A & P - Chapter 4/5 - Epithelial Tissue / Integumentary System* 2023 | Quizlet
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
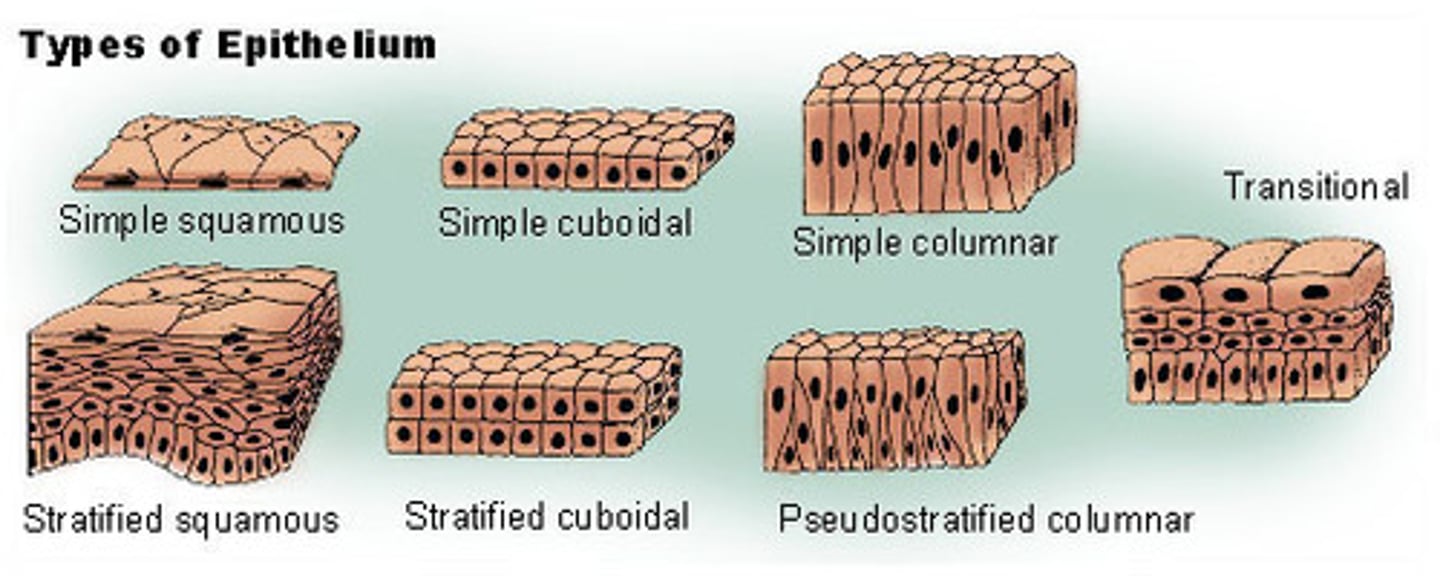
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Structure: One layer of "flat" cells, basement membrane
Function: allows material to pass by diffusion and filtration in sites where protection is not important (nutrients from CT)
Location: Air sacs of lungs, lining of heart, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, serosae
What is the Integumentary System
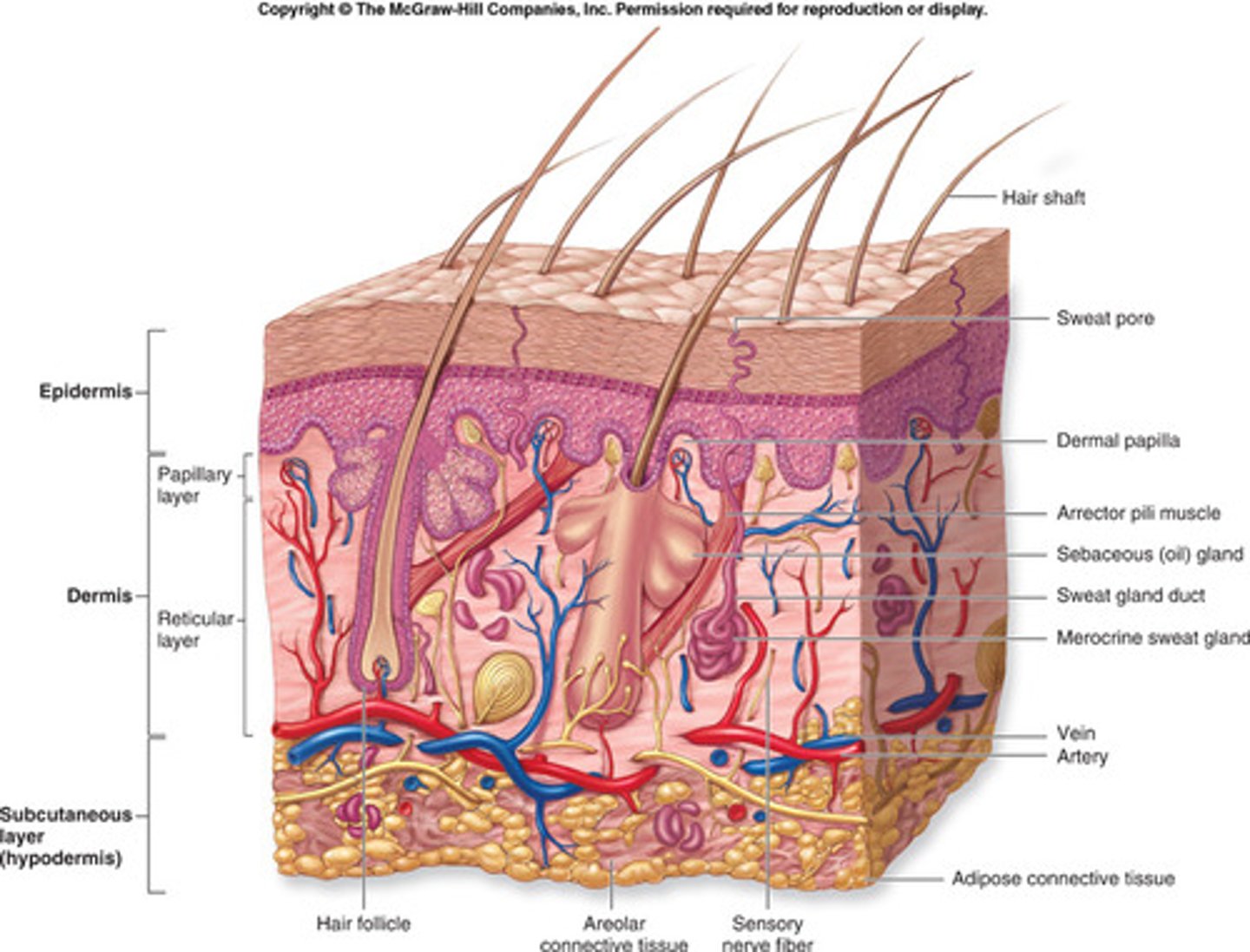
The skin - a complex set of organs that covers and protects body (3 layers: epidermis, dermis, hypodermis/subcutaneous)
Simple cuboidal Epithelium
Structure: One layer of "cube-shaped" cells, basement membrane
Function: Secretion and absorption
Location:Kidney tubules, ducts and secretory portions of small glands, ovary surface
Name the functions of the integumentary system
Waterproof, cushion, protection, excrete waste, regulate temperature, provide sensory input and synthesize vitamin D.
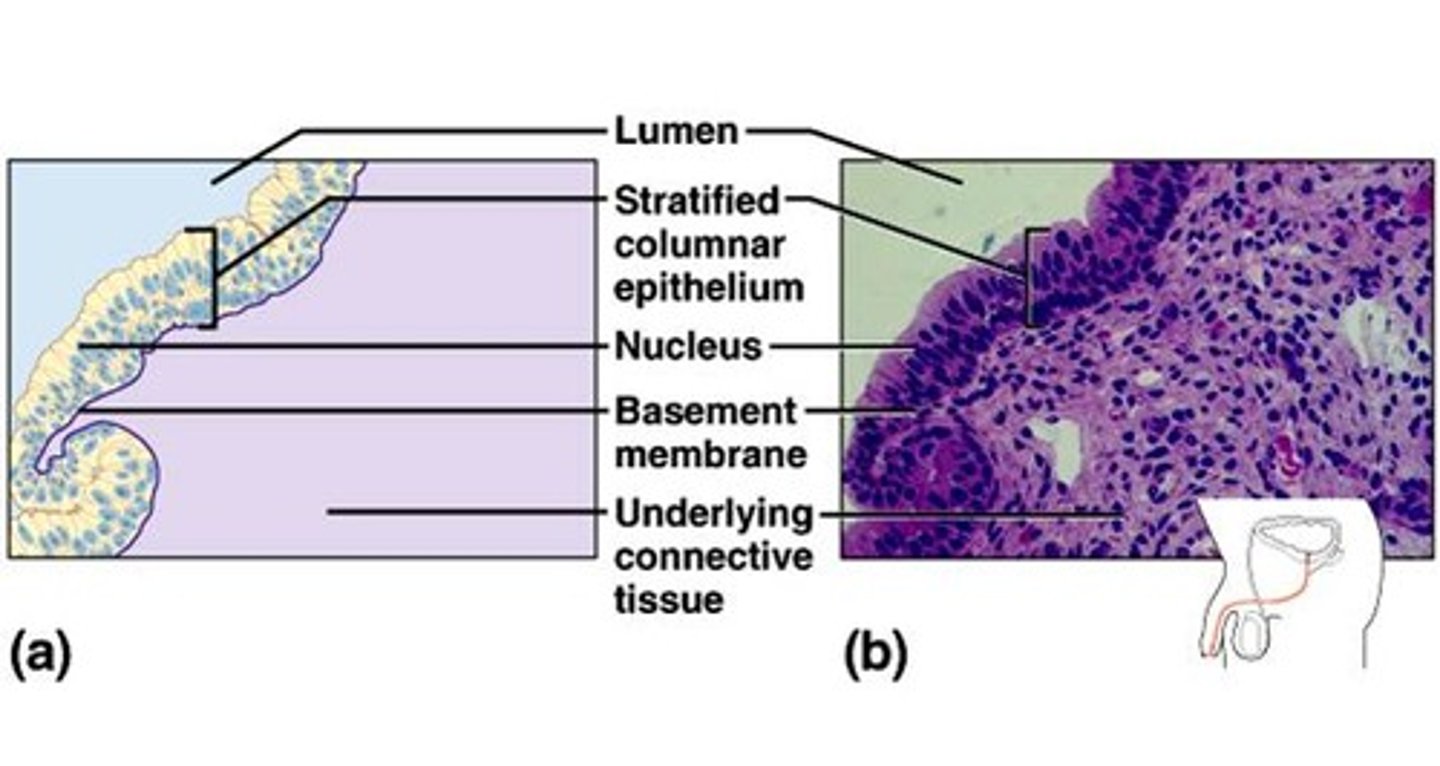
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Structure: One layer of "column-shaped" cells, basement membrane
Function: Absorption, secretion of mucus, enzymes and other substances
Location: Nonciliated type lines most of the digestive tract, gallbladder
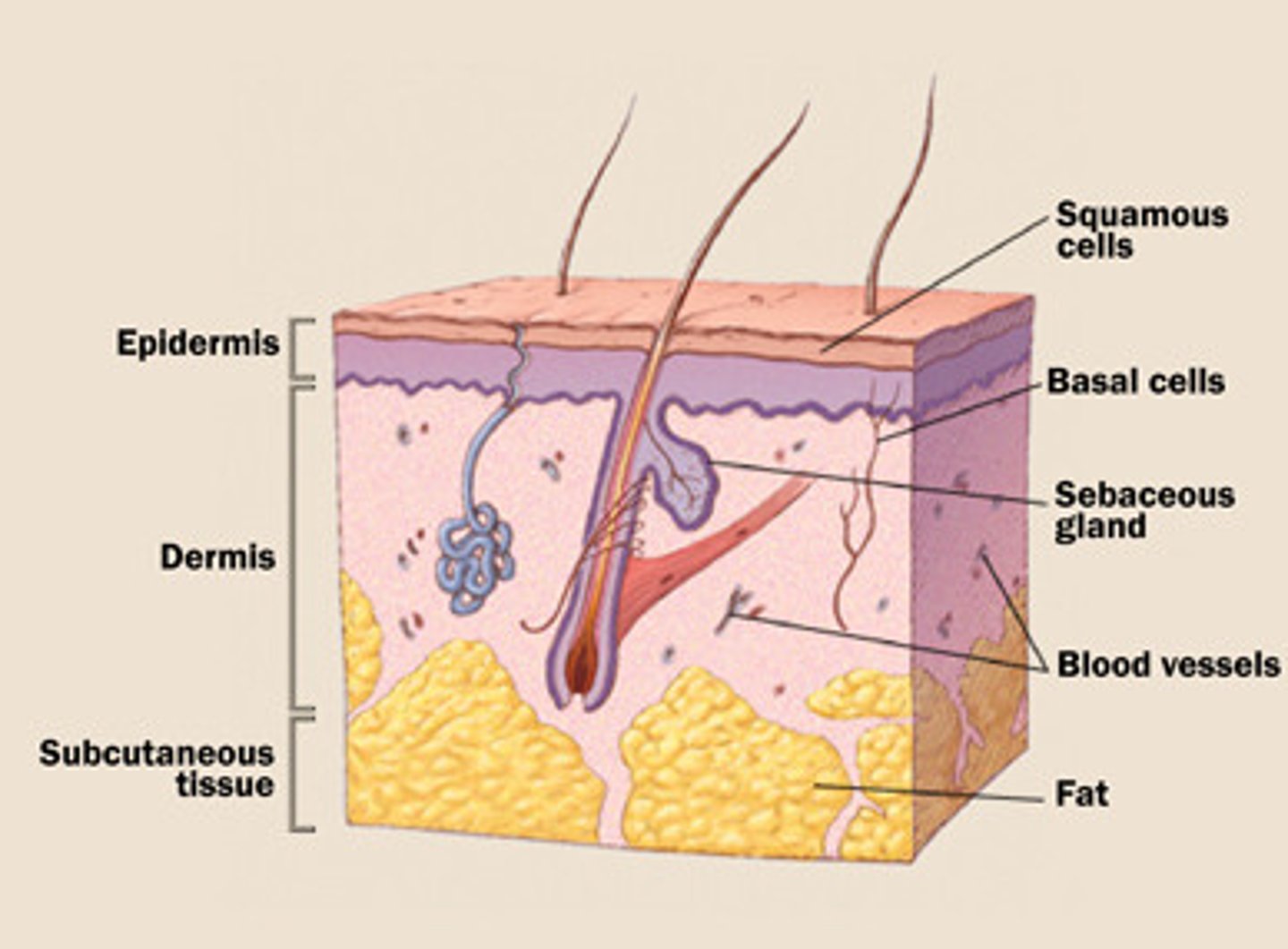
How do the structures of the integumentary system relate to its functions?
Outer layer - epidermis has keratinized protective layer; second layer- dermis has secretion glands, blood vessels, hair follicles and receptors; third layer - subcutaneous insulation & cushion
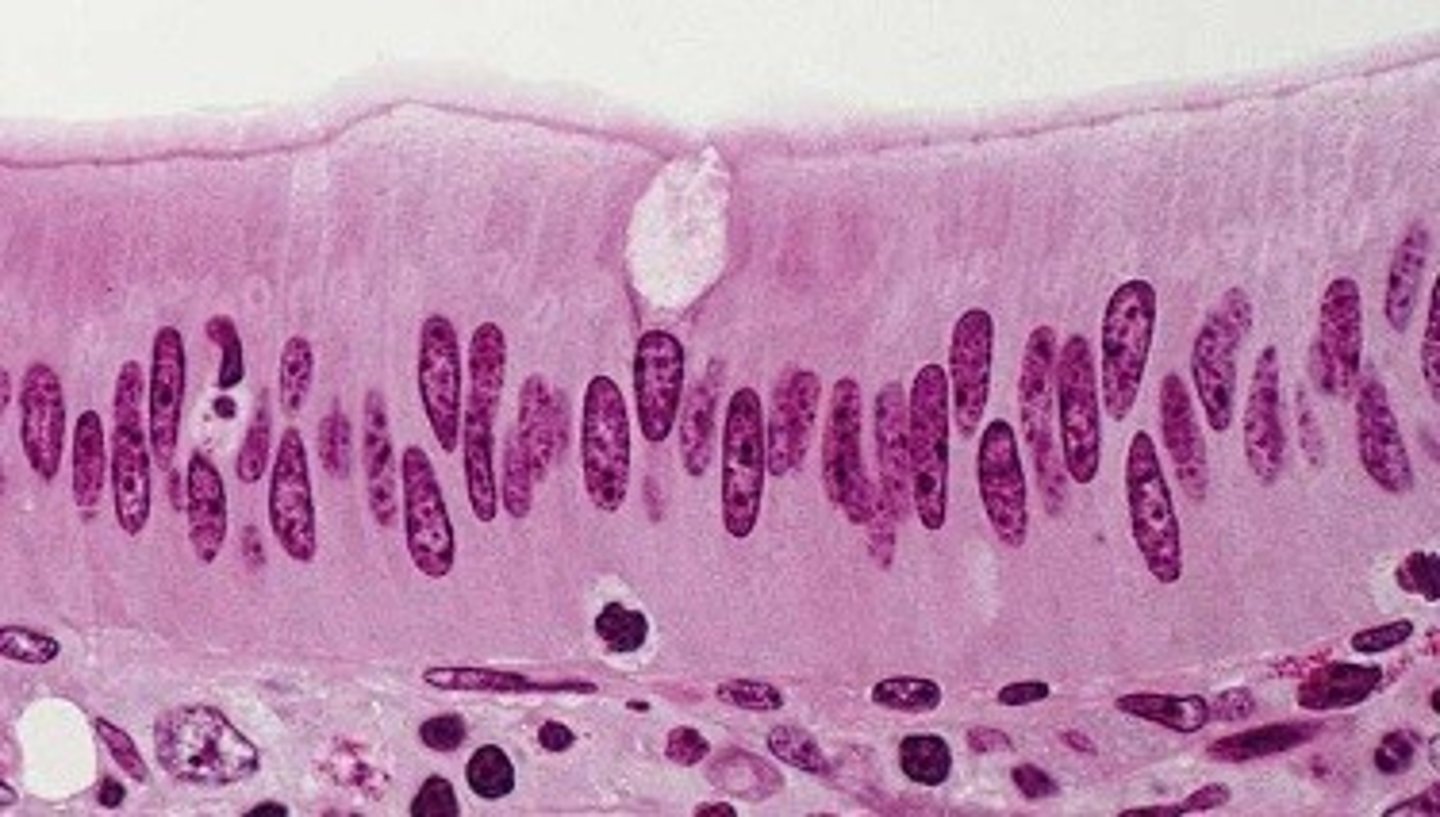
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Structure: "Falsely" stratified; looks like multiple layers but only has one layer of cells, basement membrane
Function: Secretes Mucus, traps dusts, protects lungs
Location: Lines trachea, upper respiratory tract, and male's sperm carrying ducts
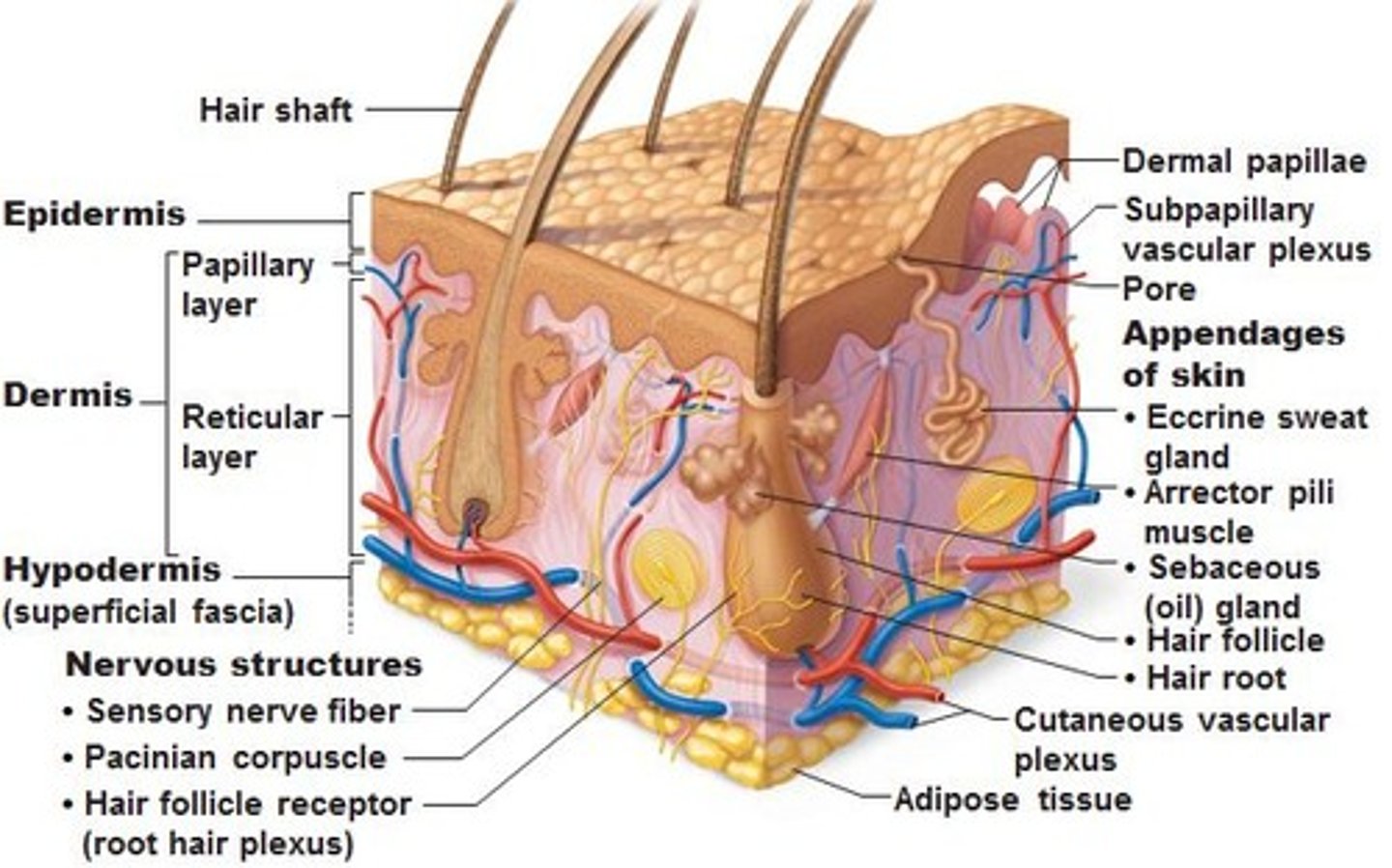
How do the structures of the integumentary system work together to maintain homeostasis in the body?
Provides protection, regulation of body temperature (sweat or shiver), sensory reception, water balance, synthesis of vitamins and hormones and absorption of materials.
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Structure: Multiple layers of "flat" cells, basement membrane
Function: Protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion
Location: moist lining of esophagus, mouth, vagina

The Skin
1.5-4.0 millimeters (mm), composed of two distinct regions, the epidermis and dermis
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Structure: Multiple layers of "square" cells, basement membrane
Function: Protection
Location: Largest ducts of sweat glands, mammary glands, and salivary gland
Epidermis
Composed of epithelial cells, is the outermost protective shield of the body. A keratinized stratified squamous epithelium consisting of 4 distinct cell types; 4 (thin) or 5 (thick) distinct layers.
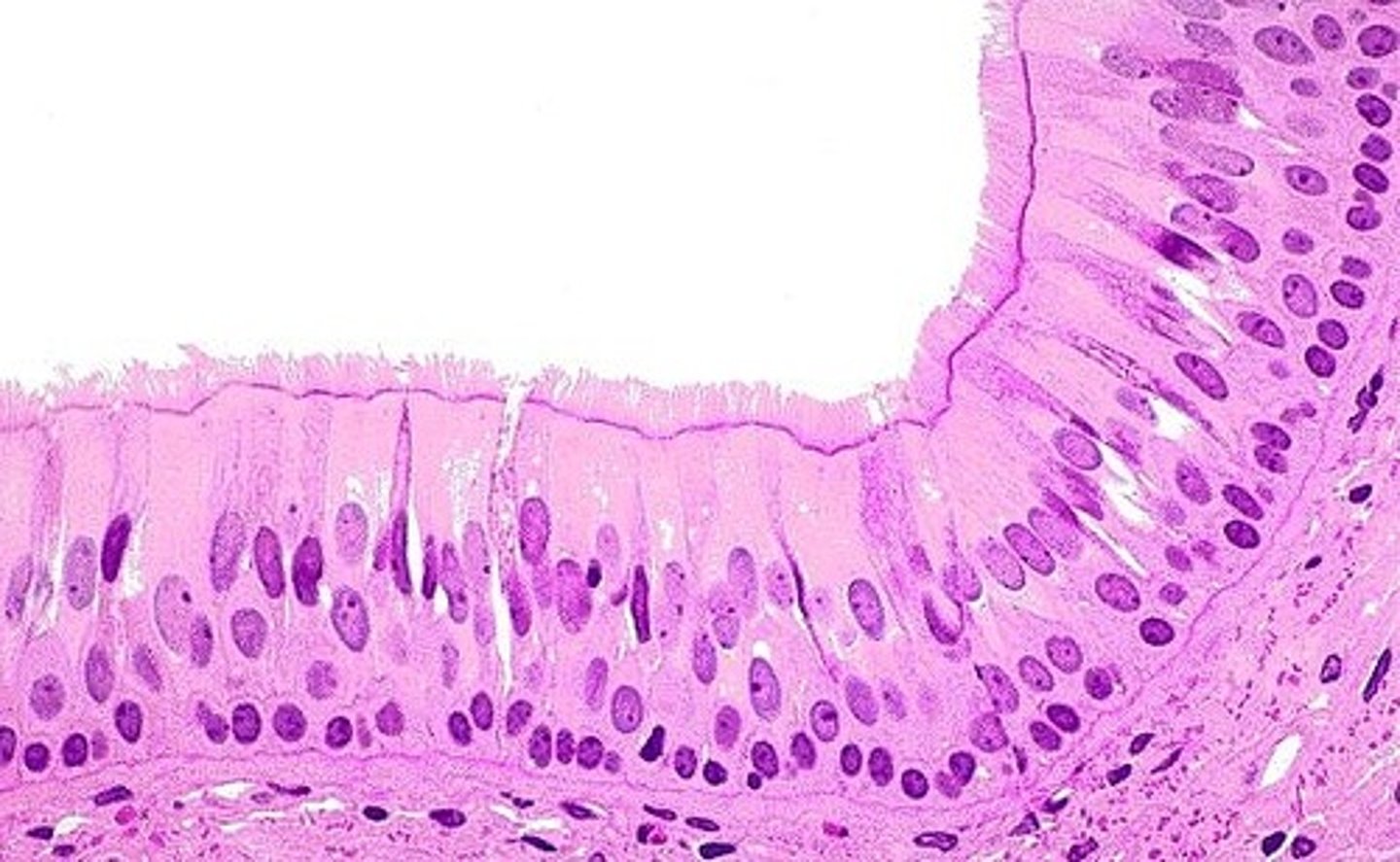
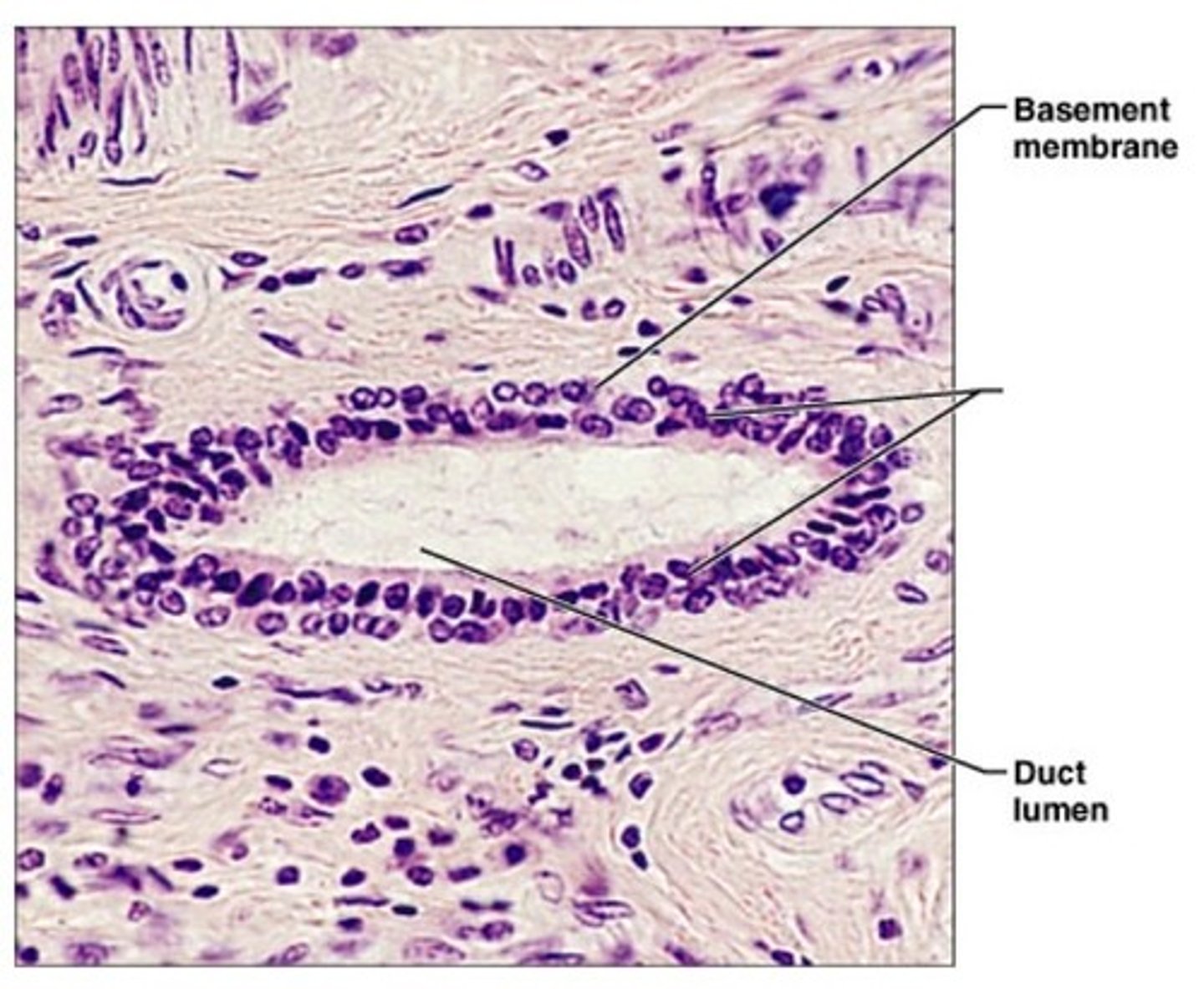
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Structure: Multiple layers of "column-shaped" cells, basement membrane
Function: Protection, secretion
Location: Rare in body, very small amounts in male urethra and in large ducts of some glands
Dermis
Makes up the bulk of the skin, is a tough leathery layer composed mostly of fibrous connective tissue. Only the dermis is vascularized.
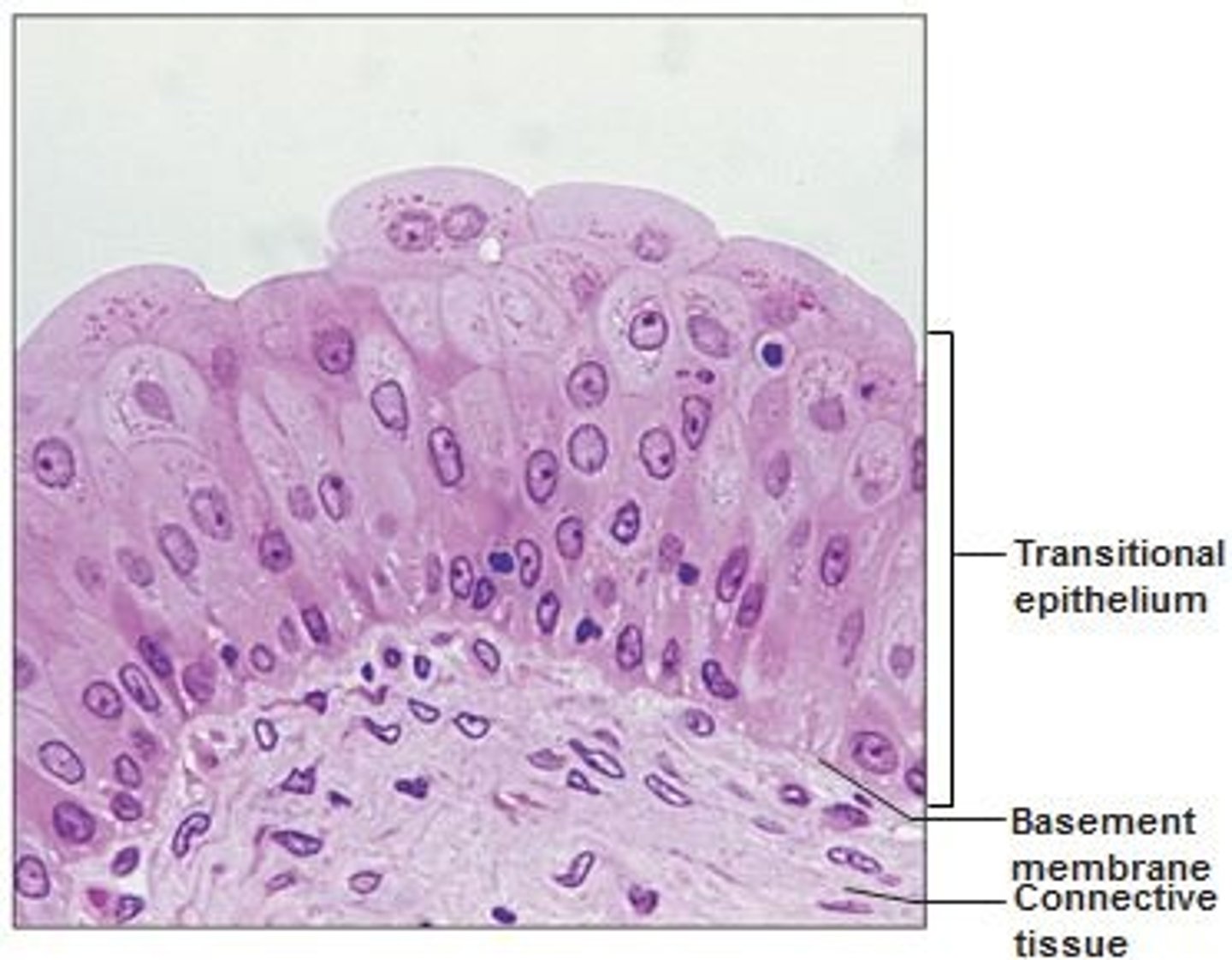
Transitional
Structure: Multiple layers of cells that can change shape due to elasticity, basement membrane
Function: Stretches readily and permits distension of urinary organ by contained urine
Location: Lines ureters, urinary bladder, and part of urethra
Hypodermis (subcutaneous)
The subcutaneous tissue deep to the skin. It is not part of the skin, but it shares some of the skins protective functions. It is superficial to the tough connective tissue wrapping (fascia) of the skeletal muscles, consists mostly of adipose tissue. Functions: Anchors the skin to the underlying structures (mostly muscle), acts as a shock absorber/insulator.
Name the cells of the Epidermis
Keratinocytes 90% (protection), Melanocytes 8% (color), Langerhan (immunity), and Merkel/tactile cells (touch sensation).
Keratinocytes
Main role is to produce keratin, a fibrous protein that helps give the epidermis its protective properties.
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue (CT)
Makes up the reticular layer of the dermis. Contains collagen and elastic fibers for strength and flexibility.
Melanocytes
The spider-shaped epithelial cells that synthesize the pigment melanin, are found in the deepest layer of the epidermis (basale). More UV light exposure = more melanin is produced. All humans have same number of melanocytes.
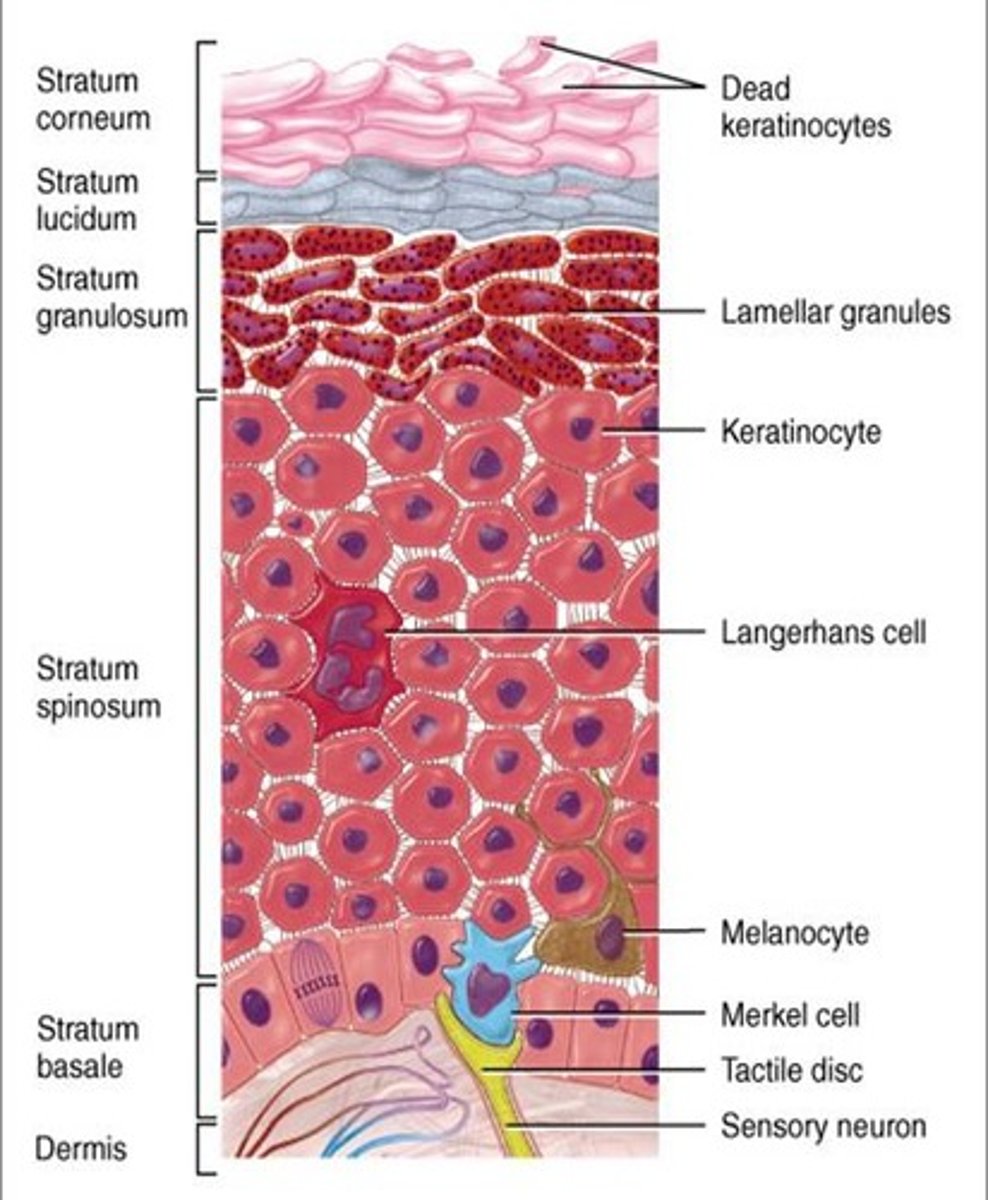
Langerhans cells
They ingest foreign substances and are key activators of the immune system. Arise from bone marrow and migrate to the epidermis.
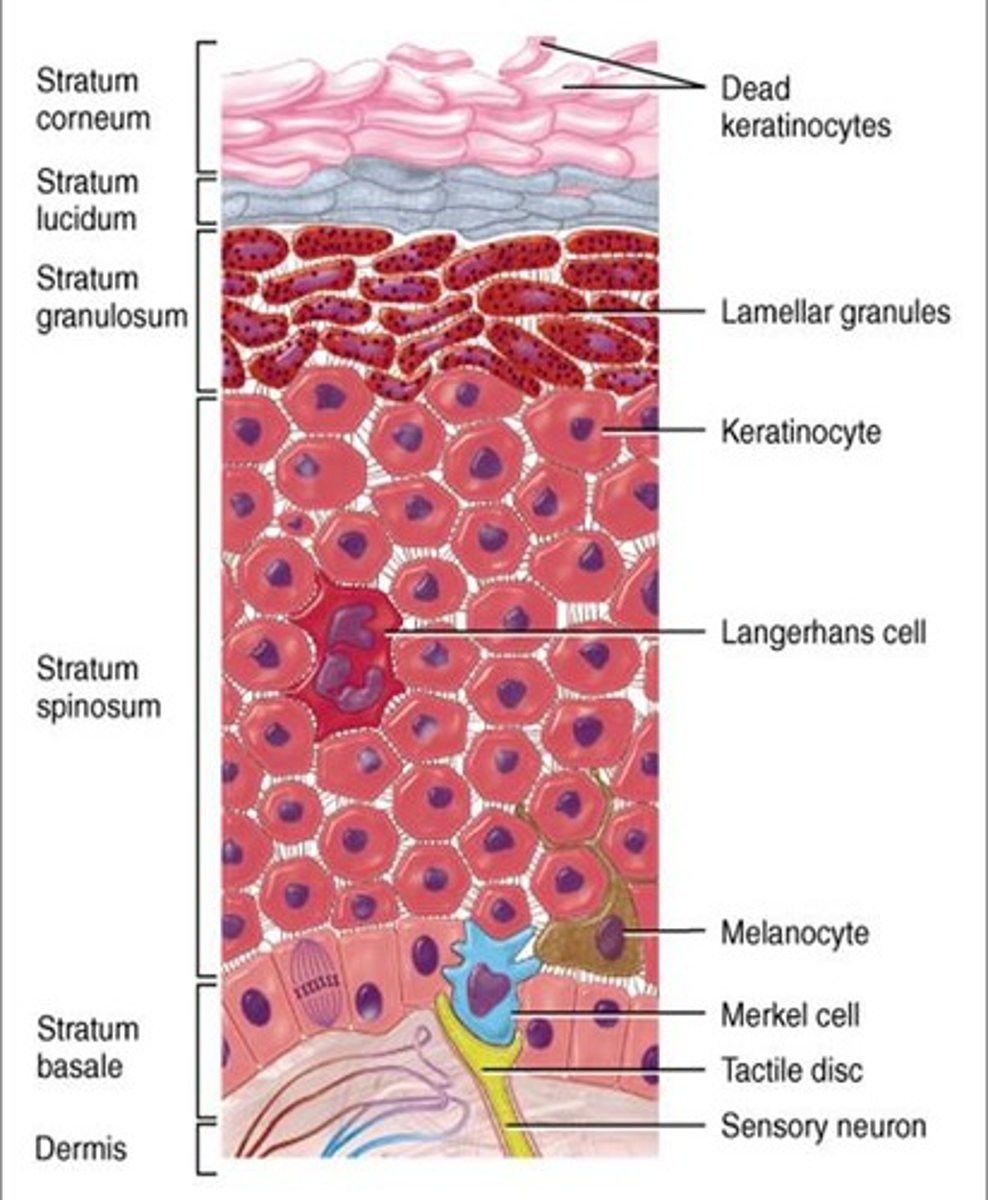
Merkel or Tactile Cells
Stratum Basale. Shaped like a spiky hemisphere. Each cell is associated with a disc like sensory nerve ending. (touch receptors)

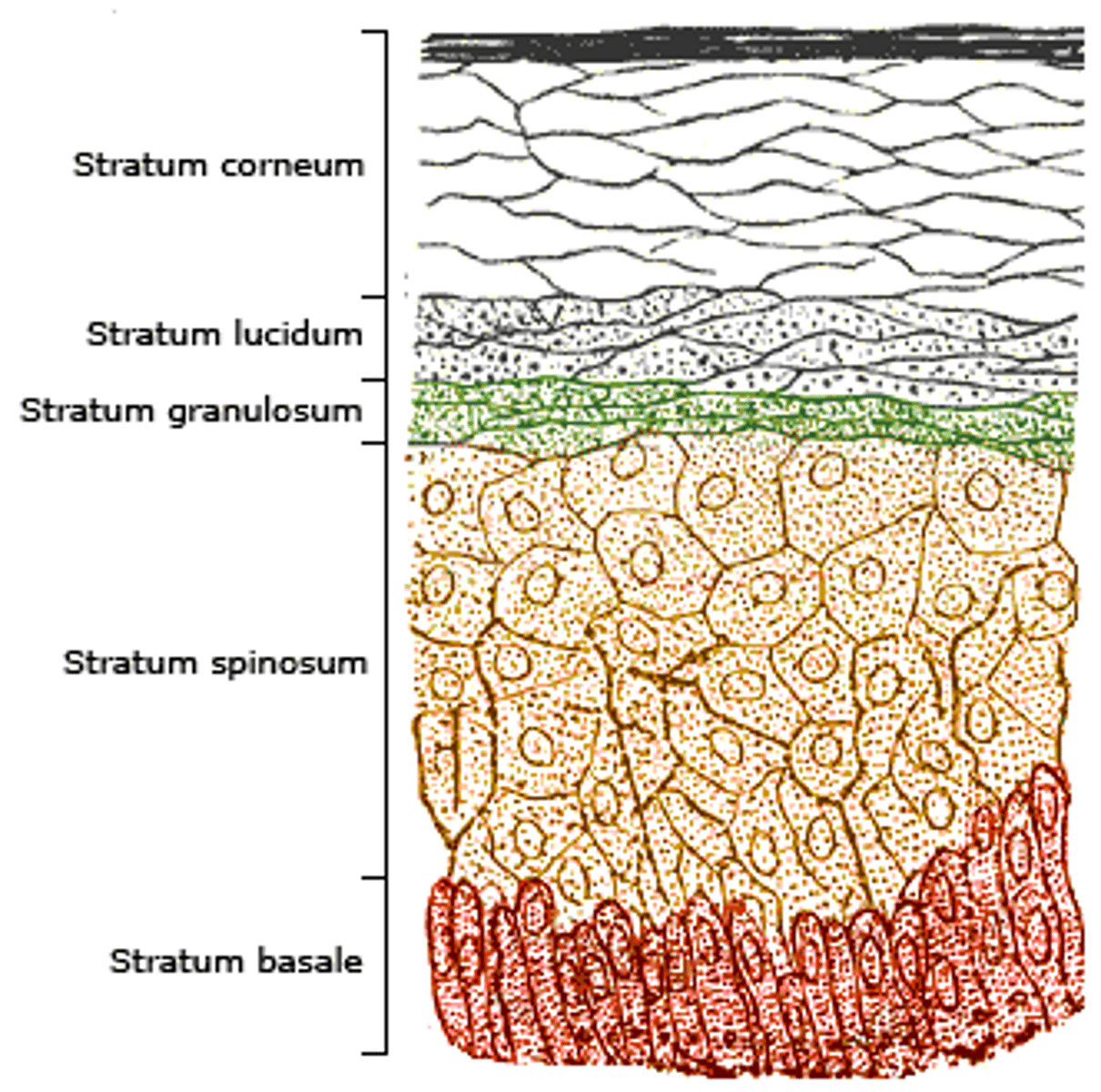
Layers of the Epidermis
Thick skin which covers the palms, fingertips, and soles of feet; Epidermis consists of 5 layers (thick), Order superficial to deep: Stratum Corneum, Stratum Lucidum (thick only), Stratum Granulosum, Stratum Spinosum and Stratum Basale.
MNEUMONIC: Cancun, Leaves, Great, Sun, Burns
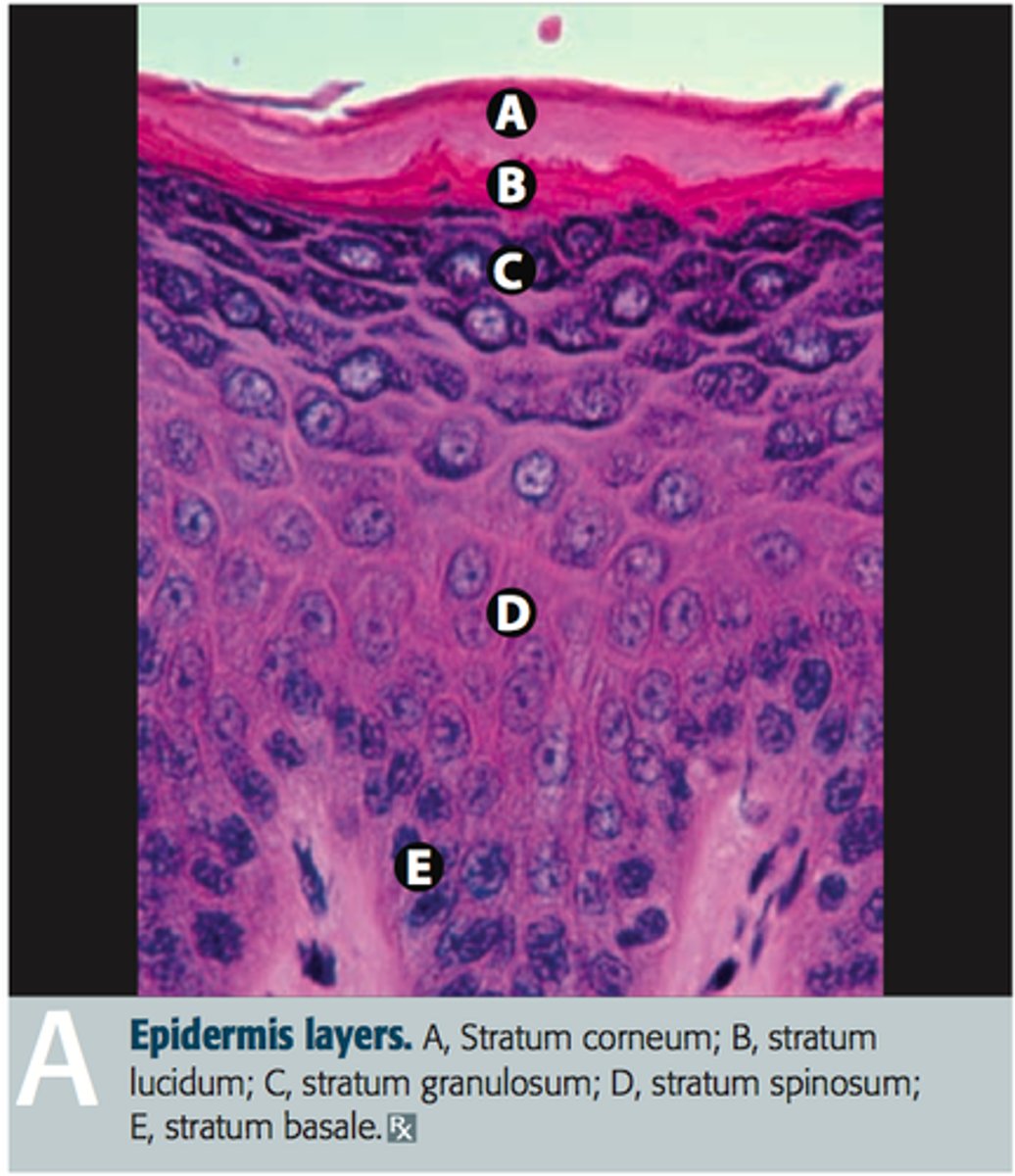
Stratum Corneum (Horny Layer)
20 to 40 cell layers of dead, flat keratinized, membranous sacs, accounts for up to 3/4s of epidermal thickness.
Functions: Protects from abrasion and penetration, Waterproofs, Barrier against biological, chemical, and physical assaults
Stratum Lucidum (Clear Layer)
Appears as a clear translucent band just above the stratum granuosum. 2 to 3 rows of flat, dead keratinocytes. (plantar and palmer only)
Stratum Granulosum (Granular Layer)
Thin layer that consists of 3 to 5 layers in which keratinocyte appearance changes drastically and the process of keratinization (in which the cells fill with the protein keratin) begins. Keratohyaline help form keratin in upper layers, and lamellated granules spew a water resistent glycolipid into the extracellular space slowing water loss across epidermis making the outter skin more tough.
Stratum Spinosum (Prickly Layer)
Several cell layers thick, cells contain a weblike system. Keratinocytes appear to have spines and are scattered among abundant melanin granules and Langerhans' cells.
Stratum Basale (Basale Layer)
Deepest epidermal layer firmly attached to the dermis, takes 25-45 days to flake off in the stratum corneum layer, 10 - 25% made of melanocytes
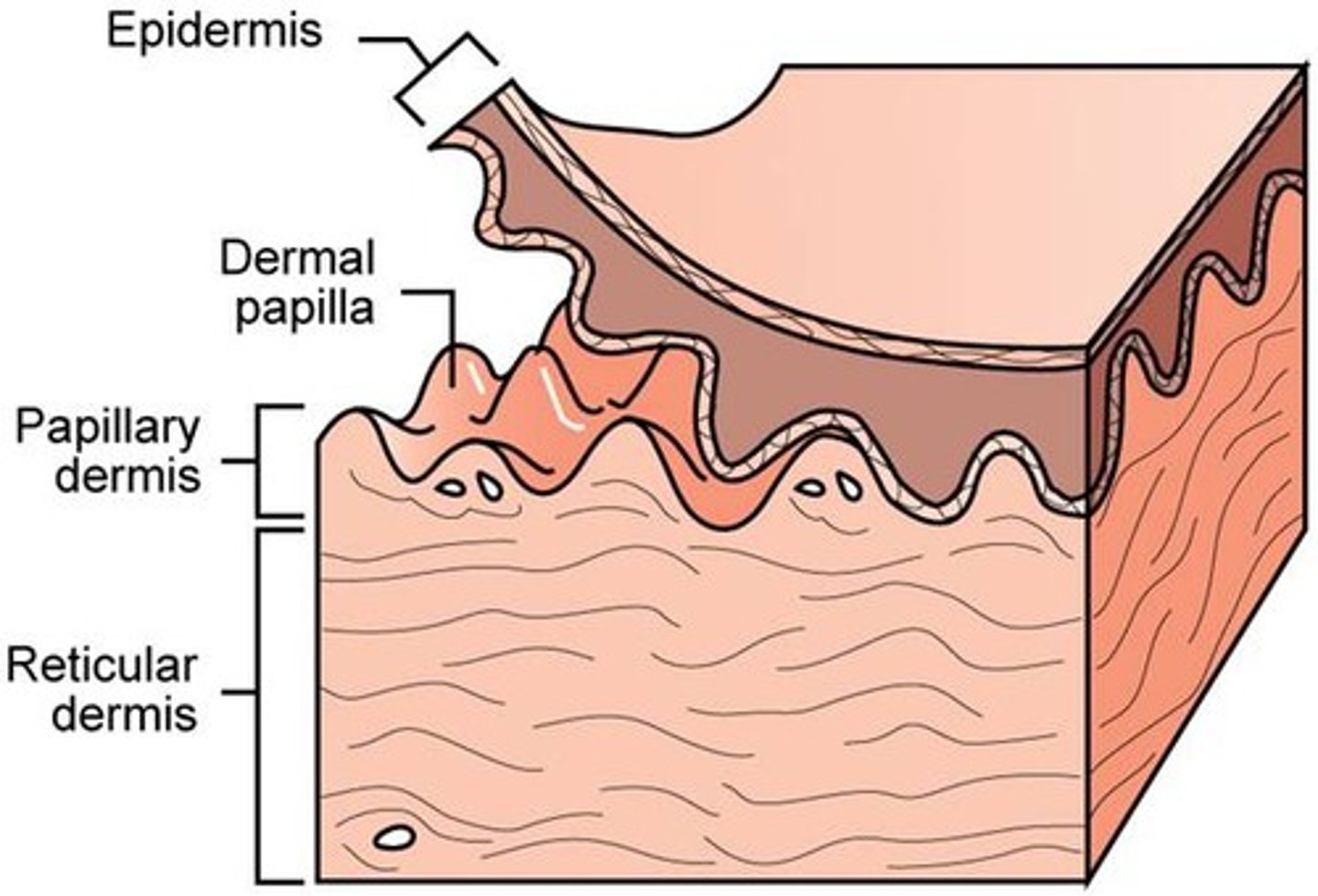
Dermis - 2
The second major skin region, is strong flexible connective tissue. Its cells are fibroblast, macrophages and occasional mast cells. Richly supplied with nerve fibers, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels. Has two layers, papillary and reticular layers
Papillary Layer
Thin superficial layer is aerolar connective tissue, with fine interlaced mat of loosely woven collegen and elastic fibers. Has superior surface callled dermal papillae. 20% of dermis (80% is reticular)
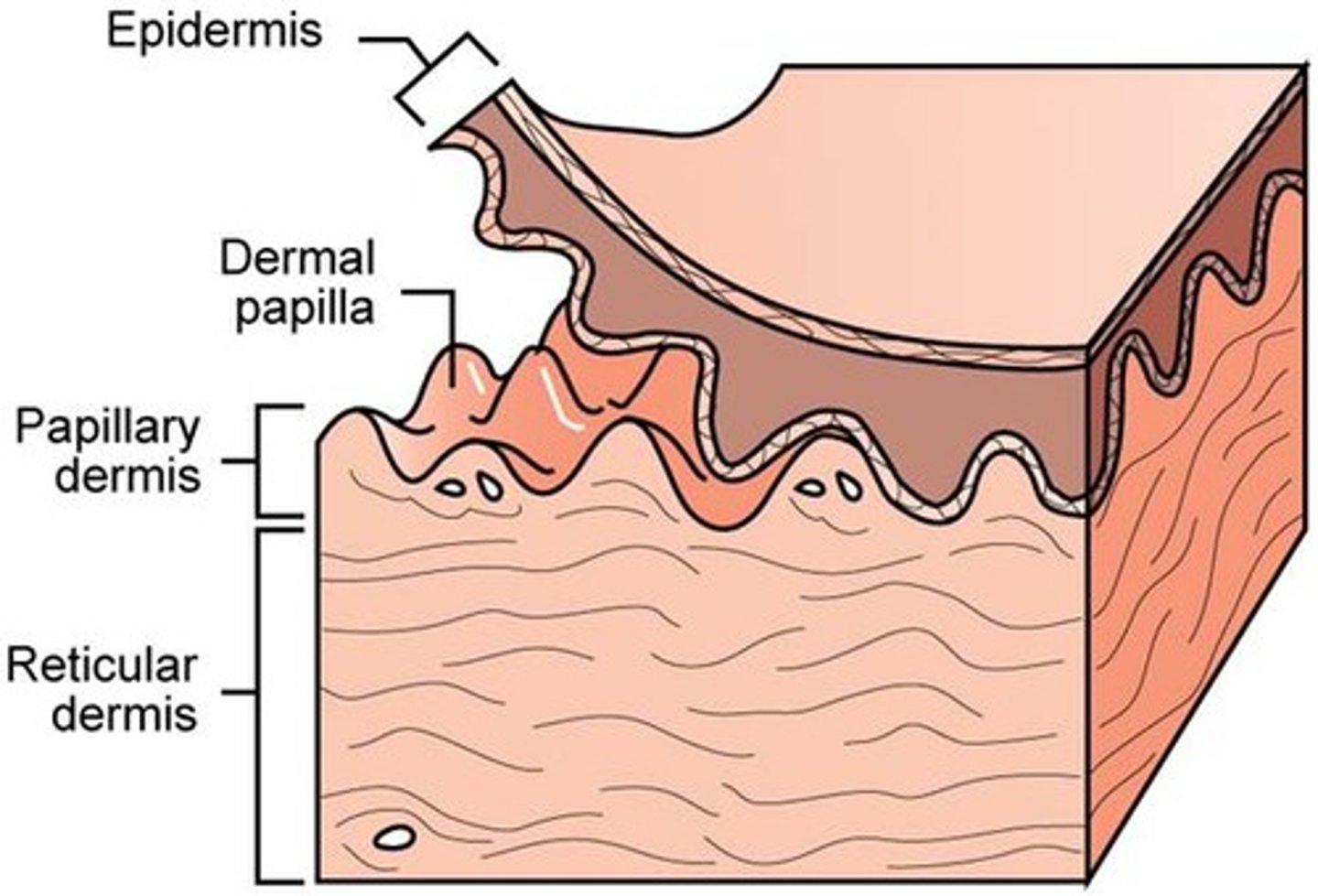
Dermal Papillae
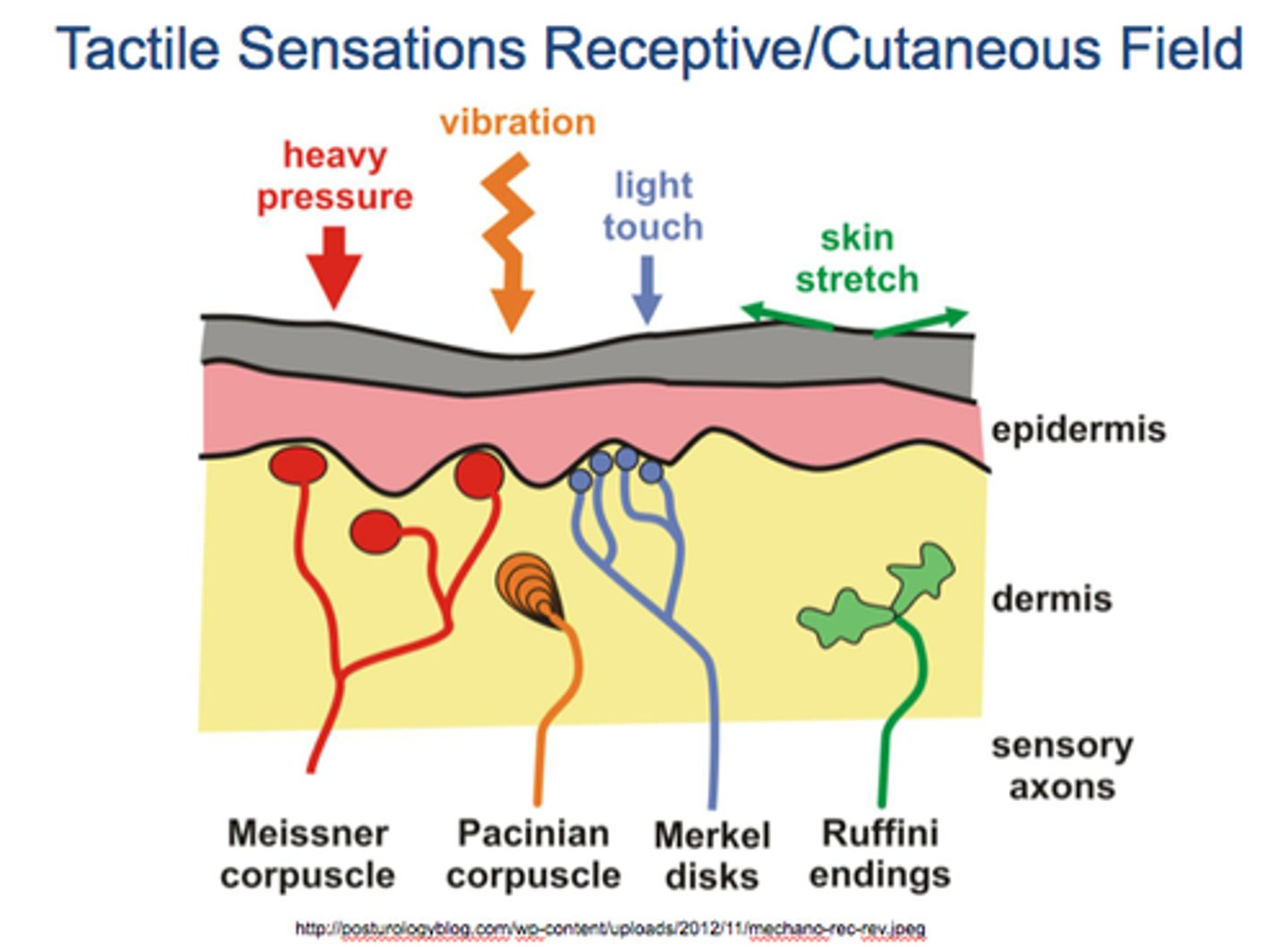
Meissner's corpuscles (touch receptors), free nerve endings (pain receptors), and capillaries for diffusion to occur (to epidermis)
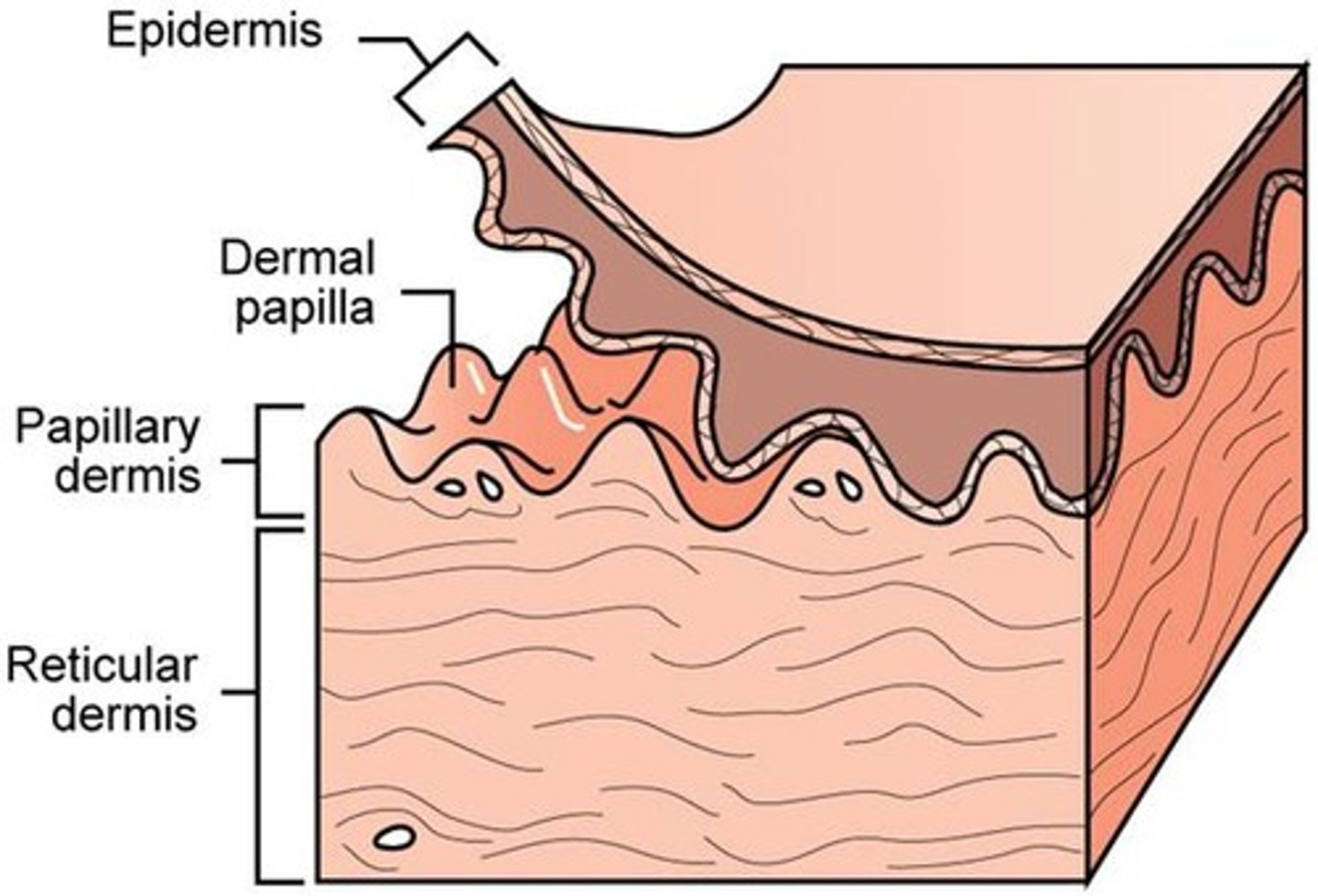
Reticular Layer
Accounts for 80% of the thickness of the dermis, it is coarse, irregularly arranged, and dense fibrous connective tissue. Collagen fibers provide strength and resiliency, Elastic fibers provide stretch-recoil properties.
Skin Color
Three pigments contribute to skin color: melanin, carotene, and hemoglobin.
Melanin
Made in the melanocytes - yellowish-brown to black color

Carotene
Yellow to orange pigment. Its color is most obvious in palms and soles of feet, where stratum corneum is the thickest.
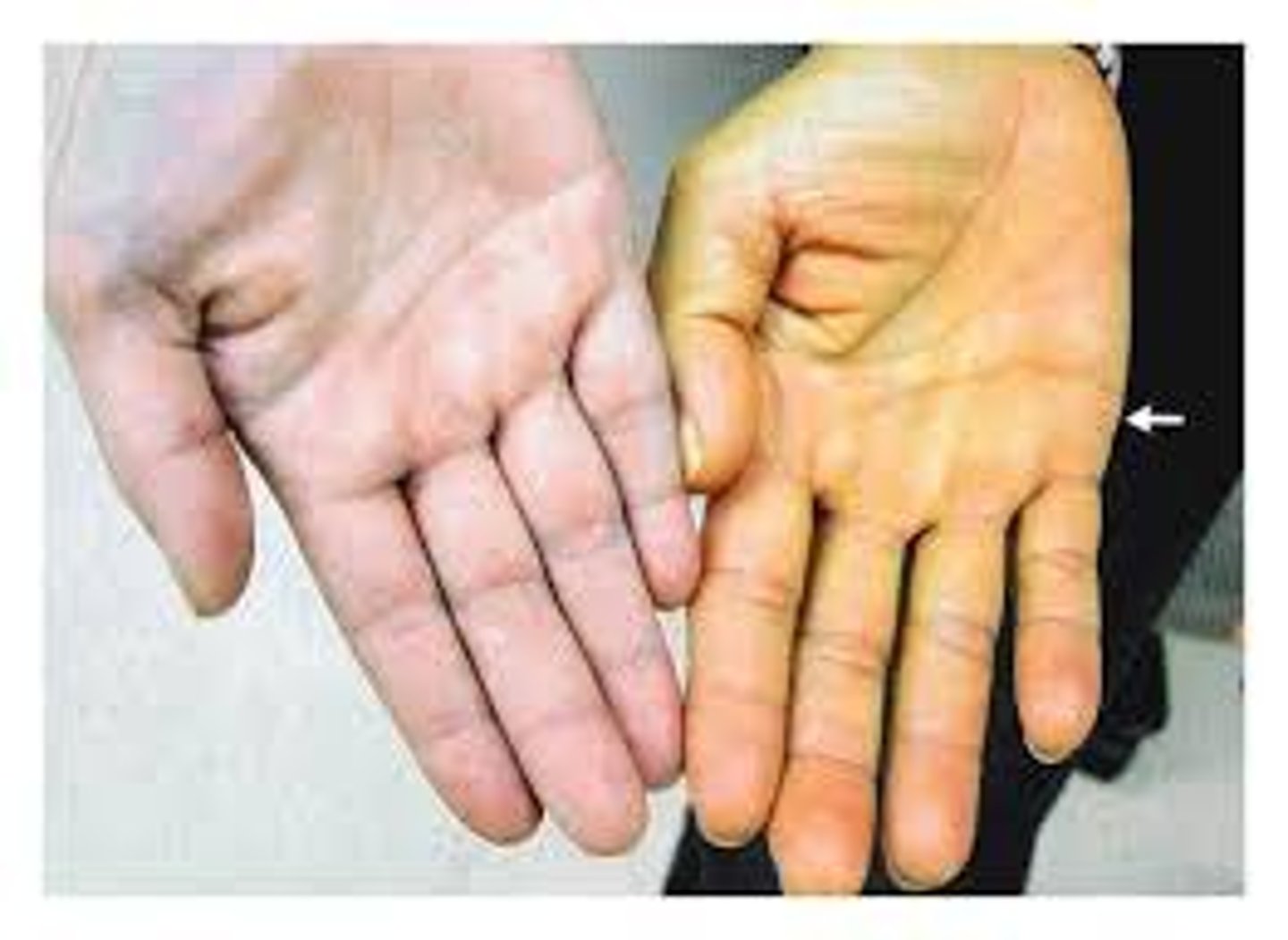
Hemoglobin
The pinkish hue of fair skin, refects oxygenated hemoglobin in the blood cells circulating through dermal capillaries.
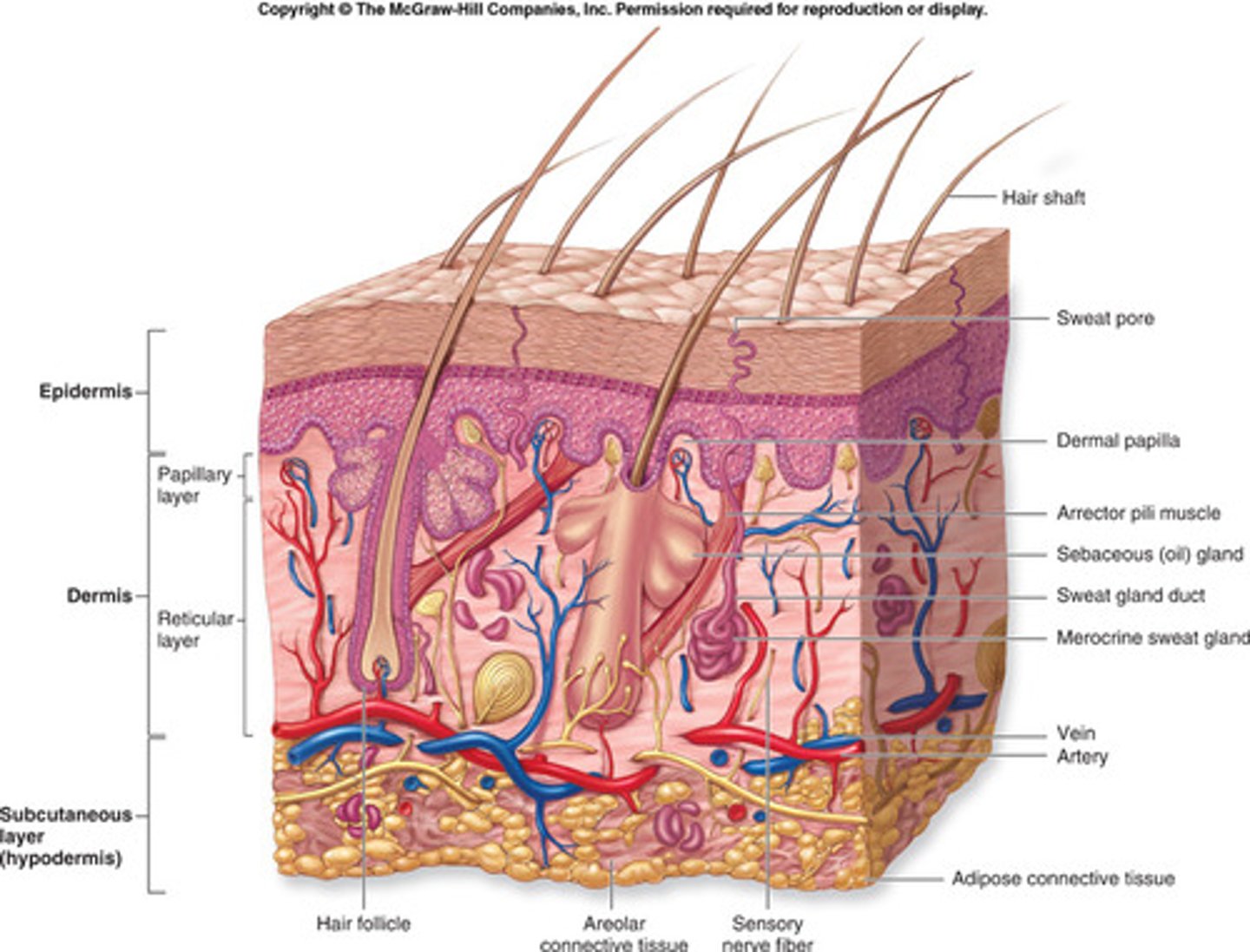
Accessory Organs of the Integumentary System
The nails, sudoriferous (sweat) glands, sebaceous (oil) glands, and hair.
Eccrine Sweat Glands
Secreting glands, are far more numerous and are abundant on palms, soles of feet and forehead. Each is a simple, coiled, tubular gland. Ducts connect to pores. Sweat: 99% water, NaCl, vitamin C, antibodies, dermcidin and metabolic wastes.

Sudoriferous Glands
Two types of glands: eccrine (everywhere except pubic/armpits) AND apocrine (pubic area and armpits). Are distributed all over the body, except nipples and parts of external genitalia. Up to 3 million per person.
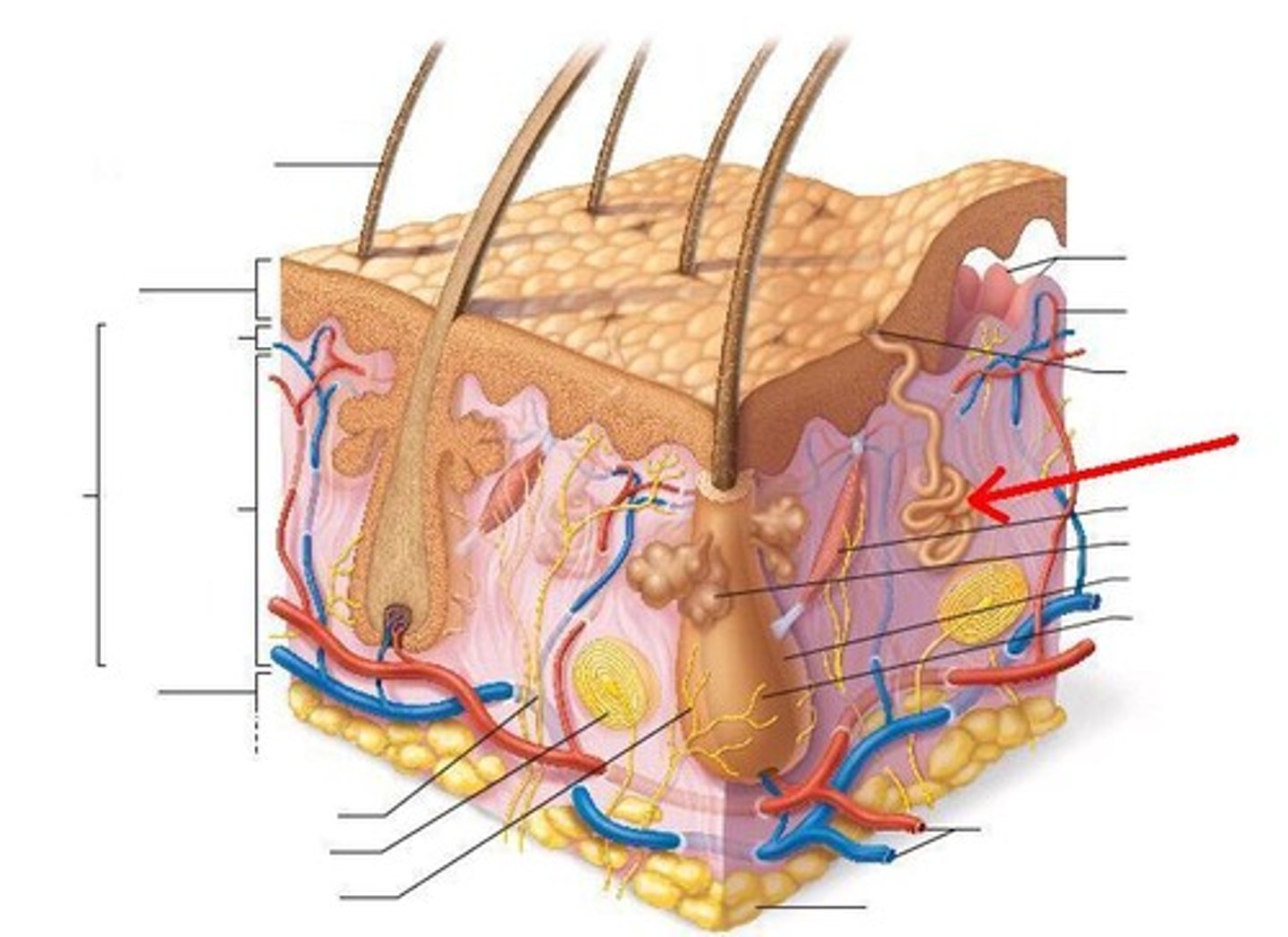
Apocrine Sweat Glands
Approx. 2000 of them are confined in axillary and anogenital areas. Release product by exocytosis. They are larger and lie deeper in the dermis, and ducts empty into hair follicles. Sebum: sweat + fatty substances and proteins. Functional from puberty onward (as sexual scent glands?)
Ceruminous Glands
Modified specialized apocrine glands found in the lining of the external ear canal. Secretion mixes with sebum and produces cerumen or earwax.

Sebaceous (Oil) Glands
Simple branched alveolar glands that are found all over the body except in the thick skin of palms and soles. Small on body trunk and limbs but large on face neck and upper chest. Secrete oily substance called sebum. Most develop from hair follicles, Become active at puberty.
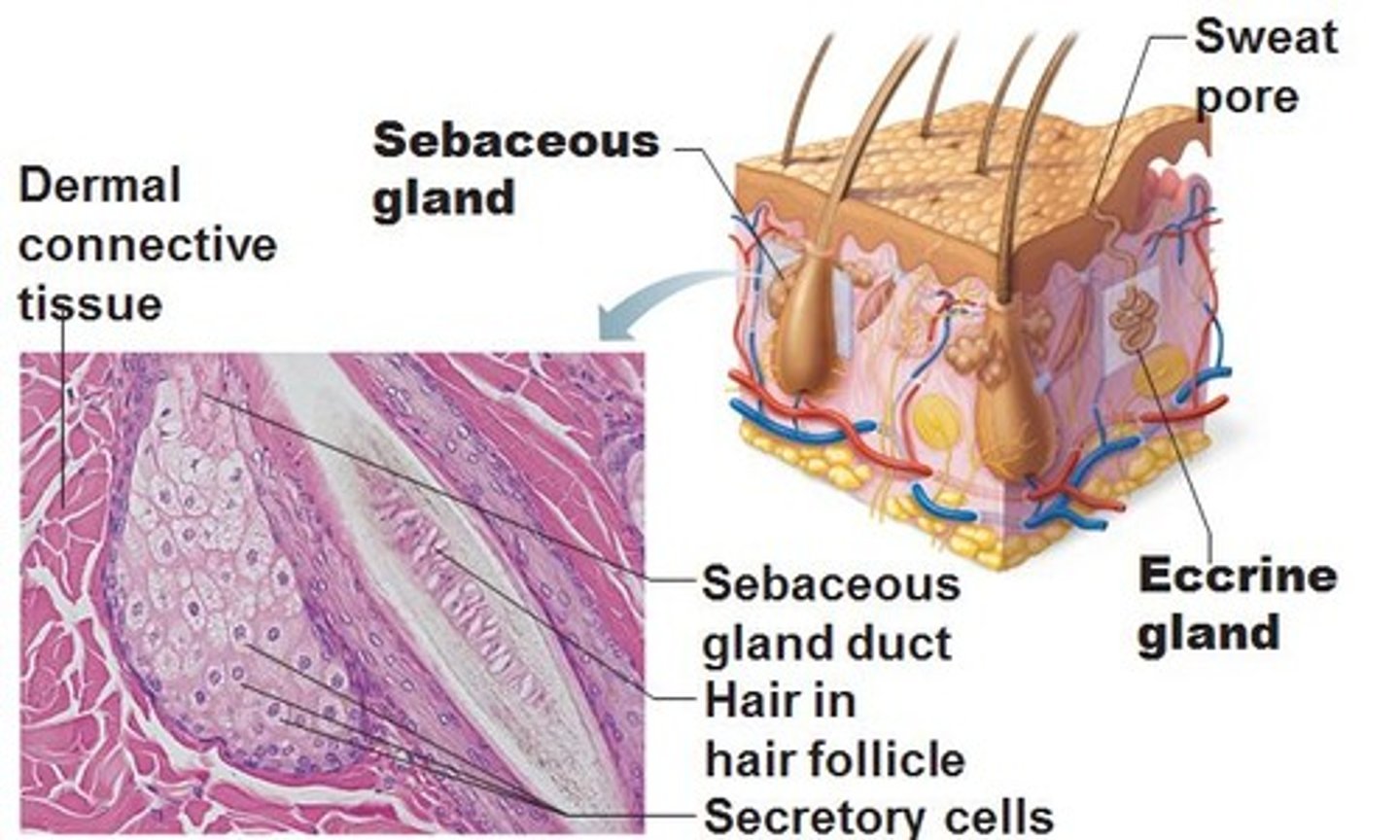
Sebum
Oily holocrine secretion. Bactericidal. Softens hair and skin.
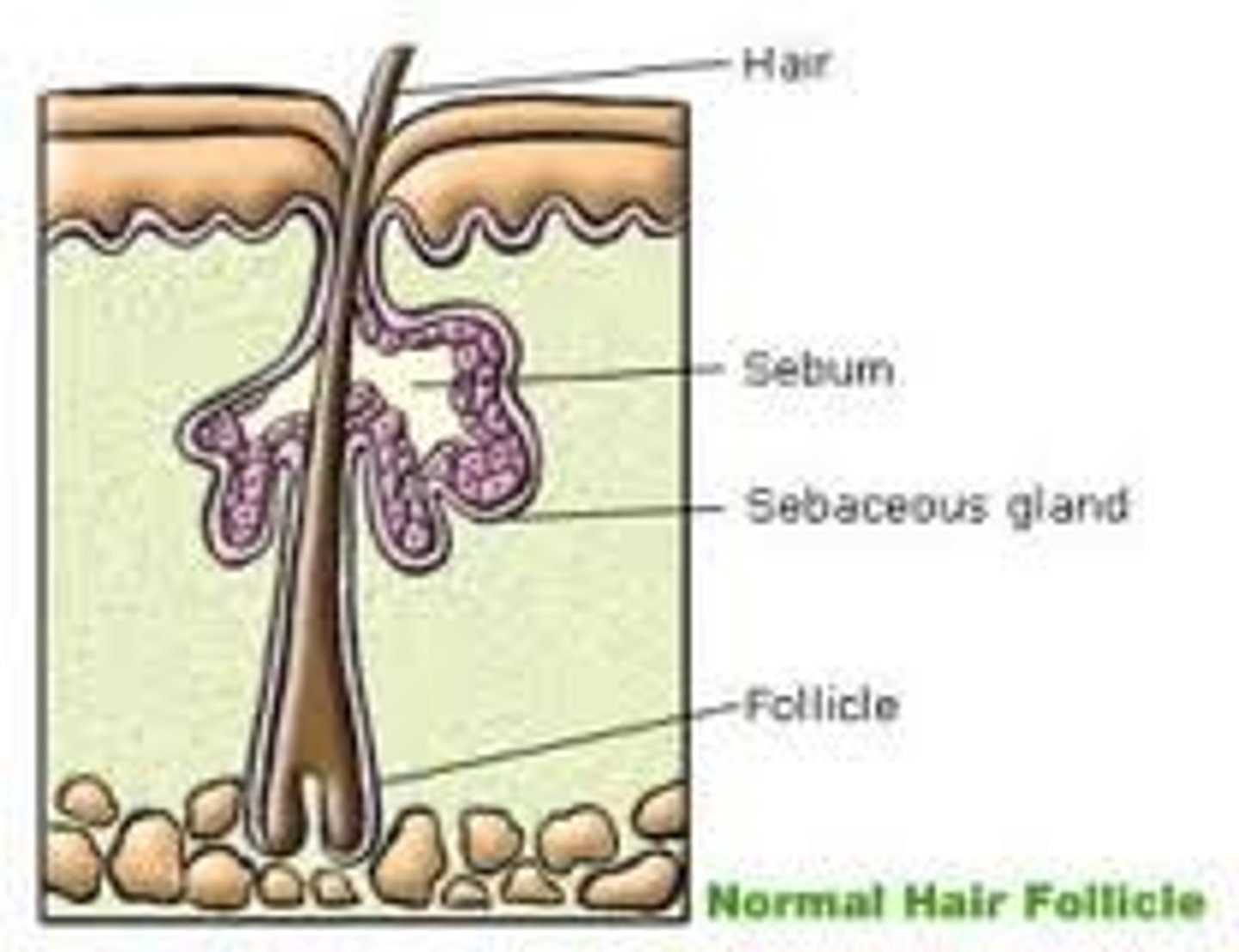
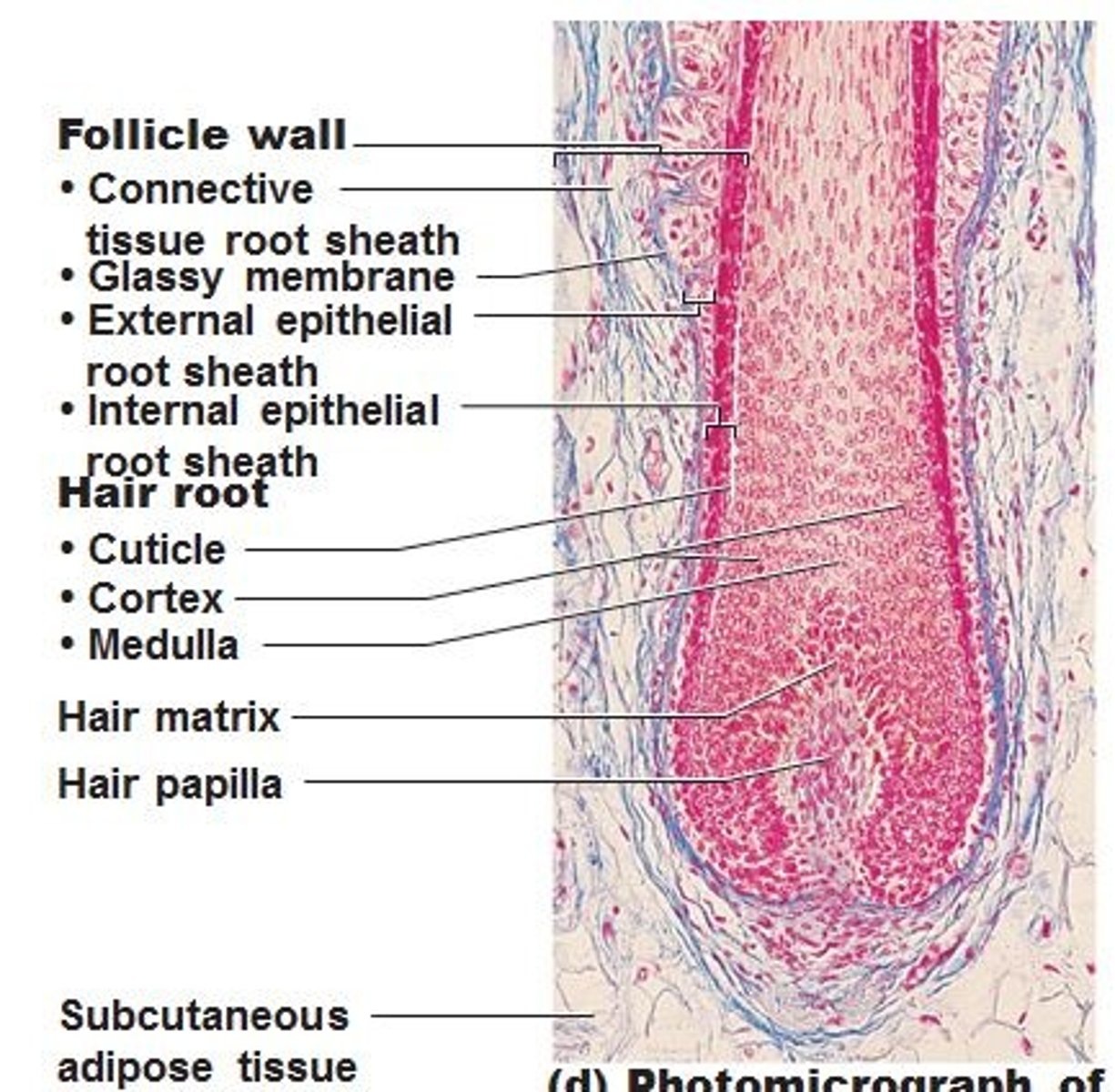
Pili (Hair)
Produced by hair follicles, consists of dead keratinized cells.
Functions: Alerting the body of touch, prevents heat loss, and protects against sunlight
Distribution: Entire surface except palms, soles, lips, nipples, and portions of external genitalia.
Contains hard keratin; more durable than soft keratin of skin
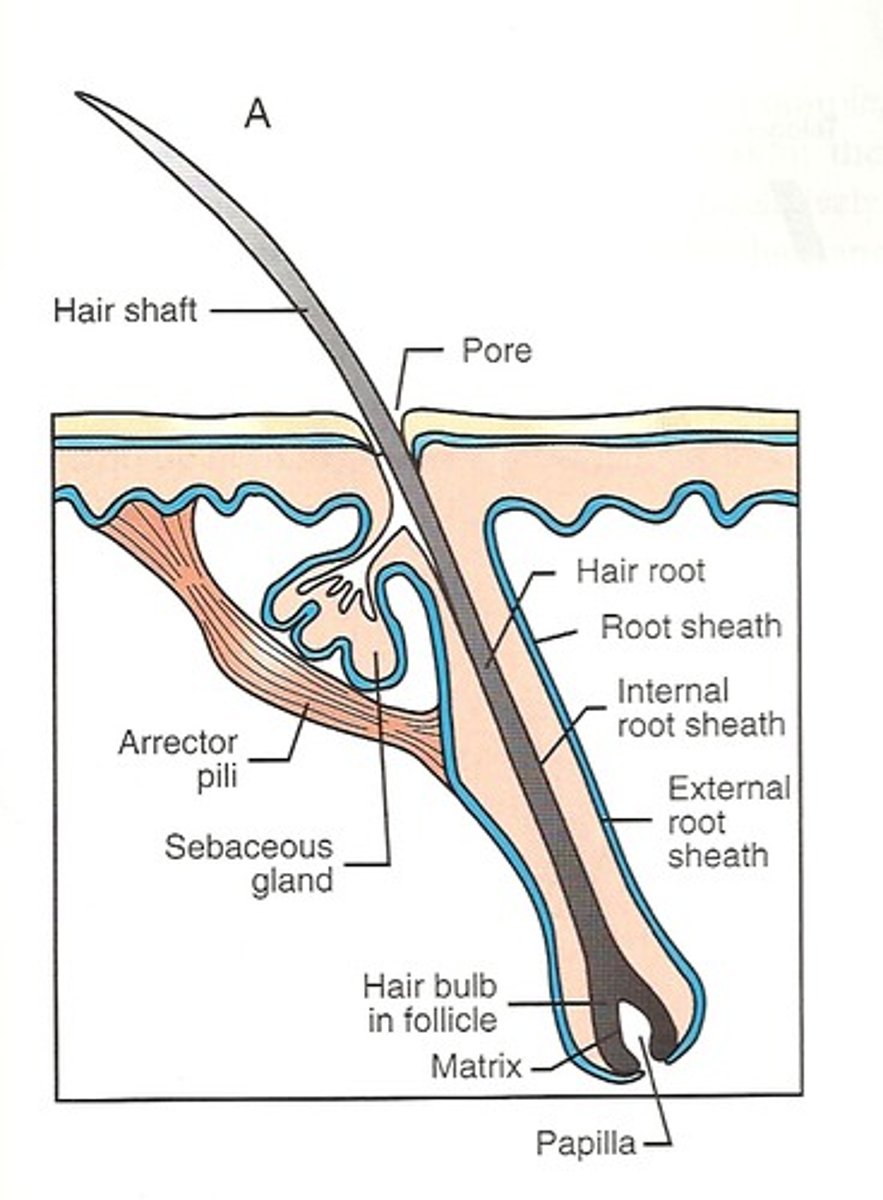
Hair Follicles
Two-layered wall: outer connective tissue root sheath, inner epithelial root sheath, Hair bulb: expanded deep end
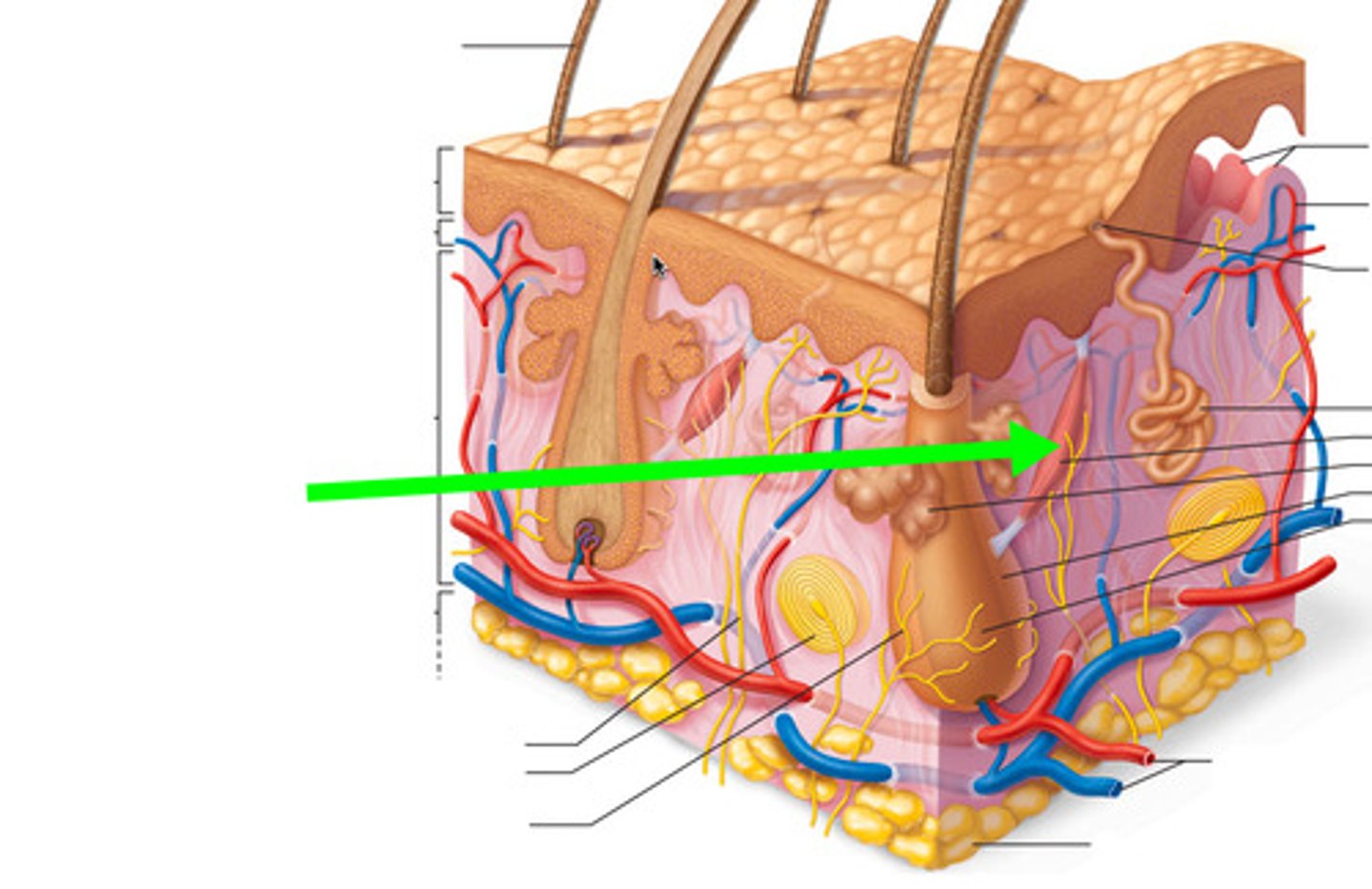
Hair follicle receptor (root hair plexus)
Sensory nerve endings around each hair bulb. Stimulated by bending a hair
Arrector pili
Smooth muscle attached to follicle, Responsible for "goosebumps"
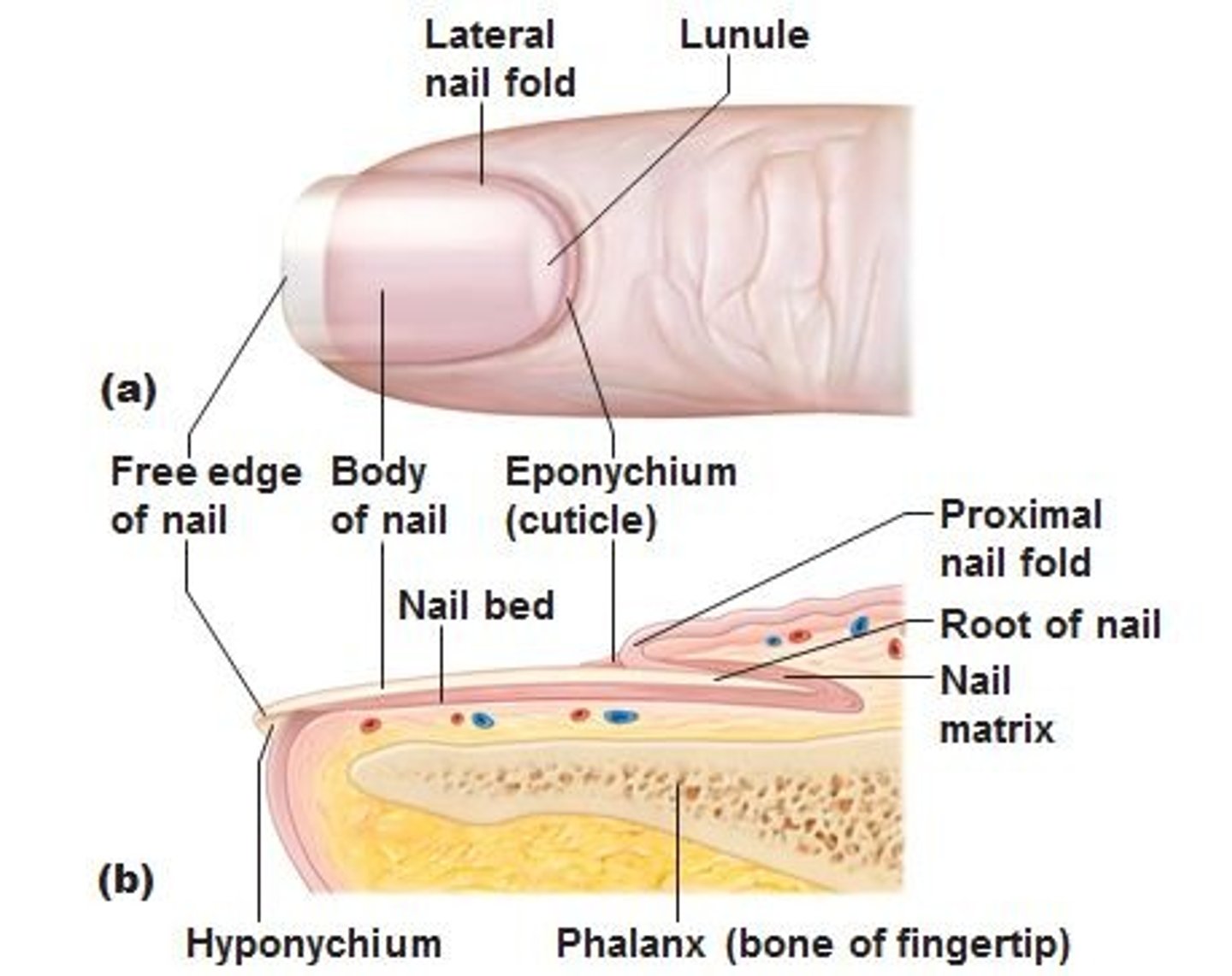
Nail
Scalelike modification of the epidermis on the distal, dorsal surface of fingers and toes.
Functions of Integumentary System
1. Protection
2. Body Temperature Regulation
3. Cutaneous Sensation
4. Metabolic Functions
5. Blood Reservoir
6. Excretion
Cutaneous Sensations
Temperature, touch, pain, and pressure
Metabolic Functions
Synthesis of vitamin D
Blood Reservoir
The dermal vascular supply can hold up to 5% of body's blood volume.
Excretion
Limited amounts of nitrogenous wastes and salt are eliminated in sweat.
Skin Cancer
Most skin tumors are benign. Risk factors: overexposure to UV radiation, frequent irritation of the skin.
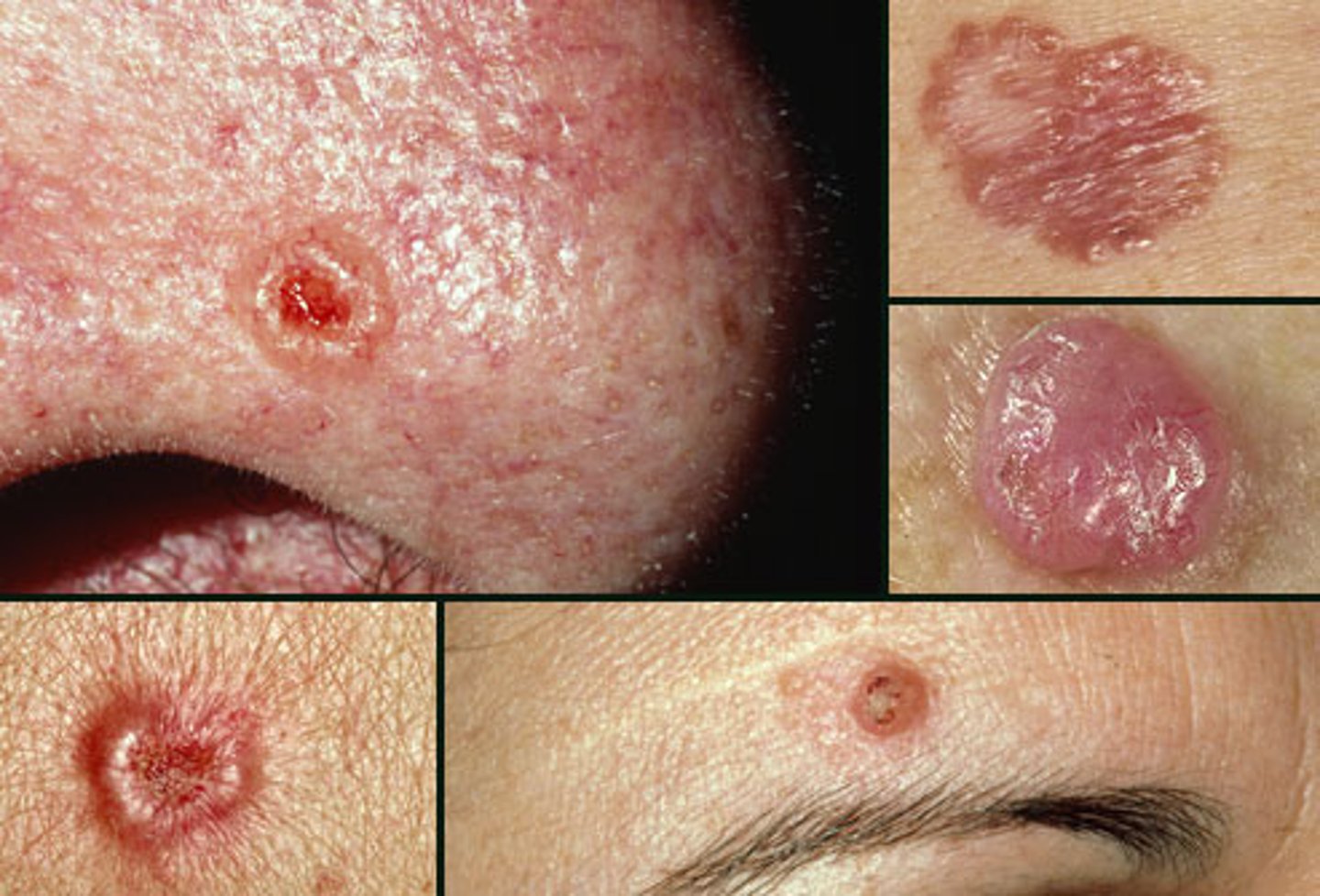
Melanoma
Most dangerous. Involves melanocytes. Highly metastatic and resistant to chemotherapy. Treated by wide surgical excision accompanied by immunotherapy.
Characteristics (ABCD rule)
A: Asymmetry; the two sides of the pigmented area do not match
B: Border exhibits indentations
C: Color is black, brown, tan, and sometimes red or blue
D: Diameter is larger than 6 mm (size of a pencil eraser)

Connective Tissue
protects, supports, and binds organs together
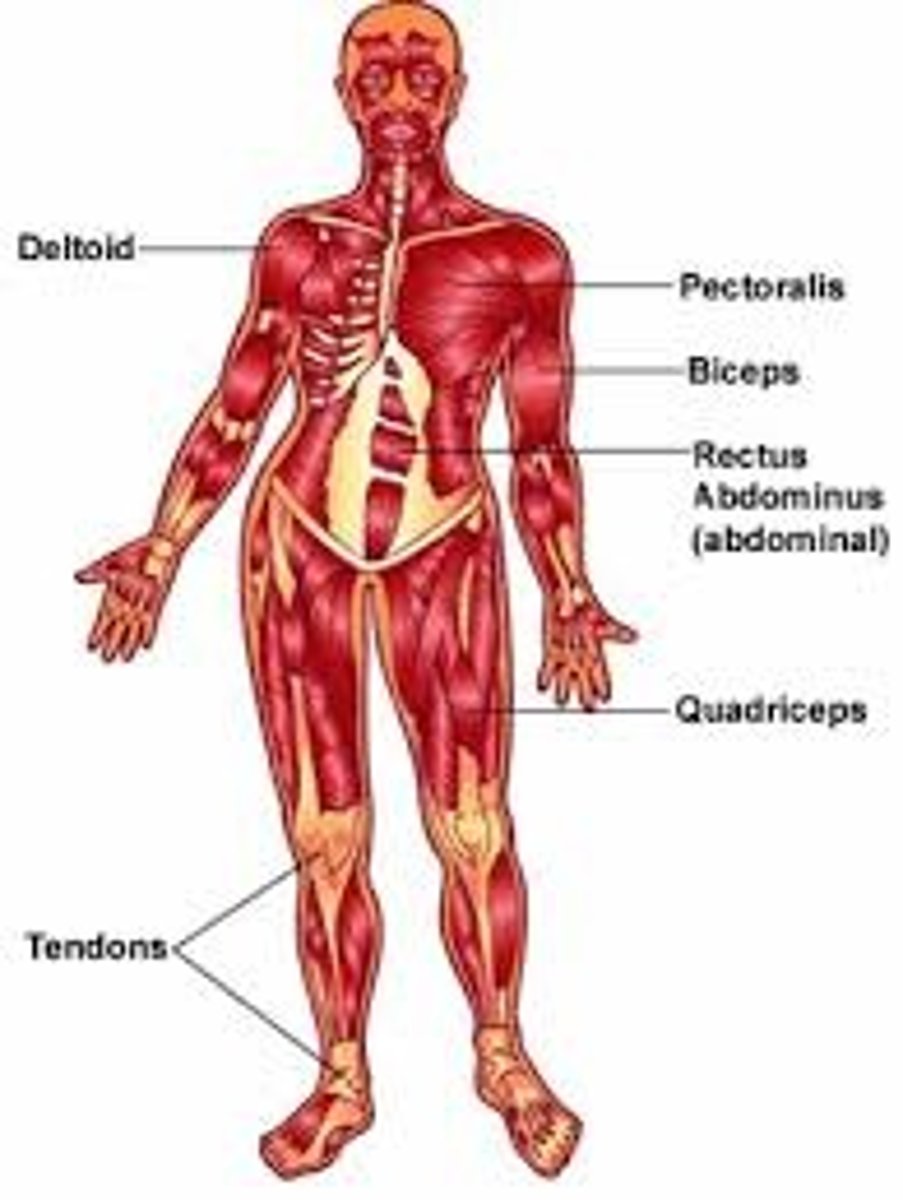
Muscular Tissue
Contracts and moves the various parts of the body.
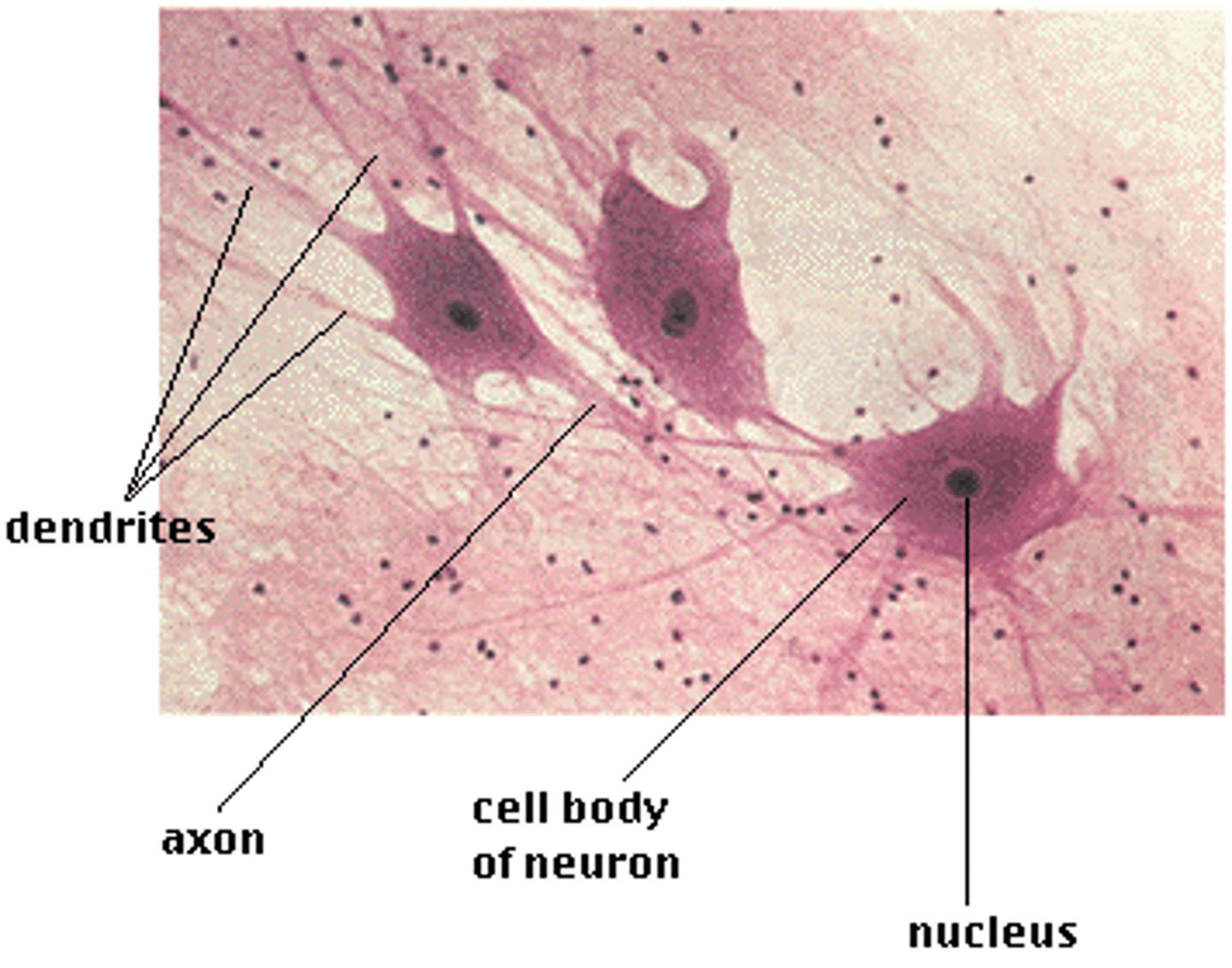
Epithelial Tissue
Tissue that covers outside of the body and lines organs and cavities.
Nervous Tissue
A body tissue that carries electrical messages back and forth between the brain and every other part of the body.