial (first-degree)
involves only the top layer of the skin, epidermis, skin turns red but does not blister or burn through top layer, ex: sunburn
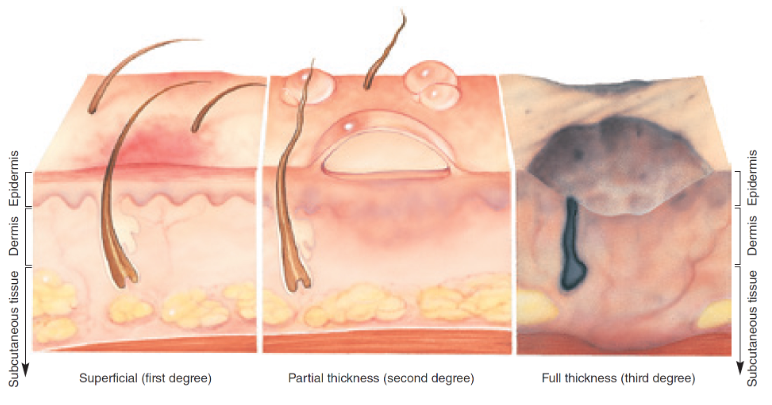
55
New cards
partial-thickness (second-degree)
involve the epidermis and some portion of the dermis but not subcutaneous tissue, blisters and skin that is white to red, moist, and mottled
56
New cards
full-thickness (third-degree)
affect all layers of the skin and may affect subcutaneous layers, muscle, bone, and internal organs, leaving the area dry, leathery, and white, dark brown, or charred
57
New cards
rules of nines (adult)
\-
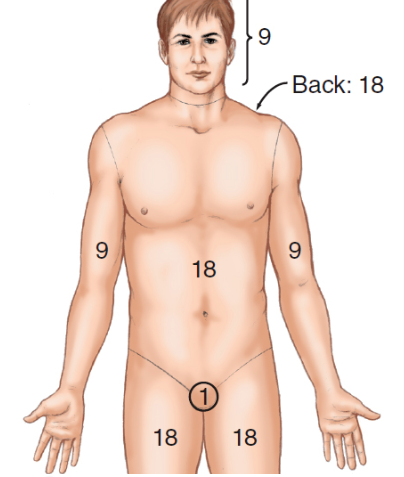
58
New cards
rules of nines (child)
12 and 16.5
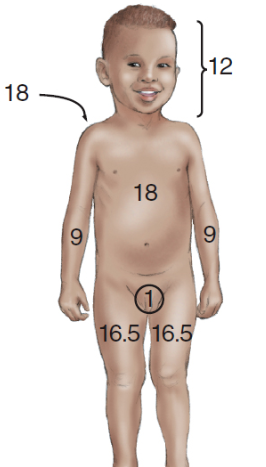
59
New cards
rule of nines (infants)
18 and 13.5
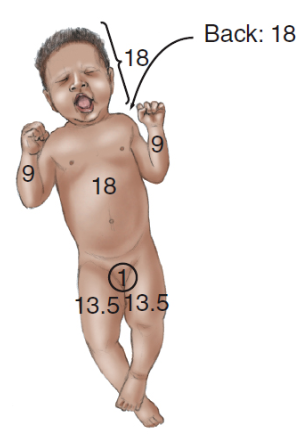
60
New cards
care for chemical and thermal burn
brush off dry chemicals from the skin and clothing before flushing patient with water, remove patient’s clothing, shoes, stockings, gloves, and jewelry and eyeglasses
61
New cards
CMS
circulatory, motor, sensory
62
New cards
care of injuries to face and neck
face/neck care

63
New cards
care of injuries around the mouth
mouth care

64
New cards
care of injuries of the eye
eye care, normal eye: entire circle of iris is visible, pupils are round, usually equal in size, and react equally when exposed to light, both eyes move in same direction when following moving finger

65
New cards
care of neck injuries
neck care

66
New cards
signs and symptoms of head injury
give supplemental oxygen to patient suspected of head injury

67
New cards
raccoon eyes
bruising under the eyes
68
New cards
battle sign
bruising behind an eye
69
New cards
traumatic brain injury (TBI)
insult to the brain capable of producing physical, intellectual, emotional, social, and vocational changes, primary (direct), secondary (inderect)
70
New cards
cerebral edema
swelling in the brain
71
New cards
central neurogenic hyperventilation
abnormal breathing pattern associated with increased intracranial pressure, characterized by deep, rapid breathing, similar to kussmaul respiration but without acetone breath odor
72
New cards
cushing triad
high blood pressure, decreased heart rate, irregular respirations
73
New cards
concussion
mild TBI, temporary loss or alteration of part or all of the brain’s ability to function without physical damage to the brain
74
New cards
signs and symptoms of head or spinal injury
\-

75
New cards
paraplegia v. quadraplegia
\-
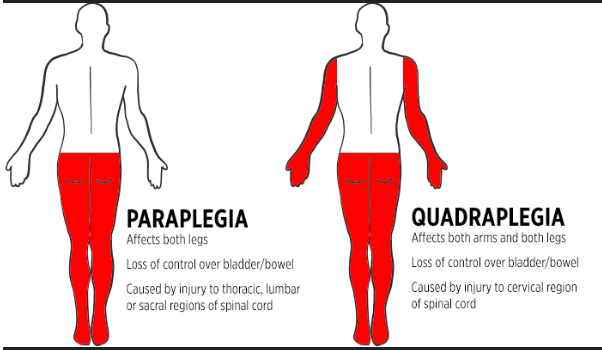
76
New cards
signs and symptoms of chest injury
chest injury, tachypnea (rapid respiration), shallow breaths

77
New cards
crepitus
sensation felt when broken bone ends grind together
78
New cards
paradoxical motion
one segment, flail segment, of the chest wall moves opposite the rest of the chest (normal: out with expiration, in with inspiration)
79
New cards
deadly dozen chest injuries
\-

80
New cards
pneumothorax
accumulation of air or gas in pleural cavity
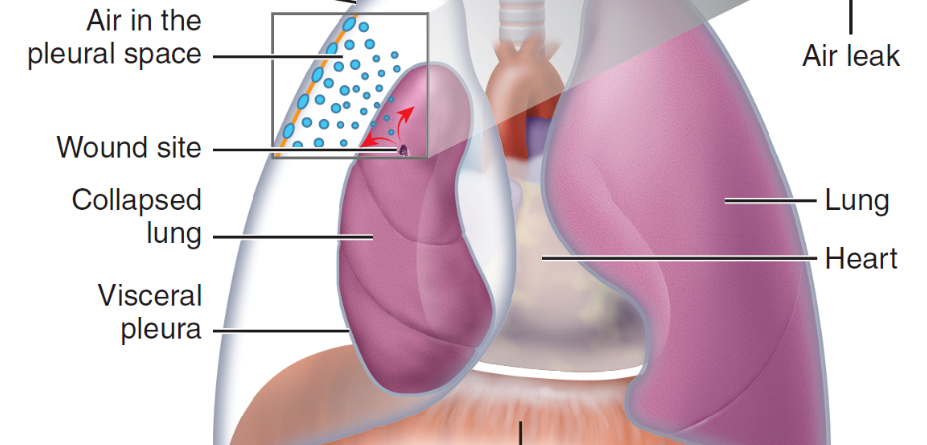
81
New cards
open pneumothorax or sucking chest wound
open or penetrating chest wall wound through which air passes during inspiration and expiration, creating a sucking sound
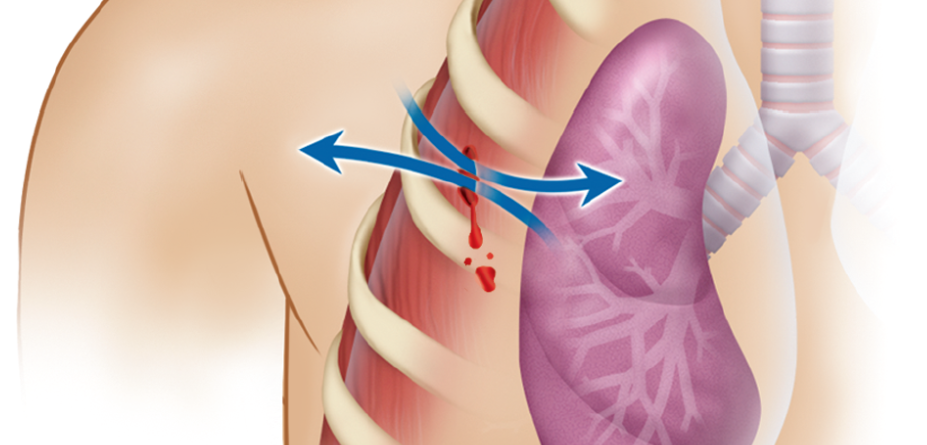
82
New cards
simple pneumothorax
any pneumothorax that is free from significant physiologic changes and does not cause drastic changes in the vital signs of the patient
83
New cards
tension pneumothorax
an accumulation of air or gas in the pleural cavity that progressively increases pressure in the chest and interferes with cardiac function
84
New cards
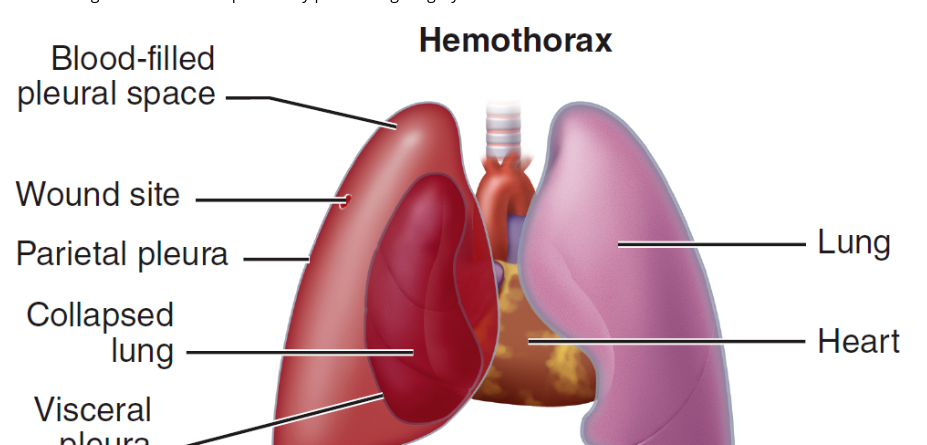
hemothorax
blood in the pleural space
85
New cards
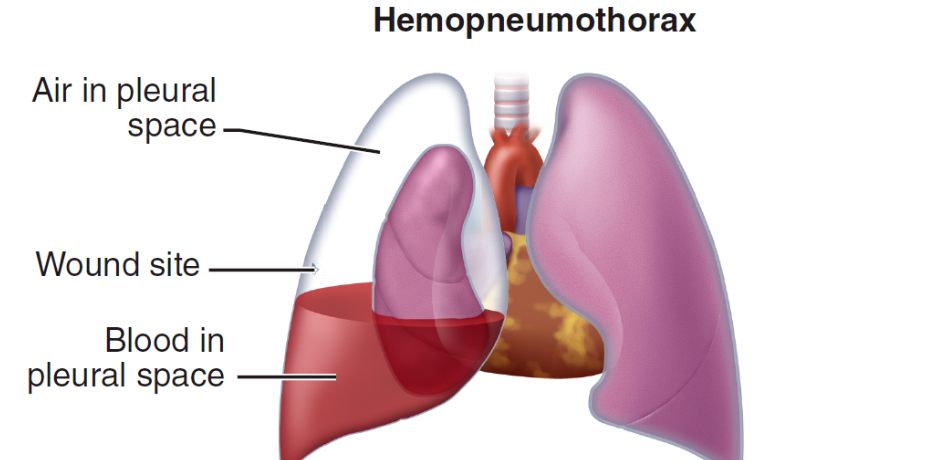
hemopneumothorax
accumulation of blood and air in the pleural space of the chest
86
New cards
cardiac tamponade
compression of the heart as a result of buildup of blood or other fluid in the pericardial sac, leading to decreased cardiac output
87
New cards
rib fractures
\-

88
New cards
flail chest
condition in which two or more adjacent ribs are fractured in two or more places or in association with fracture of the sternum so that a segment of chest wall is detached from rest of the thoracic cage

89
New cards
pulmonary contusion
injury or bruising of lung tissue that results in hemorrhage
90
New cards
other fractures
sternum (significant force required) and clavicle
91
New cards
tramatic asphyxia
seen after a severe force is applied to the chest, forcing blood from the great vessels back into the head and neck, suggest underlying injury to the heart and a pulmonary contusion
92
New cards
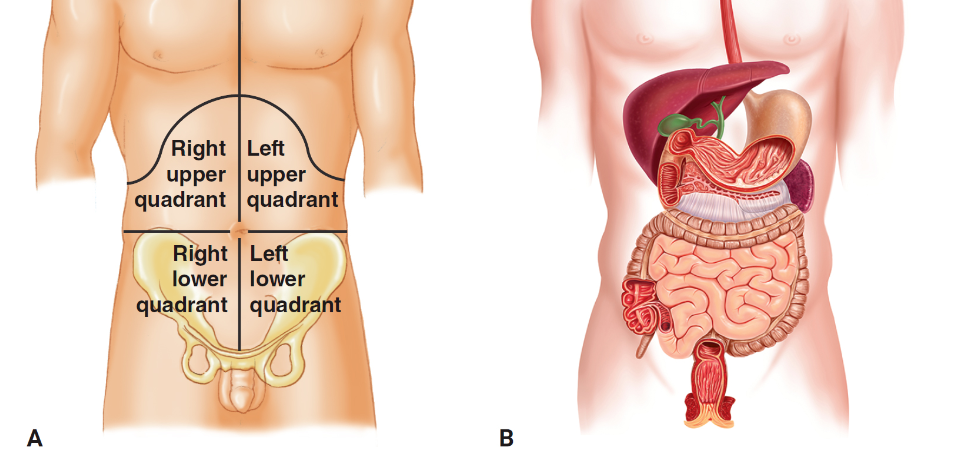
abdominal quadrants
\-
93
New cards
right upper quadrant
gallbladder, duodenum, liver, small portion of pancreas
94
New cards
right lower quadrant
large portions of large and small intestines, appendix
95
New cards
left upper quadrant
spleen, most of the stomach, larger portion of pancreas
96
New cards
left lower quadrant
portions of large and small intestines
97
New cards
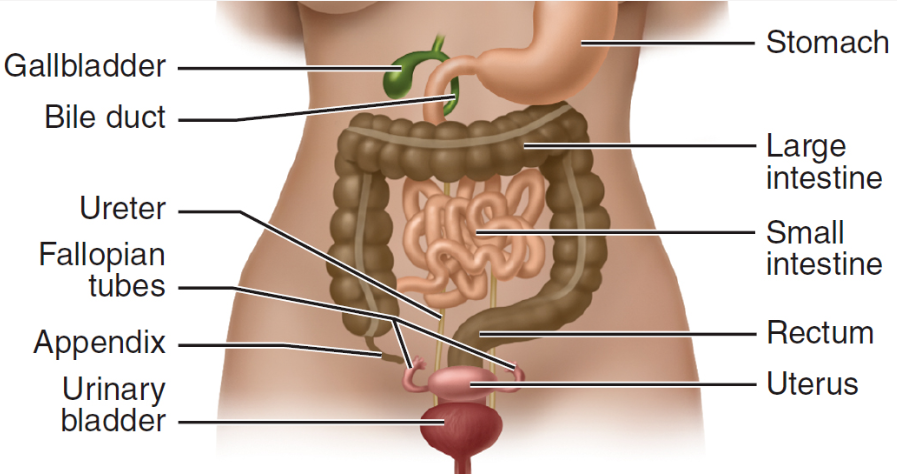
hollow organs
structures through which materials pass, stomach, intestines, urinary bladder
98
New cards
solid organs
solid masses of tissue where much of the chemical work of the body takes place (liver, spleen, pancreas, kidneys), rich blood supply
99
New cards
peritoneum
membrane lining the abdominal cavity
100
New cards
three levels of velocities (trauma)
\-
