41 - Human Reproduction
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Draw a large diagram of the human male reproductive system
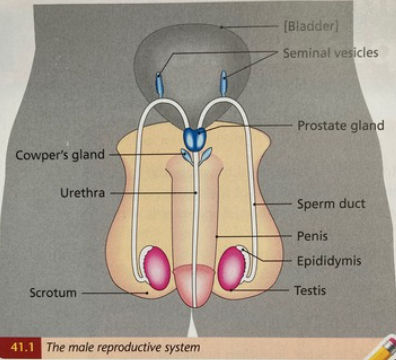
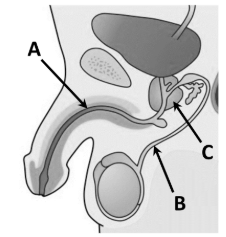
Give the names of tubes A and B and the name of gland C
A: Urethra
B: Sperm duct
C: Prostate
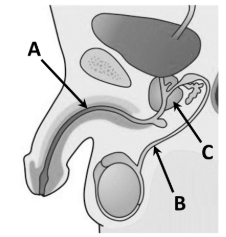
Give one function for each structure labelled A, B and C
A: Release semen or release urine
B: Carries sperm from testes to urethra
C: Produces seminal fluid
Give the function of the epididymis
To store sperm or to allow sperm to mature
In which part of the male reproductive system does meiosis occur?
Testes
Explain the importance of meiosis in the production of sperm
To produce haploid cells or to maintain parental chromosome number or introduce variation
Name the male sex hormone produced by the testes
Testosterone
Which part of the male reproductive system is directly involved in copulation?
Penis
How many chromosomes are found in the nucleus of a typical human sperm cell?
23
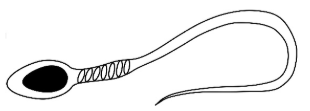
Indicate the location of the mitochondria on this diagram of the human sperm cell
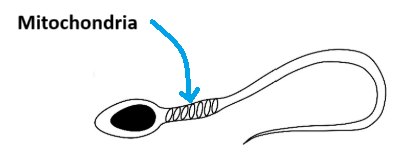
Suggest why a sperm cell needs to many mitochondria
They need a lot of energy or need to swim long distances
Mitochondria are inherited exclusively from the mother. Suggest why this is the case
Only the head of the sperm enters the egg
no sperm mitochondria enter the egg
State the approximate survival times of the egg and sperm within the female reproductive tract
Egg: 12 - 48 hours
Sperm: 0 - 7 days
What is meant by the term inferitility?
Inability to produce offspring
Give one cause of male infertility and a corrective measure
Cause: low sperm count / low sperm mobility
Corrective measure: IVF
Give any two methods of contraception
Mechanical / surgical / natural / chemical / named examples
Give one named example of natural contraception
Abstinence or rhythm
Draw a labelled diagram of the human female reproductive system
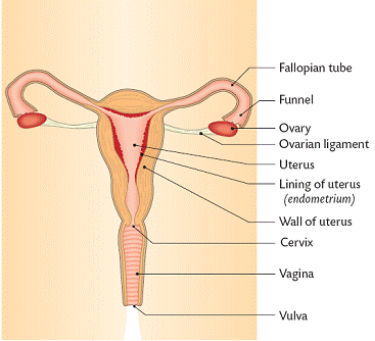
Where do the following occur in the female reproductive system:
Egg production
Fertilisation
Implantation
Ovary
Fallopian tube
Uterus
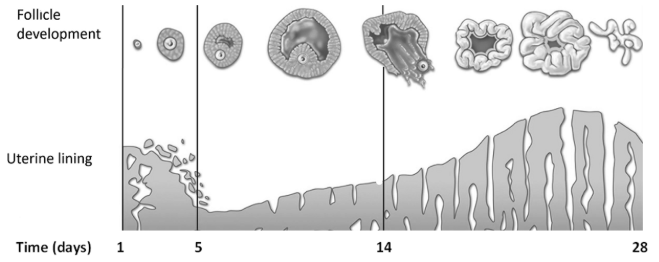
How long is the typical menstrual cycle in a human female?
28 - 31 days
What is the role of the menstrual cycle?
To prepare uterus for pregnancy
What is meant by the term menstruation?
Breaking down of the endometrium
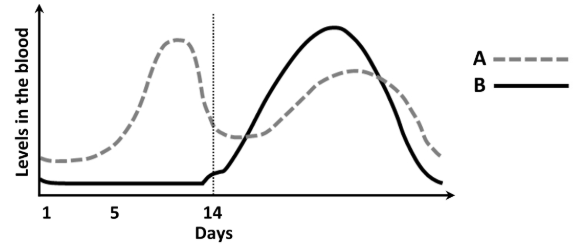
Name each of the hormone A and B
A: Oestrogen
B: Progesterone
Describe one effect on the female reproductive system of the low levels of hormones A and B
Menstruation or FSH produced or new follicle starts developing
Explain why hormone A levels increase after approximately day 5
Follicle secretes more oestrogen or FSH stimulates production of oestrogen
FSH and LH each play a role in the cycle. Where in the body are these hormones produced?
Pituitary gland
Give the functions of the other two named hormones involved in the cycle
Oestrogen: causes endometrium to build up or inhibits FSH or stimulates LH
Progesterone: maintains endometrium or inhibits LH or inhibits FSH
What event occurs around day 14 of the menstrual cycle?
Ovulation or release of egg (from the ovary)
Explain why hormone B levels increase in the days after day 14
Corpus luteum secretes progesterone or LH stimulates production of progesterone
The graafian follicle increases in size during the first half of the menstrual cycle.
Name the main hormone the graafian follicle produces
Oestrogen
Name the structure that the graafian follicle develops into after day 14
Corpus luteum
Give the function of the hormone you named in the previous question
Repair of the endometrium
What hormone is responsible for causing ovulation?
Luteinising hormone (or LH)
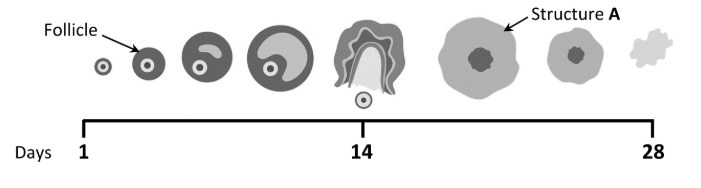
What name is given to structure A?
Corpus luteum
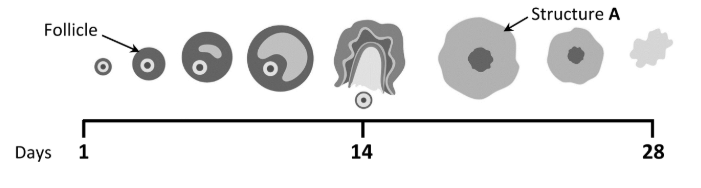
Name the main hormone that is produced by structure A
Progesterone
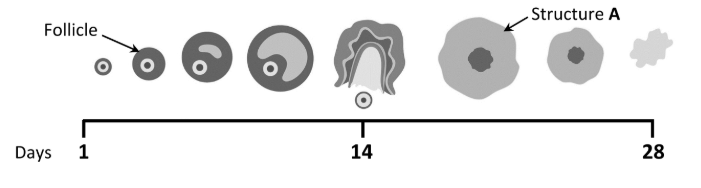
Describe what happens to structure A if fertilisation of an egg cell does not occur
It degenerates (towards the end of the menstrual cycle)
Does the graph indicate that the woman became pregnant during this menstrual cycle? Explain your answer
No
Explain: uterine lining breaks down at the end or corpus luteum breaks down
Name a menstrual disorder and state a cause and a possible treatment
Name: Fibroids
Cause: Hormonal imbalance
Possible treatment: Hormonal medication
What is meant by the term secondary sexual characteristics?
Features that distinguish male from female other than sex organs or features that emerge at puberty
Give two examples of a secondary sexual characteristic present in males
Deep voice / enlarged muscles / wide shoulders / body hair / enlargement of penis
Give the names of two structures that are formed in the days following fertilisation up to the point of implantation
Morula
Blastocyst
True or false
The morula forms before the blastocyst in human reproduction
True
Name the next stage of development following formation of the zygote in humans
Morula
What is meant by the term implantation?
Embedding of the fertilised egg into the endometrium
Outline what happens to each of the following after implantation has taken place:
The level of the hormone progesterone in the blood
The endometrium
Progesterone level: Increases
Endometrium: Is maintained or thickens
Embryo cells organise into three germ layers.
Name each of these layers
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
Identify the germ layer from which the skin of the developing embryo arises
Ectoderm
From which tissues does the placenta form?
Endometrium
Chorionic
Describe the differences between the human male and female type of gamete using the following headings:
Relative numbers of each produced
Frequency of production of gametes
Relative size
A low number of female gametes and a high number of male gametes
Monthly in females and continuously in males
Large in females and small in males
Name the two tissues involved in the formation of the placenta
Tissue 1: Endometrium or uterine
Tissue 2: Embryonic or embryo tissue
Give two roles of the placenta
Movement of food or waste from mother to foetus / endocrine gland or production of hormones
Give two reasons why the blood of the mother and the foetus must not mix
Blood pressure difference / Blood group difference / to prevent transfer of certain infections
Give an outline description of the birth process, including the role of hormones
Placenta stops producing progesterone
Pituitary gland of the mother produces oxytocin
Mucus plug falls out / amniotic fluid expelled / labour of uterine contractions / cervix dilates / baby is pushed out / afterbirth / umbilical cord is cut
State one method of birth control
Condom or the (contraceptive) pill or IUD
Name the hormone responsible for milk production
Prolactin
State two biological benefits of breastfeeding
Balanced supply of nutrients / supplies antibodies / correct temperature
Give an advantage and a disadvantage of sexual reproduction in organisms
Advantage: Increased variation
Disadvantage: Requires two parents or longer life cycle
Explain the term in vitro fertilisation
Gametes fuse
Outside the body
Suggest a reason for the removal of several eggs
To increase chance of successful implantation